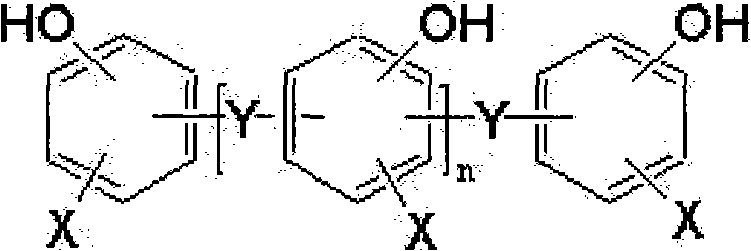Method for preparing phosphor modified flame retardation stiffening agent
A hardener, phosphorus-modified technology, applied in the field of flame-retardant and heat-resistant phosphorus-modified flame-retardant hardeners, which can solve low curing density, reduced gelling or hardening density, thermal properties and adhesion properties Variation etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
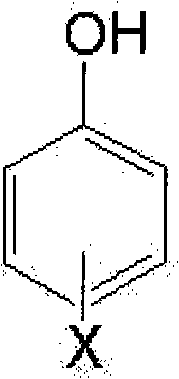
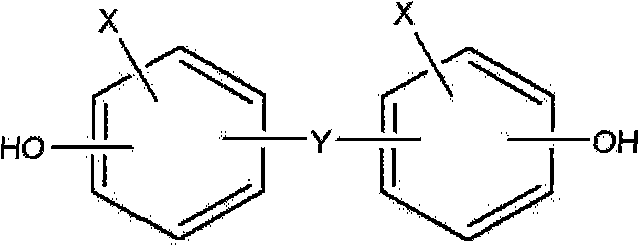
[0148] 228g (1 mole) of bisphenol A, 216g (3 moles) of paraformaldehyde, 30g of water and 10g of 50% aqueous sodium hydroxide solution were placed in a reaction bath, and then reacted at 50° C. for 5 hours under heating and stirring. Next, after adding 100 g of water thereto, neutralization was performed with 5 g of 0.1N sulfuric acid. The product was then washed three times with 100 g of water to separate and obtain a bisphenol A resol compound (304.3 g, yield 94.8%). This resole phenolic resin compound was added to 610 g of methanol, and the resole phenolic resin compound was subjected to alcoholysis at 70° C. (T) for 5 hours with stirring. Thereafter, 522.15 g (2.417 mol) of DOPO was added to the mixture, and dealcoholysis was performed at 145° C. (T) for 10 hours under heating and stirring while removing the methanol portion. After the reaction was completed, the remaining water and methanol were removed under vacuum or reduced pressure, thereby obtaining 749 g of a phosp...
Embodiment 2
[0151] 228g (1 mole) of bisphenol A, 108.4g (1.5 moles) of paraformaldehyde, 30g of water and 5g of 50% aqueous sodium hydroxide solution were placed in a reaction bath, and then reacted at 50°C for 5 hours under heating and stirring. Next, after adding 76 g of water thereto, neutralization was performed with 2.5 g of 0.1N sulfuric acid. The product was then washed three times with 76 g of water to separate and obtain a bisphenol A resol compound (260.6 g, yield 95%). This resole phenolic resin compound was added to 521 g of methanol, and the resole phenolic resin compound was subjected to alcoholysis at 70° C. (T) for 5 hours with stirring. Thereafter, 261.6 g (1.211 mol) of DOPO was added to the mixture, and dealcoholysis was performed at 145° C. (T) for 10 hours under heating and stirring while removing the methanol portion. After the reaction was completed, the remaining water and methanol were removed under vacuum or reduced pressure, thereby obtaining 460 g of a phospho...
Embodiment 3
[0154] 228g of bisphenol A, 288.4g (4 moles) of paraformaldehyde, 30g of water and 14g of 50% aqueous sodium hydroxide solution were placed in a reaction bath, and then reacted at 50° C. for 5 hours under heating and stirring. Next, after adding 116 g of water thereto, neutralization was performed with 6.7 g of 0.1N sulfuric acid. The product was then washed three times with 116 g of water to separate and obtain bisphenol A resol compound (323 g, yield 92%). This resole phenolic resin compound was added to 646 g of methanol, and the resole phenolic resin compound was subjected to alcoholysis at 70°C (T) for 5 hours with stirring. Thereafter, 675.6 g (3.128 mol) of DOPO was added to the mixture, and dealcoholysis was performed at 145° C. (T) for 10 hours under heating and stirring while removing the methanol portion. After the reaction was completed, the remaining water and methanol were removed under vacuum or reduced pressure, thereby obtaining 883 g of a phosphorus-modified...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com