Silicon carbide semiconductor device
A technology of semiconductor and silicon carbide, which is applied in the field of silicon carbide semiconductor devices, can solve the problems such as the reduction of withstand voltage characteristics of silicon carbide semiconductor devices, and achieve the effect of realizing the stability of withstand voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
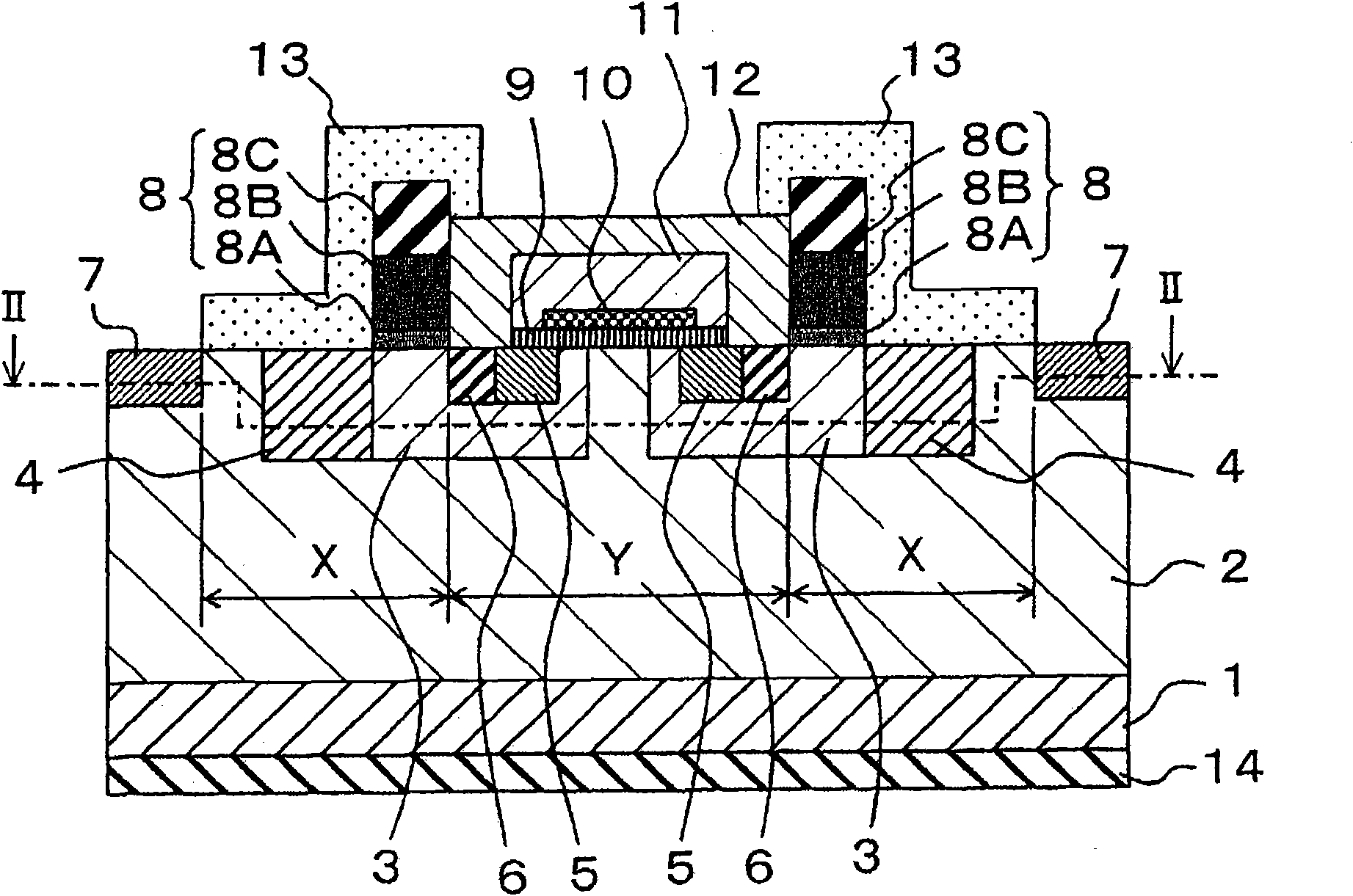
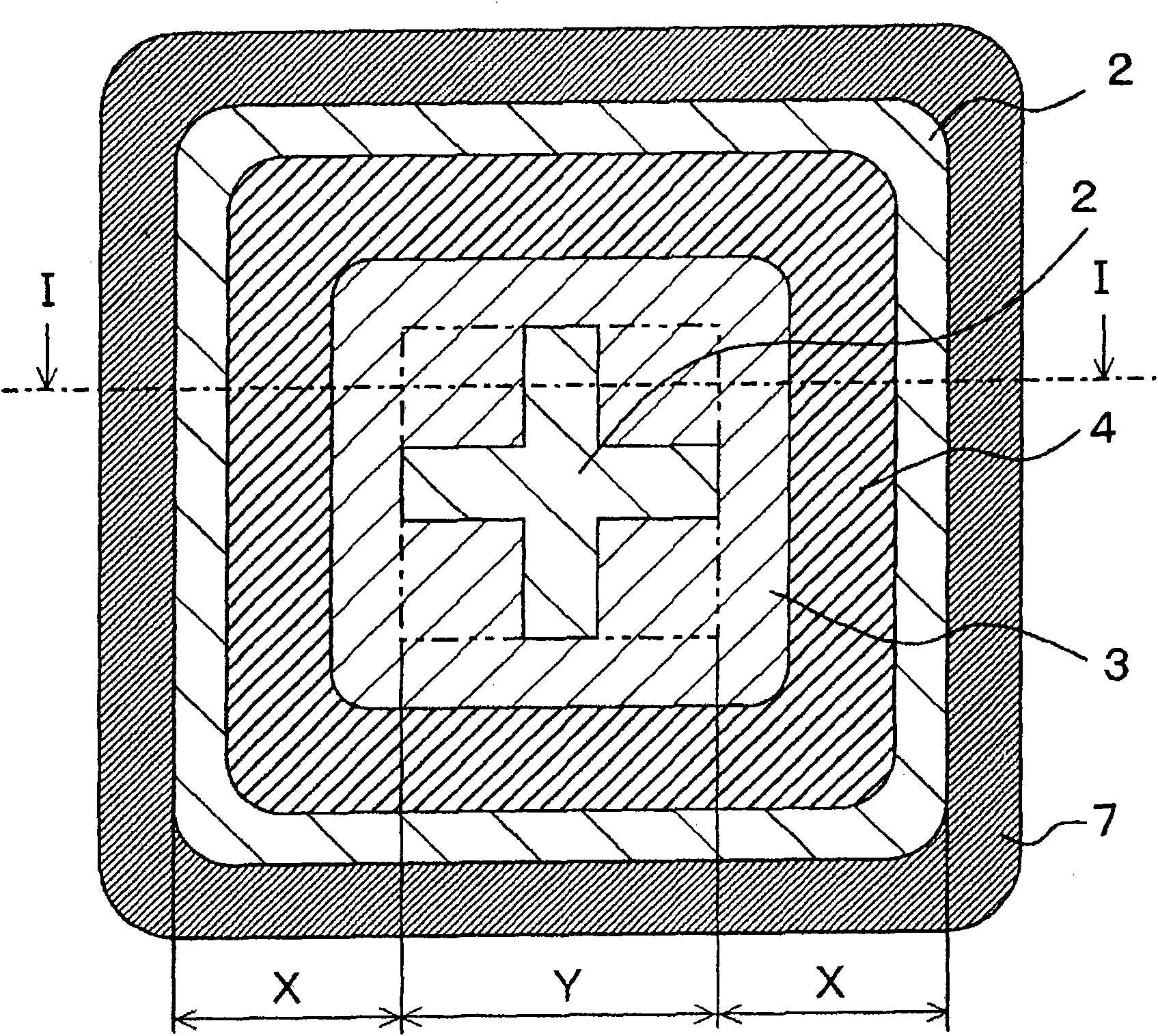
[0061] figure 1 A cross-sectional structure of the silicon carbide semiconductor device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention viewed from a side direction is shown. in addition, figure 2 A cross-sectional structure viewed from the upper direction is shown. Here, as a silicon carbide semiconductor device, a cross-sectional structure of a power MOSFET (Power Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) is shown. in addition, figure 1 Shows figure 2 The I-I profile in, figure 2 Shows figure 1 The II-II profile in . in addition, Figure 3 to Figure 12 Shows figure 1 as well as figure 2 The fabrication method of the power MOSFET is shown.
[0062] First, refer to figure 1 as well as figure 2 , to explain the structure of the power MOSFET.
[0063] 1 is n + type (first conductivity type) semiconductor substrate. 2 is n - Type (first conductivity type) silicon carbide layer (drift layer). 3 is a p-type (second conductivity type) well region as...
Embodiment
[0090] In this example, first make Figure 14 to Figure 17 The test samples (test sample A to test sample D) having four kinds of MOS capacitors as shown, and the flat band voltage was measured for each test sample. Then, the effective fixed charge density of each test sample was evaluated based on the shift amount of the flat band voltage.
[0091] Test samples A and B used the n + Type (first conductivity type) silicon carbide substrate 20 epitaxial crystal growth - n-type (first conductivity type) silicon carbide wafer composed of n-type (first conductivity type) silicon carbide layer 21 . Test samples C and D use the + p - A p-type (second conductivity type) silicon carbide wafer composed of a p-type (second conductivity type) silicon carbide layer 23 .
[0092] In the test sample A, the oxide film 24 as an inorganic protective film was formed on the surface of the n-type silicon carbide wafer by chemical vapor growth using TEOS gas. In the test sample B, the thermal...
Embodiment approach 2
[0120] Figure 23 A cross-sectional structure of a silicon carbide semiconductor device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention viewed from a side direction is shown. in addition, Figure 24 A cross-sectional structure viewed from the upper direction is shown. Here, a cross-sectional structure of a Schottky diode is shown as a silicon carbide semiconductor device. in addition, Figure 23 Shows Figure 24 The I-I profile in, Figure 24 Shows Figure 23 The II-II profile in . in addition, Figure 25 to Figure 31 Shows Figure 23 as well as Figure 24 The fabrication method of the Schottky diode is shown. In addition, in Figure 23 to Figure 31 , for the cross-sectional structure and manufacturing process of the power MOSFET shown in Embodiment 1 Figure 1 to Figure 12 The same or equivalent parts are attached with the same symbols.
[0121] First, refer to Figure 23 as well as Figure 24 , to explain the structure of the Schottky diode.
[0122] 1 is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com