Targeted exogenous gene integration method
An exogenous gene, site-specific integration technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as reducing the controllability and safety of transgenes, the complexity of gene expression regulation, and inability to achieve results, so as to eliminate safety concerns and avoid target gene expression. Silence, overcoming the effect of positional effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
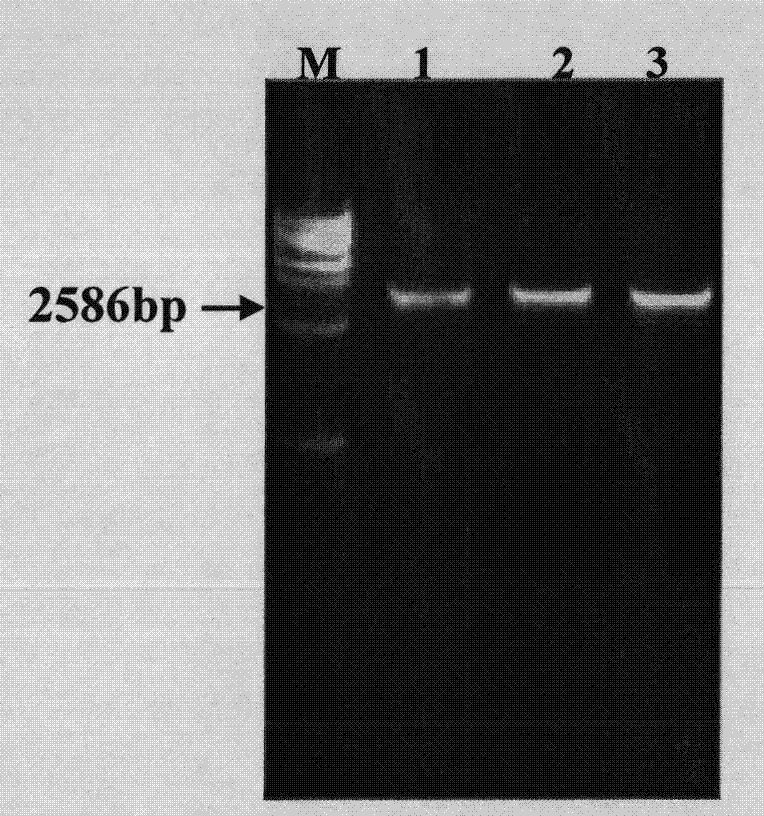
[0031] Example 1: as1-casein locus site-directed integration of other target gene targeting vector construction (taking human lysozyme gene as an example)
[0032] 1. Construction of gene targeting vector
[0033] 1.1 Amplification and sequencing of homology arms
[0034] According to the bovine as1-casein sequence (Genebank number: X59856) published by GeneBank, an upstream primer (see SEQ ID NO.1) 5'-ATTT was designed GCGGCCGC TAATGTTCCTGTCATACAACTGTGAAT-3', introduce NotI restriction site; downstream primer (see SEQ ID NO.2) 5'-CC CTCGAG GTCAAGATCTATGTAAGAAAATAAAATAG-3', introduce XhoI restriction site, used to amplify homologous left arm (Left arm, 9354-11939, 2586bp). Simultaneously designed the upstream primer (see SEQ ID NO.3) 5'-ACGC GTC GAC AACCATGAAACTTCTCATCCTTAC-3', introduce SalI restriction site; downstream primer (see SEQ ID NO.4) 5'-ACGC GTCG AC ACATTCTTGGGTATGATAGCACTGC-3' introduced a SalI restriction site to amplify the homologous right arm (Right ...
Embodiment 2
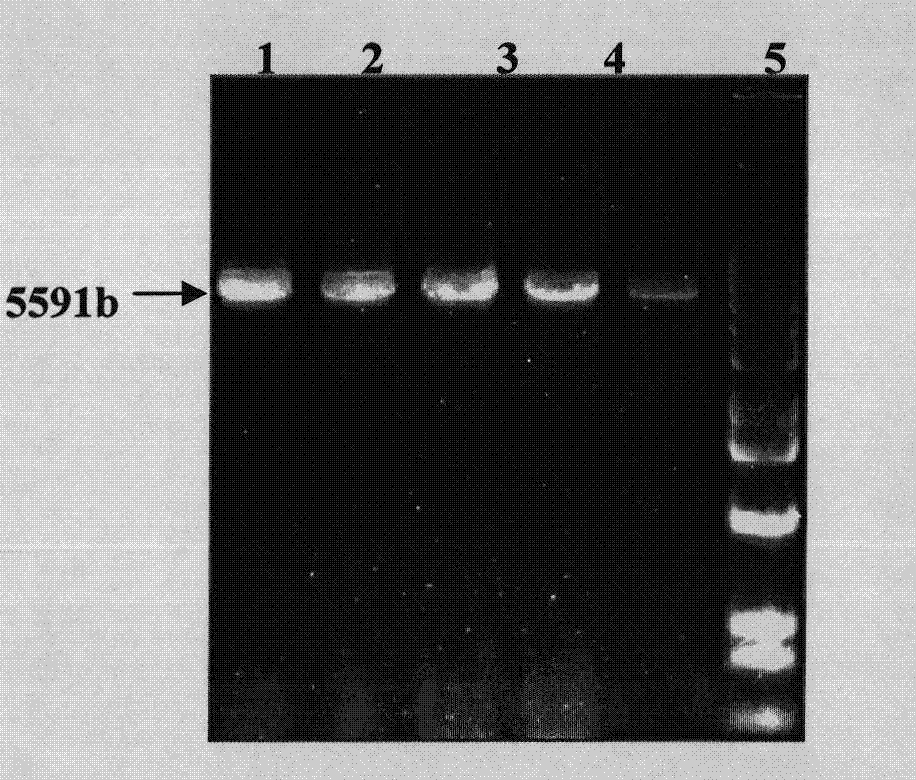
[0058] Example 2: Site-directed integration of as1-casein locus and construction of targeting vectors for other target genes (taking human lactoferrin gene as an example)
[0059] According to the above vector construction method, total mRNA was extracted from human breast tissue, and cDNA was obtained by reverse transcription. The upstream and downstream primers were designed according to the human lactoferrin gene sequence published by NCBI (Genebank number: NM_002343): hLF upstream primer, TGC AAGCTT ACCATGAAACTTGTCT (see SEQ ID NO.13); hLF downstream primer, ACG TCTAGA AGCTGGGCCATCTTCTTCG (see SEQ ID NO. 14). Using the cDNA obtained by reverse transcription as a template, the 2155bp hLF coding region was amplified with high-fidelity enzymes, subcloned into the PCDNA3.1 vector using HindIII and XbaI restriction sites, and sequenced. Sequencing results showed 100% homology with the published sequence. Utilizing upstream primer TGC CTCGAG ACCATGAAACTTGTC (see SEQ ID NO....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com