Laser penetration brazing method for dissimilar alloy
A brazing method and alloy technology, which is applied in the field of laser material processing, can solve problems affecting the mechanical properties of joints, lack of fusion, stability, and poor weld formation, so as to improve spreading and infiltration ability, good weld formation, and welding efficiency Improved effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
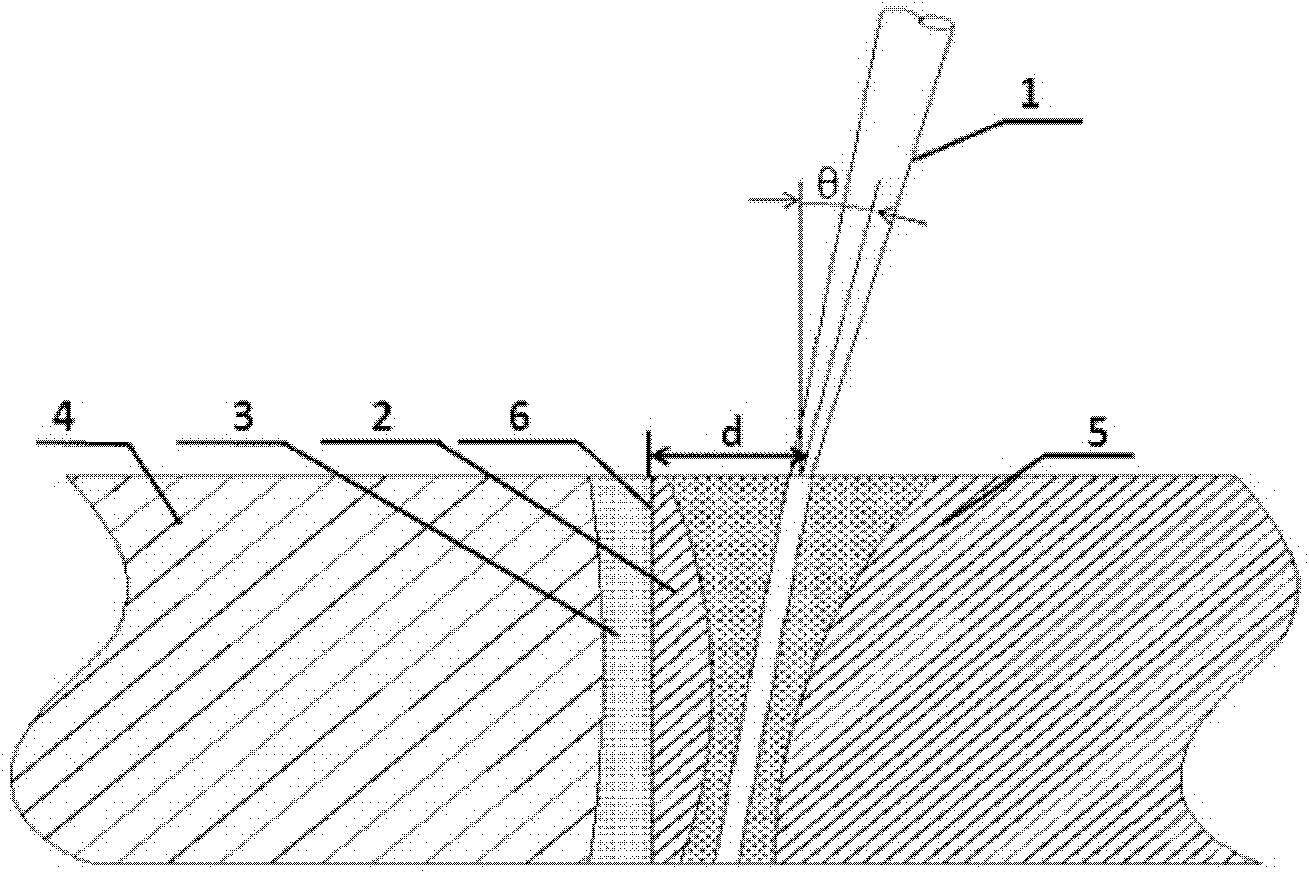
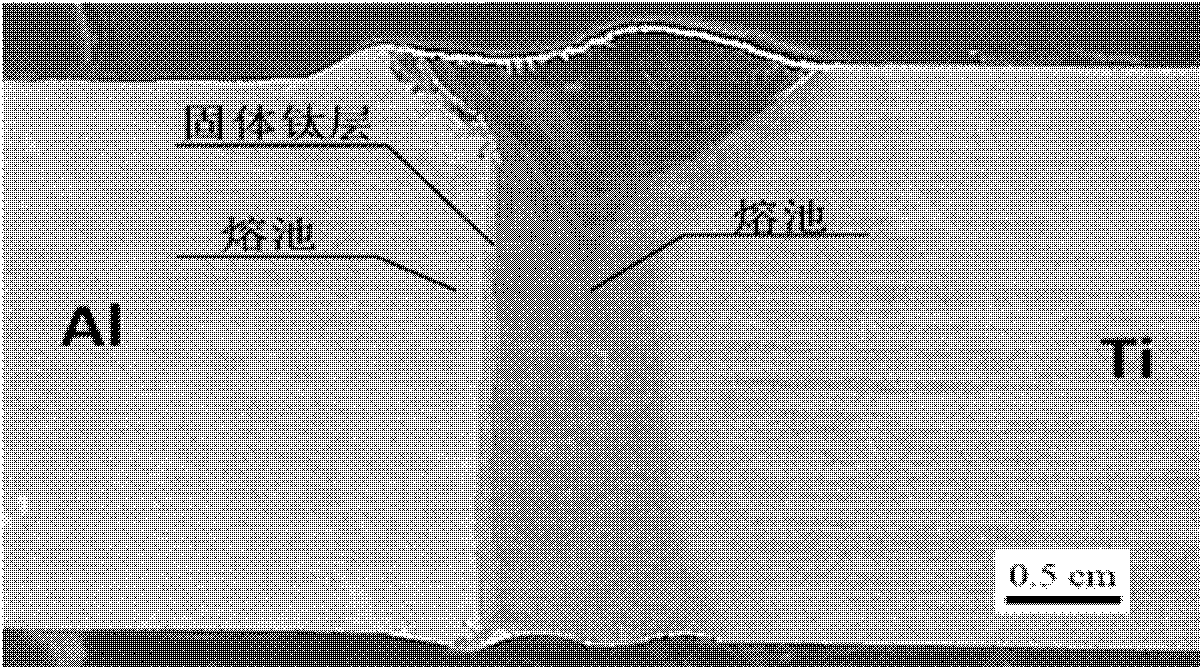
[0025] Example 1. Using a fiber laser with a wavelength of 1070nm, the focused laser beam (1) is vertically incident on the titanium alloy side, and the distance d between the laser beam (1) and the interface (6) is 0.6mm. Aluminum alloy material: 6061, titanium alloy: TC4, thickness: 3mm; laser power 3100W. figure 2 The cross-sectional view of the weld with the above parameters shows that the maximum thickness of the intermetallic compound layer formed on the upper part of the weld interface is 10 μm, and there is basically no intermetallic compound layer on the lower part.
example 2
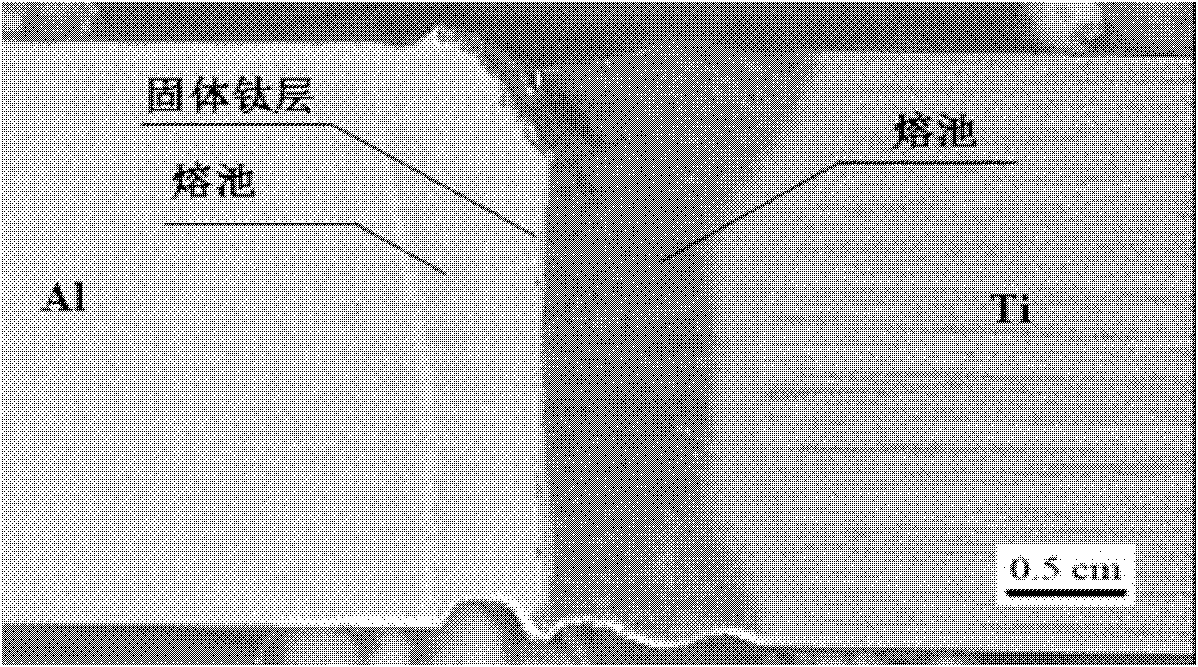
[0026] Example 2, using a fiber laser with a wavelength of 1070nm, the focused laser beam (1) is obliquely incident on the titanium alloy side, wherein the angle between the laser beam and the normal is 6°, and the distance d between the laser beam (1) and the interface (6) is 0.6 mm. Aluminum alloy material: 6061, titanium alloy: TC4, thickness: 3mm; laser power 3100W. image 3 The cross-sectional profile of the weld with the above parameters shows that a uniform intermetallic compound layer is formed at the interface of the weld with a thickness of about 5 μm.
[0027] Depend on figure 2 ,3 It can be seen that the welding seam obtained by the present invention has no obvious defects such as cracks and pores, and the welding process is stable. At the same time, due to the existence of a solid intermediate layer in the titanium alloy at the interface, it avoids the mixing of the two metals in a liquid state to produce a thicker intermetallic compound layer. Performance is i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com