Oxidized cellulose nanofibers and preparation method thereof
A technology for oxidizing cellulose and nanofibers, which is applied to artificial filaments made of cellulose derivatives, fiber processing, filament/thread forming, etc. It can solve the problems of difficult electrospinning of cellulose solutions and achieve electrical conductivity. Enhancement, safe operation, mild degradation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] 1. Immerse 5 g of dried microcrystalline cellulose fibers in 500 ml of sodium periodate aqueous solution with a molar concentration of 0.1 mol / L. The bath ratio is 1:100. Fully wash until the pH value of the water is about 7.0, freeze-dry after dehydration.
[0021] 2. A certain amount of dry oxidized cellulose was weighed, and LiCl / DMAc was selected as the dissolution system, wherein the mass ratio of the three substances was LiCl / DMAc / oxidized cellulose (7.2 / 82.8 / 10). The prepared oxidized cellulose solution was subjected to electrospinning under high pressure conditions. The electrospinning conditions were: room temperature, voltage 28kv, flow rate of spinning solution 0.5ml / h, receiving distance 15cm.
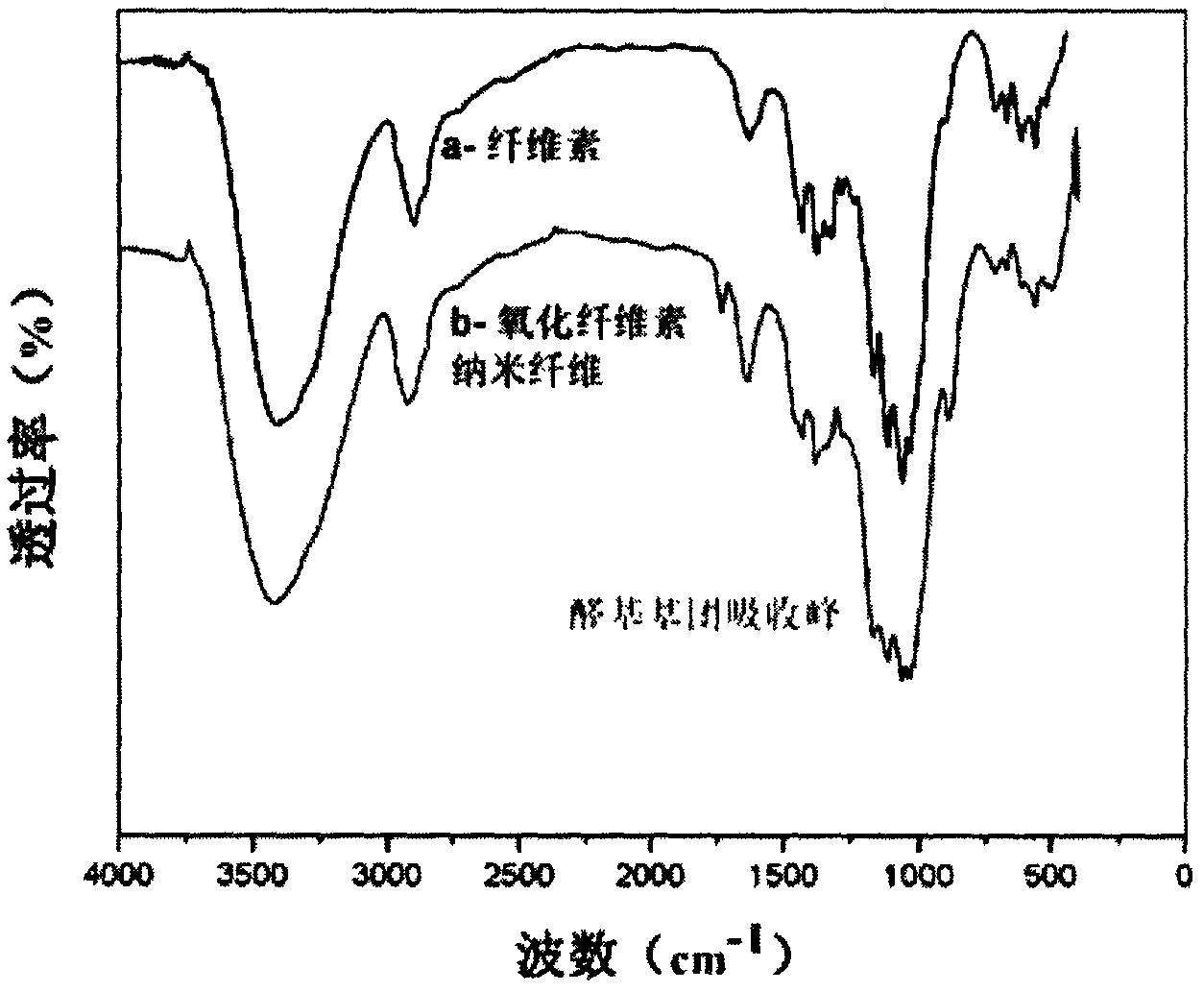
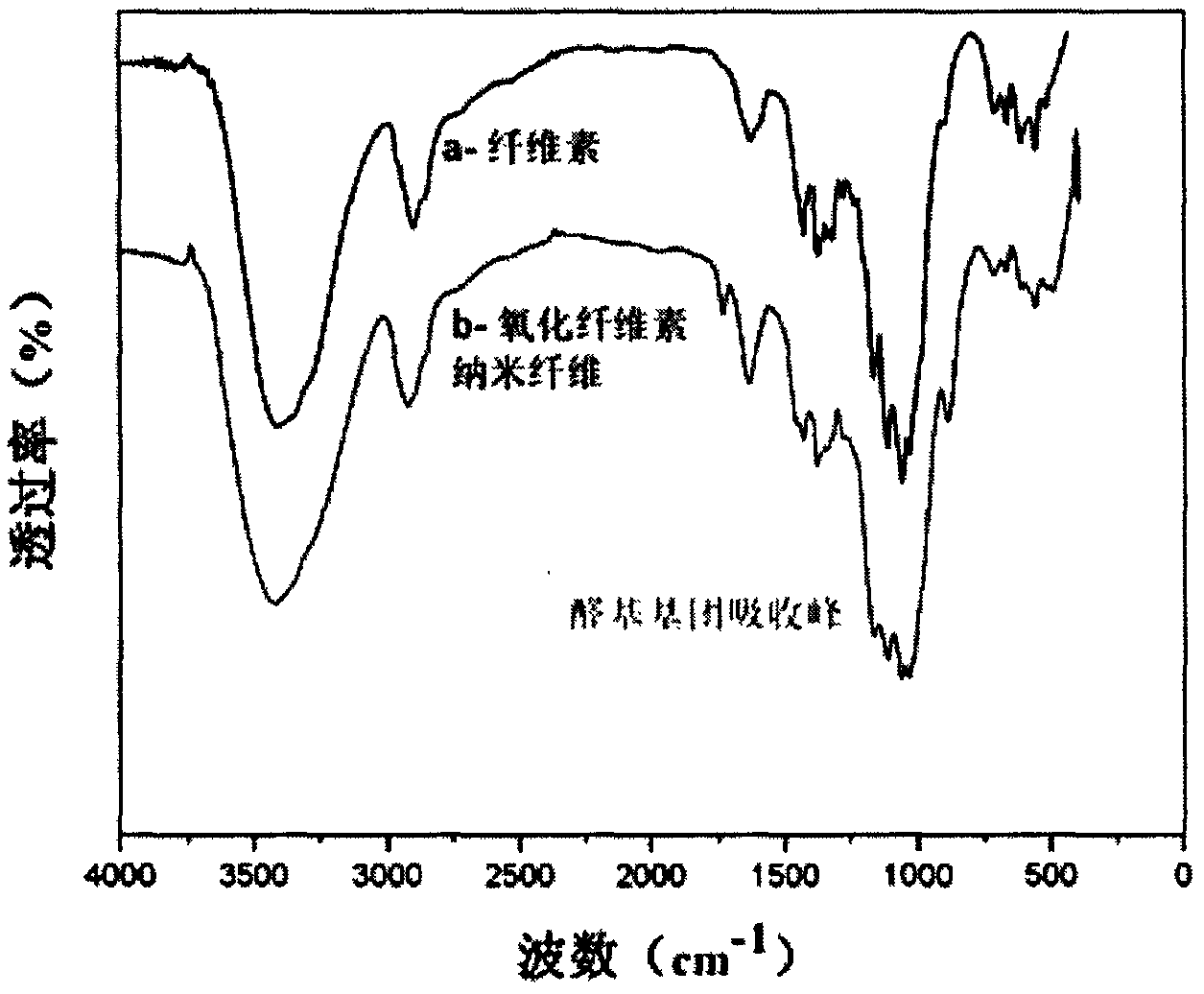
[0022] See attached figure 1 , which is the infrared spectrogram of the oxidized cellulose nanofibers provided in this example. The curve in the figure shows that the oxidized cellulose nanofibers at 1750cm -1 There is an obvious aldehyde absorption peak at , and ...
Embodiment 2
[0024] 1. Immerse 5 g of dried microcrystalline cellulose fibers in 500 ml of sodium periodate aqueous solution with a molar concentration of 0.1 mol / L. The bath ratio is 1:100. Fully wash until the pH value of the water is about 7.0, freeze-dry after dehydration.
[0025] 2. Weigh a certain amount of dry oxidized cellulose, choose NMMO / H 2 O as a dissolved system, the mass ratio of the three substances NMMO / H 2 O / oxidized cellulose is 18 / 72 / 10, and the dissolution temperature is 80°C. The prepared oxidized cellulose solution was electrospun under high pressure conditions. The electrospinning conditions were: room temperature, voltage 30kv, spinning solution temperature 80°C, temperature spinning solution flow rate 0.5ml / h, receiving distance 15cm, receiving The device temperature is 80°C, and the spinning time is 5h. The average diameter of the fibers of the obtained non-woven fabric is 230 nm, and the thickness of the non-woven fabric is between 0.1 and 0.15 mm.
Embodiment 3
[0027] 1. Immerse 5 g of dried cotton linters in 500 ml of sodium periodate aqueous solution with a molar concentration of 0.1 mol / L, the bath ratio is 1:100, oxidize in the dark at 50°C for 48 hours, and use deionized water Fully wash until the pH value of the water is about 7.0, freeze-dry after dehydration.
[0028] 2. Weigh a certain amount of dry oxidized cellulose, and select LiCl / DMAc as the dissolution system, wherein the mass ratio of the three substances LiCl / DMAc / oxidized cellulose is 8 / 84 / 8. The prepared oxidized cellulose solution was electrospun under high pressure conditions. Electrospinning conditions are: room temperature, voltage 28kv, spinning solution flow rate 0.5ml / h, receiving distance 15cm, spinning time 5h. The average diameter of the obtained non-woven fabric fiber is about 220nm, and the thickness of the non-woven fabric is between 0.1-0.15mm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com