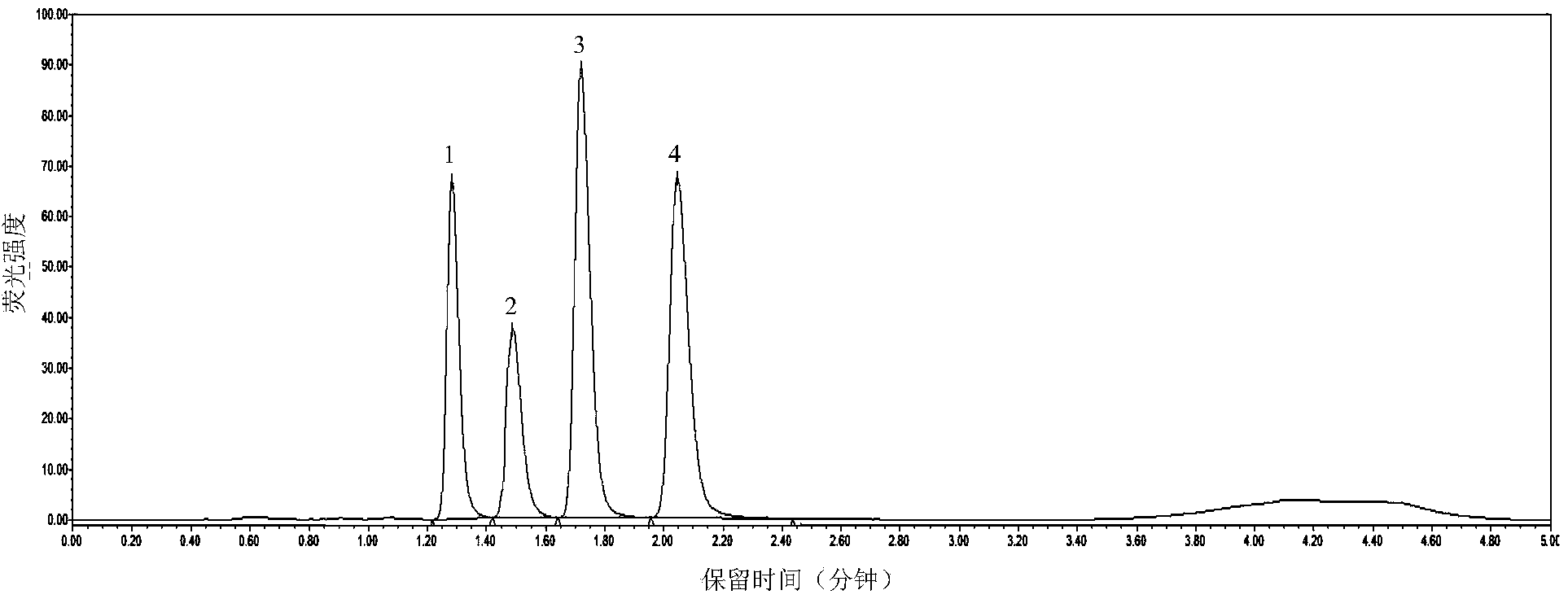
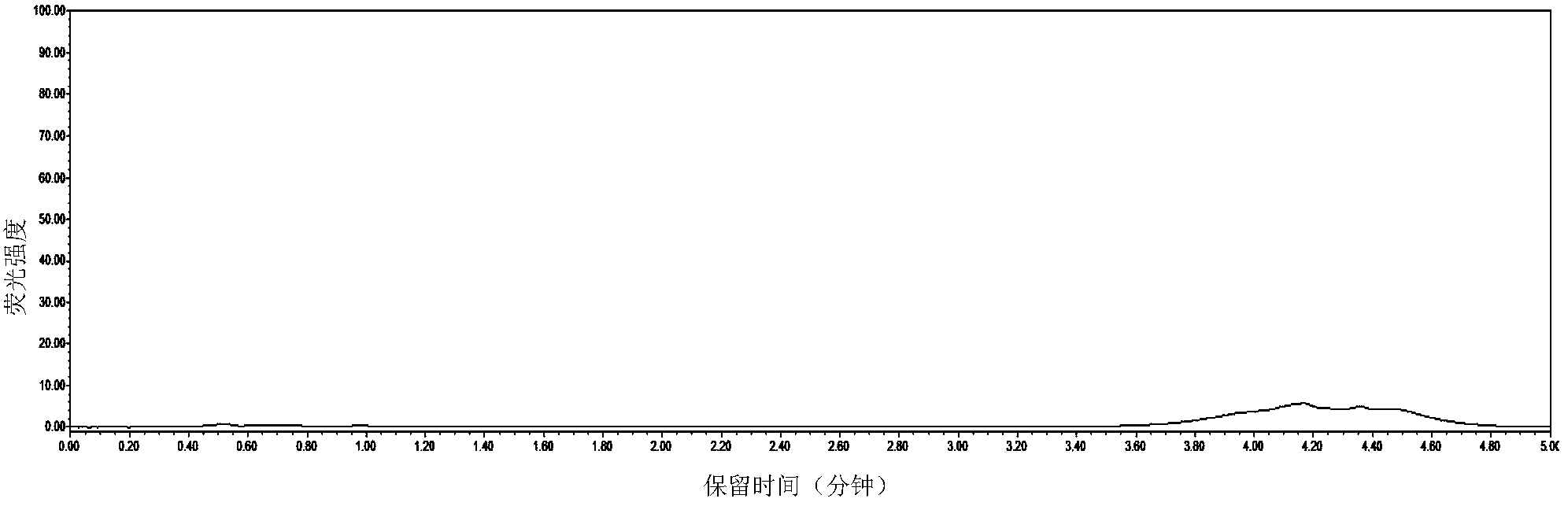
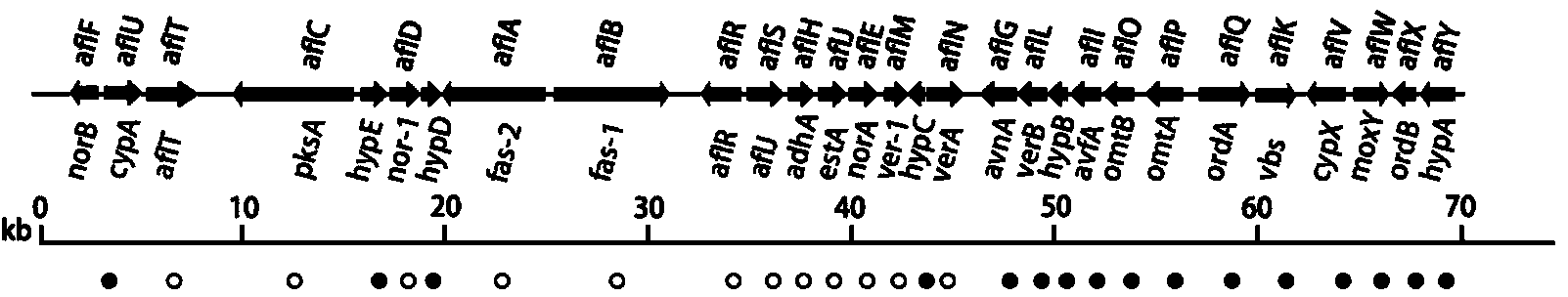
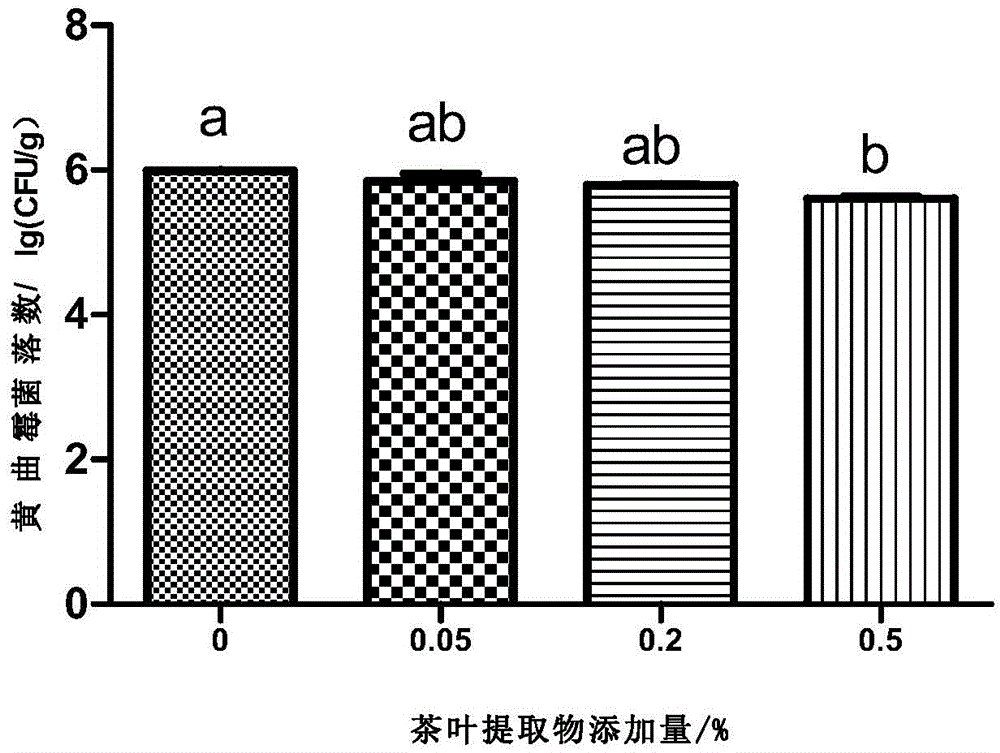
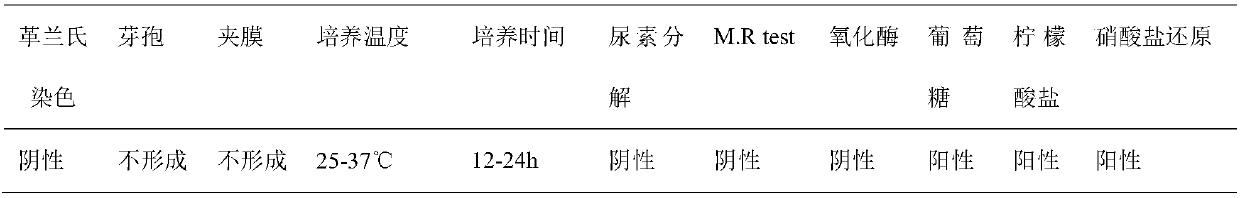
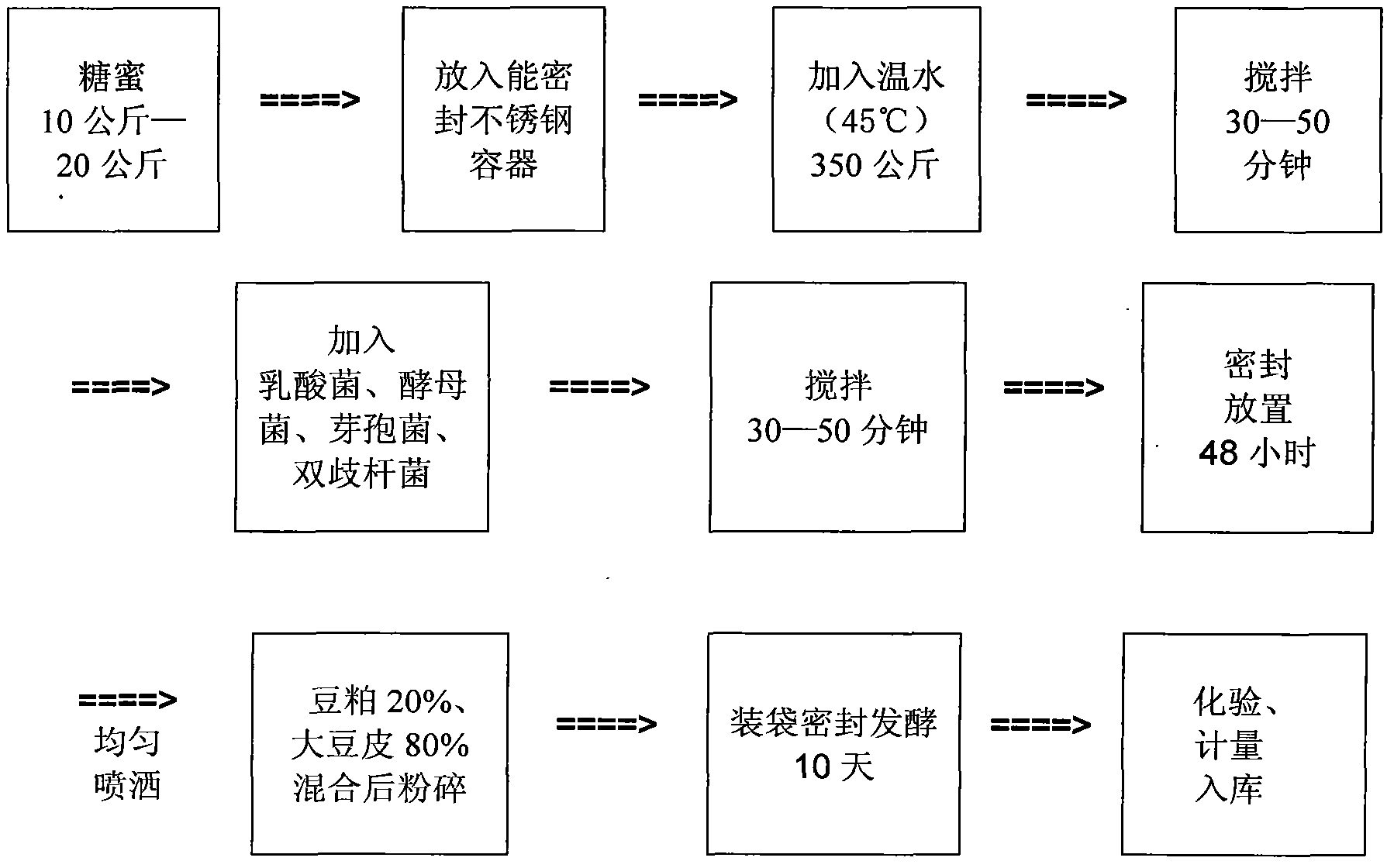
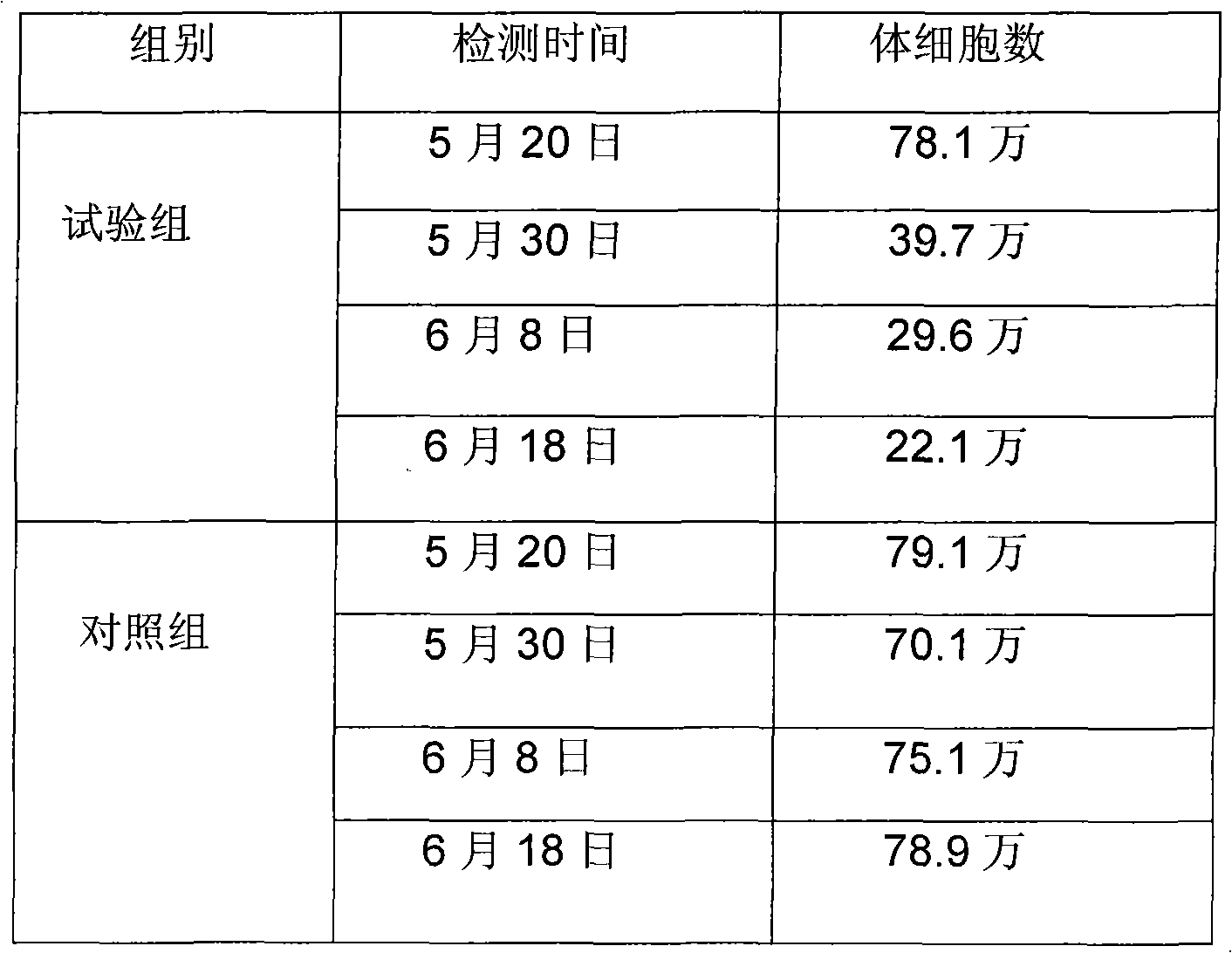
Patents
Literature
108 results about "Aflatoxin contamination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
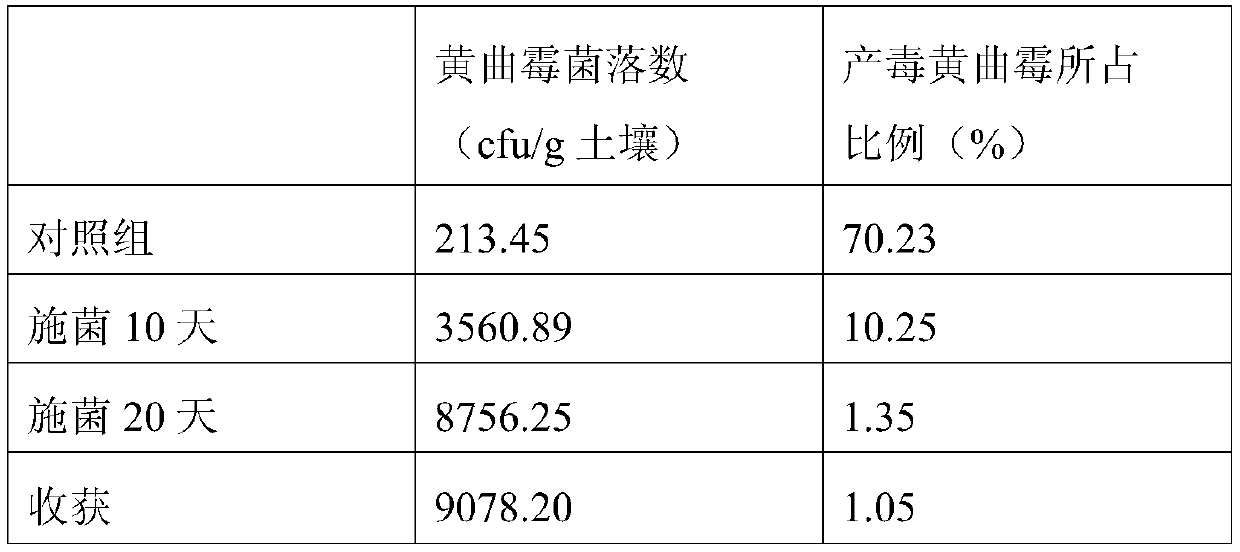
Aflatoxin is a fungal toxin that commonly contaminates maize and other types of crops during production, harvest, storage or processing. Exposure to aflatoxin is known to cause both chronic and acute hepatocellular injury. In Kenya, acute aflatoxin poisoning results in liver failure and death in up to 40% of cases.
Aspergillus flavus producing no aflatoxin and application thereof
ActiveCN103509723AReduce pollutionAvoid infectionFungiMicroorganism based processesSporeMicroorganism
The invention discloses an aspergillus flavus strain producing no aflatoxin. The aspergillus flavus strain producing no aflatoxin, provided by the invention, is specifically aspergillus flavus GZ-17; the preservation number of the aspergillus flavus strain in the general microbiology center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms is CGMCC No.8050. Experimental results show that the aspergillus flavus strain GZ-17 provided by the invention plays a role in restraining the poison production of the aspergillus flavus strain producing the aflatoxin; when the concentration ratio of the strain to a toxic producing fungus spore is 105: 105, the poison production restrained ratio of bacterium producing no poison to the bacterium producing poison is nearly 96%. The strain has important significance for restraining the infection of the aspergillus flavus producing poison to agricultural products and reducing the aflatoxin pollution in the agricultural products.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
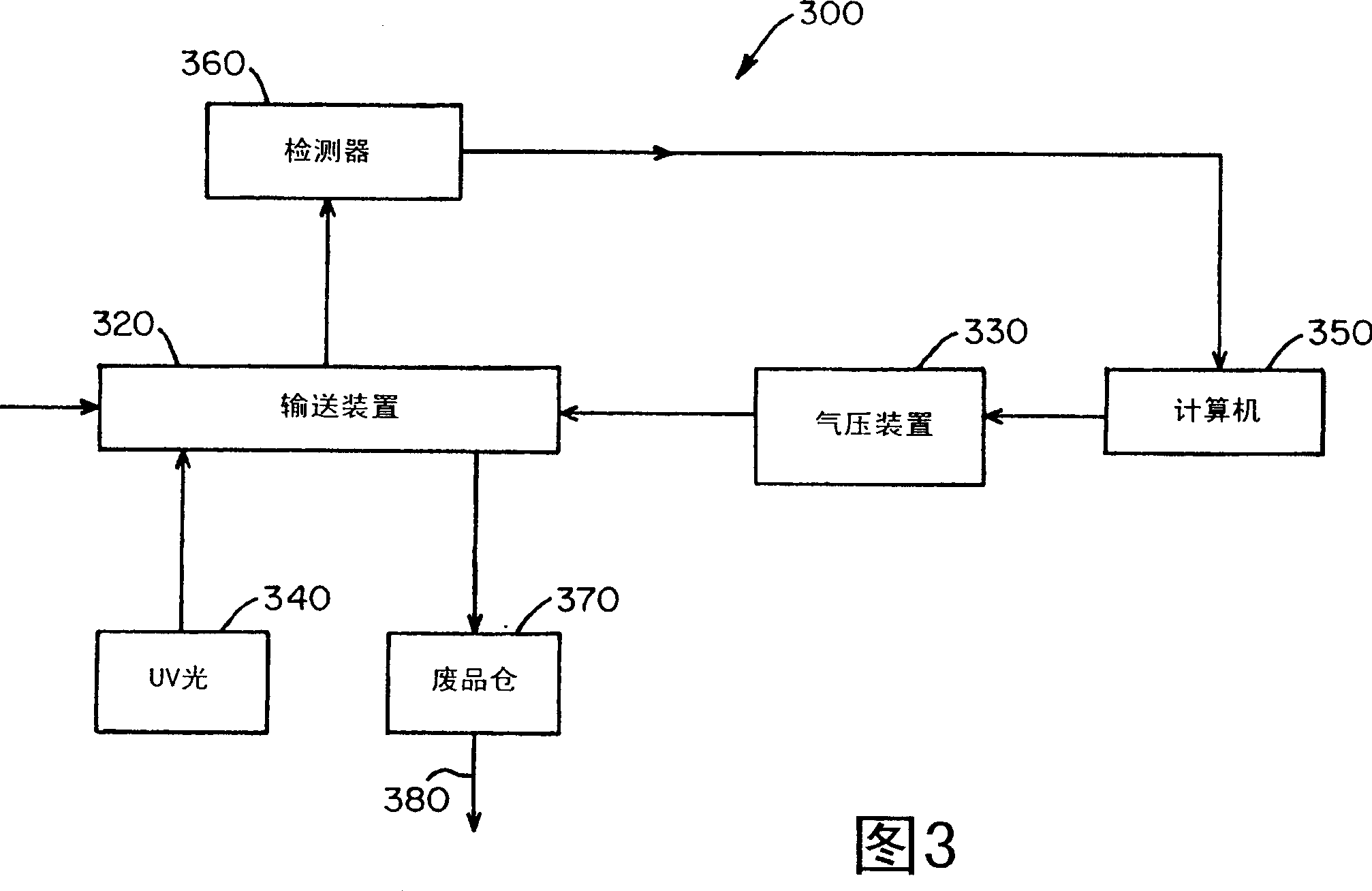
Aflatoxin detecting and sorting apparatus
ActiveCN103234945AEasy to distinguishImprove online recognition rateFluorescence/phosphorescenceColor imageFluorescence
The invention provides an aflatoxin detecting and sorting apparatus. The apparatus comprises a plurality of ultraviolet light sources, a material slide rail, and optical signal receiving devices positioned at the front and back sides of a material to be detected respectively, the ultraviolet light sources are symmetrically distributed at two sides of the tail end of the material slide rail through treating a material falling locus as an symmetric axis, the ultraviolet light sources irradiate the surface of the material and excite the fluorescence of the material, and the optical signal receiving devices collect the R, G and B fluorescence signals of the same material in a same position, convert the R, G and B fluorescence signals to electric signals, and combine the three-way electric signals to form a color image. The apparatus has the advantages of online obtaining the weak color fluorescence signal of the material, convenience for the effective distinguishing of the aflatoxin material, and improvement of the online recognition rate of aflatoxin polluted materials.
Owner:HEFEI MEIYA OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Method for identifying and evaluating toxigenic capability of toxigenic strain of aflatoxin
ActiveCN109557314ARapid virulenceRapid Identification EvaluationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAflatoxin contaminationPcr method
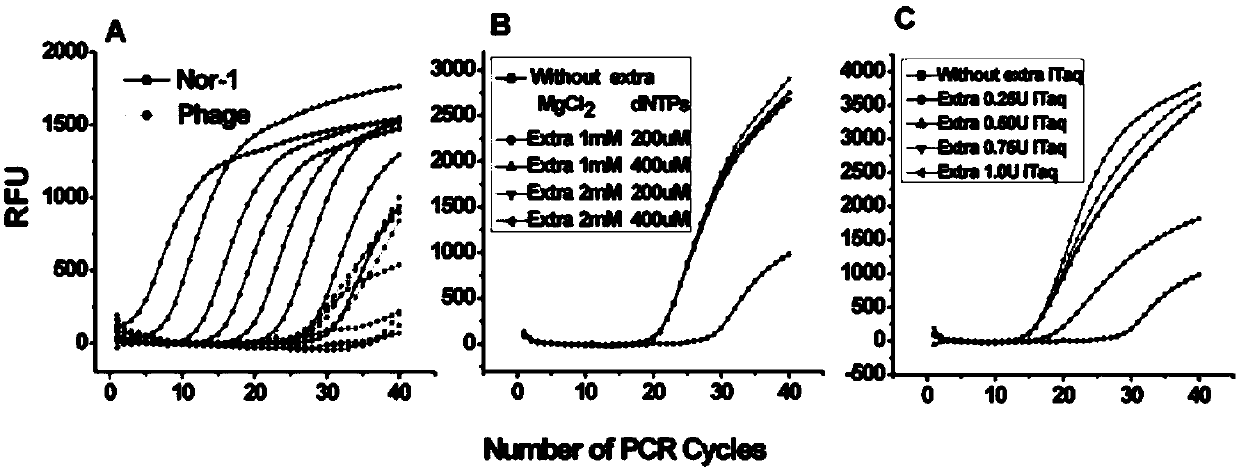
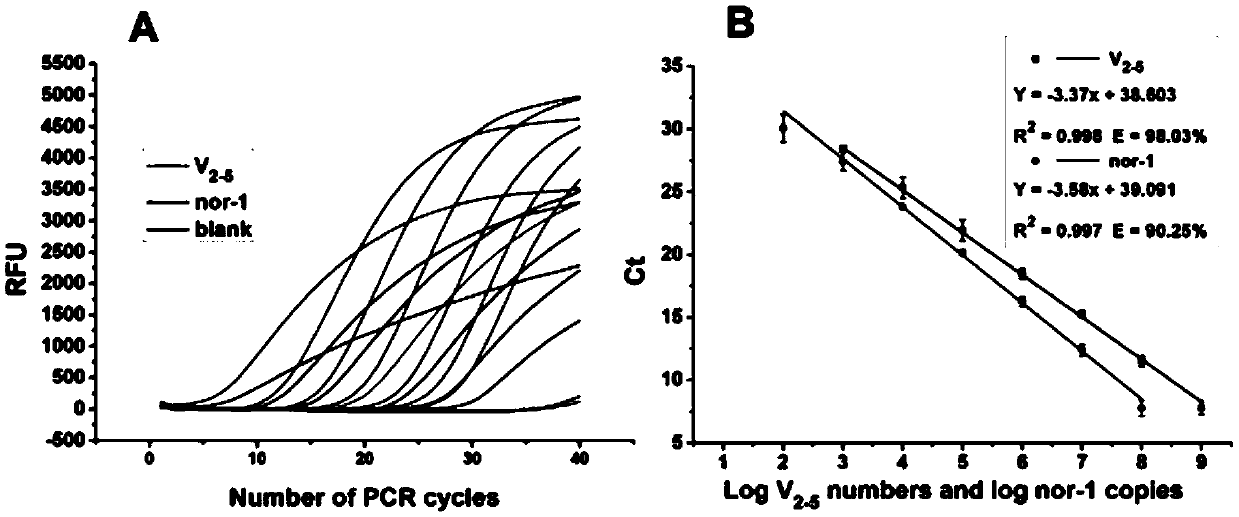
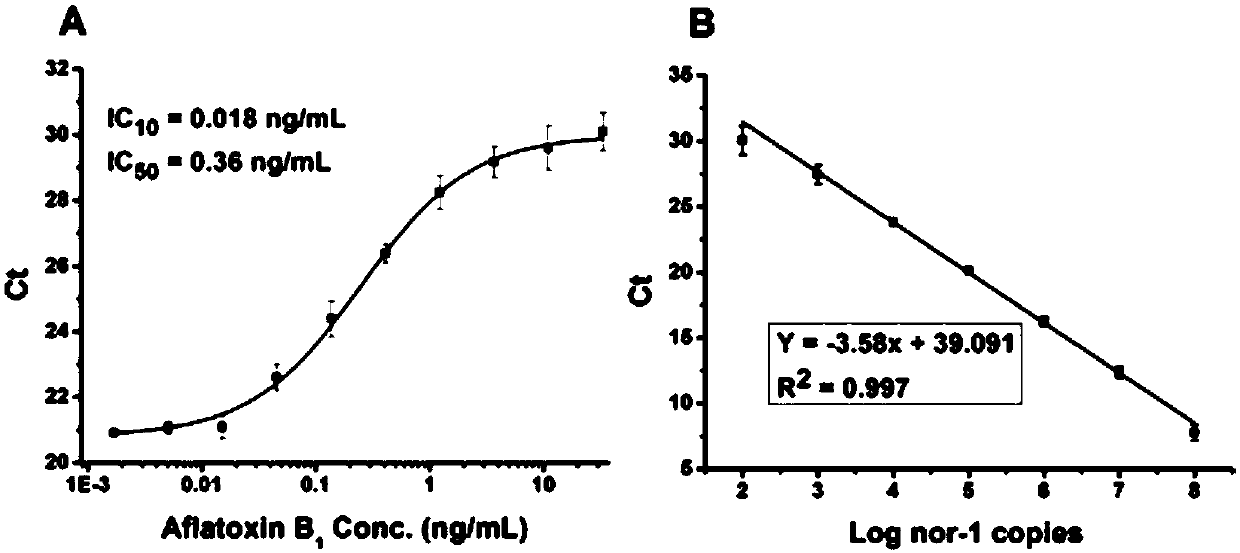
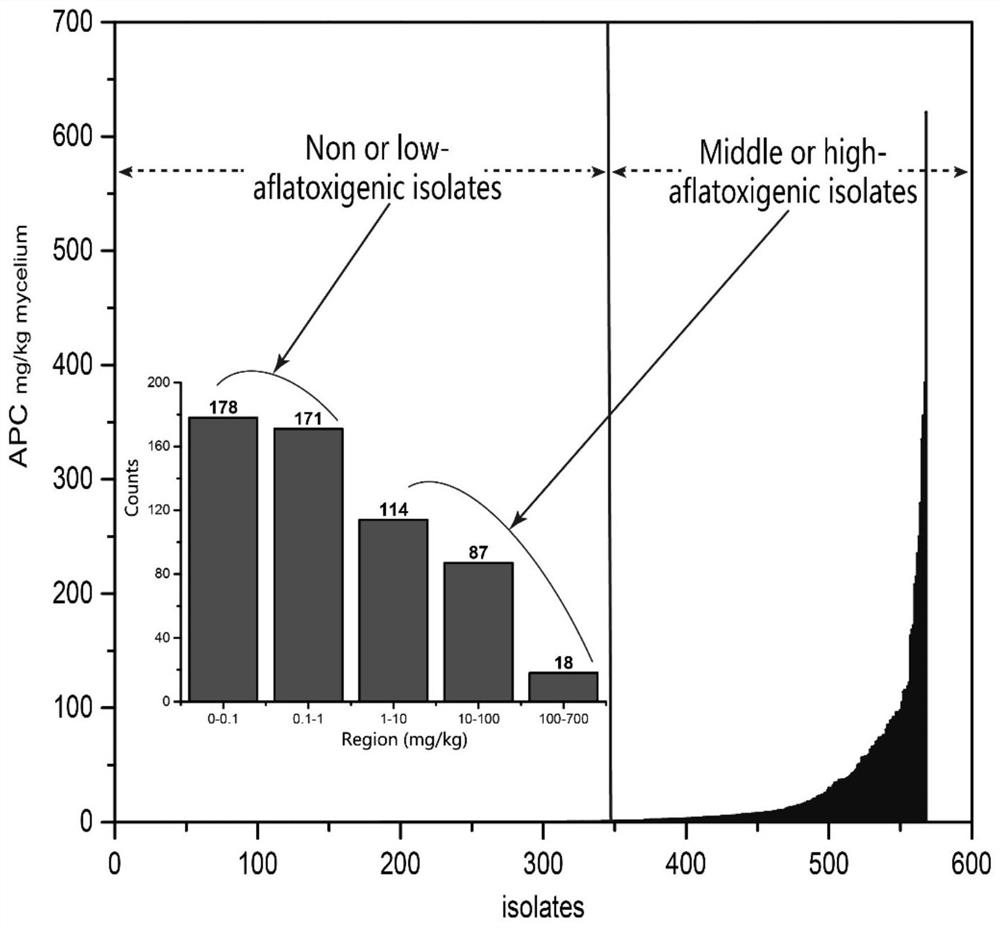
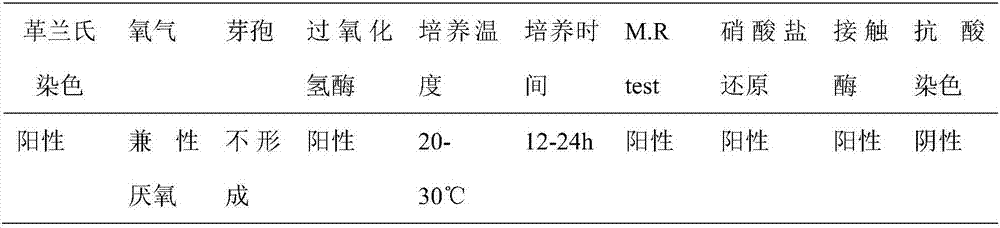
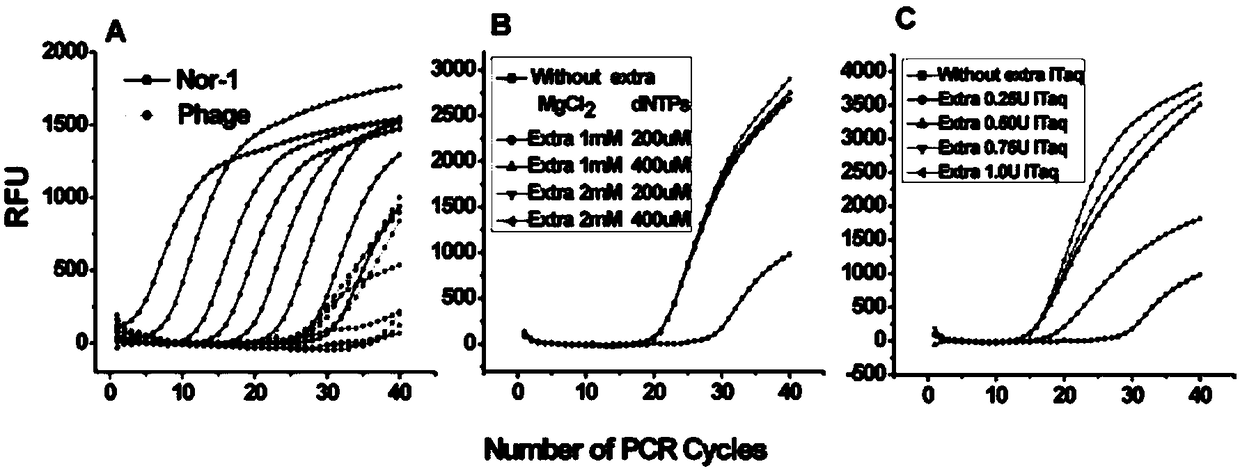
The invention, which belongs to the biological field, particularly relates to a method for identifying and evaluating the toxigenic capability of a toxigenic strain of aflatoxin. A ratio of the aflatoxin yield to the Nor-1 gene transcription amount is determined and the high relative stability is realized. An aflatoxin strain toxigenic capability identification model is established and thus a regression equation between the aspergillus flavus toxigenic capability and the AFT / Nor-1 ratio is obtained. With determination of the AFT / Nor-1 ratio, the toxigenic capability of the aspergillus flavus strain is identified and evaluated rapidly and accurately, so that the method has the important significance in aflatoxin pollution early warning and prevention controlling. Besides, a synchronous detection RT-PCR method for the aflatoxin yield and the nor-1 gene transcription amount is also established; and the AFT / Nor-1 ratio obtained based on the synchronous detection RT-PCR method is reliable and accurate and can be used as the identification index for determining the toxigenic capability of the aspergillus flavus strain.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method and system for assay and removal of harmful toxins during pocess of tobacco products
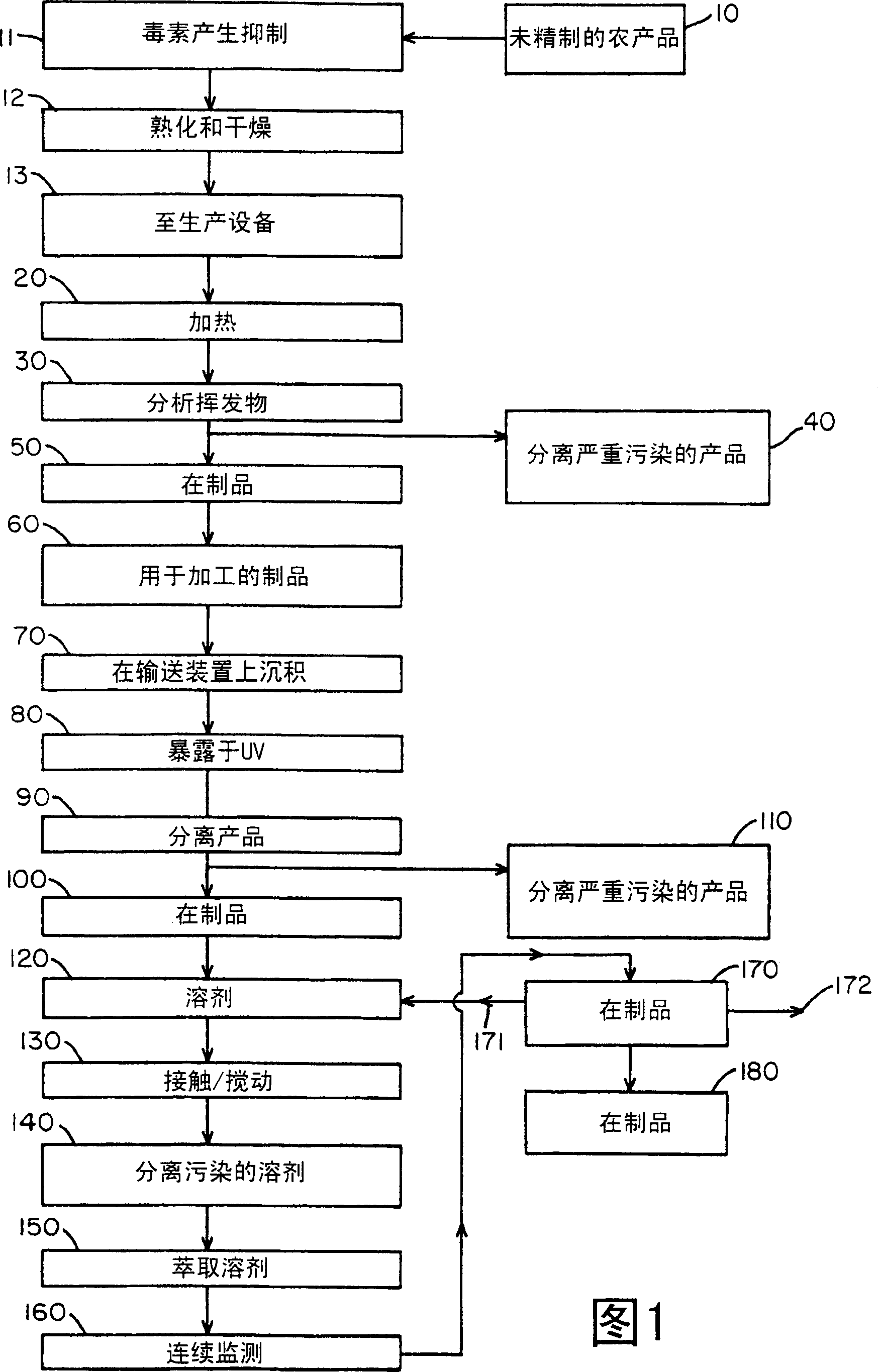
InactiveCN1384714AInhibitionReduce toxin levelsTobacco preparationOrganic chemistryQuality controlEndotoxin Contamination
The present invention relates to methods and systems for the continuous analysis (160) and removal (410) of toxins from tobacco. Products, such as tobacco contaminated with mycotoxins, especially aflatoxins and benzopyrene and their precursors, are treated, usually in a solvent medium, to remove the toxin contamination from the tobacco. As an example, all noxious toxins eluted from the wash solvent (150) are continuously monitored (160) by immunoantibody UV fluorescence analysis. A quality control process ensures that harmful toxins are removed from the tobacco before further processing. Purification of extraction solvent streams and readditives ensures safe reuse or disposal of solvents or readditives.
Owner:凯丽·斯科特·莱恩
Aspergillus flavus strain incapable of producing aflatoxin and application of aspergillus flavus strain in biological prevention and control of aflatoxin pollution of peanuts
The invention belongs to the field of the environmental biotechnology, and specifically relates to an aspergillus flavus strain incapable of producing aflatoxin and an application of the aspergillus flavus strain in biological prevention and control of aflatoxin pollution of peanuts. The aspergillus flavus strain incapable of producing aflatoxin is named as aspergillus flavus NAFFHN396, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on May 28, 2015, and the preservation serial number is CGMCC No: 10927. The aspergillus flavus strain incapable of producing aflatoxin with deletion of an aflatoxin synthetic cluster gene is obtained, and has an obvious inhibiting effect for the yield of the toxin of the strain with strong capacity of producing aflatoxin, thus a biocontrol bacterium source is provided for the biological prevention and control of the toxic aspergillus flavus generated in the field in the future, the aspergillus flavus strain is separated from China, has good colonization capacity in peanuts and potential field competitive advantage, and has great significances in inhibiting infection of the peanuts by the toxin production aspergillus flavus, and reducing the pollution of the aflatoxin in the peanuts.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Non-aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus isolates
InactiveUS7361499B1Reduce aflatoxin contaminationReduce contaminationBiocideMicroorganismsAflatoxin contaminationToxin
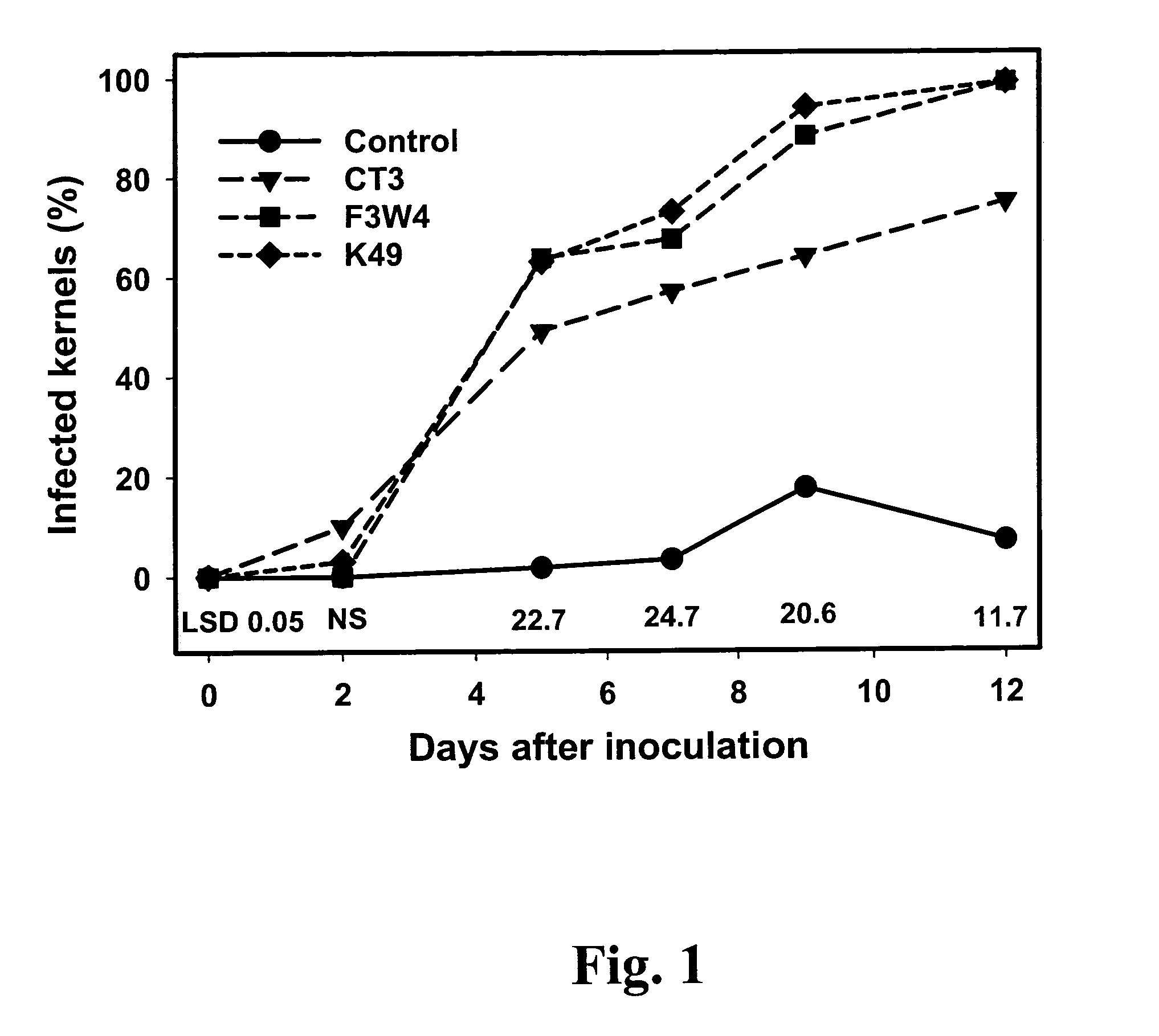
The ability of two Aspergillus flavus Link isolates (CT3 and K49) to reduce aflatoxin contamination of corn was assessed in a four-year field study (2001 to 2004). Soil was treated with six wheat inoculant treatments: toxigenic isolate F3W4; the non-toxigenic isolate K49; the non-aflatoxigenic isolate CT3, two mixtures of CT3 or K49 with F3W4; and an autoclaved wheat control, applied at 20 kg / ha. In 2001, inoculation with the toxigenic isolate increased corn grain aflatoxin levels by 167% compared to the non-inoculated control, while CT3 and K49 inoculation reduced aflatoxin levels in corn grain by 86% & 60%, respectively. In 2002, inoculation of CT3 and K49 reduced aflatoxin levels by 61% and 76% compared to non-inoculated controls, respectively. In 2001 mixtures of toxigenic and non-toxigenic isolates had little effect on aflatoxin levels, but in 2002 inoculation with mixtures of K49 and CT3 reduced aflatoxin levels 68 and 37% compared to non-inoculated controls, respectively. In 2003 and 2004, a low level of natural aflatoxin contamination was observed (8 ng / g). However, inoculation with mixtures of K49+F3W4 and CT3+F3W4, reduced levels of aflatoxin 65 to 94% compared to the toxigenic strain alone. Compared to the non-sclerotia producing CT3, strain K49 produces large sclerotia, has more rapid in vitro radial growth, and a greater ability to colonize corn when artificially inoculated, perhaps indicating greater ecological competence. Results indicate that non-toxigenic, indigenous A. flavus isolates, such as strain K49, have potential use for biocontrol of aflatoxin contamination in southern U.S. corn.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Bacillus subtilis and application of same in resisting aspergillus
InactiveCN102965306AImprove the level of prevention and controlPromote export tradeBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesActinomyces flaveolus
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis and an application of the same in resisting aspergillus. The bacillus subtilis has antagonistic action in aspergillus flavus. A method for screening the bacillus subtilis which has antagonistic action in the aspergillus flavus from soil comprises the following steps: a, bacteria isolating; b, aspergillus culturing and spore liquid preparing; c, aspergillus-resistant strain screening; and d, aspergillus-resistant strain rescreening. Through aflatoxin panel screening tests and toxin production aspergillus flavus antagonistic tests, aspergillus flavus antagonistic strains in the peanut cultivation fields and storage warehouses are screened. A method for reasonably and effectively screening the aspergillus flavus antagonistic strains is established, so that the appropriate required aflatoxin inhibition strains are obtained. The bacillus subtilis is applied to the easy aflatoxin contamination stages which are before and after harvesting crops of peanuts and the like and during storage periods and the like, the aflatoxin prevention and control levels of the crops of export peanuts and the like can be improved, export risks are lowered, and the export trade of the crops and products thereof are promoted.
Owner:中华人民共和国潍坊出入境检验检疫局
Aspergillus niger and application thereof in biological prevention and control of aflatoxin
ActiveCN104673682AGrowth inhibitionInhibition of toxin productionBiocideFungiMicroorganismAflatoxin contamination
The invention discloses Aspergillus niger and application thereof in biological prevention and control of aflatoxin. The strain is Aspergillus niger RAF106 collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on August 27, 2014 with a collection number of CGMCC NO.9608 at Yard NO.1, Building NO.3, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. Under the synergistic effect of plant polyphenol, the competition inhibiting effect of the Aspergillus niger strain screened in the invention is increased greatly. The strain is capable of remarkably inhibiting growth of Aspergillus flavus and generation of aflatoxin, and is also capable of efficiently degrading aflatoxin with high specificity, thereby having very high industrial application values. For agricultural products or feed polluted by aflatoxin, aflatoxin can be decomposed through fermentation of the strain, and the content of aflatoxin is reduced by 80.7% after corn containing aflatoxin is fermented for 48h.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Serratia marcescens biocontrol bacterium for efficiently inhibiting aspergillus flavus compounded aflatoxin and its application
The invention belongs to the field of a microorganism, and particularly relates to serratia marcescens biocontrol bacterium for efficiently inhibiting aspergillus flavus compounded aflatoxin and its application. The serratia marcescens biocontrol bacterium 3J4SM has been preserved in the China typical culture preservation center (CCTCC for short) on June 13, 2017; the preservation address is WuhanUniversity of Wuhan of China; the preservation number is CCTCC No. M2017328. The enterobacter cloacae biocontrol strain 3J4SM can be used for inhibiting aspergillus flavus compounded aflatoxin and preventing the aflatoxin pollution of grain crops.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for degrading aflatoxin in corn raw material
InactiveCN105647978AEfficient degradationMild degradationBiofuelsFermentationAflatoxin contaminationCorn flour
The invention discloses a method for degrading aflatoxin in corn raw material. The method has the advantages that on the basis of the researches on the aflatoxin distribution and conversion rule in the whole process (from corn flour raw material and fermenting mash to mature mash and vinasse after fermentation) of ethanol production through fermentation, mycotoxin degrading agent is used for efficiently degrading the aflatoxin, the aflatoxin content in the vinasse can be lowered to satisfy the aflatoxin limit requirement (not more than 50 microgram / kg) required by national feed hygienic standard (GB 13078), the degrading process and a corn flour fermenting process are synchronous, an existing ethanol production process needs not to be changed, and the ethanol conversion efficiency is unaffected; the method is mild, safe, efficient, and suitable for degrading the aflatoxin in the ethanol production process which uses corn fermentation and is polluted by the aflatoxin.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
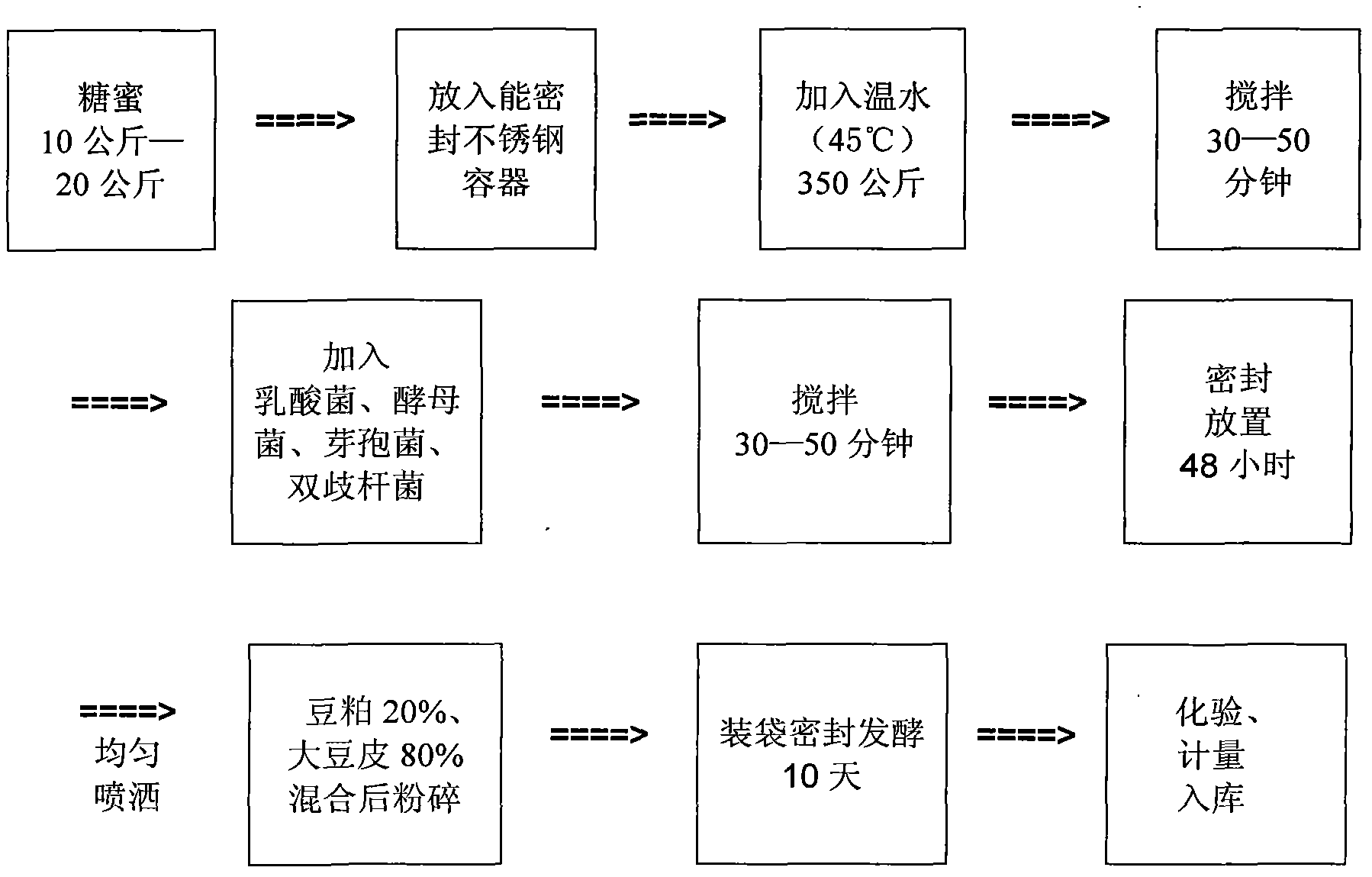
Composite microbial fermented soybean hull feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102524525APromote growth and developmentIncrease productionFood processingAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseSoybean hulls
The invention belongs to the field of breeding feed, solves the problem that milk is polluted by aflatoxin because corn serves a raw material in the conventional milk cow feed and provides composite microbial fermented soybean hull feed and a preparation method thereof. The composite microbial fermented soybean hull feed is prepared by using soybean hull as a raw material, adding byproduct bean pulp of soybean processing and combining with saccharomycetes, lactic acid bacteria, bacillus, bifidobacterium composite bacteria. The feed has good palatability and milk cows like to eat the feed. The feed can maintain the gastrointestinal flora stable, improve disease resistance of milk cows and improve quality of milk.
Owner:山东嘉冠粮油工业集团有限公司
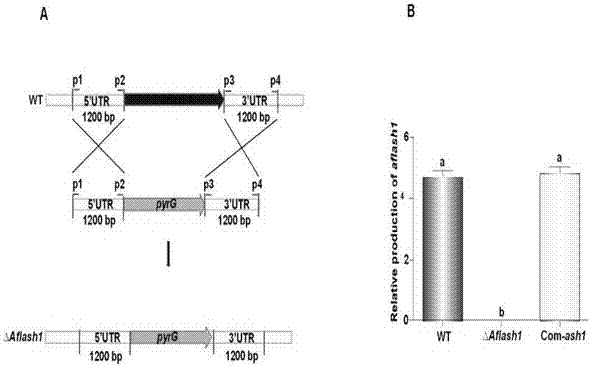
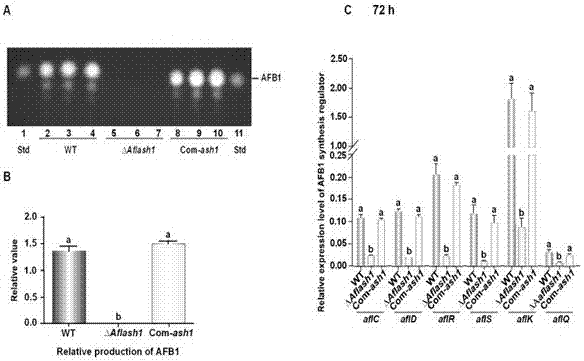
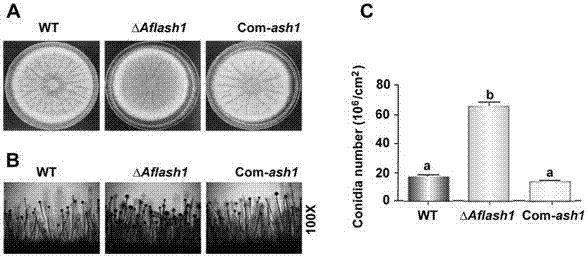
Aspergillus flavus avirulent strain and application of Aspergillus flavus avirulent strain in controlling pollution of Aspergillus flavus
InactiveCN107177516ALow densityLow sporulationFungiMicroorganism based processesVolumetric Mass DensityOrganism
The invention discloses an Aspergillus flavus avirulent strain and an application of the Aspergillus flavus avirulent strain in controlling pollution of Aspergillus flavus. In the avirulent strain, the Aspergillus flavus does not express pathogenesis related genes aflash1. The strain is non-toxic, does not produce sclerotium, produces a large quantity of spores in a culture medium and a small quantity of spores on an organism and has low pathogenicity. On the basis of the characteristics of the strain, the invention further discloses a method for controlling pollution of the Aspergillus flavus by use of the strain. More specifically, the method comprises steps as follows: by use of the characteristics that the Aspergillus flavus strain is non-toxic, does not produce sclerotium, produces a large quantity of spores in a culture medium and a small quantity of spores on an organism and has low pathogenicity, limited ecological niches are scrambled in main peanut producing areas and other susceptible areas of Aspergillus flavus through the strain and wild toxic-producing Aspergillus flavus strains, the density of the wild toxic-producing Aspergillus flavus strains is effectively reduced, and Aspergillus flavus infection to crops, Aspergillus flavus toxin pollution and aspergillosis infection caused by Aspergillus flavus toxin pollution are effectively controlled and reduced.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Granular bioplastic biocontrol composition
InactiveUS8173179B1Reduce aflatoxin contaminationReduce contaminationBiocideAnimal repellantsMicroorganismPropagule
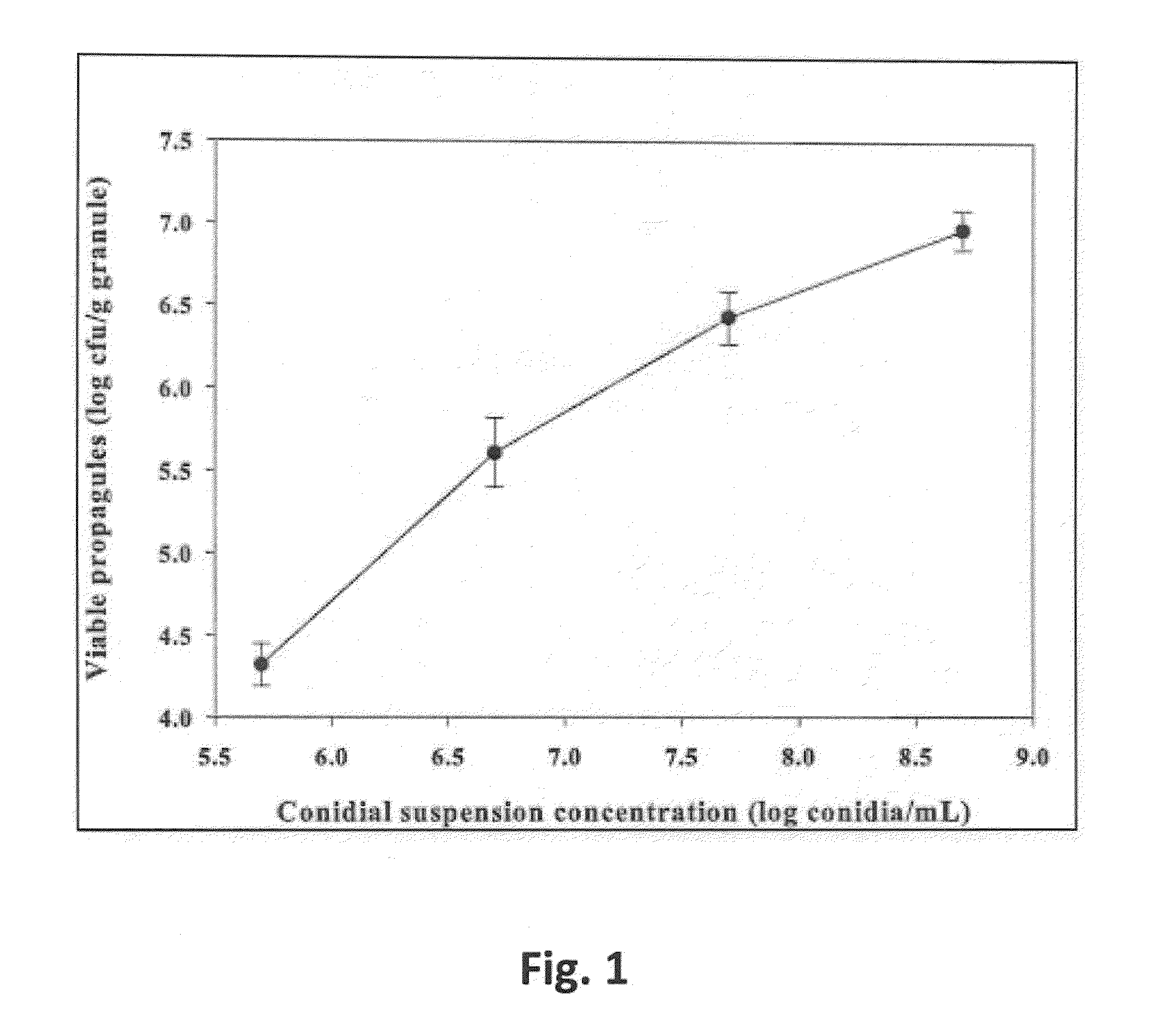
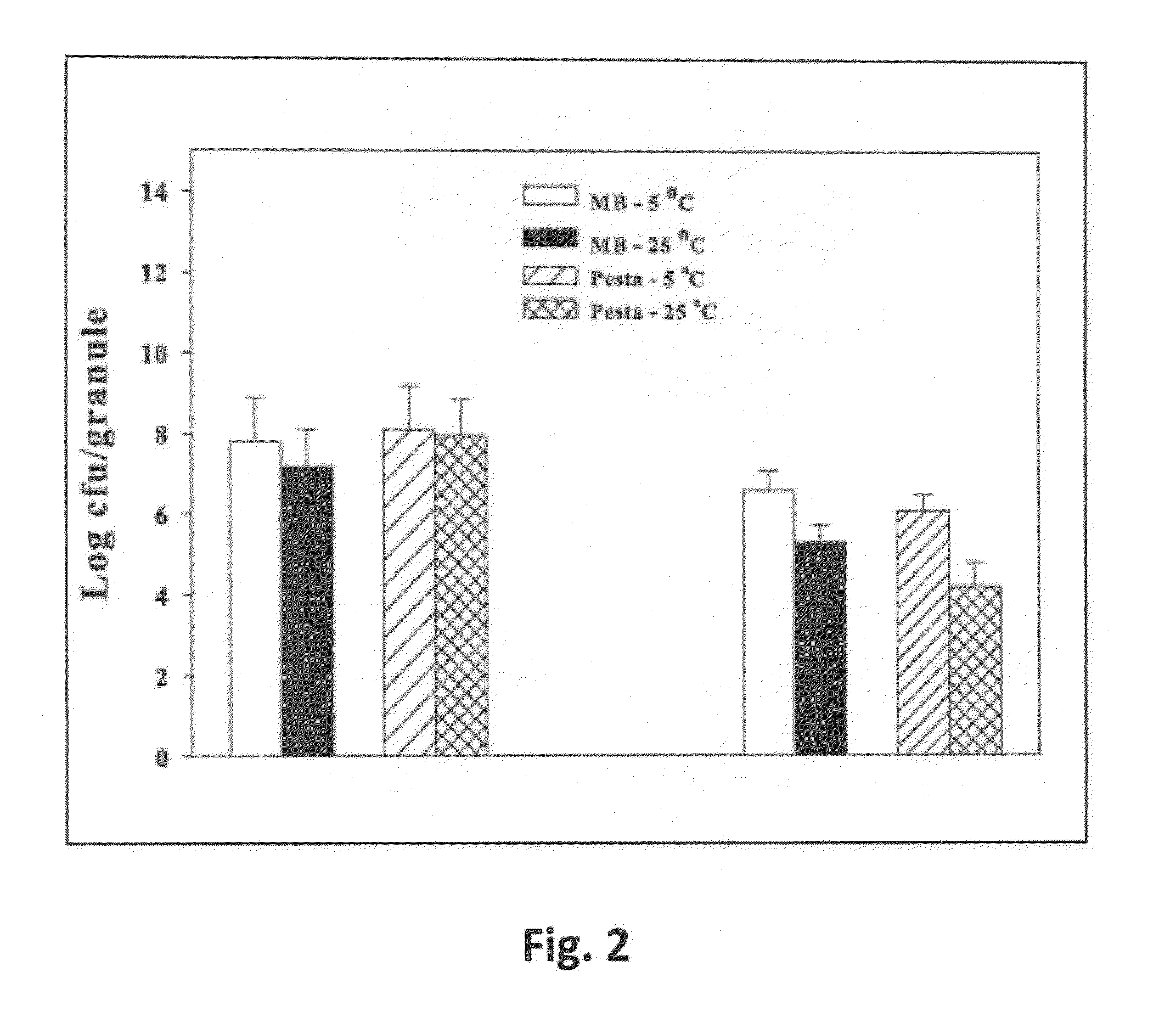
Previous research demonstrated that aflatoxin contamination in corn is reduced by field application of wheat grains pre-inoculated with the non-aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus strain NRRL 30797. To facilitate field applications of the biocontrol isolate, a series of laboratory studies were conducted on the reliability and efficiency of replacing wheat grains with the novel bioplastic formulation Mater-Bi® to serve as a carrier matrix to formulate this fungus. Mater-Bi® granules were inoculated with a conidial suspension of NRRL 30797 to achieve a final cell density of ˜log 7 conidia / granule. Incubation of 20-g soil samples receiving a single Mater-Bi® granule for 60-days resulted in log 4.2 to 5.3 propagules of A. flavus / g soil for microbiologically active and sterilized soil, respectively. Increasing the number of granules had no effect on the degree of soil colonization by the biocontrol fungus. In addition to the maintenance of rapid vegetative growth and colonization of soil samples, the bioplastic formulation was highly stable, indicating that Mater-Bi® is a suitable substitute for biocontrol applications of A. flavus NRRL 30797.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Trichoderma viride strain and application of metabolites thereof
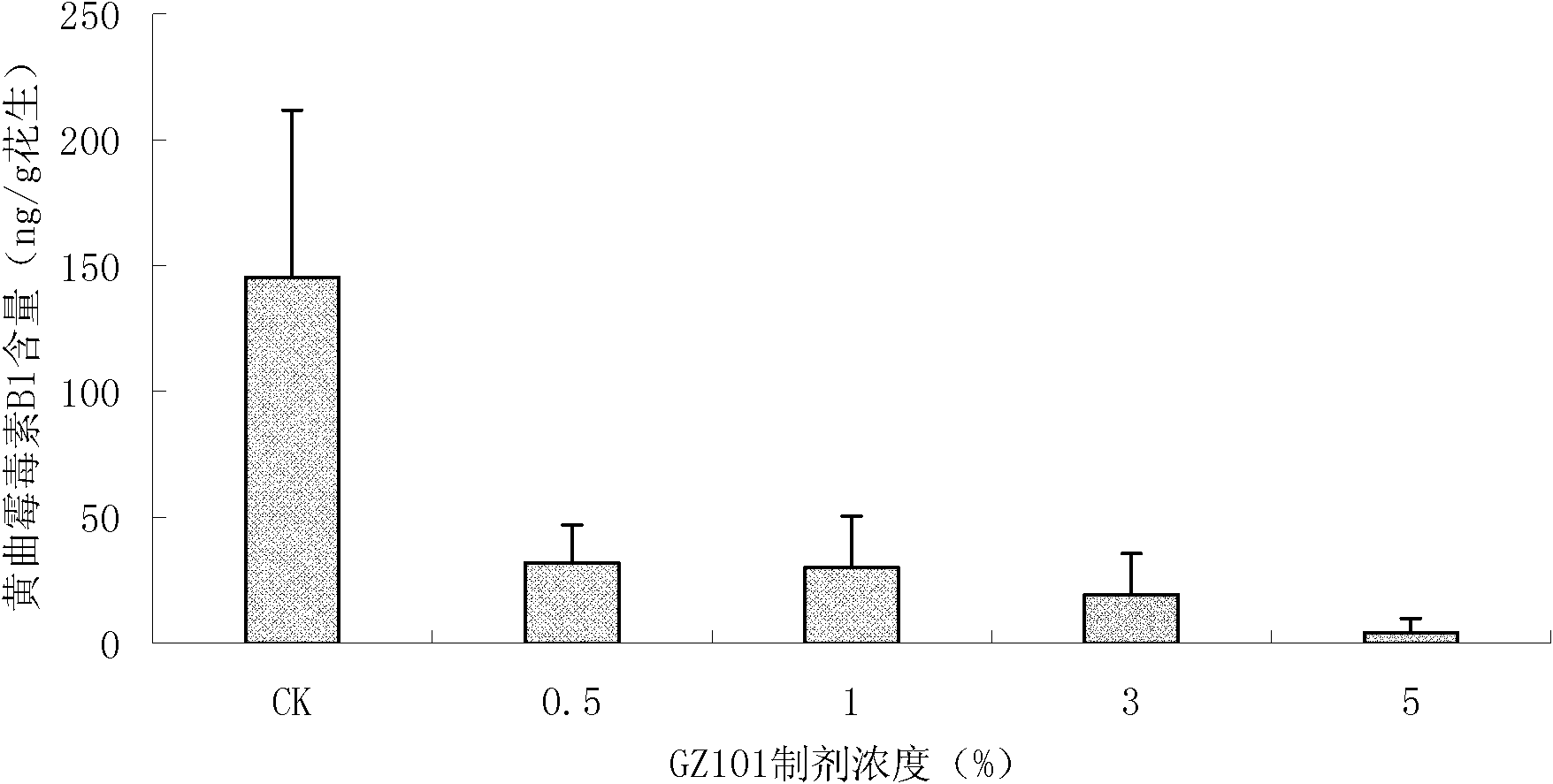
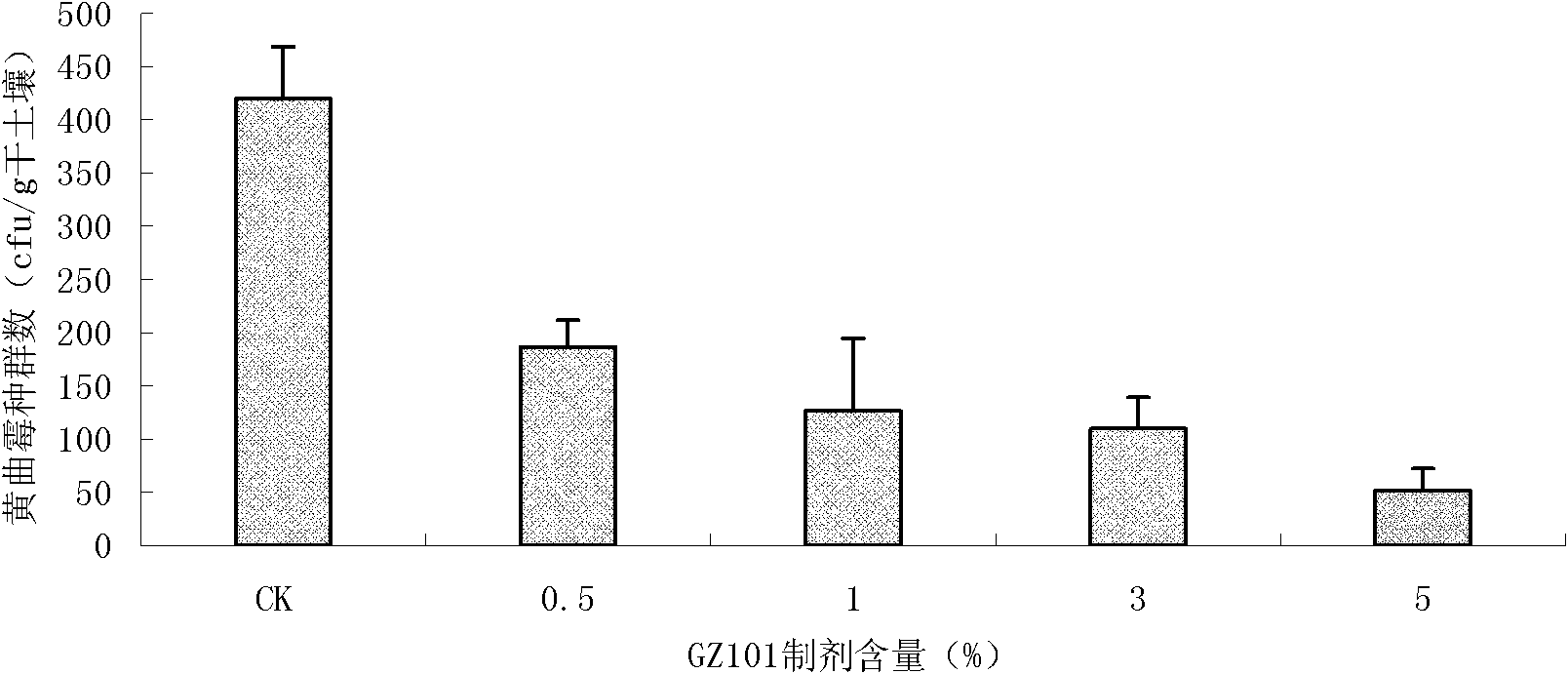
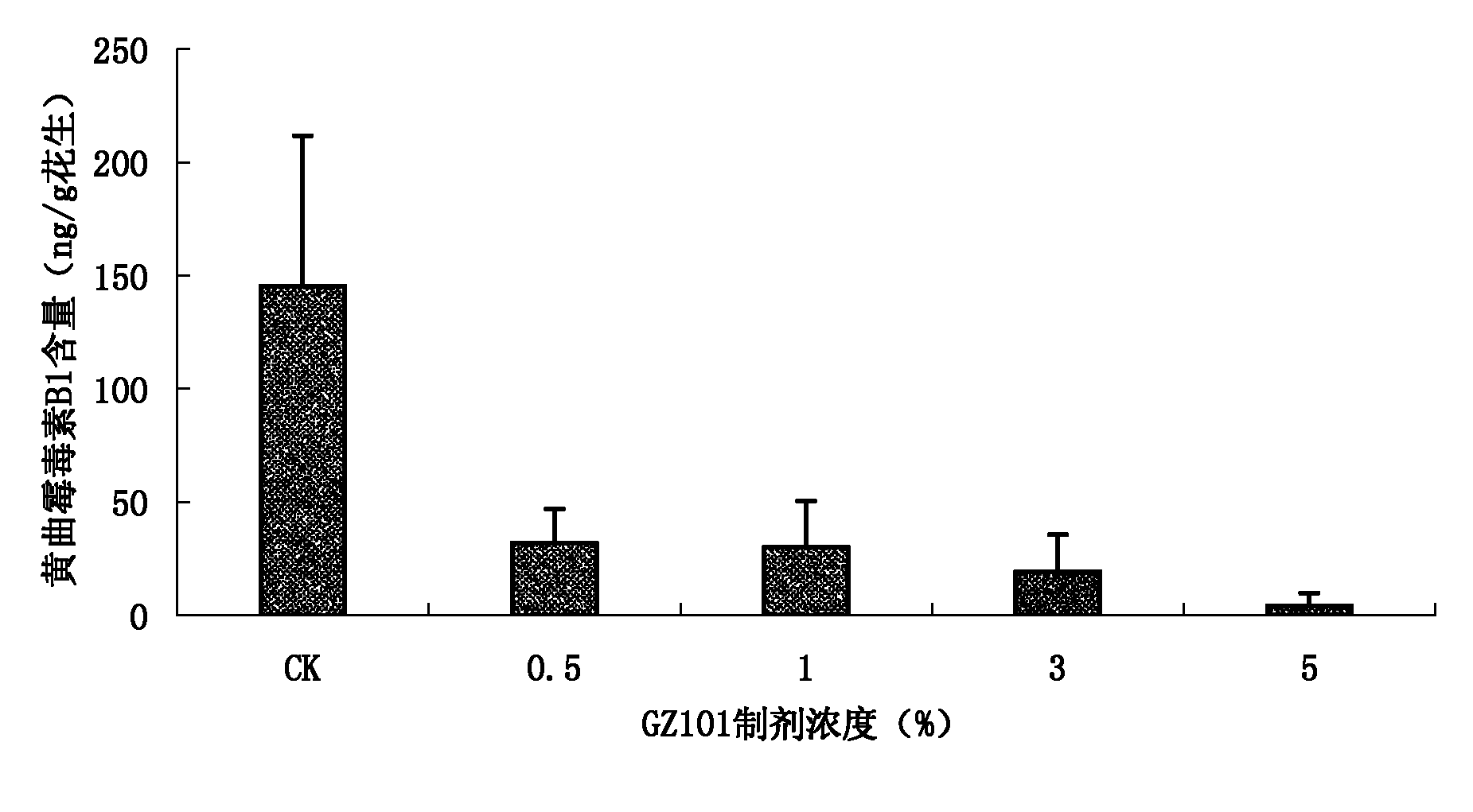
The invention discloses a trichoderma viride strain and application of metabolites thereof and belongs to the field of microorganisms and agriculture. The trichoderma viride strain has the effective antagonistic action on growth of aspergillus flavus, the name of trichoderma viride strain is the trichoderma viride GZ101 which was collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection on Nov. 4th, 2010, and the collection number is CCTCC NO: M 2010291. When the supernatant obtained by fermenting the trichoderma viride strain in the potato-dextrose agar (PDA) liquid culture medium is sprayed in the soil where peanuts are planted, the aflatoxin pollution before the peanut harvest can be effectively reduced, and the reducing rate reaches 97 percent, so that the metabolites of the trichoderma viride strain can be used for preparing a preparation for reducing the aflatoxin pollution before the peanut harvest.
Owner:CROP RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Deep-sea Bacillus aryabhattai capable of inhibiting aflatoxin
InactiveCN105039197APrevention and Control of PollutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesToxin synthesisBacillus aryabhattai
The invention provides a deep-sea bacterium capable of inhibiting synthesis of aflatoxin, in particular to Bacillus aryabhattai ZL4, isolated from light yellow calcareous ooze sediment 2796 meters deep in South Atlantic and preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center under CGMCC No. 10661. The Bacillus aryabhattai ZL4 is fermented in a screened culture medium, acquired fermented supernate is fully capable of inhibiting synthesis of aflatoxin, no toxic intermediates are generated, and the Bacillus aryabhattai ZL4 is able to inhibit the aflatoxin from the toxin synthetic means but has no inhibitory action on intestinal flora and unicellular eumycetes, saccharomyces cerevisiae. The Bacillus aryabhattai ZL4 and its fermentation products are applicable to effective control of aflatoxin contamination of fodders, grains, field crops and the like.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI +1
Aflatoxin pollution risk early warning molecule and application thereof
ActiveCN112530525AImprove accuracyOriginalMolecular entity identificationComponent separationAflatoxin contaminationToxicology
The invention relates to an aflatoxin pollution risk early warning molecule and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: weighing a quantitative sample, extracting aflatoxin pollution risk early warning molecules to obtain a sample extracting solution, and detecting and analyzing the sample extracting solution to obtain a quantitative result of the aflatoxin pollution risk early warning molecules; taking the content of one or more aflatoxin pollution risk early warning molecules as a variable, modeling by a chemometrics method to obtain a classification prediction model,and performing risk assessment based on the aflatoxin pollution risk of the classification prediction model sample, wherein the aflatoxin toxin-producing strain early warning molecule is one or a combination of more than one of versiconol (VOH), sterigmatocystin B and 5-MST. The aflatoxin pollution risk early warning molecule discovered by the method has originality, and the early warning method established according to the aflatoxin pollution risk early warning molecule can be used for early warning before aflatoxin pollution occurs.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
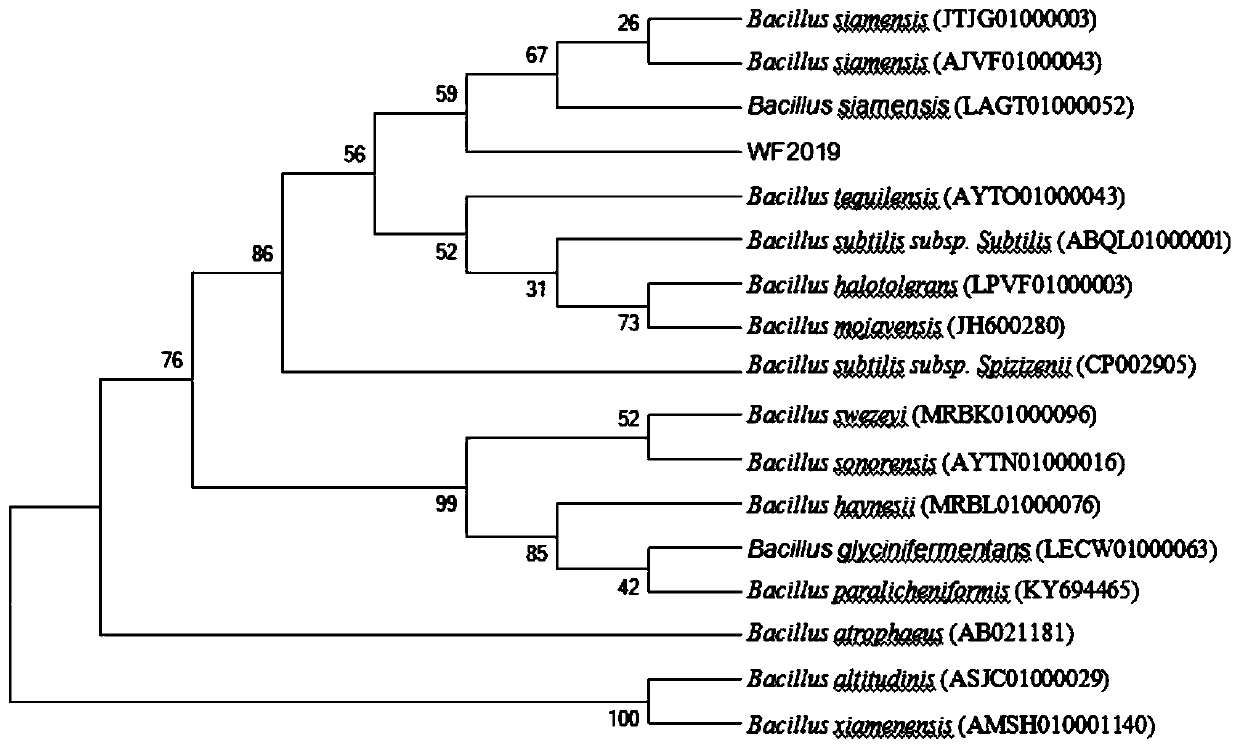
Bacillus siamensis WF2019 strain for degrading aflatoxin B1 and application of bacillus siamensis WF2019 strain
ActiveCN110564640AEfficient degradationImprove degradation rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAflatoxin contamination
The invention discloses a bacillus siamensis WF2019 strain for degrading aflatoxin B1 and an application of the bacillus siamensis WF2019 strain. The bacillus siamensis WF2019 strain capable of efficiently degrading the aflatoxin B1 is successfully separated and obtained, is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on June 18th, 2019, and has preservation number of GDMCC NO:60700. The strain can efficiently degrade the aflatoxin B1, and the degradation rate is as high as 98.9%; the environment adaptability is good, the high-temperature resistance is remarkable, and the degradation performance is still remarkable at the temperature of 60 DEG C; meanwhile, fermentation liquor or intracellular substances of the strain can also degrade the aflatoxin B1 and can be applied to detoxification of agricultural products polluted by the aflatoxin B1; in addition, the strain is pollution-free and nuisanceless in the using process. Therefore, the strain is an ideal agricultural product detoxification microorganism, and has good promotion and application prospects in the detoxification aspect of the aflatoxin B1 in the field of feed processing or food processing.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Broad bean paste fermented by mixed aspergillus oryzae and lactobacillus plantarum and preparation method of broad bean paste
InactiveCN107279748AMaintain gut healthKeep healthyFungiBacteriaLactic acid bacteriumTemperature control
The invention discloses a preparation process of broad bean paste fermented by mixed aspergillus oryzae and lactobacillus plantarum. The broad bean paste is prepared from the raw materials by weight as follows: 40-80 parts of broad beans, 12-20 parts of edible salt, 15-25 parts of flour, 0.01-0.02 parts of aspergillus oryzae powder, 0.002-0.008 parts of lactobacillus plantarum powder and 40-80 parts of water. The mixed aspergillus oryzae and lactobacillus plantarum is adopted for fermentation, the viscosity of the broad bean paste is improved, so that quality of each batch of the broad bean paste keeps uniform, the risk of pollution of a product by aflatoxin is reduced, and the safety edibility is significantly increased; meanwhile, a temperature control and humidity control technology is adopted, during koji making, the temperature is controlled at 28-32 DEG C, the humidity is controlled to be 75%-80%, the reproduction rate of dominant fermentation strains, namely, the aspergillus oryzae and the lactobacillus plantarum, is increased, koji making time is shortened to 24 hours from traditional 3-5 days, and production cost is saved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
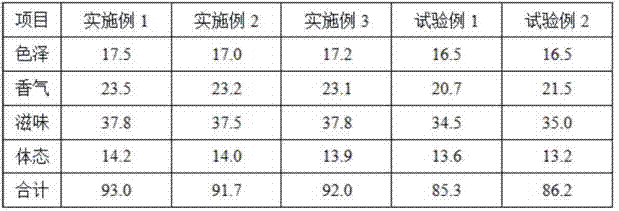
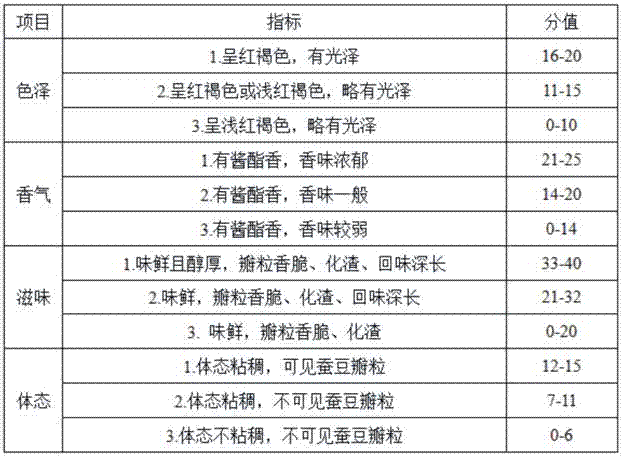
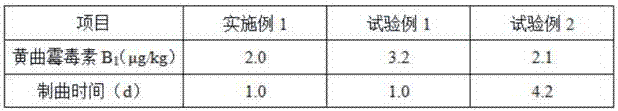
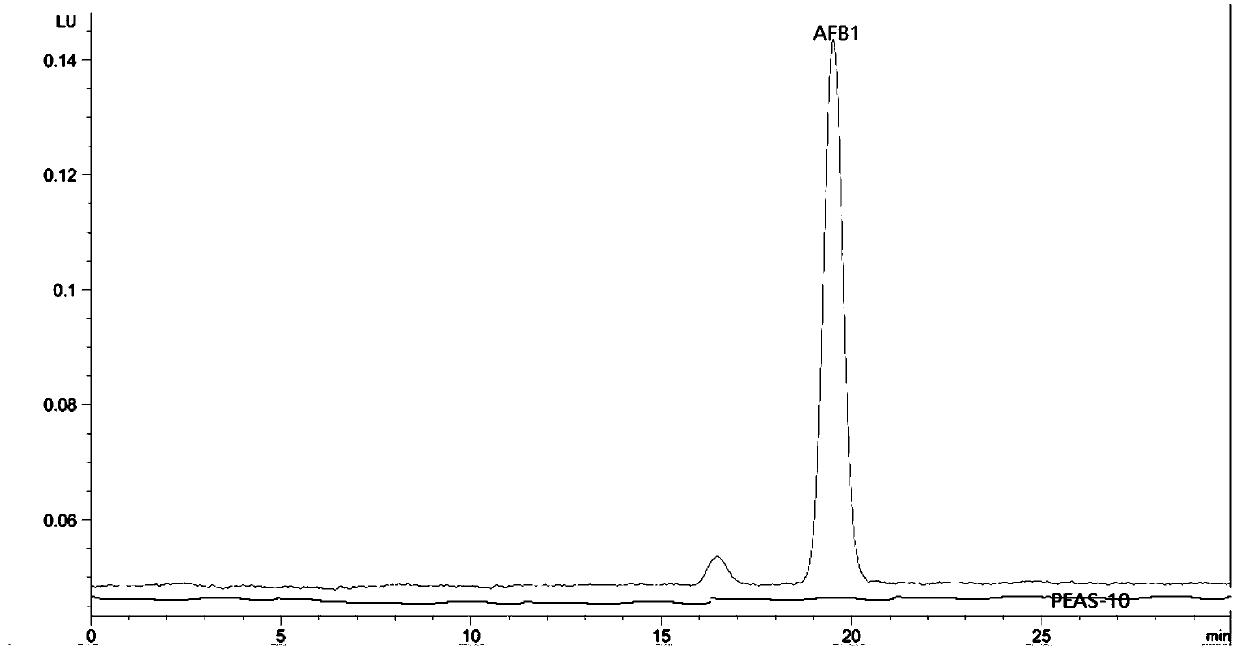
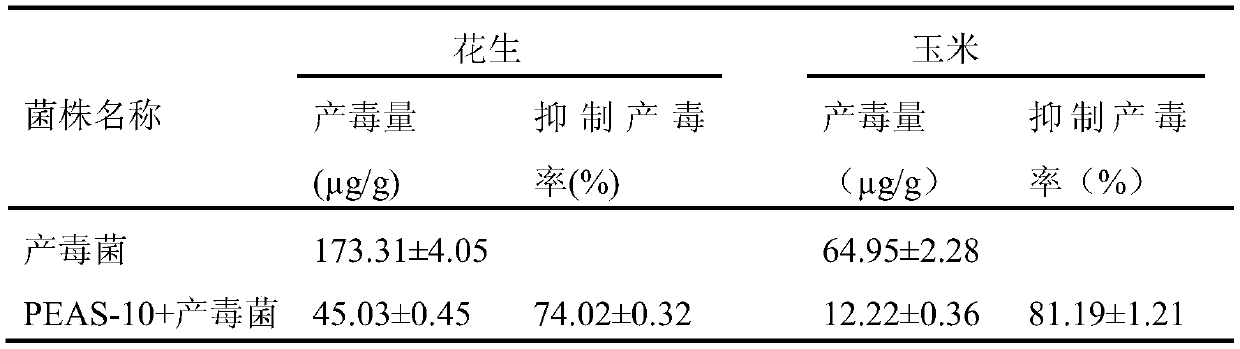
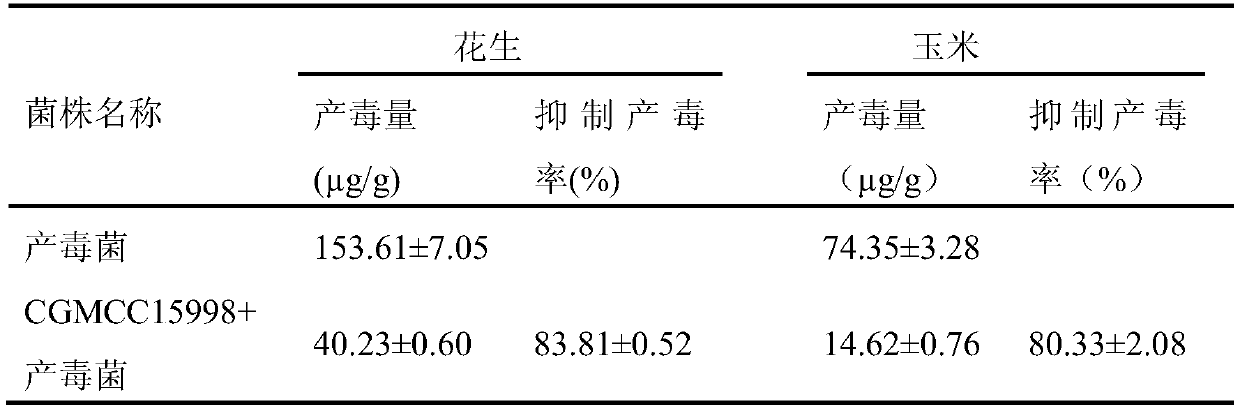
Aspergillus flavus PEAS-10 which does not produce aflatoxin and application of Aspergillus flavus PEAS-10
The invention discloses Aspergillus flavus PEAS-10 which does not produce aflatoxin and an application of the Aspergillus flavus PEAS-10 and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The Aspergillus flavus PEAS-10 which does not produce aflatoxin is preserved in the General Microbial Center of the Commision for the Protection and Management of Microbial Species in China on August, 1st, 2018, the preservation number is CGMCC NO.:15997, the address is No. 3, No. 1 Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the unit requiring preservation is Shandong Peanut Research Institute. TheAspergillus flavus PEAS-10 can grow and reproduce rapidly in the field and can effectively inhibit the growth, propagation and toxin production of the Aspergillus flavus, and has remarkable effect onpreventing and controlling aflatoxin pollution in the field; the use of the Aspergillus flavus PEAS-10 can not only reduce the occurrence of peanut diseases, but also increase the utilization rate ofsoil organic matter.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
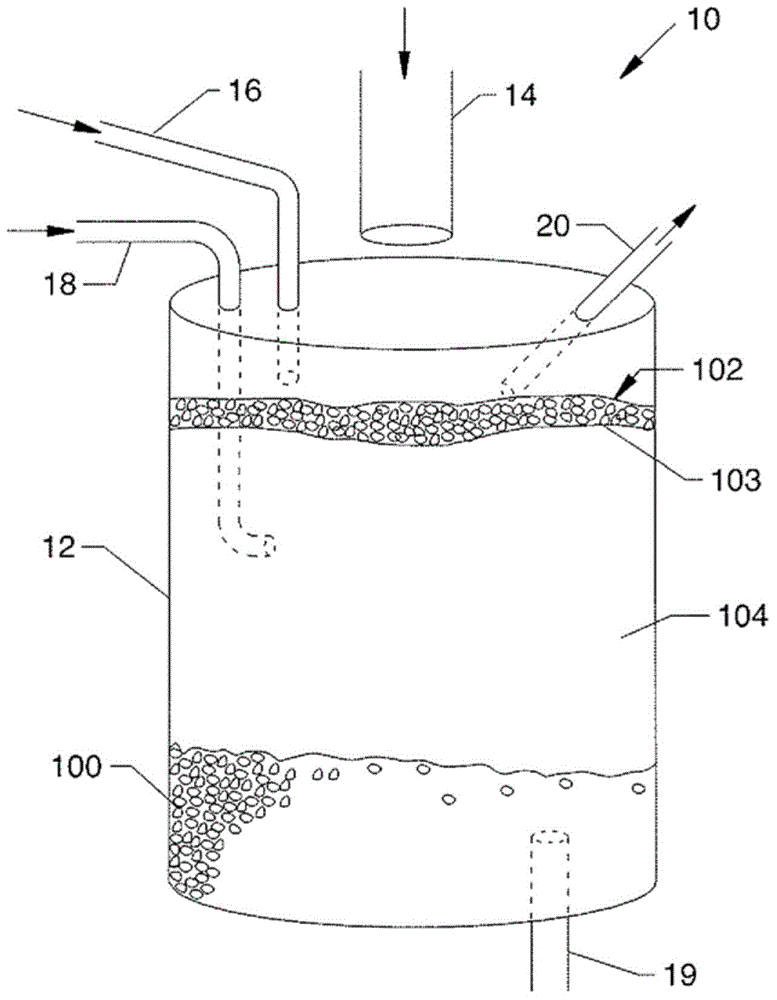
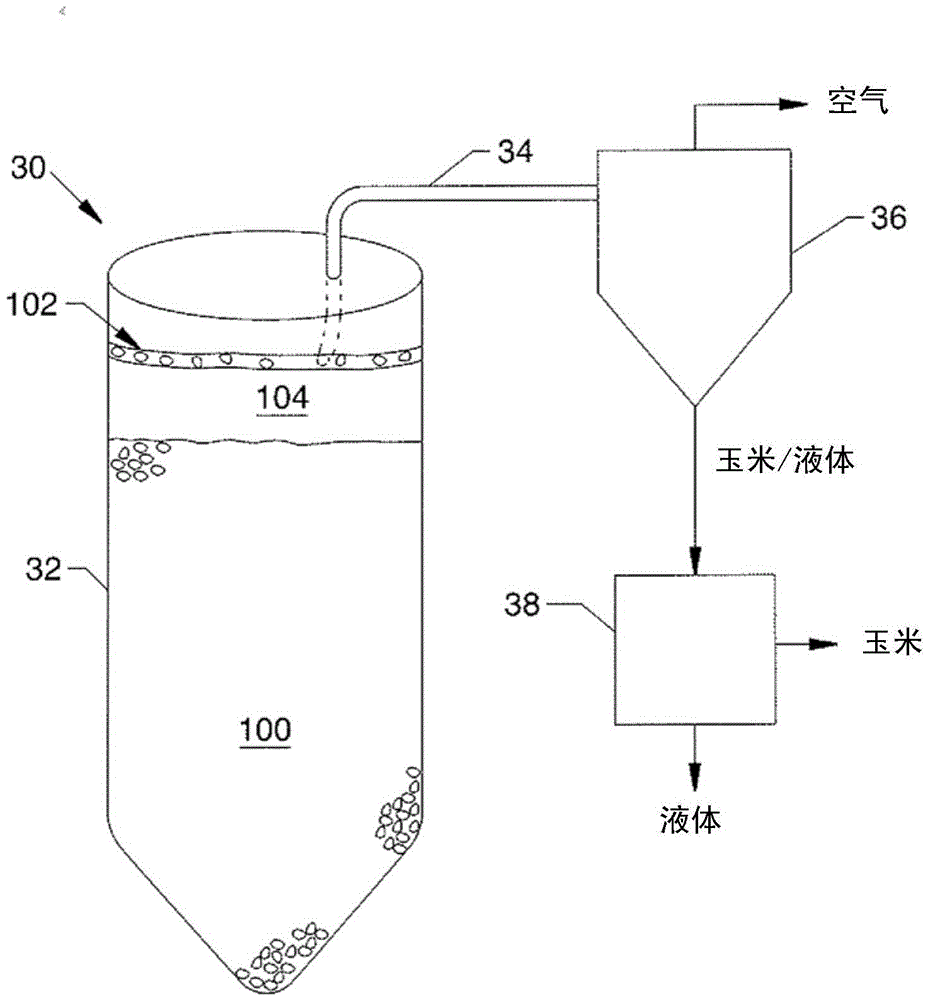
Method and apparatus for reducing aflatoxin-contaminated corn
Methods and apparatus for separating and removing aflatoxin-contaminated corn from batches of corn by a floating process, thus producing a distinguishable floating mat of contaminated corn and a separate submerged bed of uncontaminated and less contaminated corn. The methods of this disclosure include removing the floating contaminated corn mat by a vacuum mechanism or by liquid flow. The methods reduce the aflatoxin level in the submerged corn bed as much as 80% from the initial aflatoxin level, while removing no more than 15% from the batch of corn.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Method for detecting potential pollution risk of aflatoxin in peanuts and products thereof by using real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology
InactiveCN105018621AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceBenzyl chloride
The invention discloses a method for detecting potential pollution risk of aflatoxin in peanuts and products thereof by using real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology. The method utilizes a quartering process to collect the samples, utilizes a benzyl chloride process to extract the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), and designs the specific primer by using the Aspergillus flavus toxin production key gene AFLR as the target gene to perform the fluorescent quantitative PCR, judges the aflatoxin pollution risk of the sample according to the fluorescent quantitative Ct value, and establishes a relation model between the aflatoxin pollution risk and sample fluorescent quantitative Ct value. The method can quickly and accurately judge the potential pollution risk of aflatoxin in the peanuts and products thereof, has the advantages of high specificity, high stability and high sensitivity, is simple and quick for operation, and is suitable for mass detection.
Owner:张初署 +1
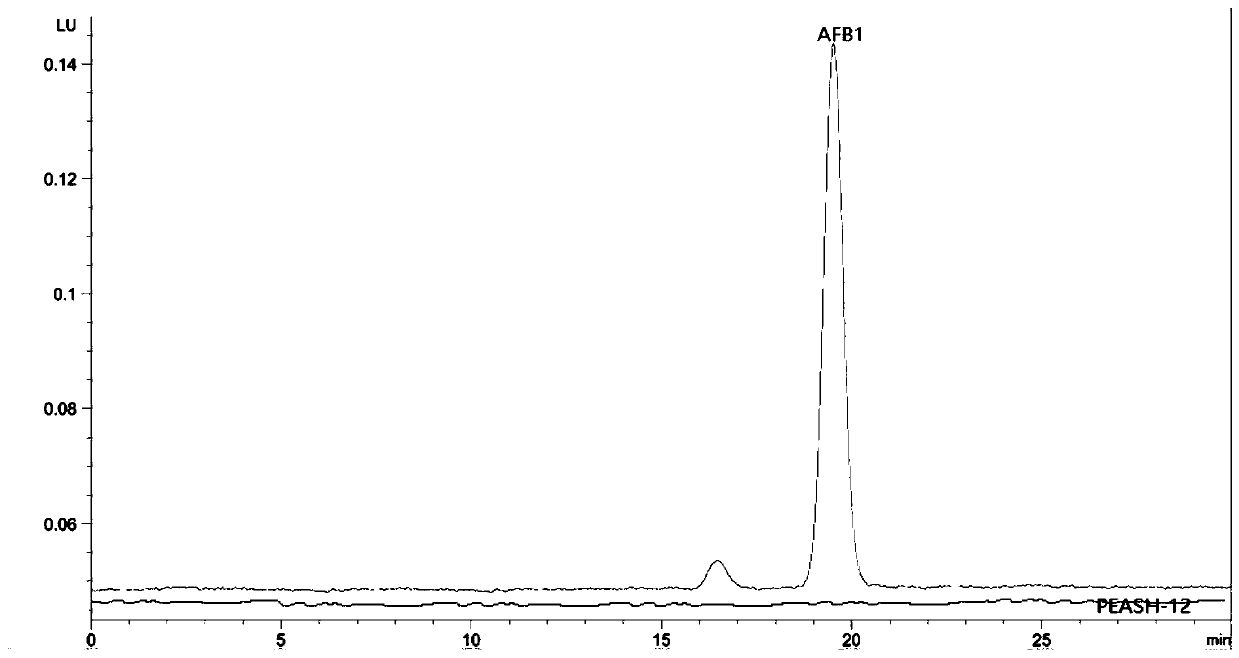
Aspergillus flavus PEASH-12 not producing aflatoxin and application of aspergillus flavus
The invention discloses aspergillus flavus PEASH-12 not producing aflatoxin and application of the aspergillus flavu, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The aspergillus flavus PEASH-12 not producing the aflatoxin is stored in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on August 1st, 2018, the preservation number is CGMCC NO:15998, the address is No.3, No.1 Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the unit requesting preservation is Shandong Peanut Research Institute. Accordingly, the strain can rapidly grow and reproduce in a field, and the growth, reproduction and toxin production of the aspergillus flavus for producing toxicity can be efficiently inhibited, and the effect of field prevention and control over aflatoxin pollution is remarkable; anaspergillus flavus PEASH-12 spore suspension not producing toxicity can not only reduce the occurrence of peanut diseases, but also increase the utilization rate of soil organic matter.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Biocontrol strain BS71 and application thereof to preventing crops from being polluted by aflatoxin
ActiveCN103789230AEnhanced inhibitory effectGood control effectBiocideBacteriaAflatoxin contaminationBacillus subtilis
The invention discloses a biocontrol strain BS71 and an application thereof to preventing crops from being polluted by aflatoxin. The biocontrol strain BS71 is bacillus subtilis BS71, with collection number of CGMCC No.8191. The application method comprises the steps of preparing a biocontrol agent of the biocontrol strain BS71 and applying the biocontrol agent to the crops. The biocontrol strain has strong antagonistic action on aspergillus flavus and can be used for preventing pollution caused by aflatoxin. The invention provides a biocontrol method for pollution caused by aflatoxin. As chemical pesticides are not used, the biocontrol strain has the advantages of no toxicity, low possibility of having resistance to drugs, environmental and biological safety and the like, and has extensive application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Aspergillus flavus mixed strain incapable of producing aflatoxin and application thereof
The invention discloses an Aspergillus flavus mixed strain incapable of producing aflatoxin. The mixed strain is formed by mixing Aspergillus flavus AF-8 and Aspergillus flavus AF-20; and the collection numbers of the Aspergillus flavus AF-8 and Aspergillus flavus AF-20 at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center are respectively CGMCC No.8964 and CGMCC No.8966. The experiment proves that the mixed strain has an inhibiting action on toxin production of the Aspergillus flavus strain capable of producing aflatoxin; the mixture of the two strains has better inhibiting effect on the bacterium capable of toxin production than a single strain; and when the spore concentration ratio of the AF-8 and AF-20 incapable of toxin production to the GD-1 capable of toxin production is 5*10<4>:5*10<4>:1*10<5>, the toxin production inhibition rate of the mixed strain incapable of toxin production for the bacterium capable of toxin production is approximately 100%. The strain has important meanings for inhibiting the toxin production Aspergillus flavus from infecting the agricultural products and lowering the aflatoxin pollution in the agricultural products.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Strain producing aflatoxin B1 degrading enzyme and application thereof
InactiveCN104498378ASolve pollutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFood safetyAflatoxin contamination
The invention discloses a bacterium Sinomonas sp.HSD8 and application thereof. The preservation number of the strain is CCTCC NO:M2014109. After fermentation culture, the activity of aflatoxin B1 degrading enzyme in the fermentation liquid is improved, the aflatoxin pollution problem in feed and food can be effectively solved, and the animal feed and food safety can be guaranteed.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
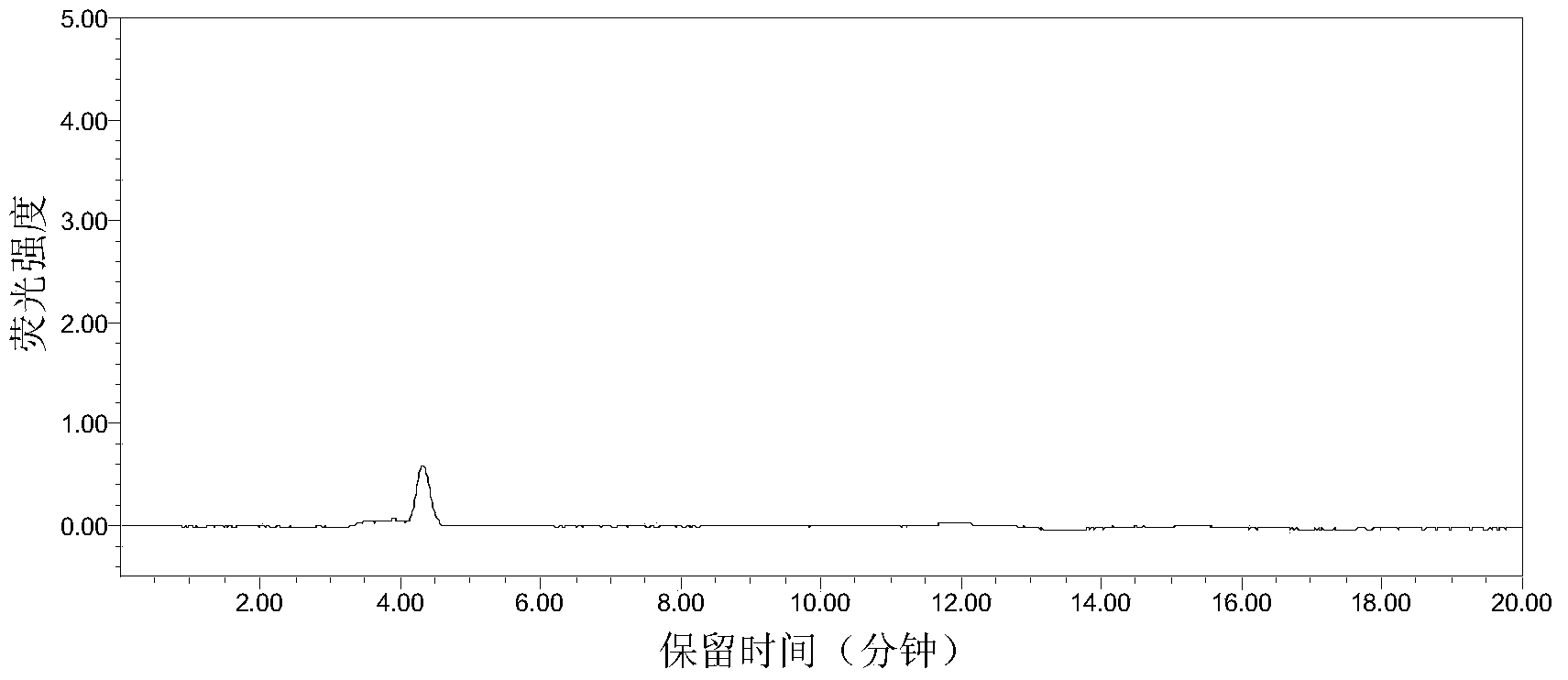
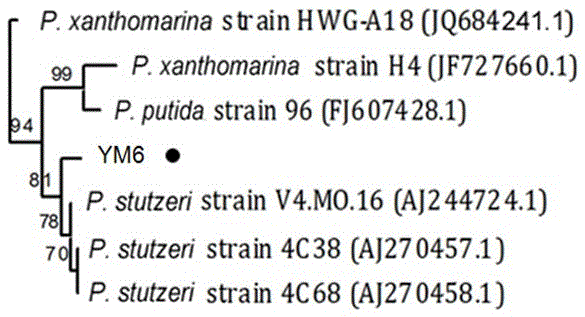
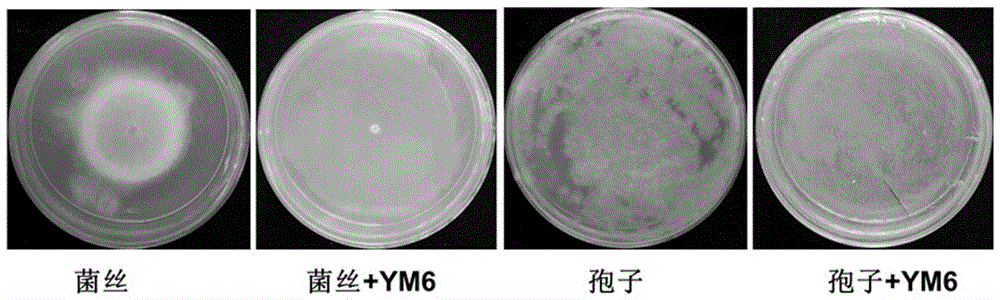
Pseudomonas stutzeri and metabolite thereof as well as application of pseudomonas stutzeri YM6 to prevention and treatment of asperigillus flavus and toxins
ActiveCN106119169AGrowth inhibitionInhibition of germinationBacteriaEdible seed preservationBiotechnologyMetabolite
The invention discloses pseudomonas stutzeri YM6 with the preservation number of CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) M2016386. A metabolite of the pseudomonas stutzeri comprises dimethyl trisulfide. The invention further discloses application of the pseudomonas stutzeri and the metabolite to inhibition of asperigillus flavus and toxins at a storage period. The pseudomonas stutzeri and the metabolite, disclosed by the invention, can be used for effectively inhibiting aspergillus flavus diseases of peanuts, corns and the like and pollution caused by asperigillus flavus toxins under sealed environments with different water activities.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Early warning method before aflatoxin pollution
ActiveCN112305099AImprove accuracyOriginalComponent separationTesting foodMass analyzerMass spectrum analysis
The invention relates to an early warning method before aflatoxin pollution. The method comprises the following steps: weighing a quantitative sample, carrying out sample toxin extraction to obtain asample extracting solution, carrying out liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometer detection analysis on the sample extracting solution, collecting mass spectrum information, carrying out qualitative analysis according to the mass spectrum information to obtain a qualitative result, and according to the corresponding chromatographic peak area, in combination with an internal standard, performing quantitative analysis based on the standard curve of the chromatographic peak area / internal standard peak area early-warning molecular concentration of each early-warning molecule to obtain quantitative results of the early-warning molecules; inputting a quantitative result of the early warning molecule of the aspergillus flavus toxin-producing strain by using the content of the earlywarning molecule as a variable and a classification prediction model obtained by modeling through a chemometrics method, and outputting a risk assessment result based on the classification predictionmodel to assess the aflatoxin pollution risk of the sample. Early warning before aflatoxin pollution occurs is realized.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Common mussel powder for effectively decreasing activity of aflatoxin and preparation method of common mussel powder
PendingCN109943420AEfficient removalInorganic non-surface-active detergent compositionsAflatoxin contaminationBiological activation
The invention discloses common mussel powder for effectively decreasing the activity of aflatoxin and a preparation method of the common mussel powder. The method comprises the following steps: selecting annual common mussels as the raw material; cleaning, and sieving; removing coats of the common mussels; carrying out calcining; carrying out aging treatment; carrying out digestive treatment; carrying out vacuum drying; and crushing the common mussels by virtue of a nano-scale crushing machine, so as to obtain the common mussel powder for effectively decreasing the activity of aflatoxin. The product prepared by the invention is shell powder prepared from natural common mussels through calcining and activation and is mixed with corns, peanuts and bean pulp polluted by aflatoxin, so that aflatoxin in the corns the, peanuts and the bean pulp can be effectively removed.
Owner:杭州航民雪贝儿生物科技有限公司 +1
Hlavobacterium breve biocontrol strain for effectively degrading aflatoxin and application of flavobacterium breve biocontrol strain
InactiveCN107988097APollution controlPromote degradationBiocideBacteriaMicroorganismAflatoxin contamination
The invention belongs to the microorganism field and particularly relates to a flavobacterium breve biocontrol strain for effectively degrading aflatoxin and application of the flavobacterium breve biocontrol strain. The flavobacterium breve biocontrol strain 3J2MO is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on June 13th, 2017 with a preservation number of CCTCC No.M2017329. The adopted flavobacterium breve biocontrol strain is capable of remarkably degrading aflatoxin and has an excellent effect on the degradation of peanuts polluted by aflatoxin. The flavobacterium breve biocontrol strain can be used for degrading aflatoxin and treating the food crops polluted by aflatoxin.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
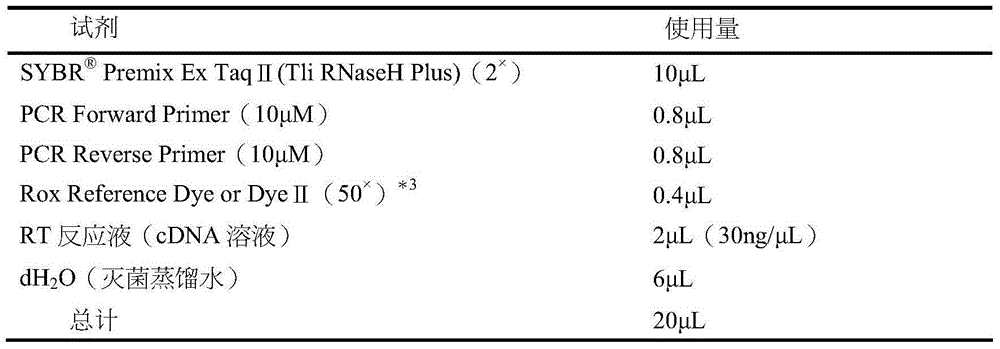
Synchronous detection RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) kit for yield of aflatoxin and quantity of Nor-1 genetic transcription and detection method of kit
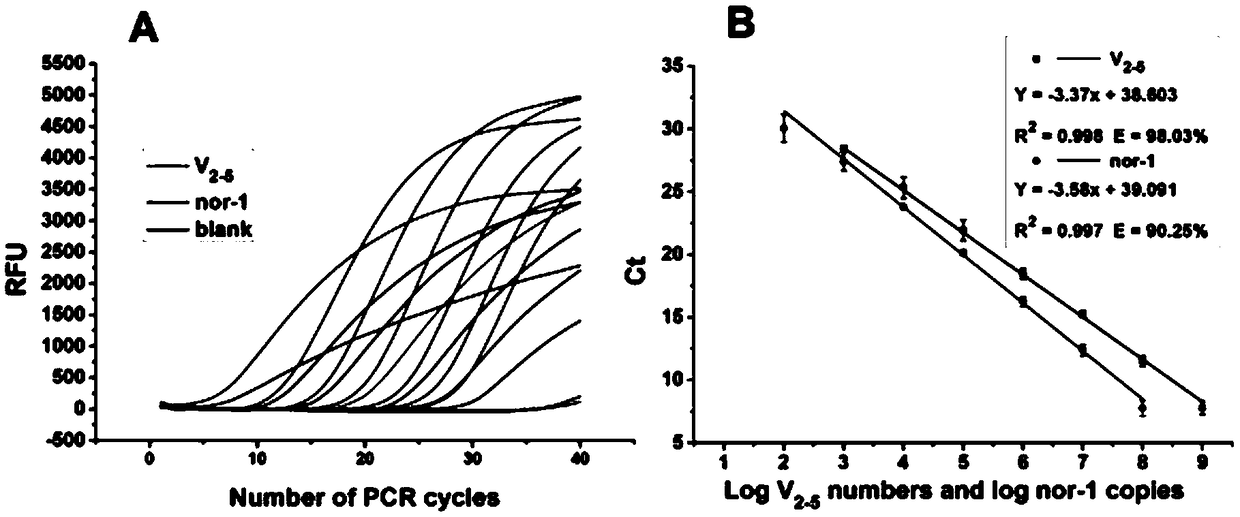
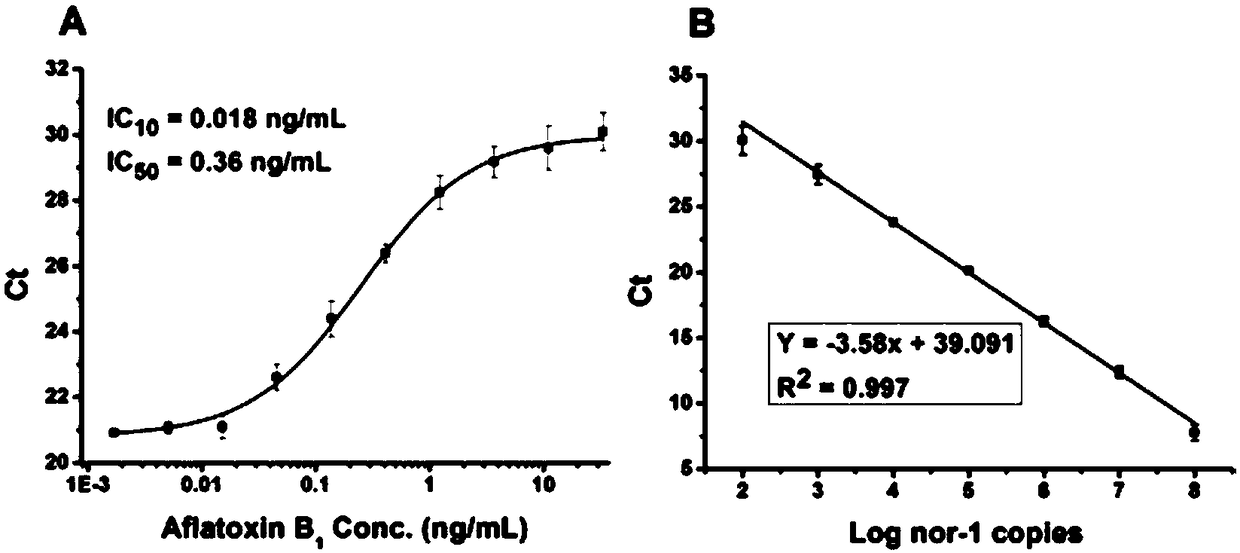
ActiveCN109468367AReduce dosageLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementLinear relationshipAflatoxin contamination
The invention belongs to the field of biologics and in particular relates to a synchronous detection RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) kit for the yield of aflatoxin and the quantity of Nor-1 genetic transcription and a detection method of the kit. The invention establishes a synchronous RT-PCR detection method for synchronously detecting the yield of aflatoxin and the quantity of Nor-1 genetic transcription, and by using the method, the yield of the aflatoxin and the quantity of Nor-1 genetic transcription are in good linear relationship with results of HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) quantitative aflatoxin and Nanodrop quantitative Nor-1 genetic transcription, therefore, AFT-Nor-1 obtained by using the synchronous detection RT-PCR method has reliableand accurate ratio results which can be used as identification indexes for judging the toxin yields of aspergillus flavus strains, rapid and accurate identification evaluation on the toxin yields of the aspergillus flavus strains is achieved, and the kit has great significances for early warning and control on aflatoxin pollution.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com