Bacillus siamensis WF2019 strain for degrading aflatoxin B1 and application of bacillus siamensis WF2019 strain
A WF2019, aflatoxin technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, bacteria, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problem that the microbial strains of aflatoxin are not resistant to high temperature and the degradation effect is not significant, and achieve significant degradation performance and high temperature resistance Performance, efficient degradation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
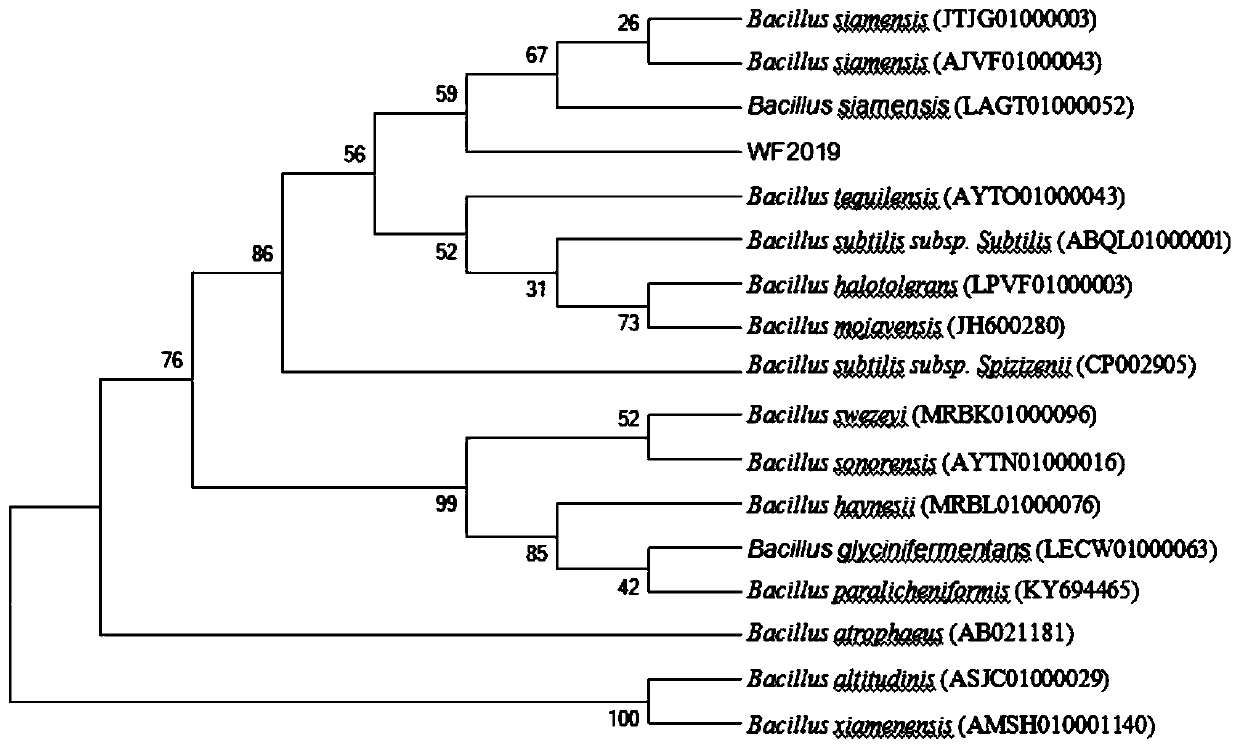
[0058] Example 1 Isolation and Identification of Bacillus siamensis WF2019
[0059] 1. Strain isolation and screening
[0060] First, carry out the primary screening of the strain, dilute 1 g of fermented food with 90 mL of sterile normal saline, and make gradient dilutions, spread the diluted solution on a solid medium with coumarin as the only carbon source, culture at 37 ° C, separate and purify the plate Colonies were cultured in a liquid medium with coumarin as the sole carbon source to obtain suspected strains capable of degrading AFB1.
[0061] Then, carry out the re-screening of the bacterial strain, put the suspected bacterial strain into a 10mL centrifuge tube, add 2mL of nutrient broth, and cultivate it at 37°C and 160r / min for 24h to obtain a fermentation broth; ) at 37° C. and 160 r / min for 72 h, and the nutrient broth without the strain plus AFB1 was used as a blank control; after the cultivation, the change of AFB1 concentration was detected by HPLC. It was fo...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Example 2 Degradation performance experiment of Bacillus siamese WF2019 to AFB1
[0075] 1. Experimental method
[0076] Take Bacillus siamese WF2019 in a 10mL test tube, add 5mL of medium, and culture at 30°C, 200r / min for 20h; take 100-300μL of bacterial liquid into a new 5mL medium, so that the OD 600 =0.02~0.05, add AFB1 so that the final concentration of AFB1 is 2 μg / mL, continue to cultivate at 30 °C and 200 r / min for 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, 96 h, and the blank control is sterile medium plus AFB1, the final concentration is 2 μg / mL mL; After the culture, the change of AFB1 concentration was detected by HPLC.
[0077] 2. Experimental results
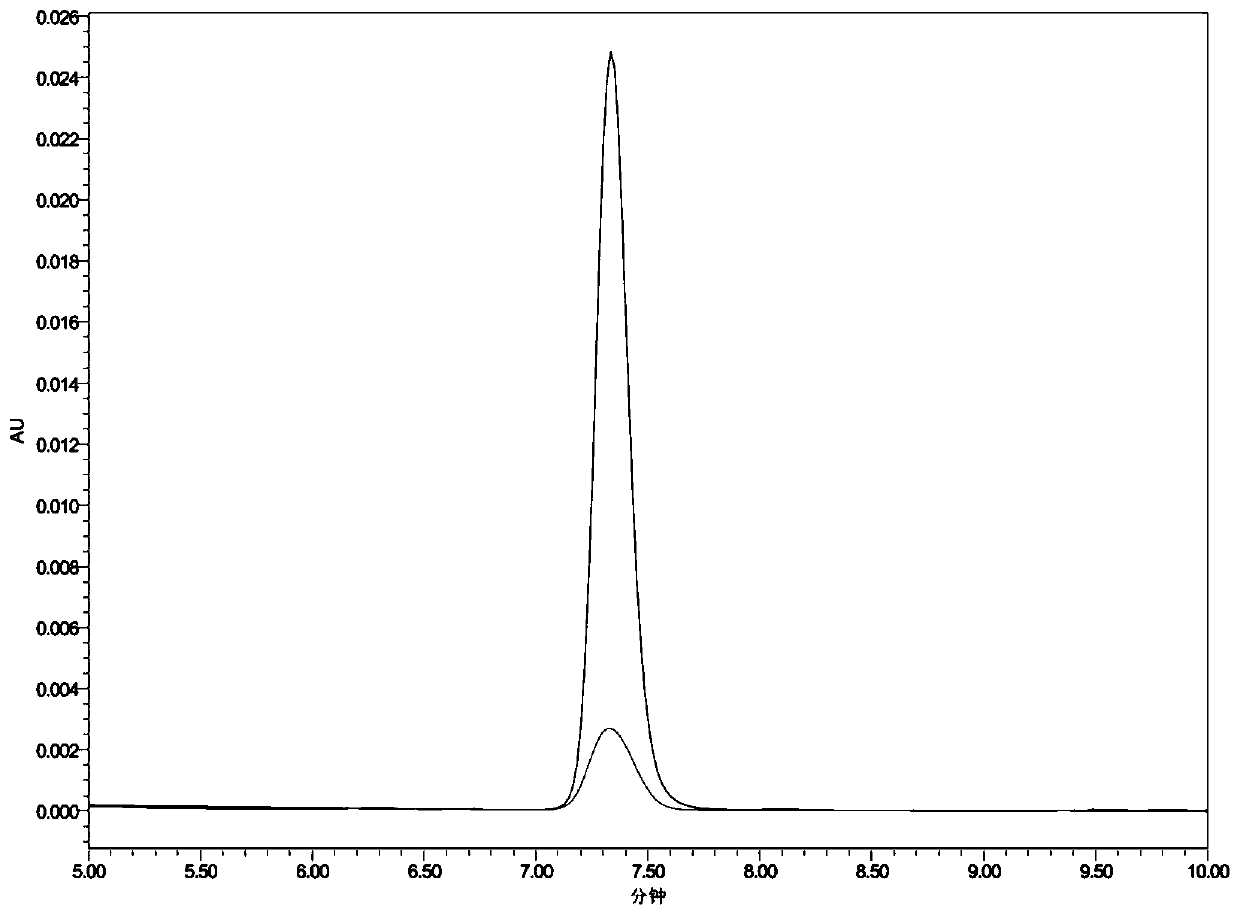
[0078] The results of the degradation performance of Bacillus siamese WF2019 on AFB1 are as follows: Figure 4 As shown, it can be seen that when cultured for 96 hours, Bacillus siamese WF2019 has the best degradation performance on AFB1, and the degradation rate is as high as 97.7%.
Embodiment 3
[0079] Example 3 Degradation performance experiment of Bacillus siamese WF2019 to different concentrations of AFB1
[0080] 1. Experimental method
[0081] Take Bacillus siamese WF2019 in a 10mL test tube, add 5mL of medium, and culture at 30°C, 200r / min for 20h; take 100-300μL of bacterial liquid into a new 5mL medium, so that the OD 600 =0.02~0.05; add different concentrations of AFB1, so that the final concentration is 1μg / mL, 2μg / mL, 4μg / mL, 8μg / mL, continue to culture at 30℃, 200r / min for 24h, 48h, 72h, 96h, blank The control was sterile medium plus AFB1, and the final concentrations were 1 μg / mL, 2 μg / mL, 4 μg / mL, and 8 μg / mL; after the culture, the change of AFB1 concentration was detected by HPLC.
[0082] 2. Experimental results
[0083] The degradation performance results of Bacillus siamese WF2019 to different concentrations of AFB1 are as follows: Figure 5 As shown, it can be seen that when cultured for 96 hours, Bacillus siamese WF2019 has the best degradation...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com