Process for producing high content phosphor-gypsum baking-free bricks
A production process and phosphogypsum technology, applied in the field of building wall materials, can solve the problems of high equipment requirements, low phosphogypsum content, high material and structure requirements, and achieve low drying equipment requirements, simple production process, and operability. strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
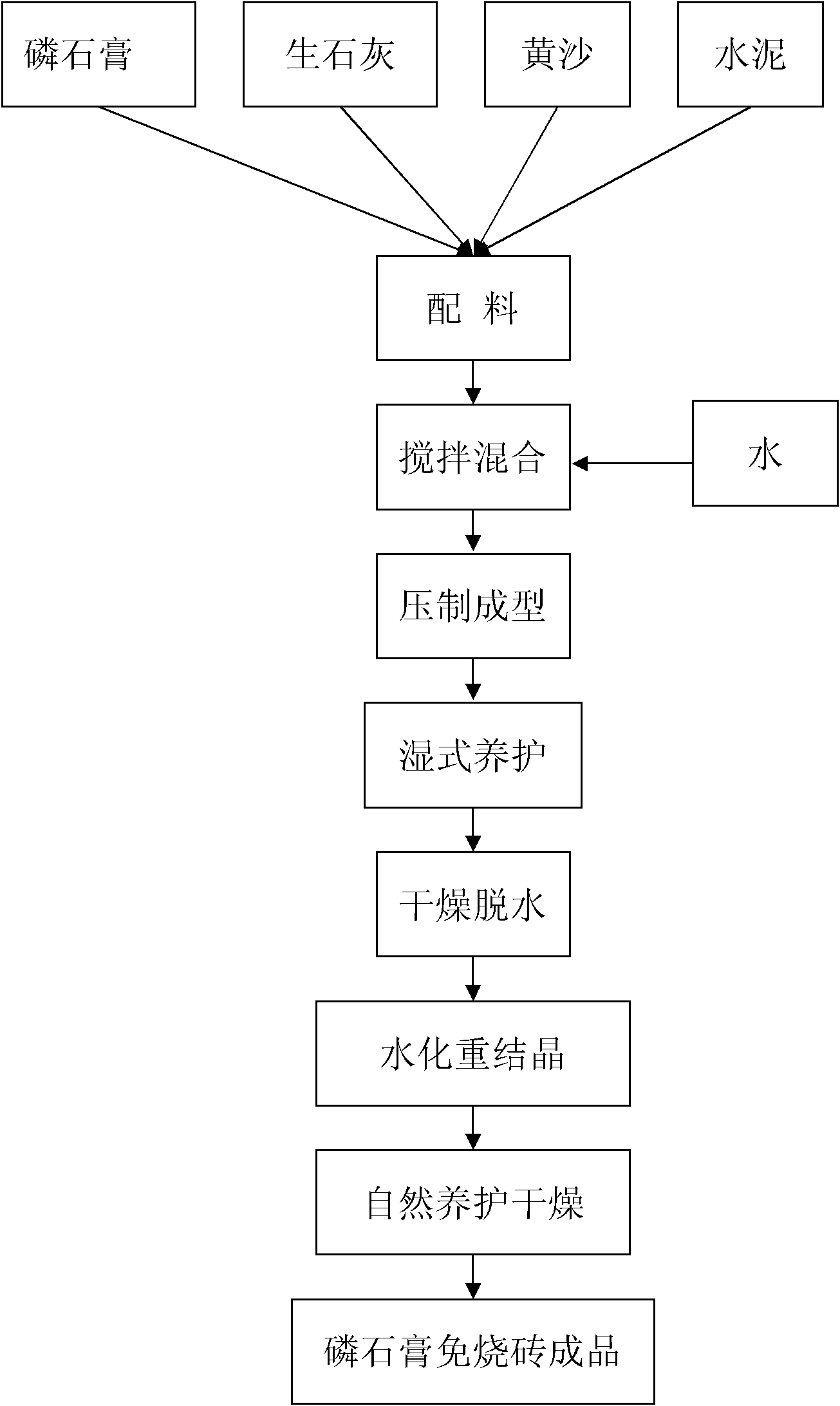
[0032] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of production technology of high content phosphogypsum unburned brick, it comprises the following steps:
[0033] (1) Ingredients: The batch material is mixed by phosphogypsum, lime (quicklime), yellow sand and cement; according to the mass percentage of each raw material of the batch material: 80.0% phosphogypsum, 2.0% lime, 10.0% yellow sand, 8.0% cement, select phosphogypsum, lime, yellow sand and cement; select water according to 8% of batch weight, and reserve;
[0034] (2) Stirring and mixing: putting phosphogypsum, lime, yellow sand and cement into a mixer and stirring and mixing to obtain a batch; adding water to the batch and fully stirring and mixing to obtain a batch;
[0035] (3) Compression forming: the mixed material cloth is pressed in a brick press under a pressure of 20MPa to form a brick, and the size specification is 240mm×115mm×53mm;
[0036] (4) Wet curing: spray water 4 times intermittently on the 1st day after the ...
Embodiment 2
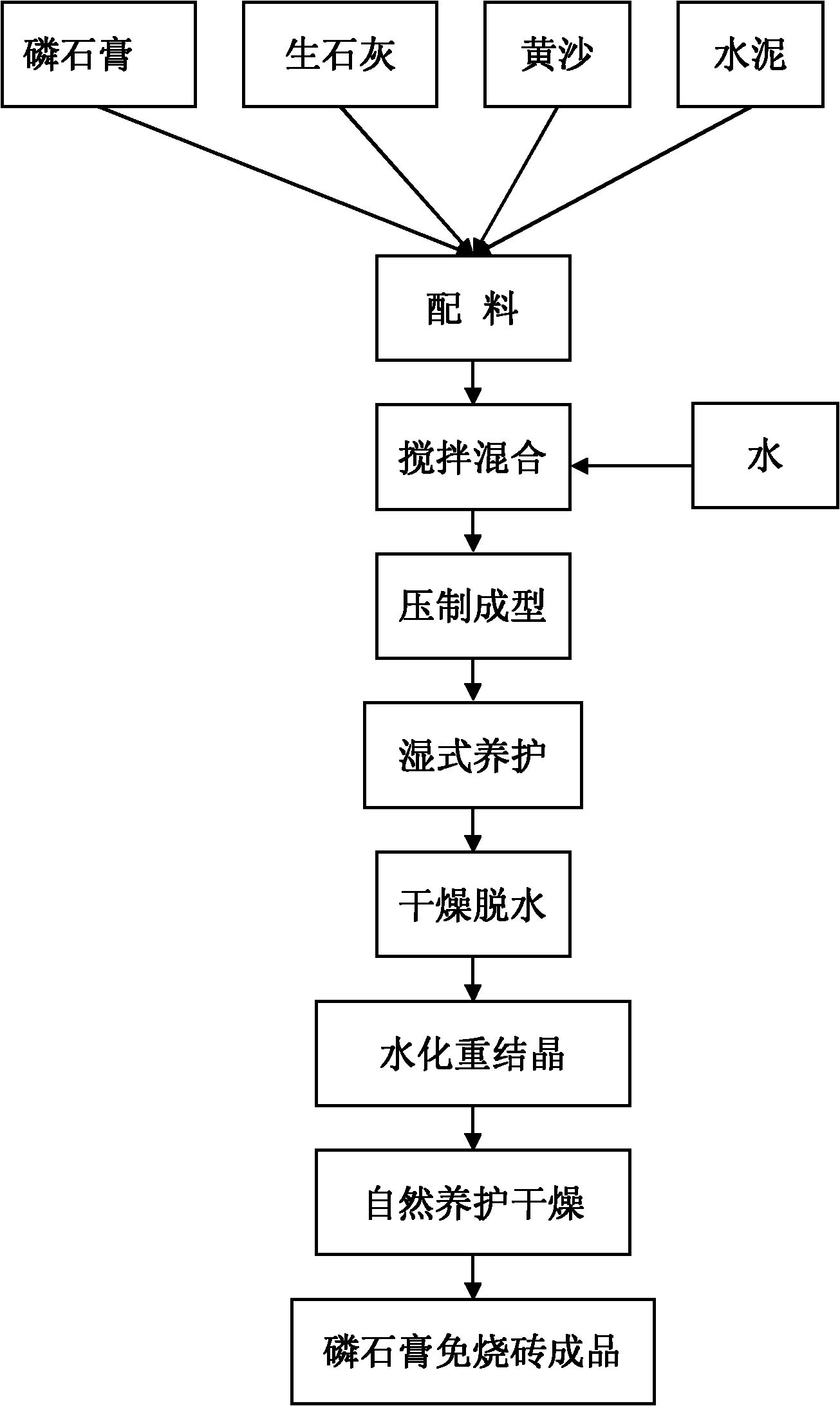
[0042] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of production technology of high content phosphogypsum unburned brick, it comprises the following steps:
[0043] (1) Ingredients: The batch material is mixed with phosphogypsum, lime (quicklime), yellow sand and cement; according to the mass percentage of each raw material of the batch material: 85.0% phosphogypsum, 2.5% lime, 2.5% yellow sand, 10.0% cement, choose phosphogypsum, lime, yellow sand and cement; choose water according to 5% of the weight of the batch, and set aside;
[0044] (2) Stirring and mixing: putting phosphogypsum, lime, yellow sand and cement into a mixer and stirring and mixing to obtain a batch; adding water to the batch and fully stirring and mixing to obtain a batch;
[0045] (3) Compression forming: the mixed material cloth is pressed in a brick press under a pressure of 20MPa to form a brick, and the size specification is 240mm×115mm×53mm;
[0046] (4) Wet maintenance: Spray water intermittently 5 times on th...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Such as figure 1 Shown, a kind of production technology of high content phosphogypsum unburned brick, it comprises the following steps:
[0053] (1) Batching: the batching material is mixed by phosphogypsum, lime (for quicklime) and cement; according to the mass percentage of each raw material of the batching material: 90.0% phosphogypsum, 3.0% lime, 7.0% cement, choose phosphogypsum, Lime and cement; choose water according to 3% of the weight of the batch, and reserve it;
[0054] (2) Stirring and mixing: putting phosphogypsum, lime and cement into a stirrer and stirring and mixing to obtain a batch; adding water to the batch and fully stirring and mixing to obtain a batch;
[0055] (3) Compression forming: the mixed material cloth is pressed in a brick press under a pressure of 30MPa to form a brick adobe, with a size of 240mm×115mm×53mm;
[0056] (4) Wet maintenance: on the first day after the adobe is formed, water is intermittently poured 4 times until the surfac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mechanical strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com