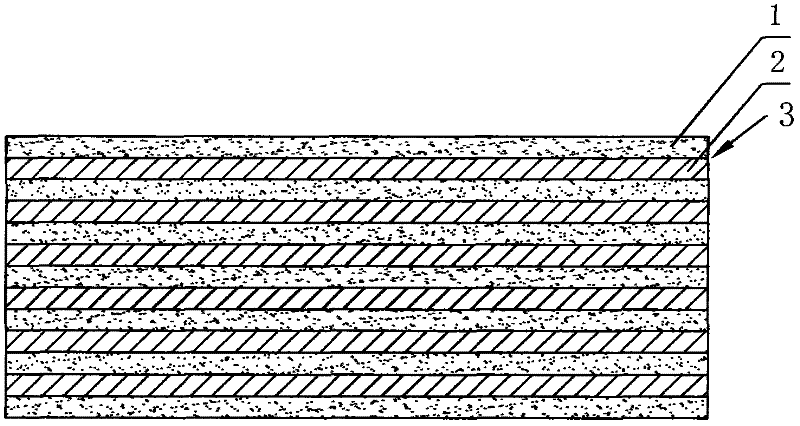
Low-temperature co-firing ceramic wave-absorbing material and preparation method thereof
A technology of low-temperature co-fired ceramics and wave-absorbing materials, applied in reactors, nuclear engineering, shielding, etc., can solve problems such as damage shape, difficulty in film formation, poor effect of sheet-shaped wave-absorbing materials, etc., and achieve good wave-absorbing performance and process Simple, Widely Applicable Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Firstly, the low temperature co-fired ceramic nanopowder raw material is dispersed in a solvent to prepare a ceramic slurry.
[0029] The solvent is water, so that the prepared ceramic slurry has a certain viscosity and fluidity, so that it can be removed in the subsequent low-temperature sintering process without affecting the performance of the finished product.
[0030] The ceramic nanopowder adopts low-temperature co-fired glass ceramics that can be sintered in an inert atmosphere filled with nitrogen.
[0031] Then, the ceramic slurry is cast into a film on the glass fiber cloth sheet-like wave-absorbing material mixed with carbon fibers through a waterfall casting process. The waterfall casting process is to store the ceramic slurry in a container at a high place, and a slit is opened at the lower end of the container, and the ceramic slurry passes through the slit at a certain speed due to gravity or extrusion from above to form a casting waterfall; A conveyor b...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Firstly, the low temperature co-fired ceramic nanopowder raw material is dispersed in a solvent to prepare a ceramic slurry.
[0037] Various organic solvents can be used as the solvent, so that the prepared ceramic slurry has a certain viscosity and fluidity. It is advisable to use a mixed organic solvent that can be removed in the subsequent low-temperature sintering process without affecting the performance of the finished product.
[0038] Ceramic nanopowder adopts low-temperature co-fired ceramic nanopowder mixed with absorbing fiber or metal, and low-temperature co-fired glass ceramics that can be sintered in a reducing atmosphere filled with hydrogen.
[0039] Then, the ceramic slurry is cast into a film on the glass fiber cloth sheet-like wave-absorbing material mixed with carbon fibers through a waterfall casting process. The waterfall casting process is to store the ceramic slurry in a container at a high place, and a slit is opened at the lower end of the con...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Firstly, the low temperature co-fired ceramic nanopowder raw material is dispersed in a solvent to prepare a ceramic slurry.
[0045] An organic solvent is used as the solvent, so that the prepared ceramic slurry has a certain viscosity and fluidity, and it is advisable to use a mixed organic solvent that can be removed in the subsequent low-temperature sintering process without affecting the performance of the finished product.
[0046] Ceramic nanopowder adopts low-temperature co-fired ceramic nanopowder mixed with oxide powder, preferably low-temperature co-fired glass ceramics that can be sintered in a reducing atmosphere, to further optimize the absorbing performance.
[0047] Then, the ceramic slurry is cast into a film on the glass fiber cloth sheet-like wave-absorbing material mixed with carbon fibers through a waterfall casting process. The waterfall casting process is to store the ceramic slurry in a container at a high place, and a slit is opened at the lower...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com