Patents
Literature
872 results about "Co-fired ceramic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
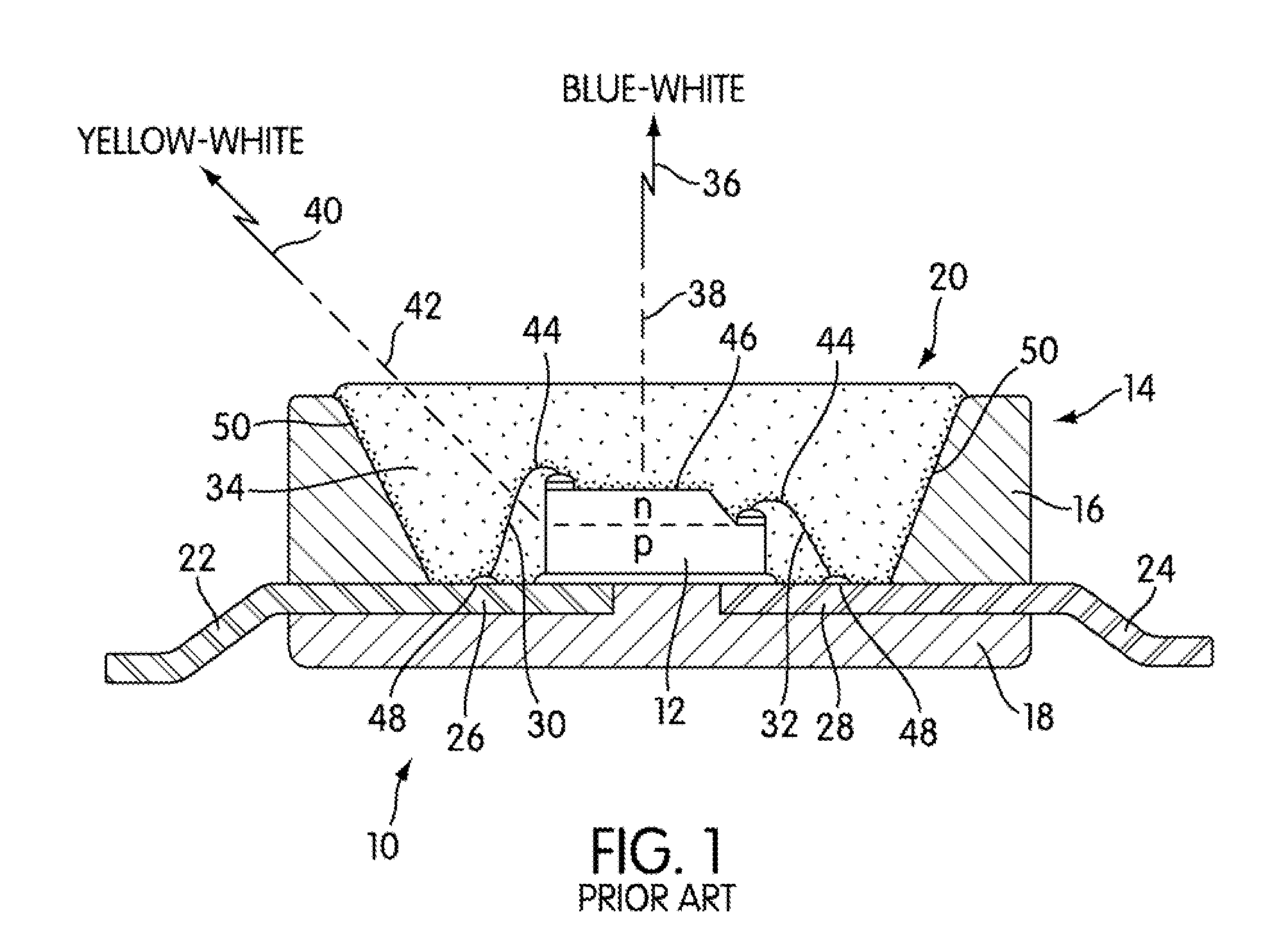
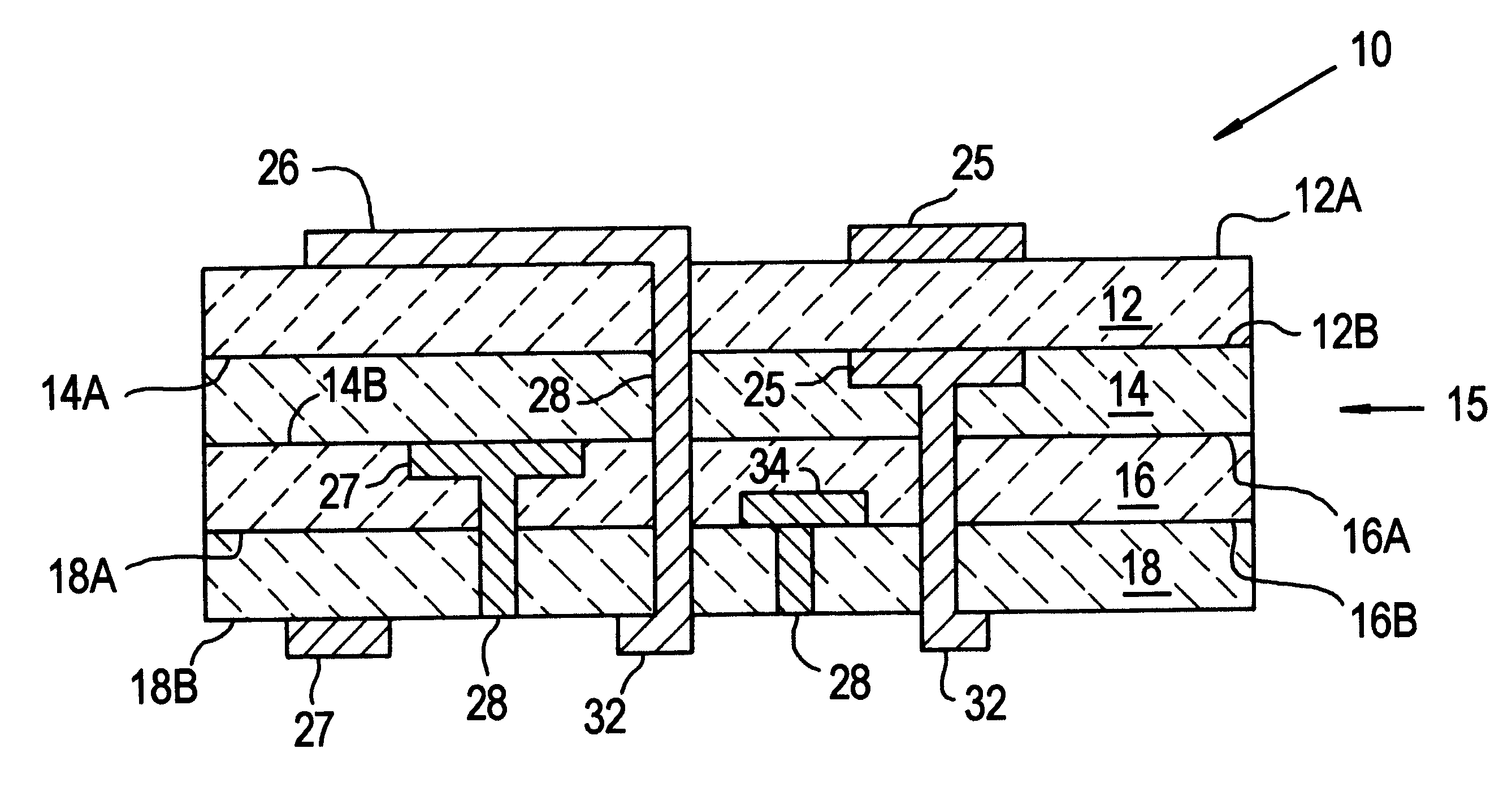
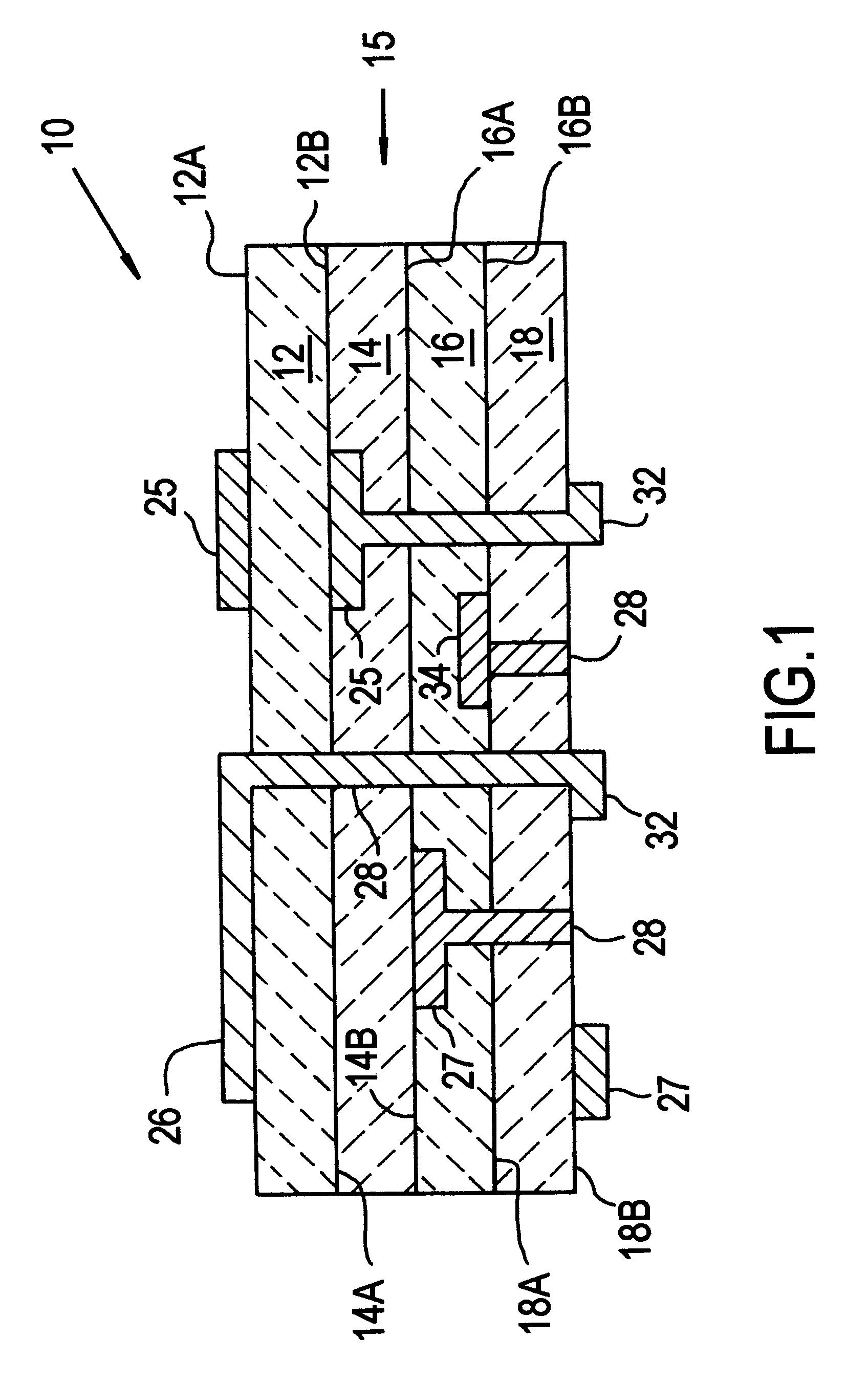
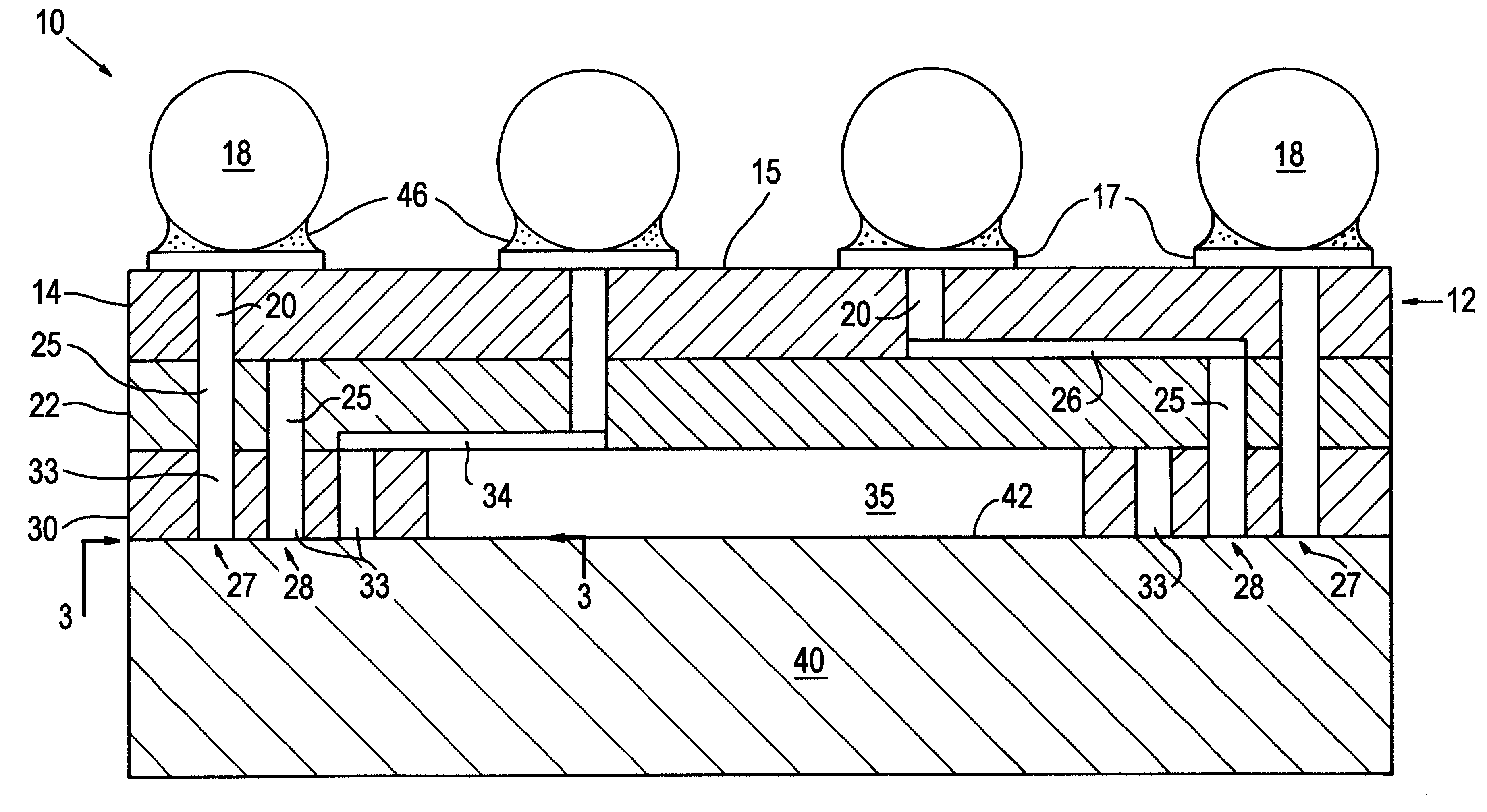
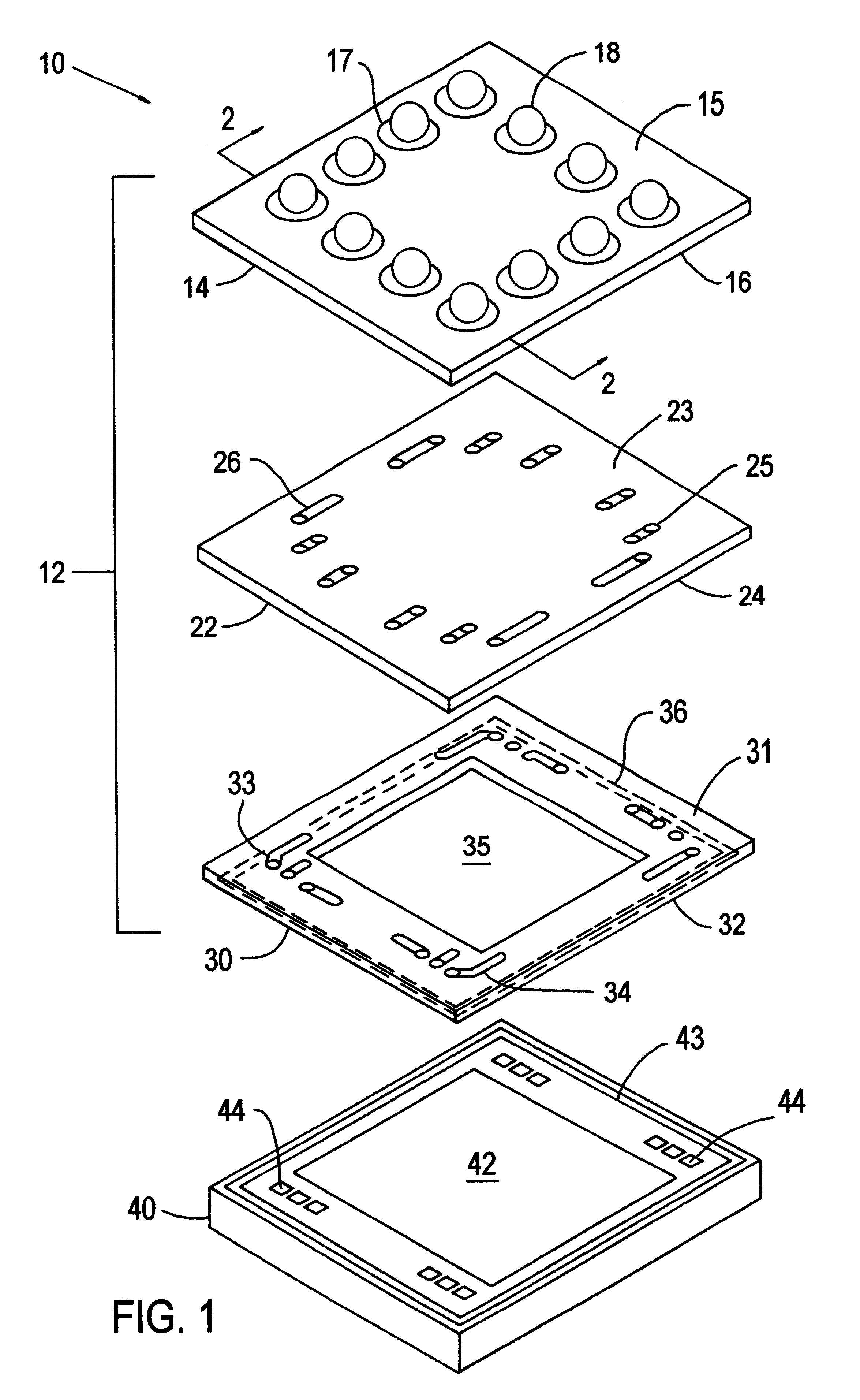
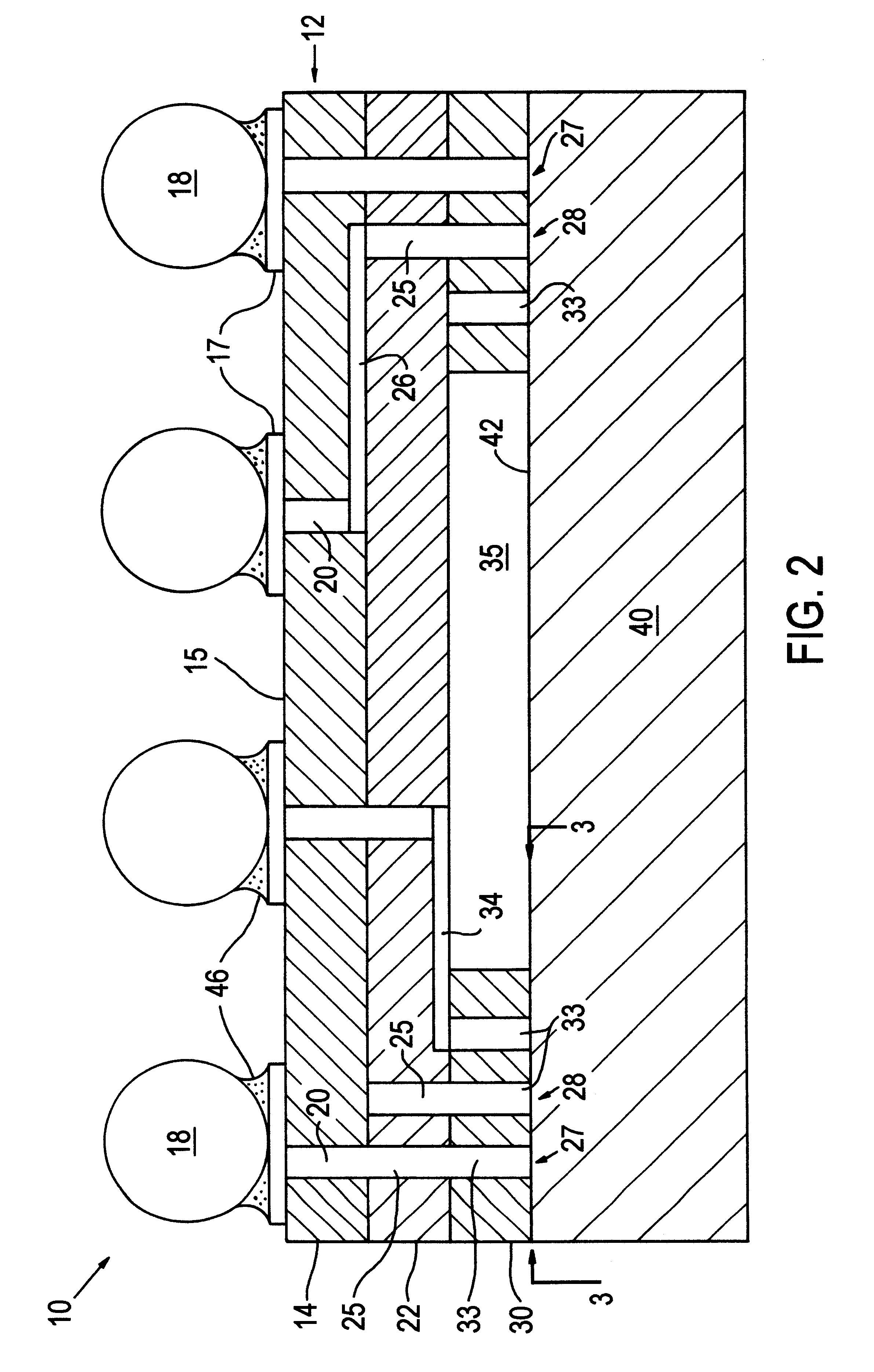
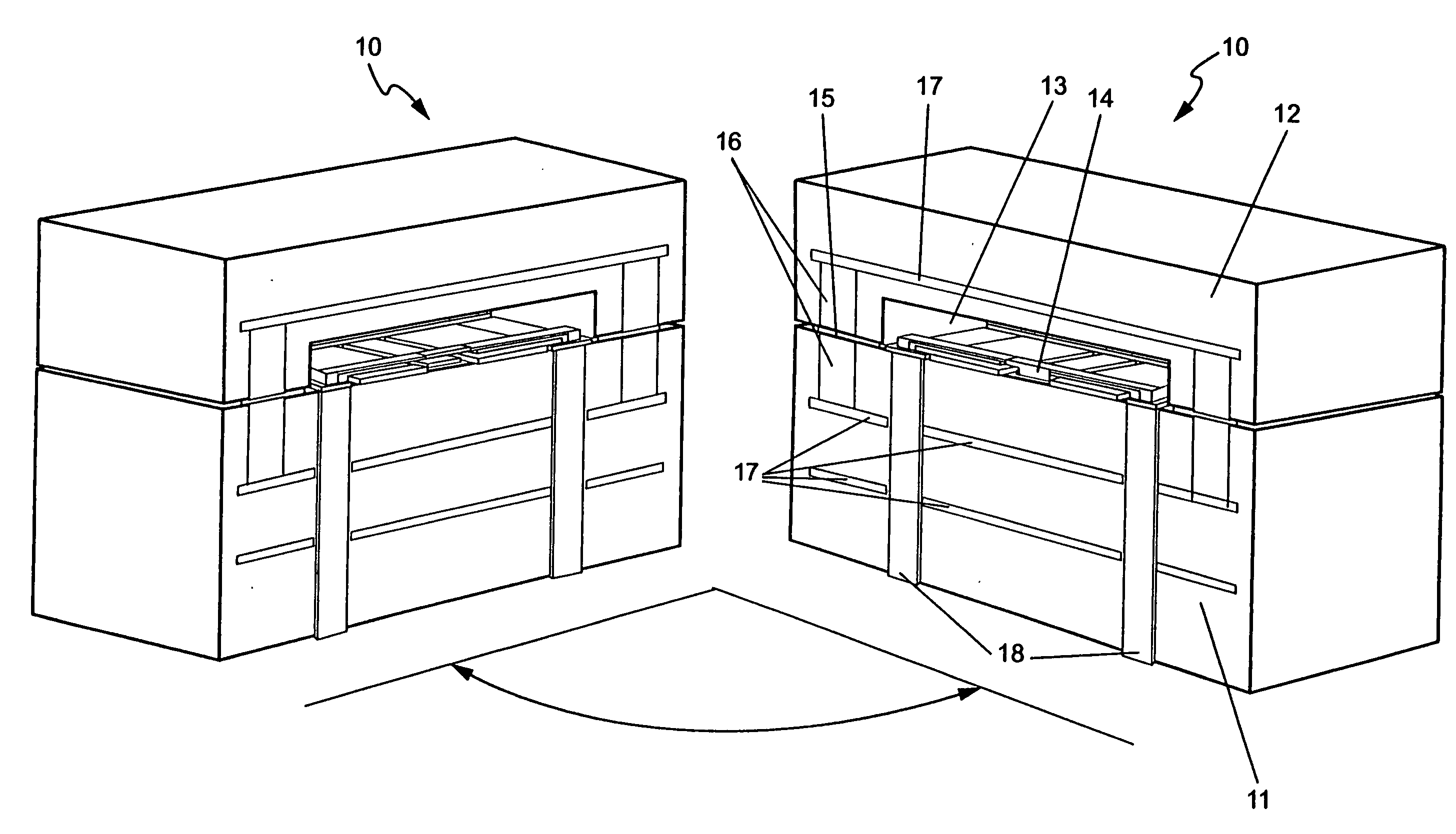
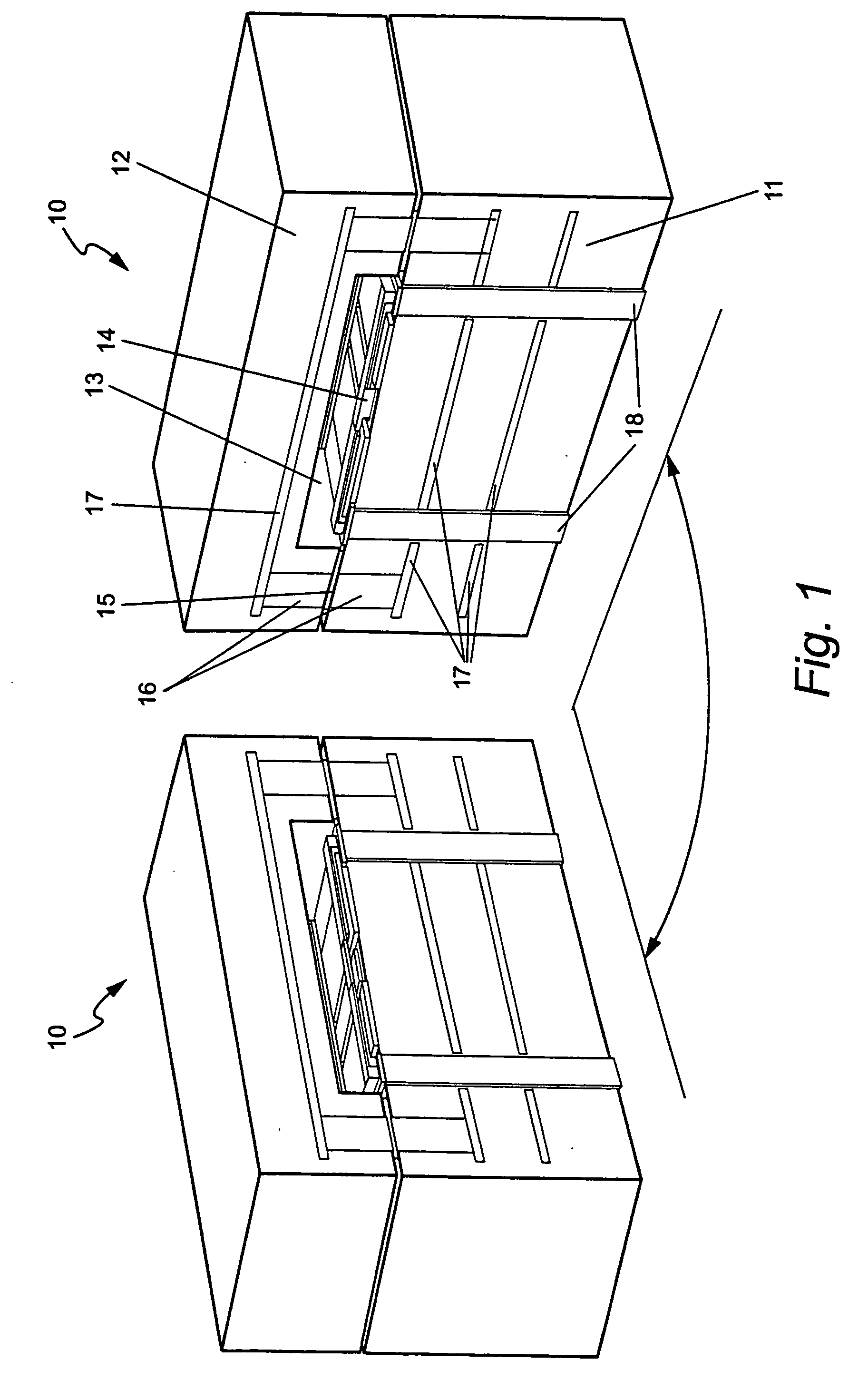
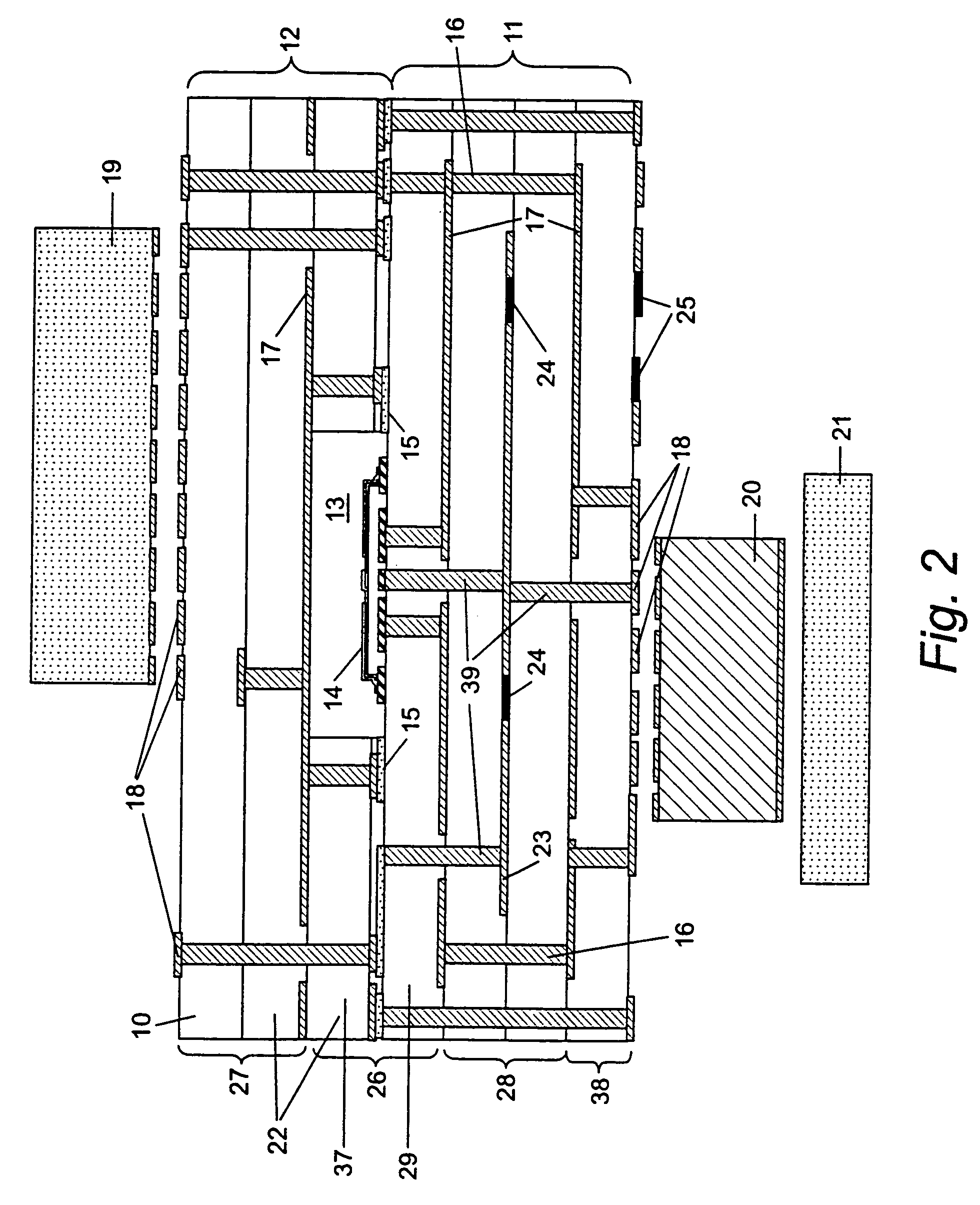
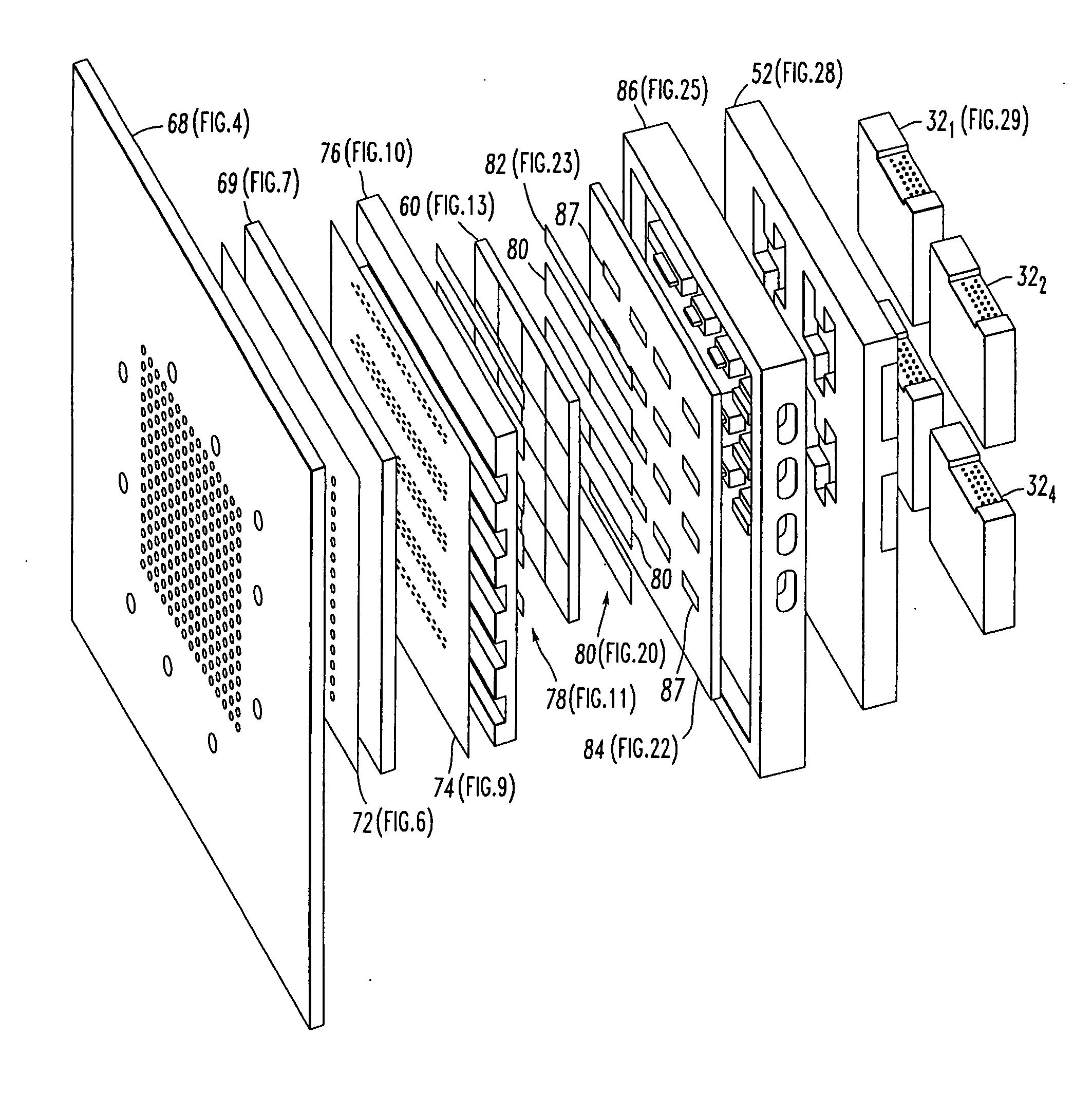
Co-fired ceramic devices are monolithic, ceramic microelectronic devices where the entire ceramic support structure and any conductive, resistive, and dielectric materials are fired in a kiln at the same time. Typical devices include capacitors, inductors, resistors, transformers, and hybrid circuits. The technology is also used for robust assembly and packaging of electronic components multi-layer packaging in the electronics industry, such as military electronics, MEMS, microprocessor and RF applications.
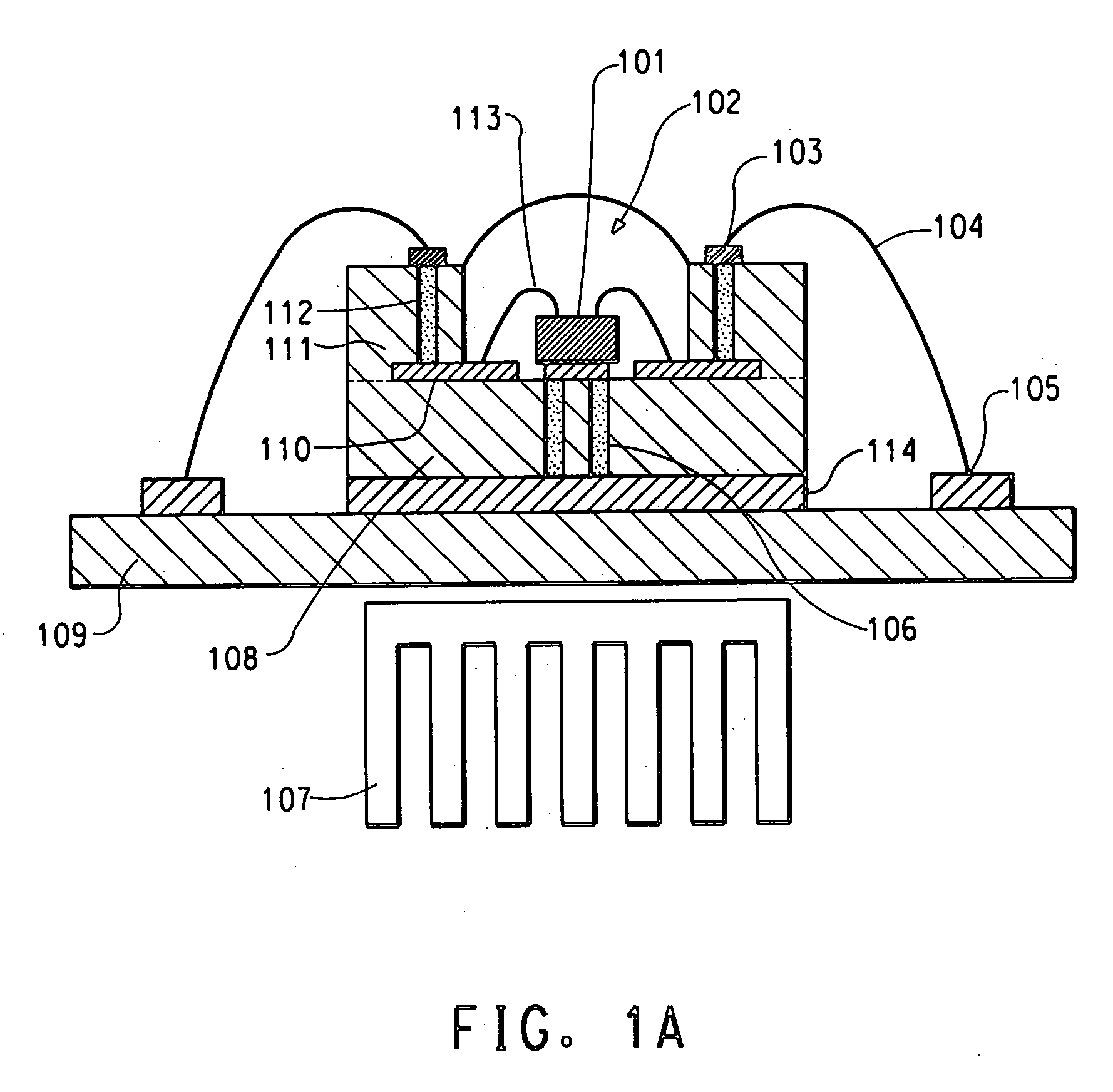
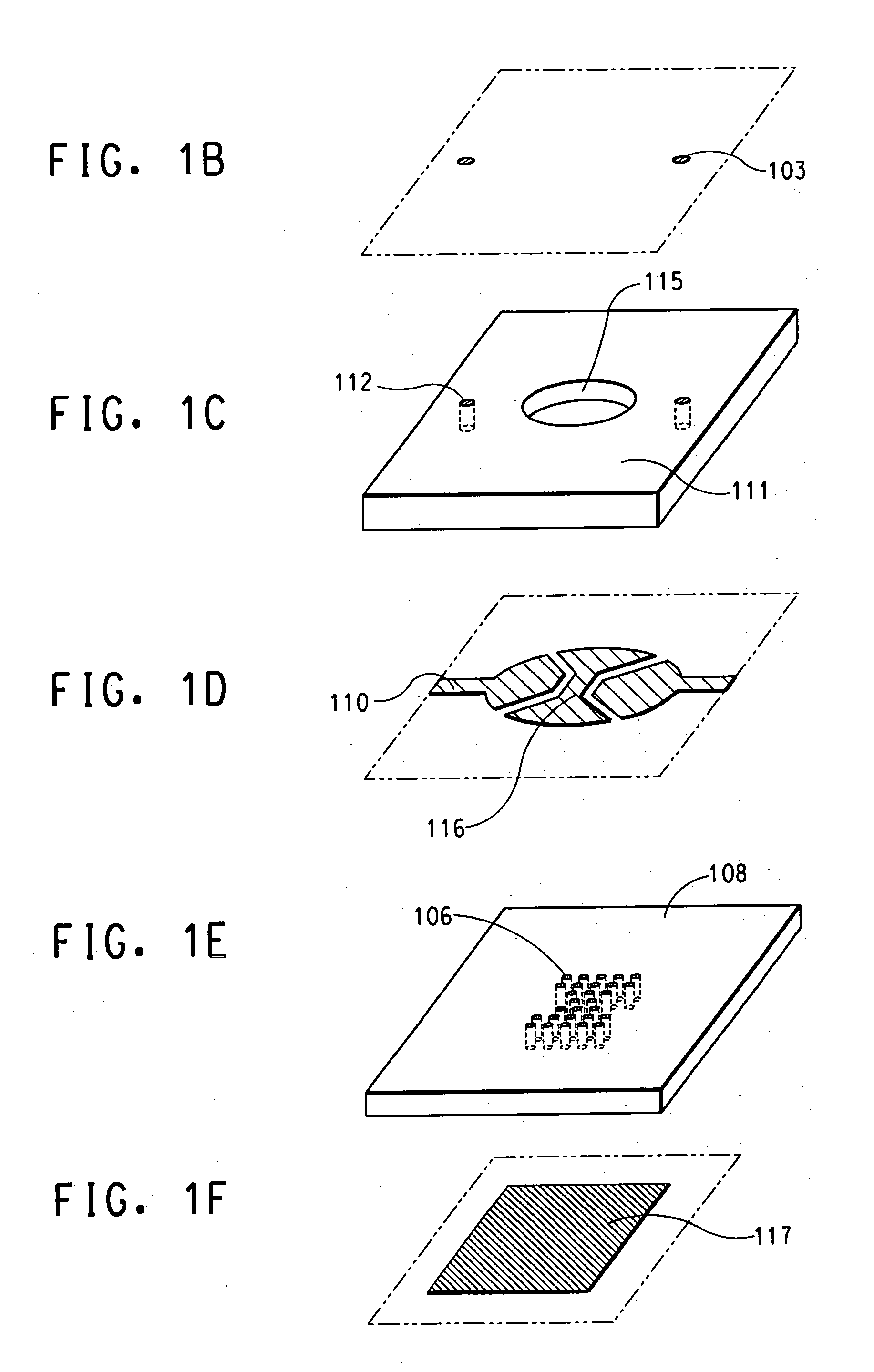
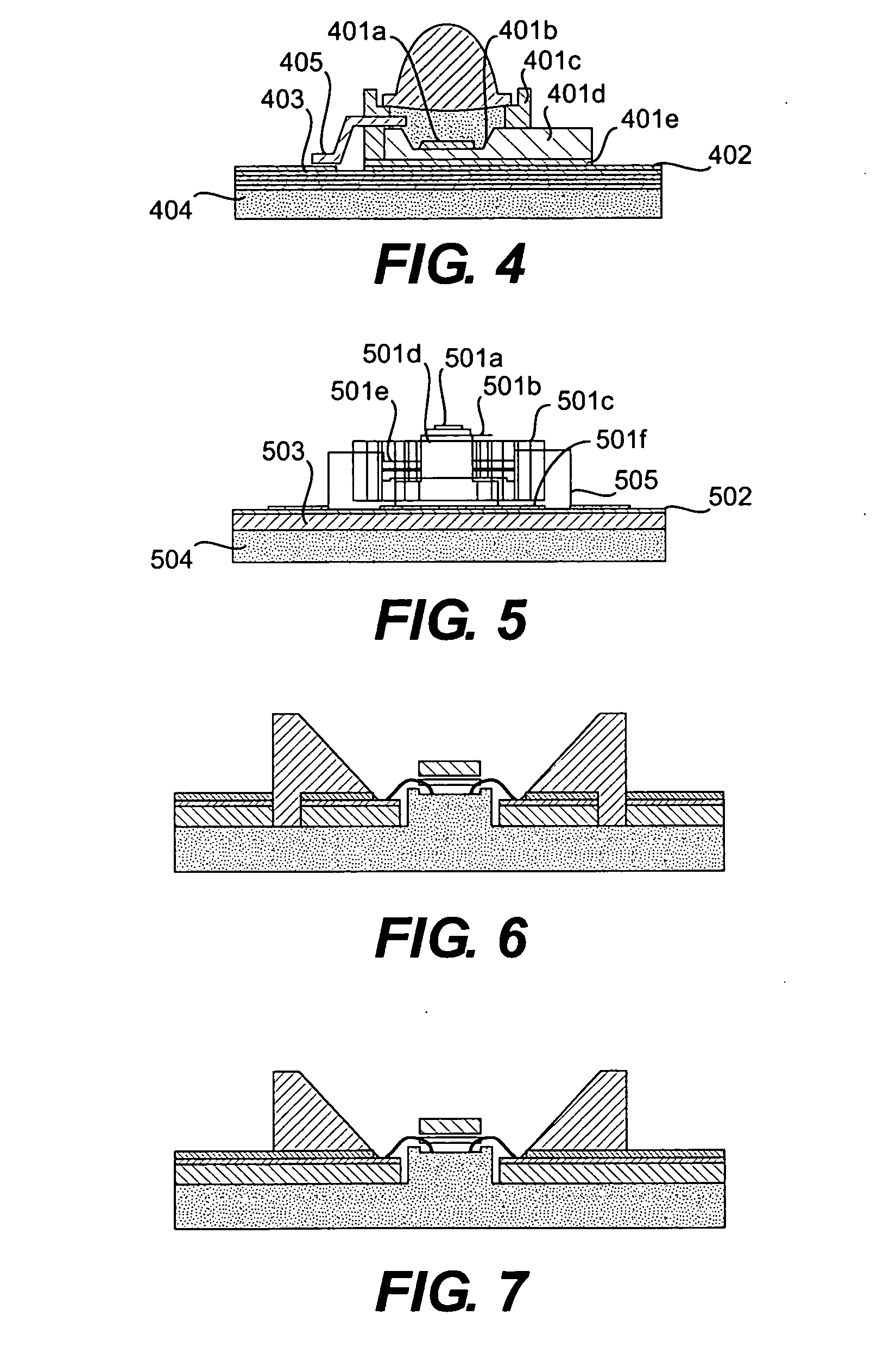
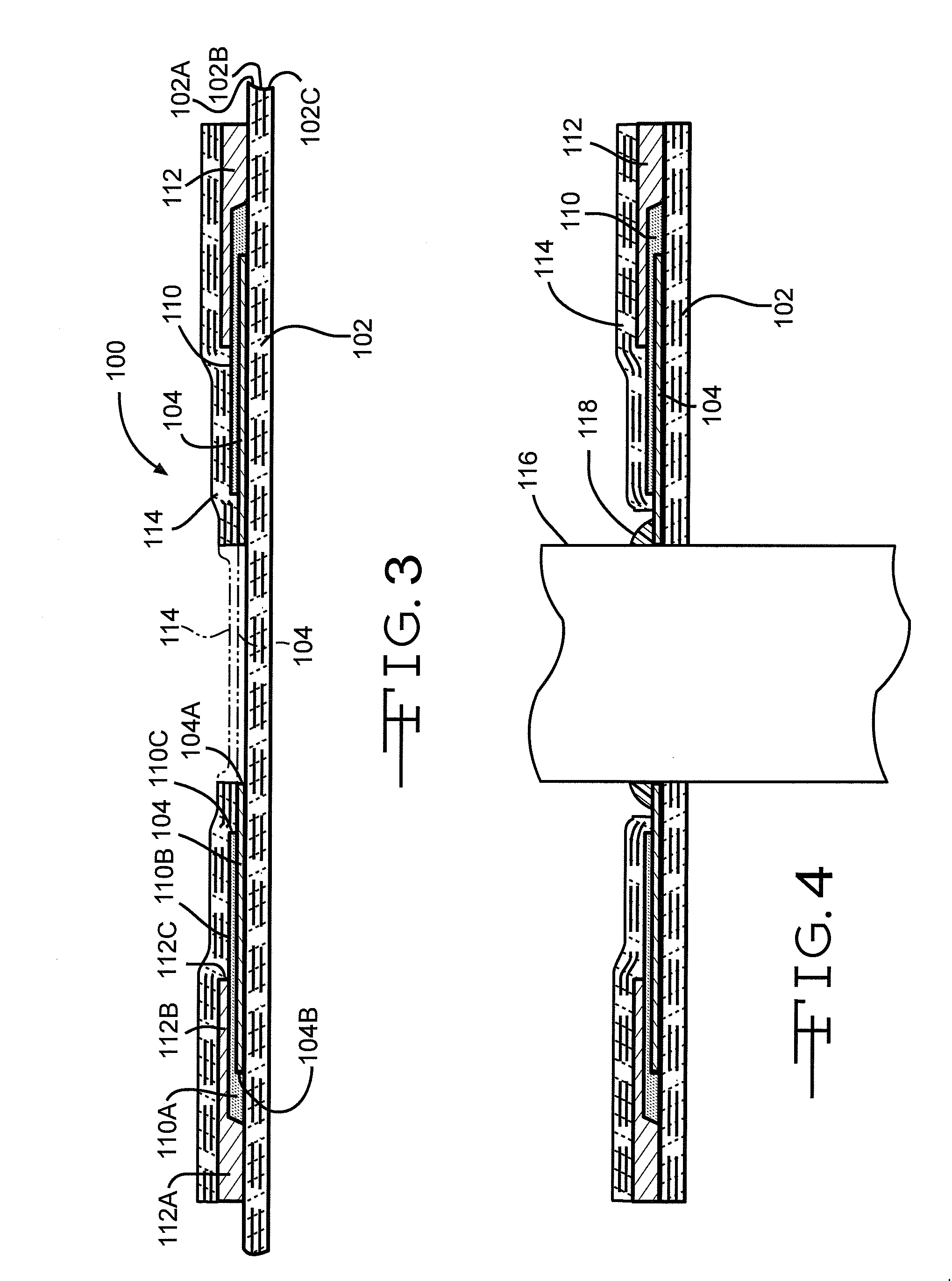
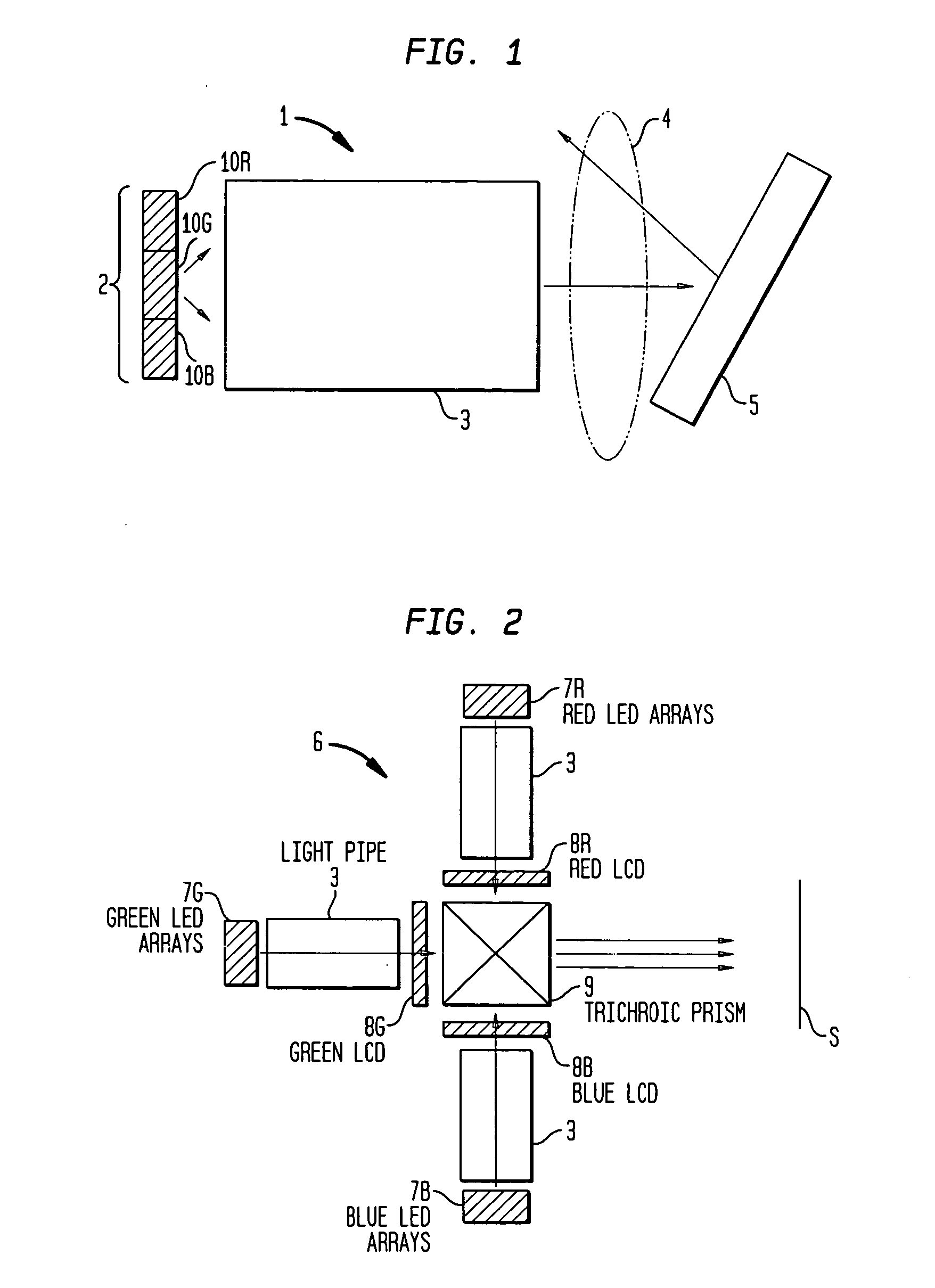
Light emitting devices with phosphor wavelength conversion and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20100181582A1Reduces the formation of air bubblesEasy to fillSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhosphorPlanar substrate
A light emitting device comprises: a package (low temperature co-fired ceramic) having a plurality of recesses (cups) in which each recess houses at least one LED chip and at least one phosphor material applied as coating to the light emitting light surface of the LED chips, wherein the phosphor material coating is conformal in form. In another arrangement a light emitting device comprises: a planar substrate (metal core printed circuit board); a plurality of light emitting diode chips mounted on, and electrically connected to, the substrate; a conformal coating of at least one phosphor material on each light emitting diode chip; and a lens formed over each light emitting diode chip.
Owner:INTEMATIX
Low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) tape compositions, light emitting diode (LED) modules, lighting devices and method of forming thereof
The present invention provides LTCC (low temperature co-fired ceramic) tape compositions and demonstrates the use of said LTCC tape(s) in the formation of Light-Emitting Diode (LED) chip carriers and modules for various lighting applications. The present invention also provides for the use of (LTCC) tape and LED modules in the formation of lighting devices including, but not limited to, LED devices, High Brightness (HB) LED backlights, display-related light sources, automotive lighting, decorative lighting, signage and advertisement lighting, and information display lighting.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
High power light-emitting diode package comprising substrate having beacon
InactiveUS20080019133A1Reduce heat resistance requirementsDecreasing junction temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsCo-fired ceramicPrinted circuit board
Disclosed herein is a package structure including at least one high power light-emitting diode to exhibit excellent heat release properties. In the package structure, a light-emitting diode chip which generates heat is directly attached to a beacon processed to protrude from part of a heat spreader having high heat conductivity, whereby an electrical wiring portion is separated from a heat release portion, thus maximizing heat release properties and realizing high luminance and reliability. The package structure is composed of a beacon formed on a metal or non-metal substrate having high heat conductivity to mount a high power light-emitting diode chip, to increase heat release properties; a wiring portion provided on the same line as the diode to input and output power and signals; and a reflection cup having a cavity, which may be inserted into or attached to the heat spreader or the wiring substrate, including a low temperature co-fired ceramic substrate, a high temperature co-fired ceramic substrate, or a printed circuit board.
Owner:KOREA PHOTONICS TECH INST
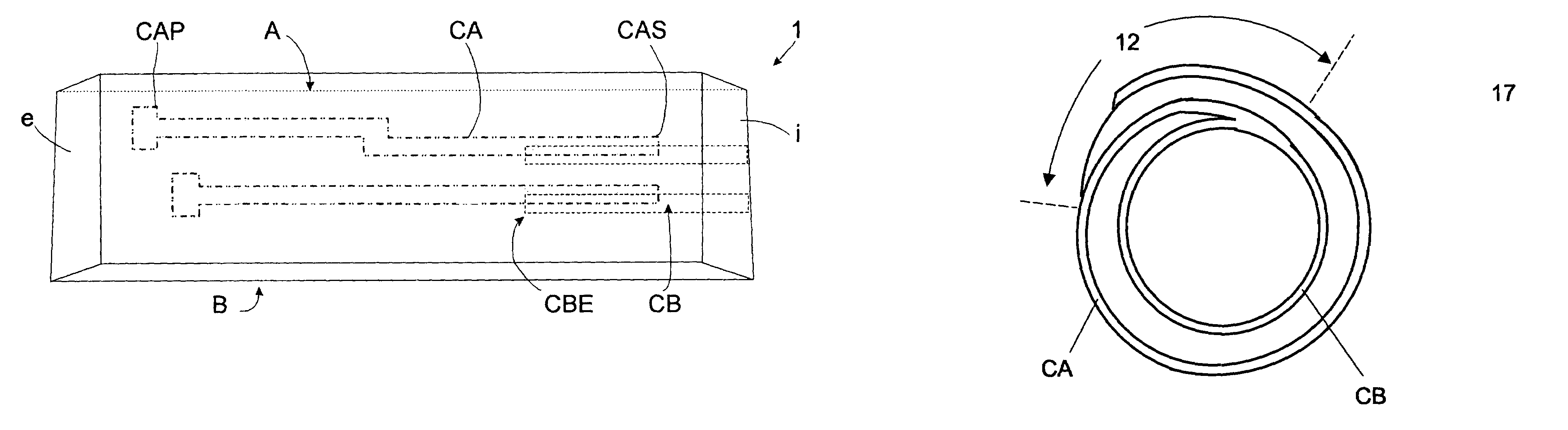
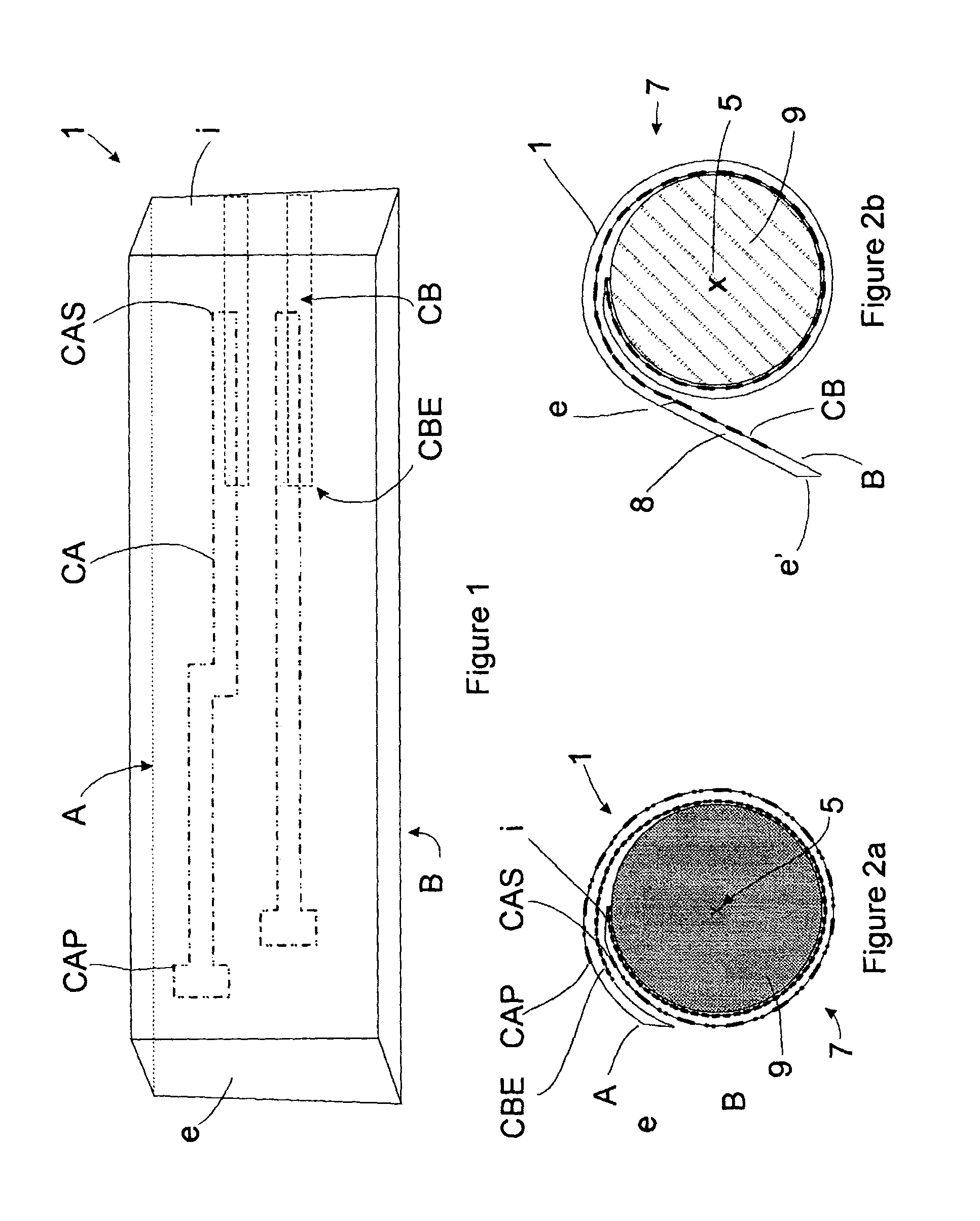
Method for producing a tube
ActiveUS7155812B1Printed circuit assemblingLine/current collector detailsElectrical conductorDrift tube
A method is described for producing tubular substrates having parallel spaced concentric rings of electrical conductors that can be used as the drift tube of an Ion Mobility Spectrometer (IMS). The invention comprises providing electrodes on the inside of a tube that are electrically connected to the outside of the tube through conductors that extend between adjacent plies of substrate that are combined to form the tube. Tubular substrates are formed from flexible polymeric printed wiring board materials, ceramic materials and material compositions of glass and ceramic, commonly known as Low Temperature Co-Fired Ceramic (LTCC). The adjacent plies are sealed together around the electrode.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Low temperature co-fired ceramic with improved registration
InactiveUS6205032B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh densityMetallurgy
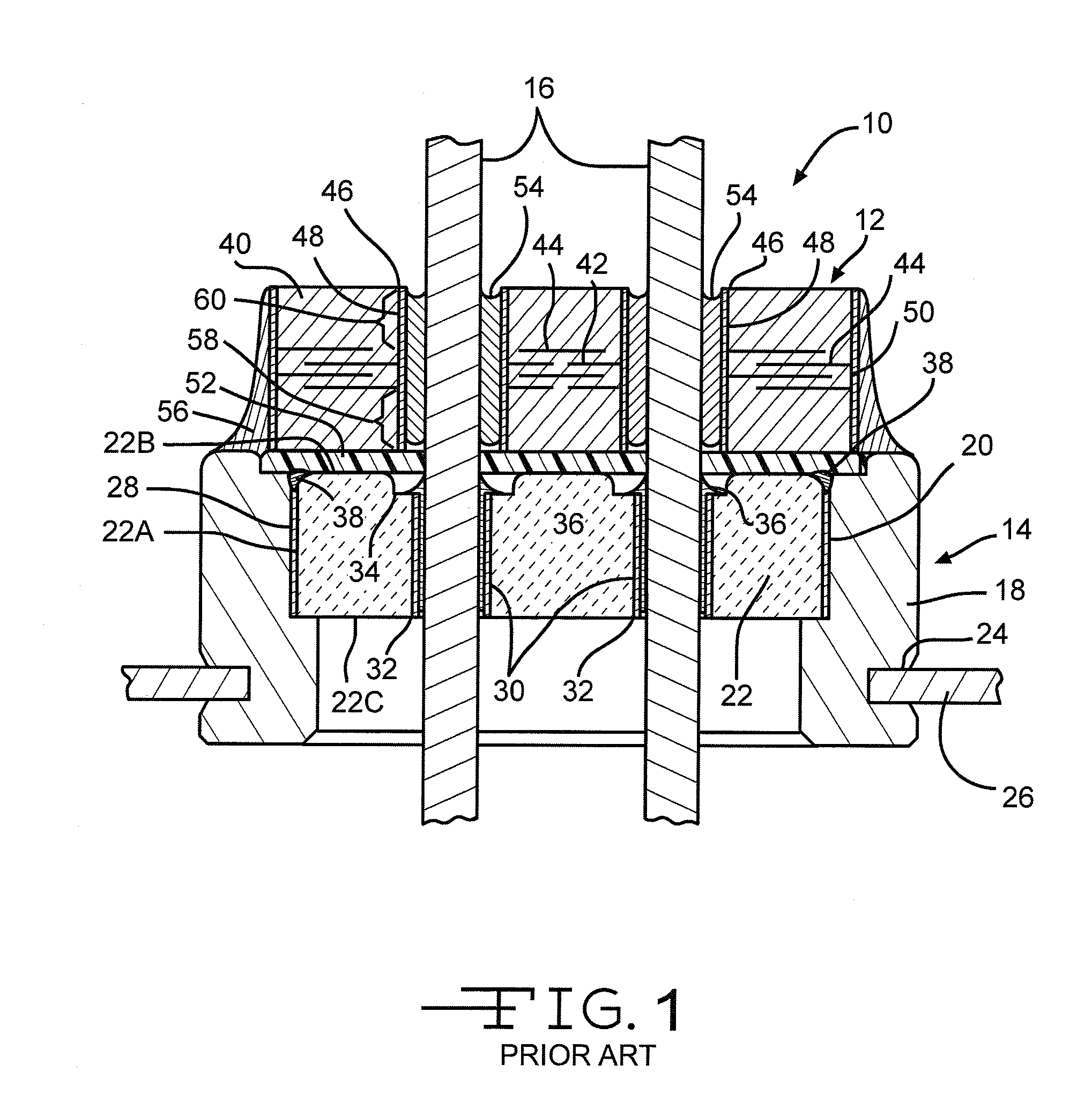
A low temperature co-fired ceramic assembly (LTCC) with a constraining core to minimize shrinkage of outer ceramic layers during firing. The outer ceramic layers have high density circuit features. A ceramic core includes several ceramic layers. Several via holes are located in the first and second ceramic layers. Several low density circuit features are located on the ceramic layers that make up the core. Outer ceramic layers are placed top and bottom of the ceramic core. The outer ceramic layers have via holes and high density circuit features. The circuit features patterned on the ceramic layers include resistors, capacitors, circuit lines, vias, inductors, or bond pads. The ceramic core is fired first in a furnace. The outer layers are then laminated to the ceramic core and fired. The ceramic core controls the shrinkage rate of the outer ceramic layers during firing allowing higher density circuit features on the outer layers.
Owner:CTS CORP ELKHART
Flip chip package for micromachined semiconductors
InactiveUS6225692B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialSolder ball
A hermetic multilayered ceramic semiconductor package for micromachined semiconductor devices. A low temperature co-fired ceramic assembly has a cavity and a top and bottom surface. Several vias extend between the top and bottom surfaces and several solder spheres are located on the top surface and are electrically connected to the vias. A micromachined semiconductor device abuts the bottom surface and covers the cavity such that a movable portion of the micromachined semiconductor device is unconstrained to move within the cavity. Solder is used to connect the vias to solder bumps on the semiconductor device. A seal ring is located between the micromachined semiconductor device and the ceramic assembly for hermetically sealing the micromachined semiconductor device.
Owner:CTS CORP ELKHART
Integrated Filter Feedthrough Assemblies Made From Low Temperature Co-Fired (LTCC) Tape
InactiveUS20070217121A1Prevent leakageAvoid spreadingAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyScreen printingState of art
A filter capacitor comprising a substrate of at least one layer of a low temperature co-fires ceramic (LTCC) tape supporting alternating active and ground electrode layers segregated by a dielectric layer is described. The substrate is preferably a laminate of three LTCC tapes pieces that are heated under pressure and at a relatively low temperature to become a laminate that maintains its shape and structure dimensions even after undergoing numerous sintering steps. Consequently, relatively thin active and ground electrode layers along with the intermediate dielectric layer can be laid down or deposited on the LTCC substrate by a screen-printing technique. A second laminate of LTCC tapes is positioned on top of the active / dielectric / ground layers to finish the capacitor. Consequently, a significant amount of space is saved in comparison to a comparably rated capacitor or, a capacitor of a higher rating can be provided in the same size as a conventional prior art capacitor.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) tape compositions, light emitting diode (LED) modules, lighting devices and method of forming thereof
InactiveUS7550319B2Extended service lifeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCeramicsEffect lightDisplay device
The present invention provides LTCC (low temperature co-fired ceramic) tape compositions and demonstrates the use of said LTCC tape(s) in the formation of Light-Emitting Diode (LED) chip carriers and modules for various lighting applications. The present invention also provides for the use of (LTCC) tape and LED modules in the formation of lighting devices including, but not limited to, LED devices, High Brightness (HB) LED backlights, display-related light sources, automotive lighting, decorative lighting, signage and advertisement lighting, and information display lighting.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
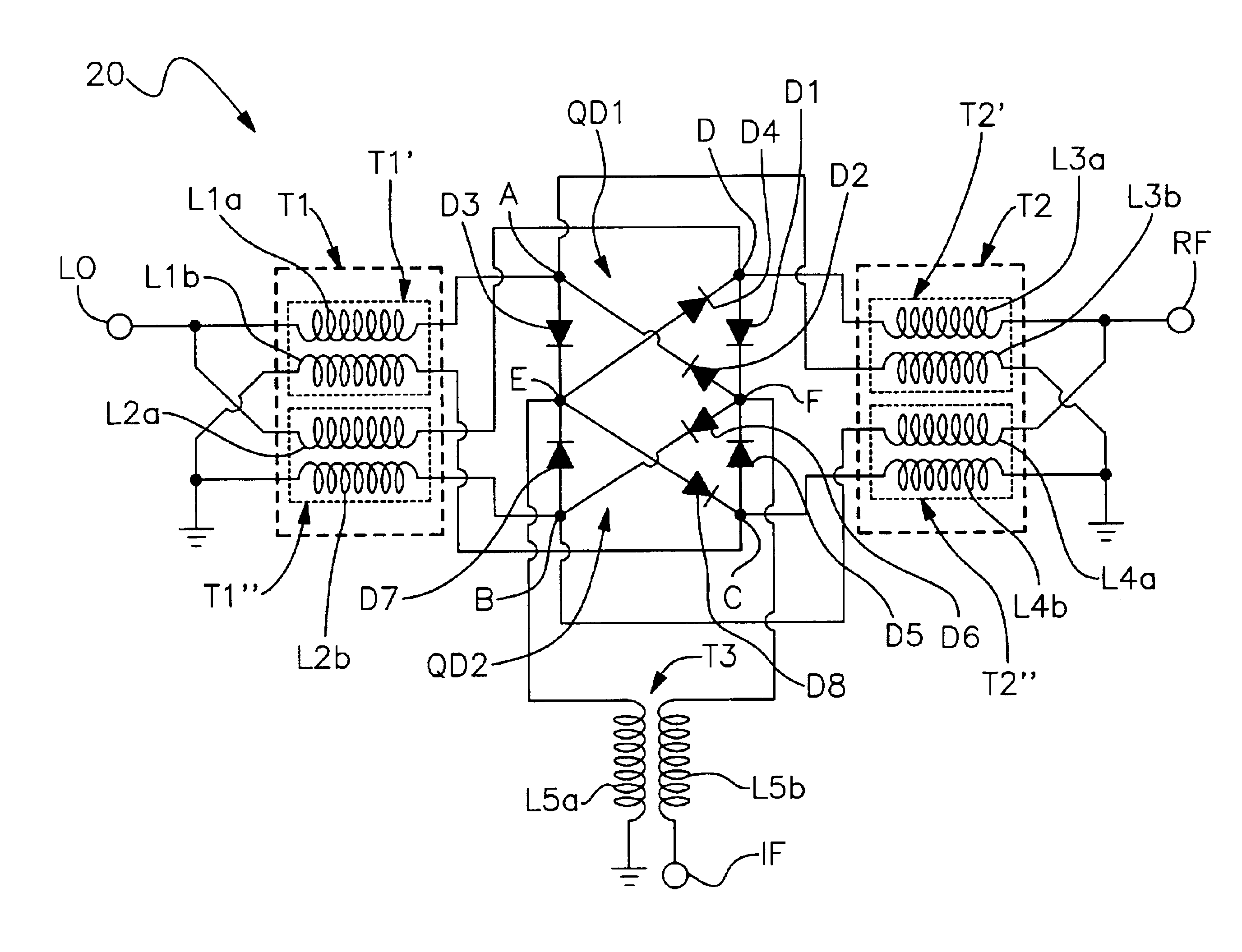
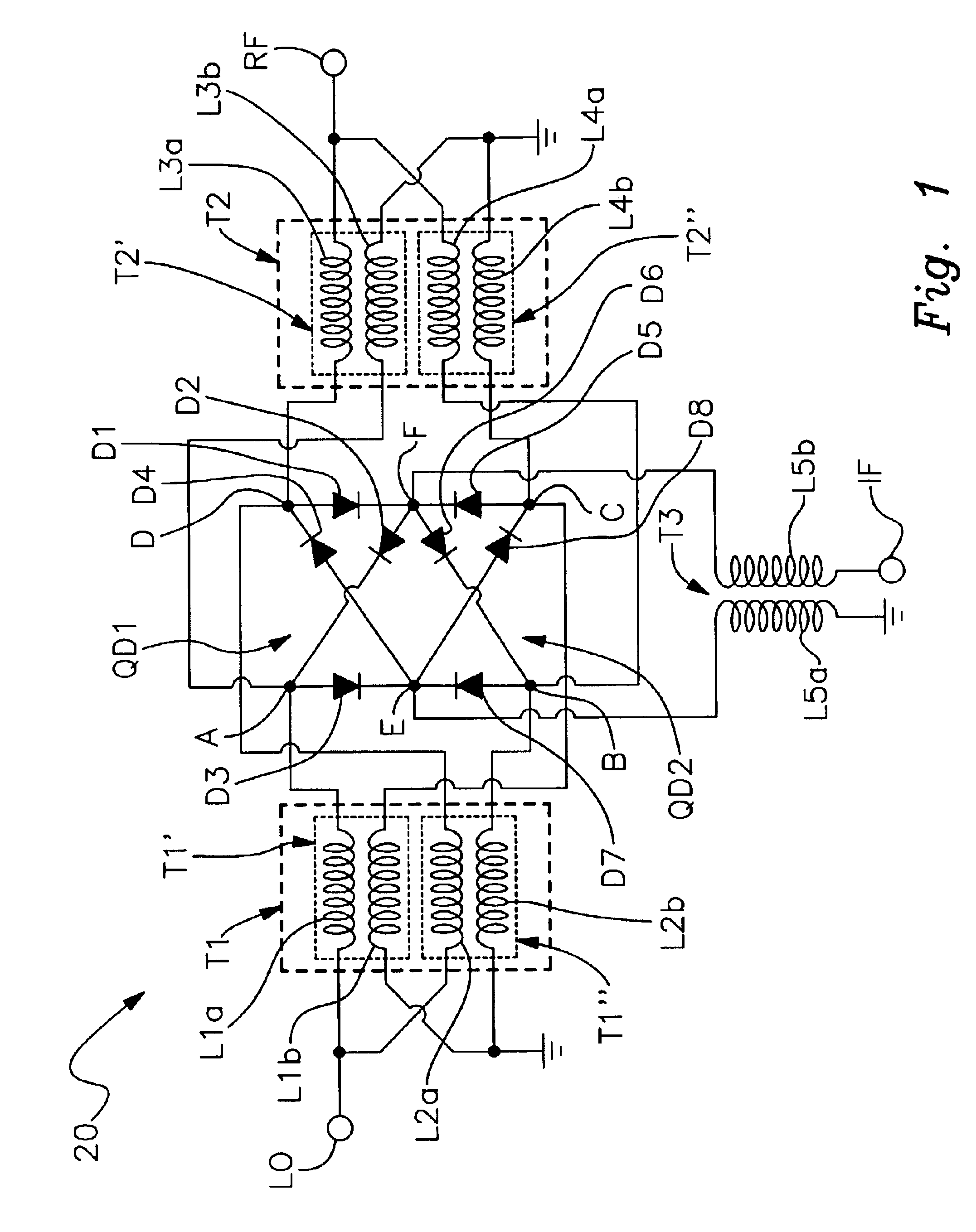
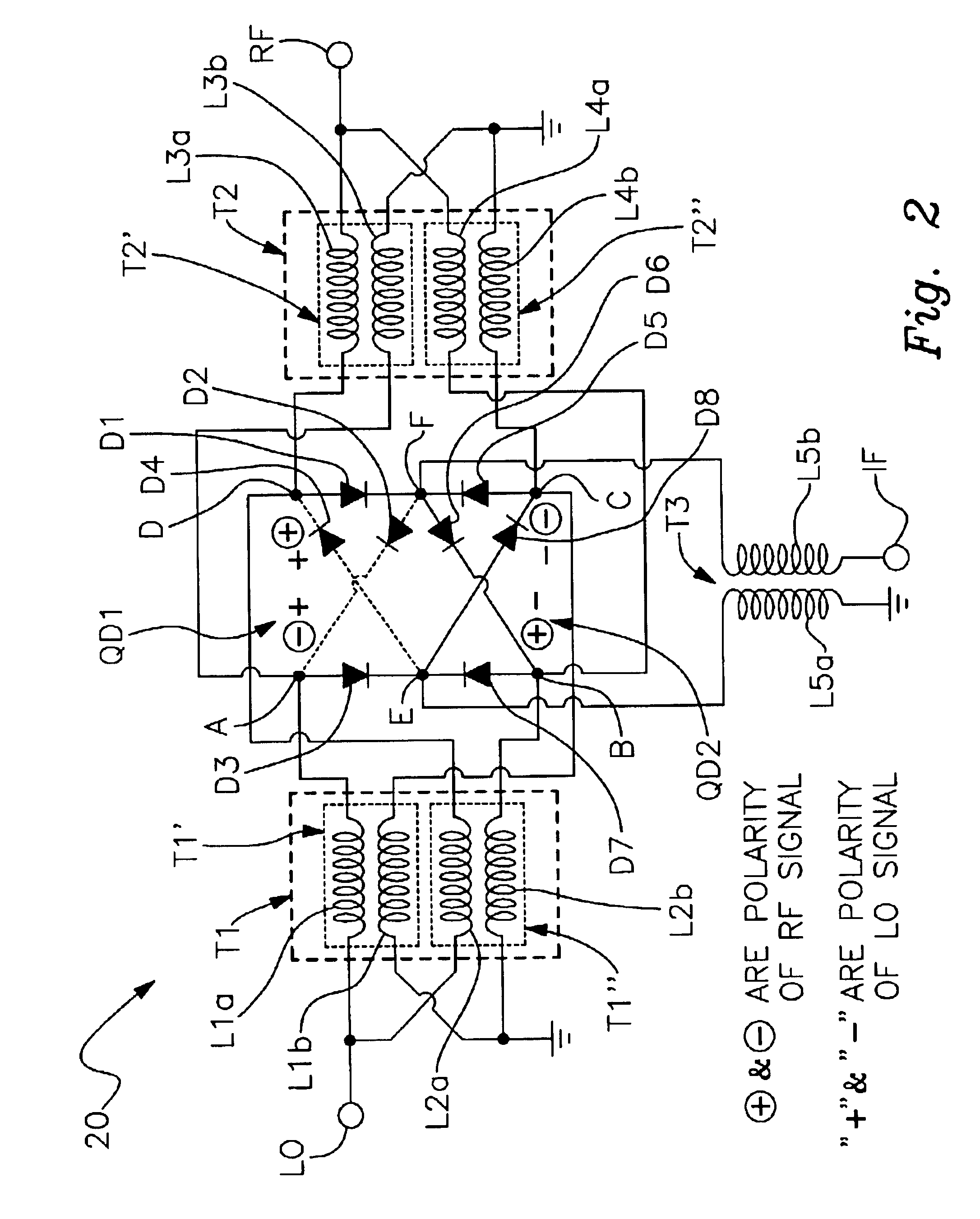
Triple balanced mixer
ActiveUS6917796B2Small sizeEasy to assembleModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmission noise suppressionBalanced mixerPlanar substrate
Owner:SCI COMPONENTS
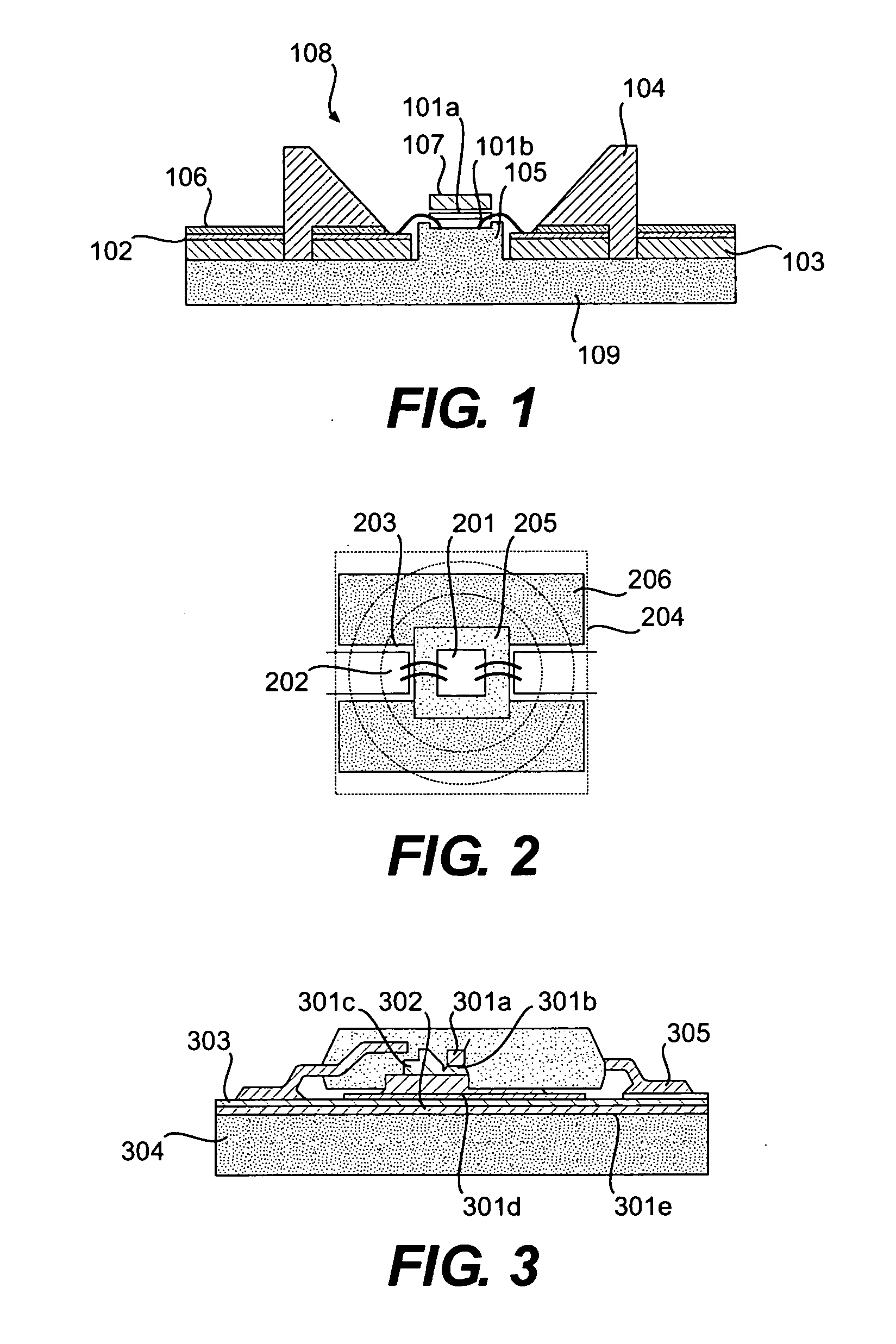
MEMS-based variable capacitor
ActiveUS6909589B2Low loss tangentSimple processMechanically variable capacitor detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceClosed loop
A variable capacitor device using MEMS or micromachining techniques wherein thin-films of materials are deposited, patterned and etched to form movable micromechanical elements on the surface of a substrate composed of either semiconductor, glass, metal, or ceramic material. In one embodiment of the present invention to achieve higher frequency performance as well as other benefits, the substrate is comprised of Low-Temperature Co-Fired Ceramics (LTCC). The variable capacitor is an electrostatically actuated micromechanical device and if fabricated on a LTCC multi-layered substrate material has continuous electrical connections through the layers. The same LTCC substrate material can also be used to enclose the device by selectively removing a portion of the upper substrate so as to form a cavity. The two substrates are then bonded together to enclose and protect the variable capacitor. An integrated circuit can be incorporation onto the multi-level substrate structure to enable a electronic closed-loop controlled variable capacitor module. The integrated circuit is flip-chip bonded at the bottom of the substrate structure with appropriate electrical connections between the integrated circuit and the MEMS variable capacitor device. A variation of the present invention utilizes a zipper actuation method wherein the tuning ratio of the variable capacitor is increased to very high levels. Yet another variation of the present invention utilizes a differential gap between the top and bottom electrodes such that the actuation electrodes do not physically contact one another. Yet another implementation of the present invention uses an extra set of electrodes or mechanical mechanism so as to lock the value of the capacitor indefinitely. Yet another implementation uses shaped actuation electrodes so as to linearize the relationship between the applied actuation voltage and the resultant capacitance of the device.
Owner:FOR NAT RES INITIATIVES
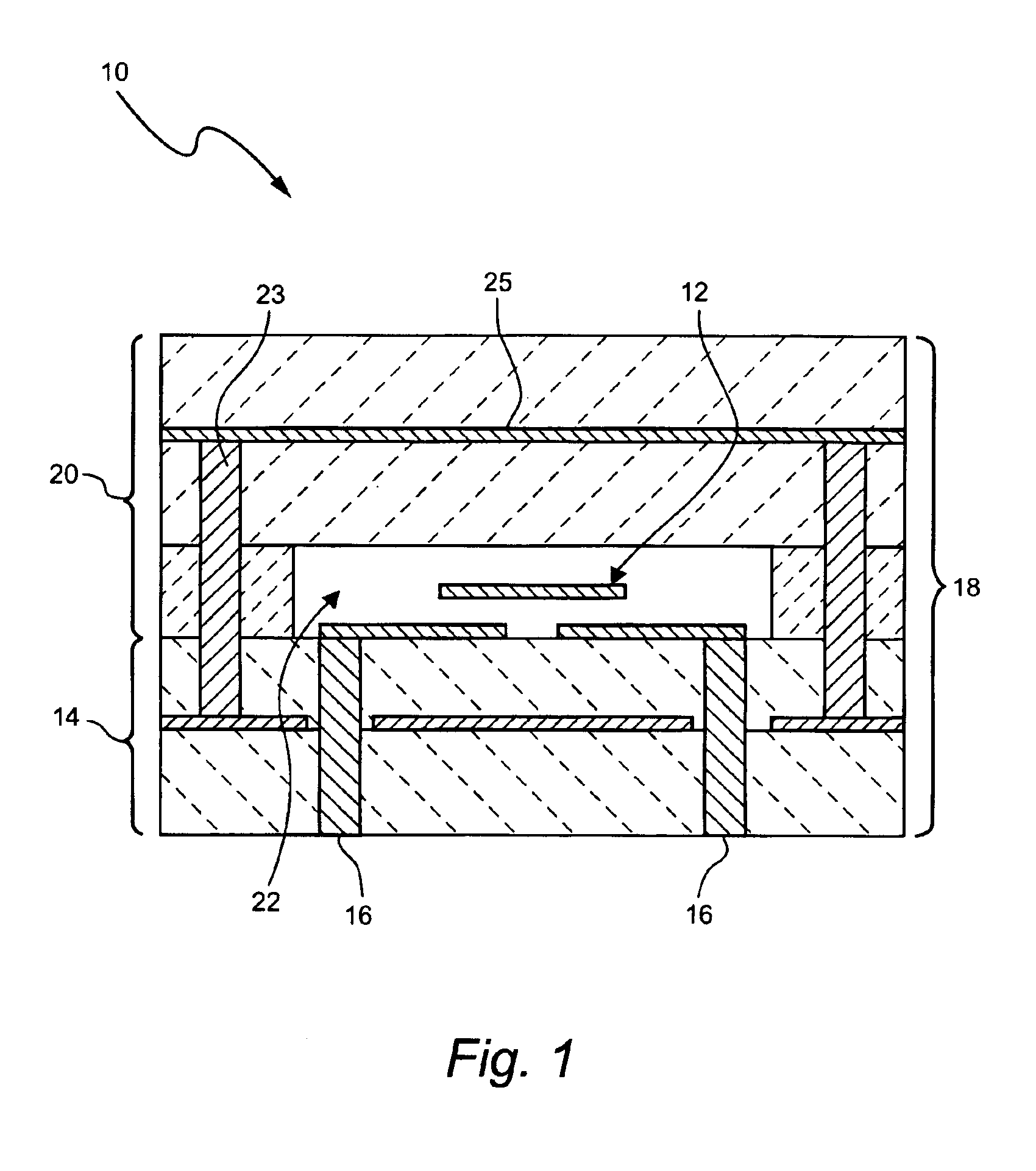
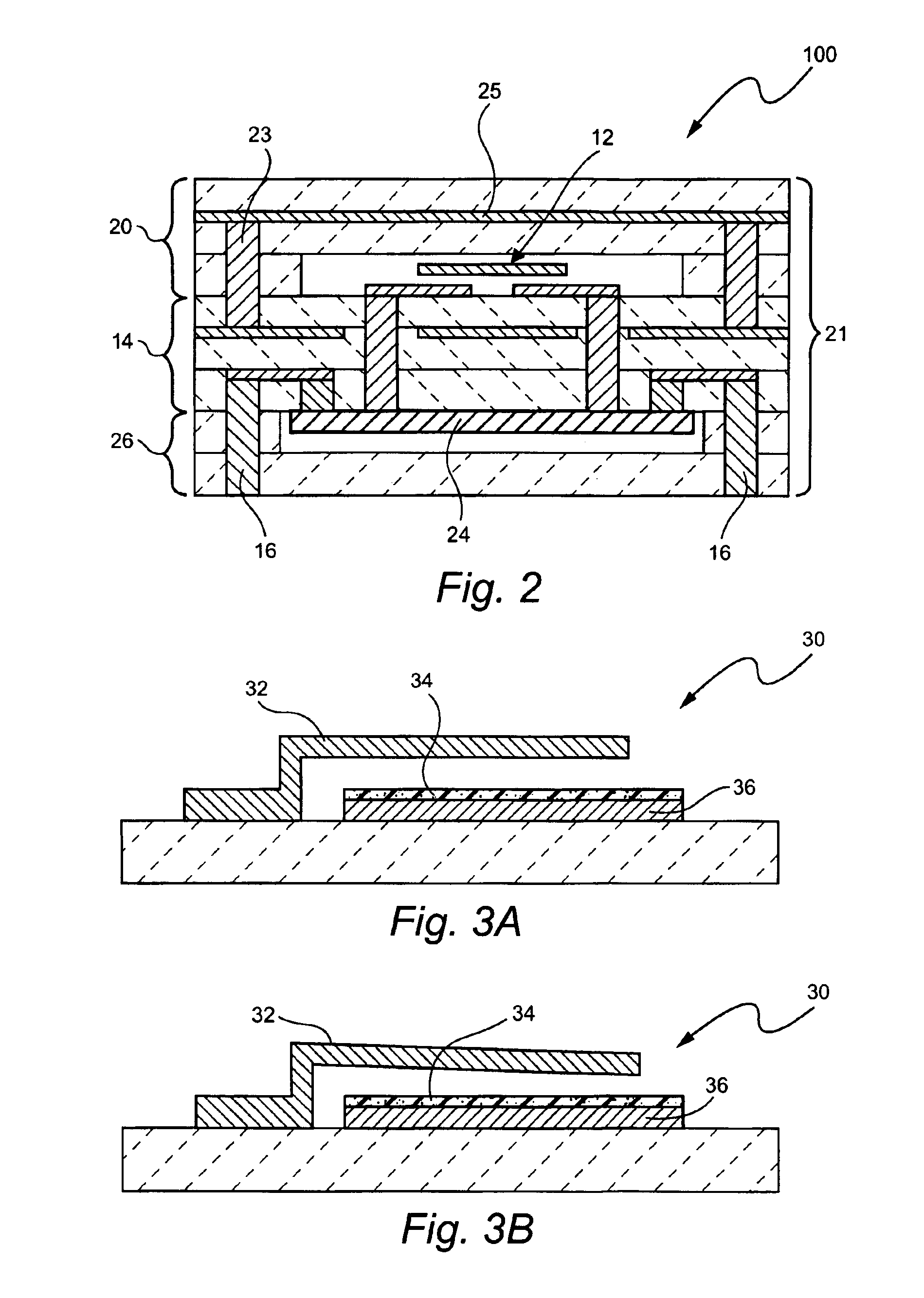
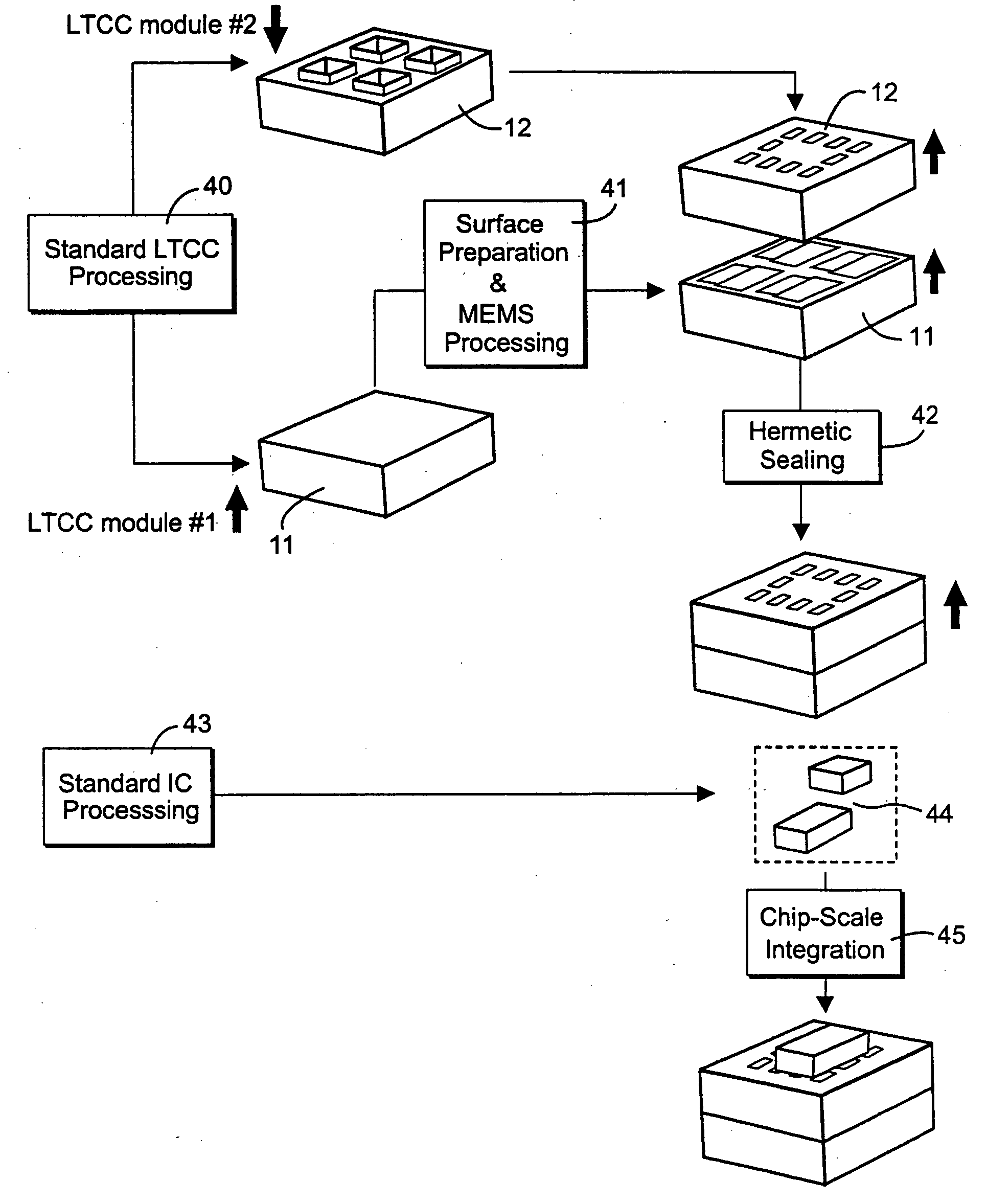
Method of fabricating radio frequency microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) devices on low-temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) substrates
InactiveUS20050161753A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricRadio frequency microelectromechanical system
A phased-array antenna system and other types of radio frequency (RF) devices and systems using microelectromechanical switches (“MEMS”) and low-temperature co-fired ceramic (“LTCC”) technology and a method of fabricating such phased-array antenna system and other types of radio frequency (RF) devices are disclosed. Each antenna or other type of device includes at least two multilayer ceramic modules and a MEMS device fabricated on one of the modules. Once fabrication of the MEMS device is completed, the two ceramic modules are bonded together, hermetically sealing the MEMS device, as well as allowing electrical connections between all device layers. The bottom ceramic module has also cavities at the backside for mounting integrated circuits. The internal layers are formed using conducting, resistive and high-k dielectric pastes available in standard LTCC fabrication and low-loss dielectric LTCC tape materials.
Owner:FOR NAT RES INITIATIVES
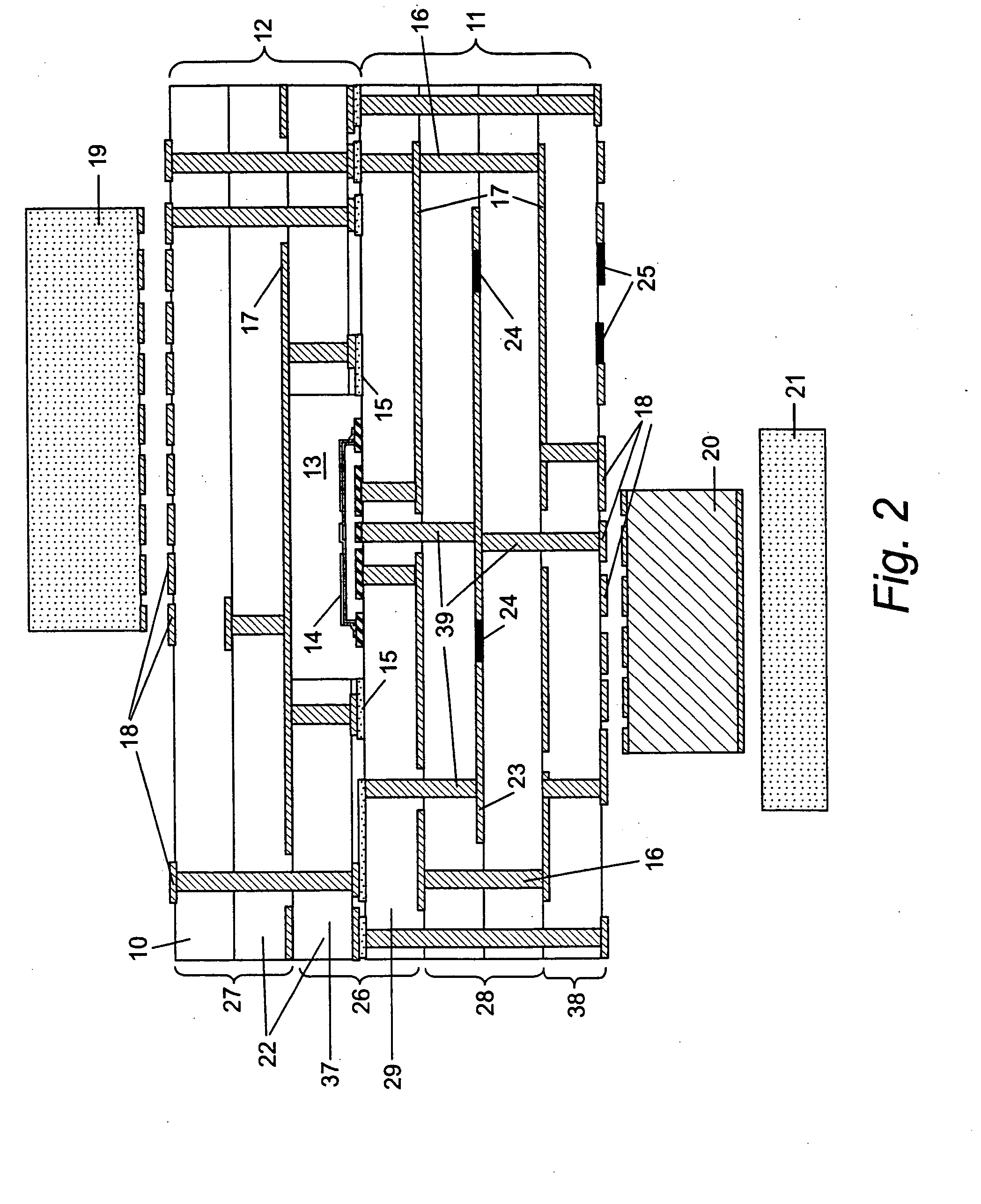
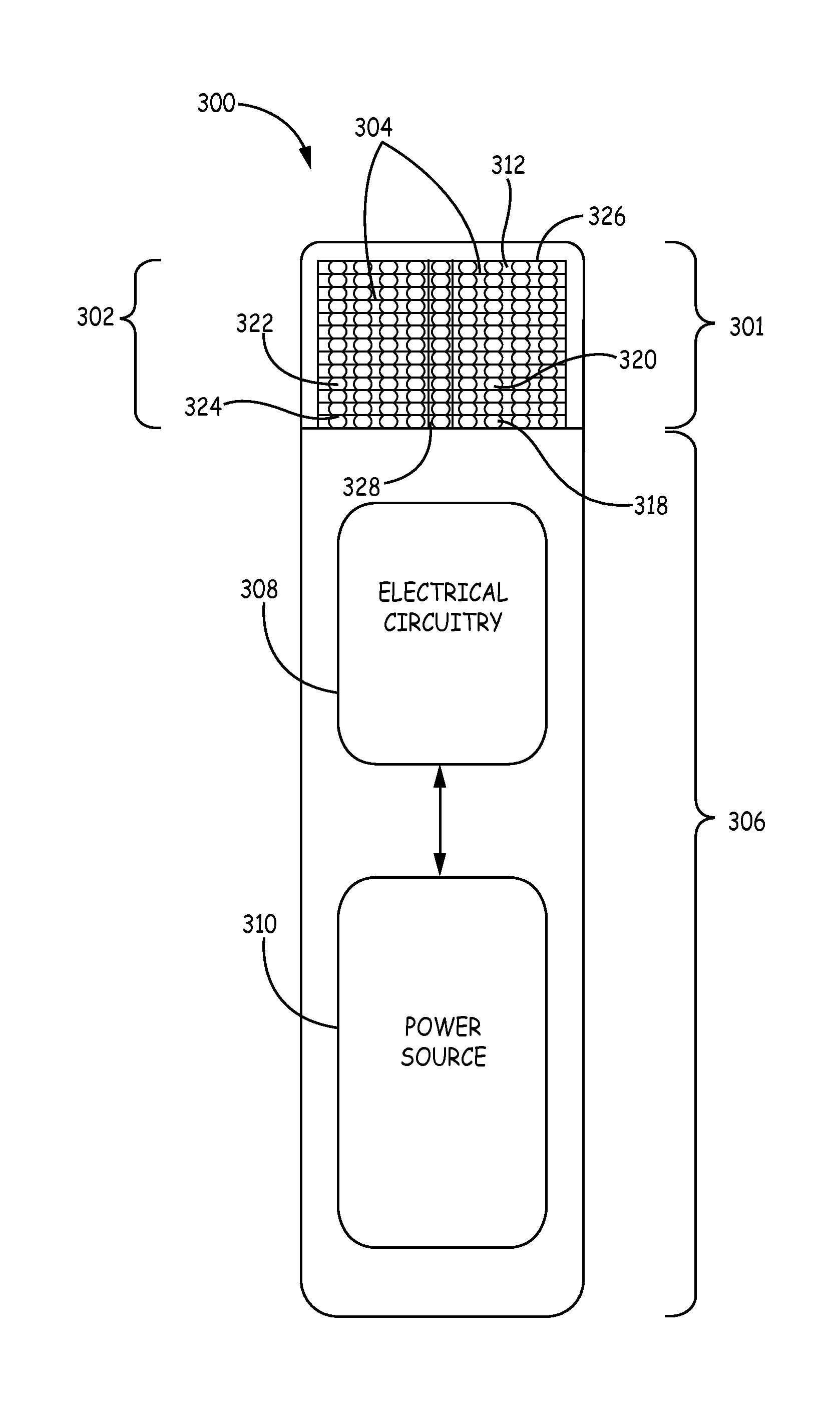
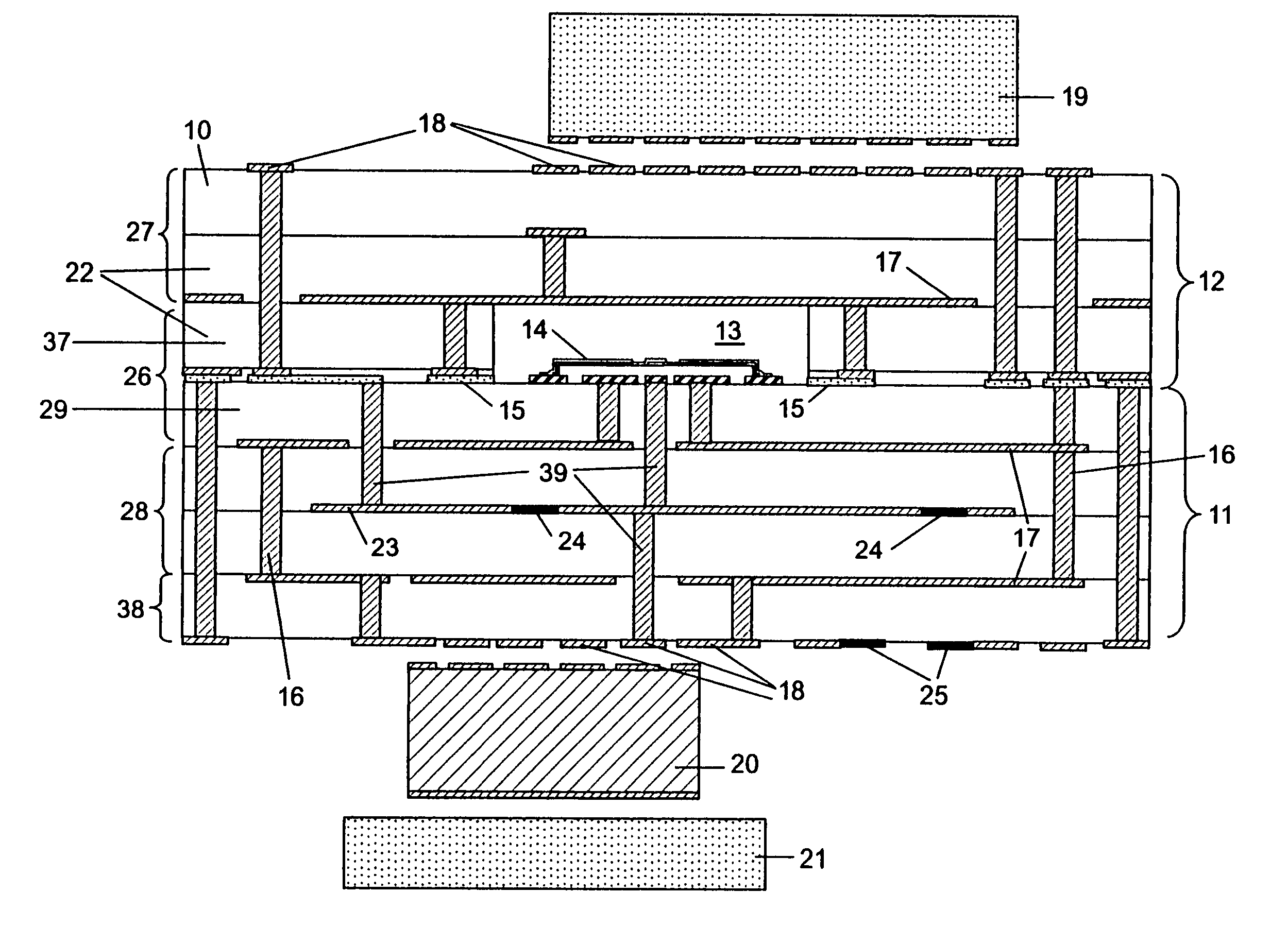
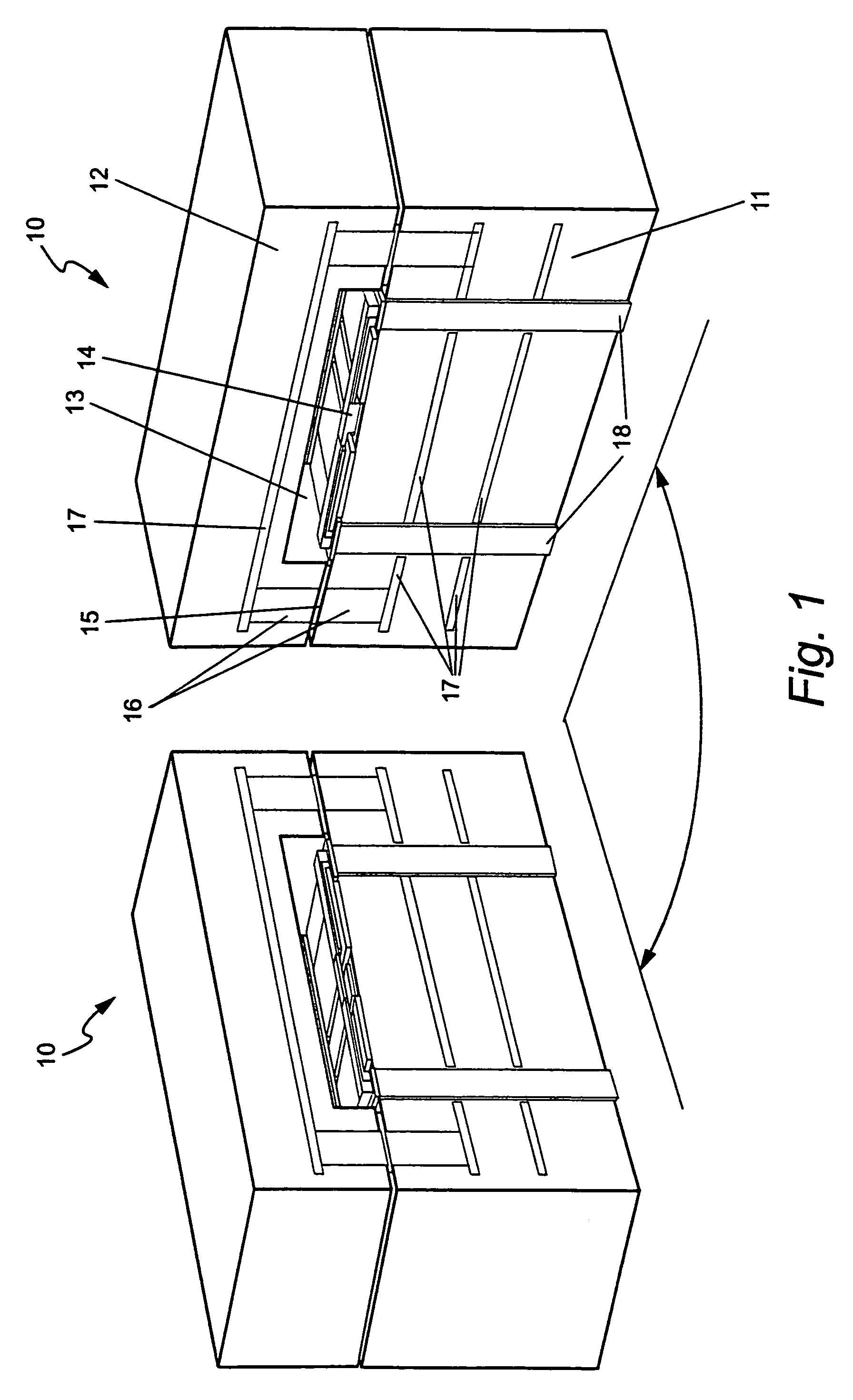
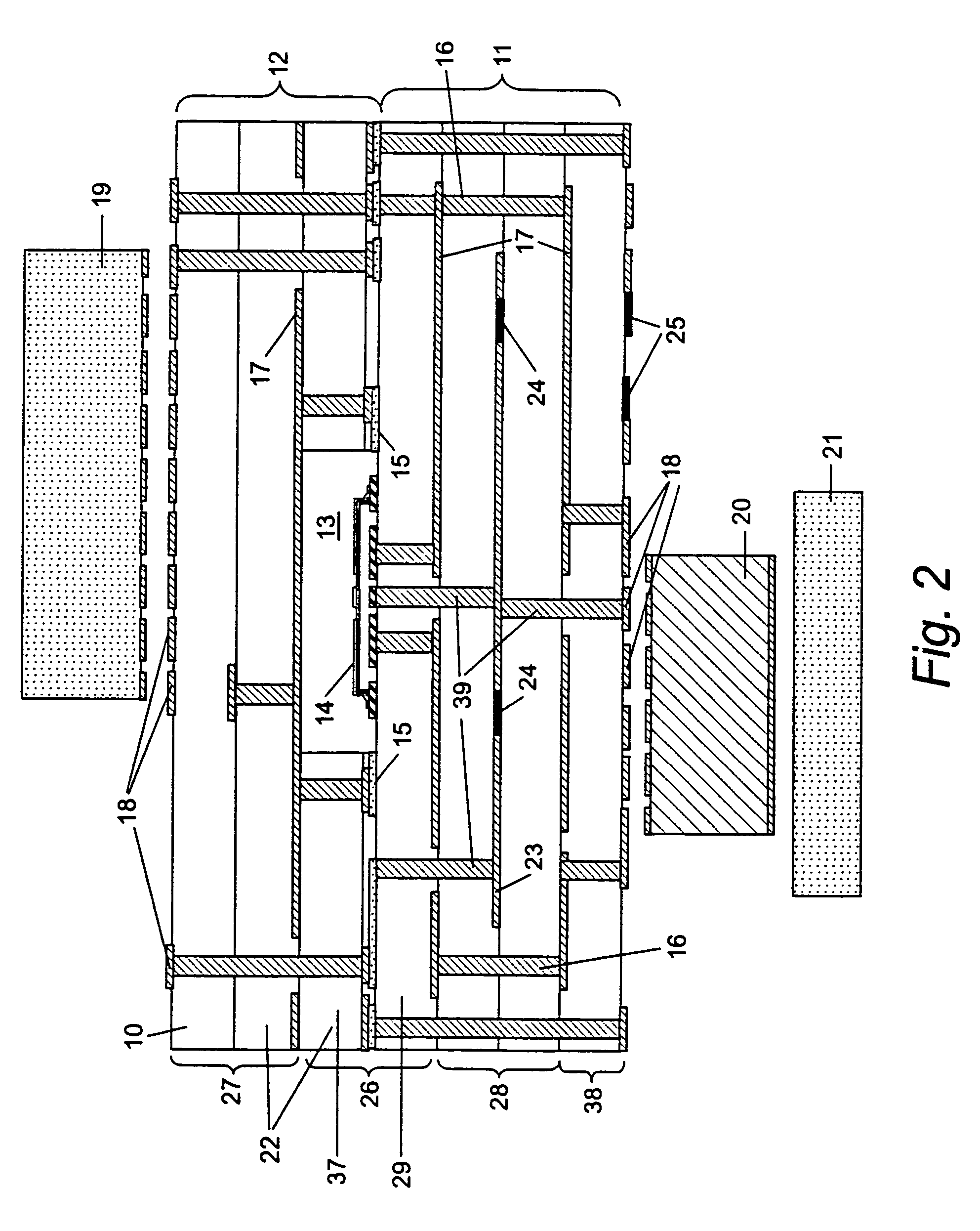
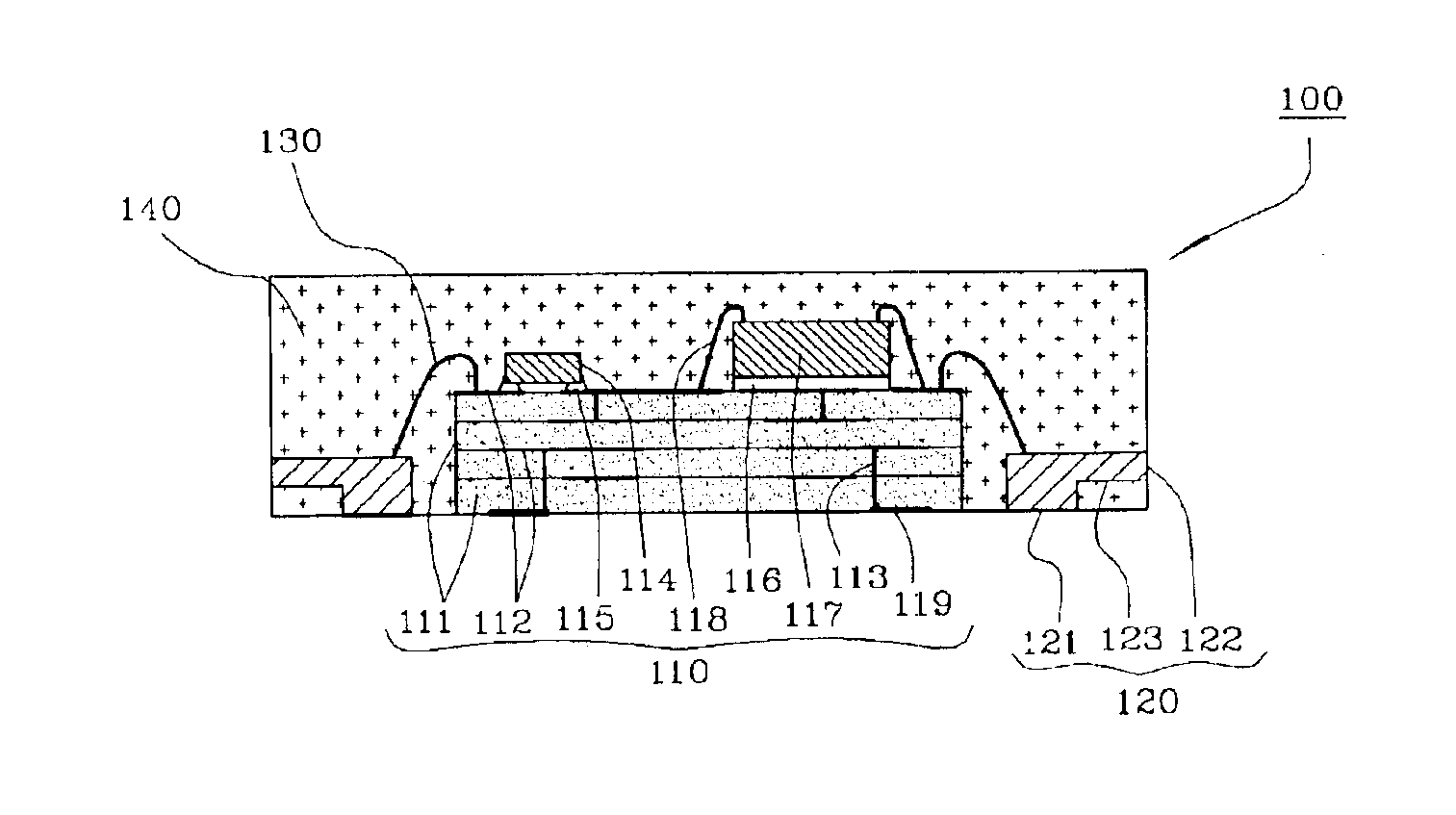
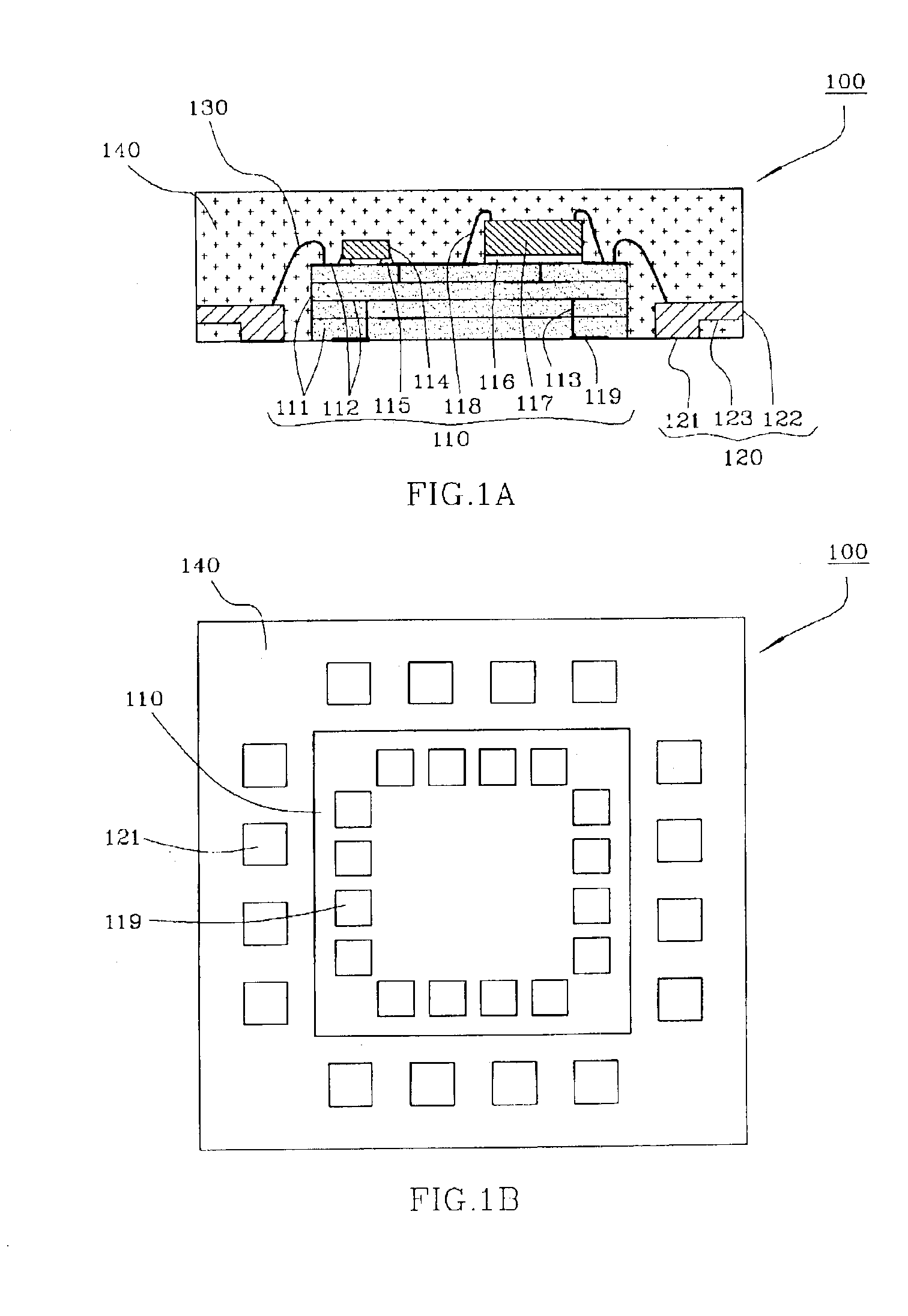
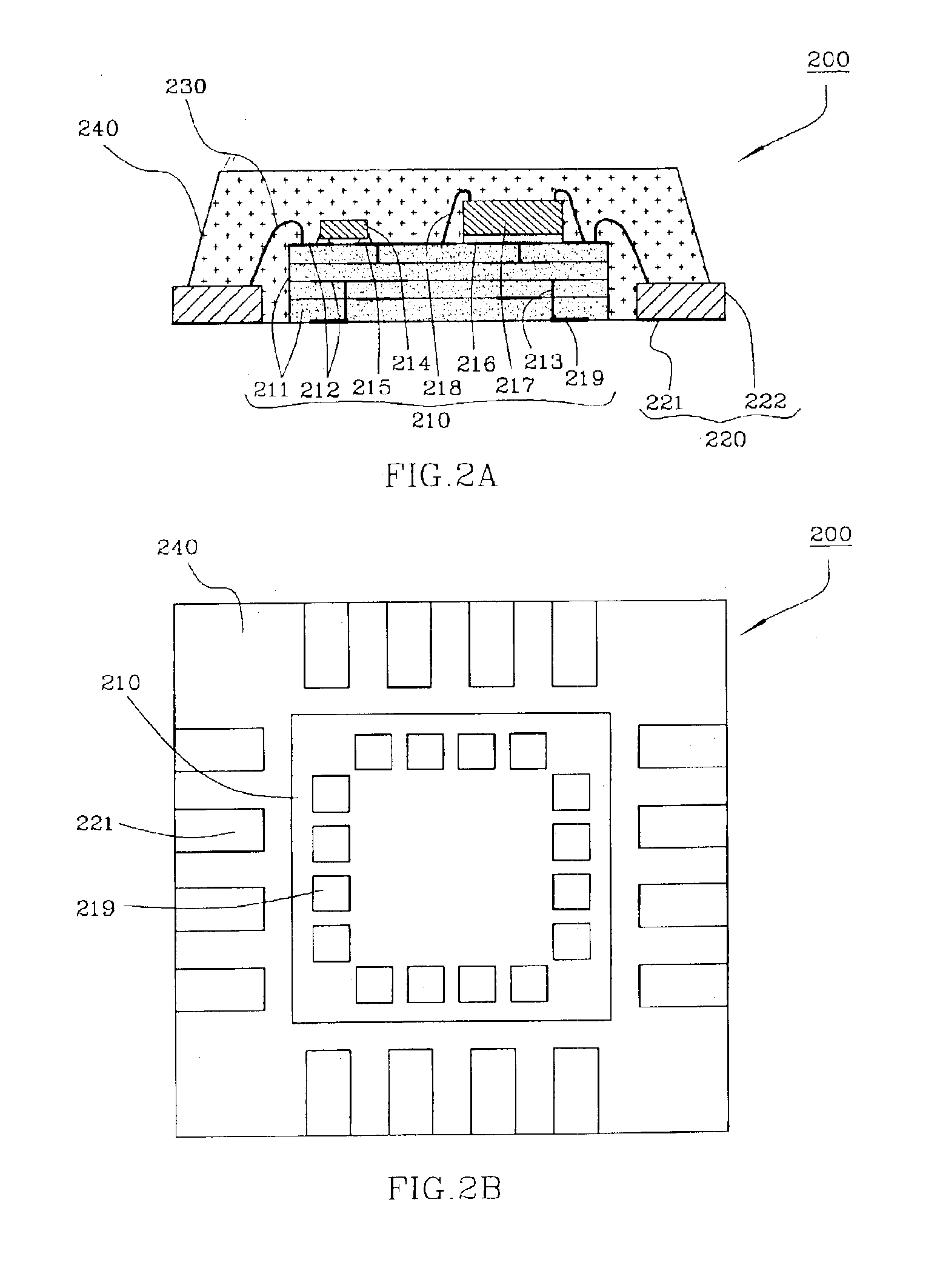
Implantable medical devices having cofire ceramic modules and methods of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20150214604A1Facilitate telemetrySmall sizeLine/current collector detailsElectrotherapyComputer moduleConductive materials
An implantable medical device (IMD) and methods of fabricating the same are provided. An IMD can include a housing and a cofire ceramic module (CCM) coupled to the housing. The CCM can include an antenna cofire-integrated in the CCM. The antenna can include a plate composed of conductive material, and conductive antenna elements that are annular substrates having perimeters substantially coextensive with the perimeter of the plate. The antenna can also include interconnections. A first set of interconnections can be coupled between the plate and one of the conductive antenna elements, and a second set of interconnections can be coupled between the conductive antenna elements. The antenna can also include a feed line conductively coupled to the plate. In some embodiments, the feed line can be substantially serpentine-shaped to adjust impedance in the CCM.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method of fabricating radio frequency microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) devices on low-temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) substrates
InactiveUS20050167047A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricRadio frequency microelectromechanical system
A phased-array antenna system and other types of radio frequency (RF) devices and systems using microelectromechanical switches (“MEMS”) and low-temperature co-fired ceramic (“LTCC”) technology and a method of fabricating such phased-array antenna system and other types of radio frequency (RF) devices are disclosed. Each antenna or other type of device includes at least two multilayer ceramic modules and a MEMS device fabricated on one of the modules. Once fabrication of the MEMS device is completed, the two ceramic modules are bonded together, hermetically sealing the MEMS device, as well as allowing electrical connections between all device layers. The bottom ceramic module has also cavities at the backside for mounting integrated circuits. The internal layers are formed using conducting, resistive and high-k dielectric pastes available in standard LTCC fabrication and low-loss dielectric LTCC tape materials.
Owner:FOR NAT RES INITIATIVES
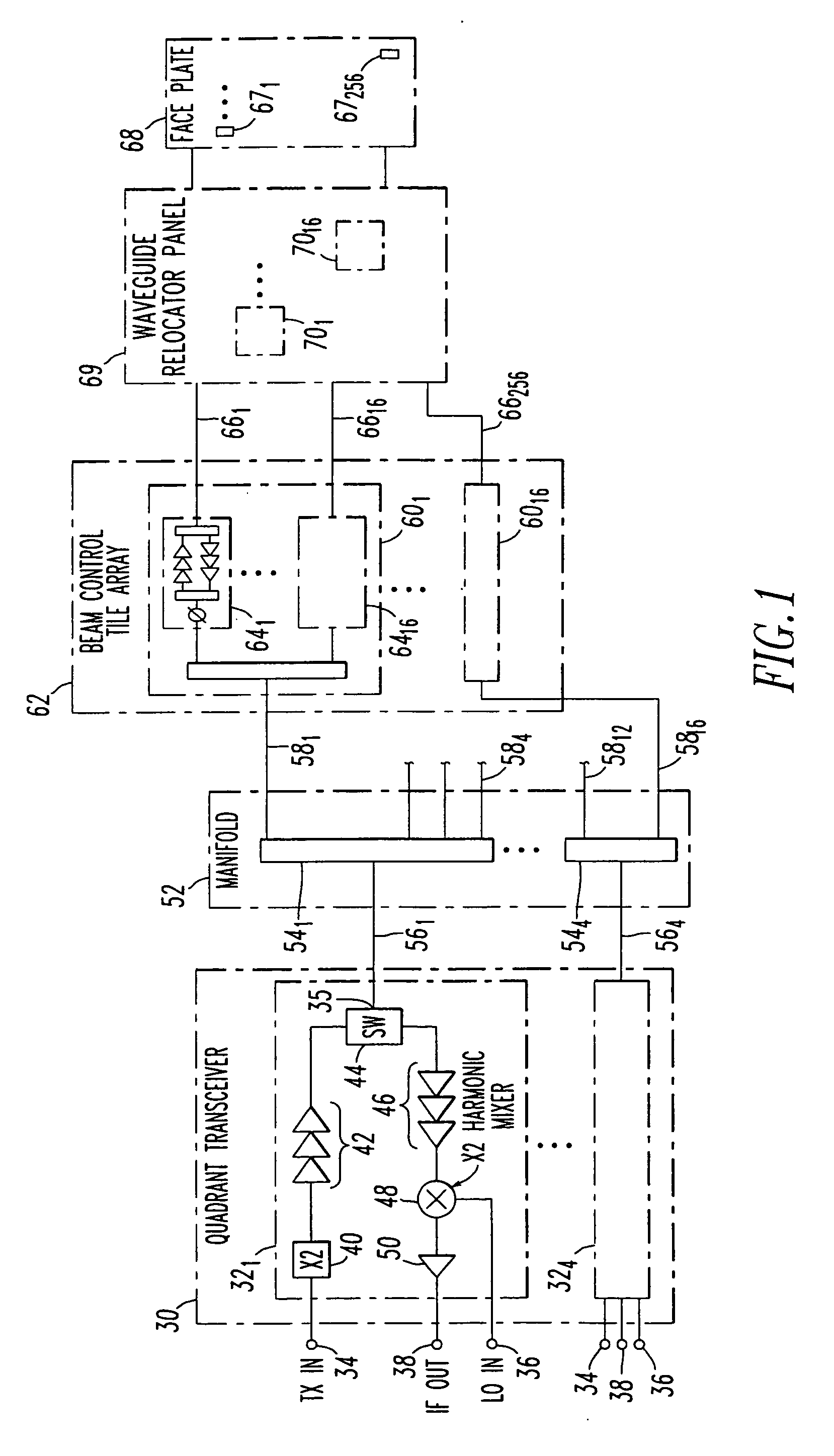
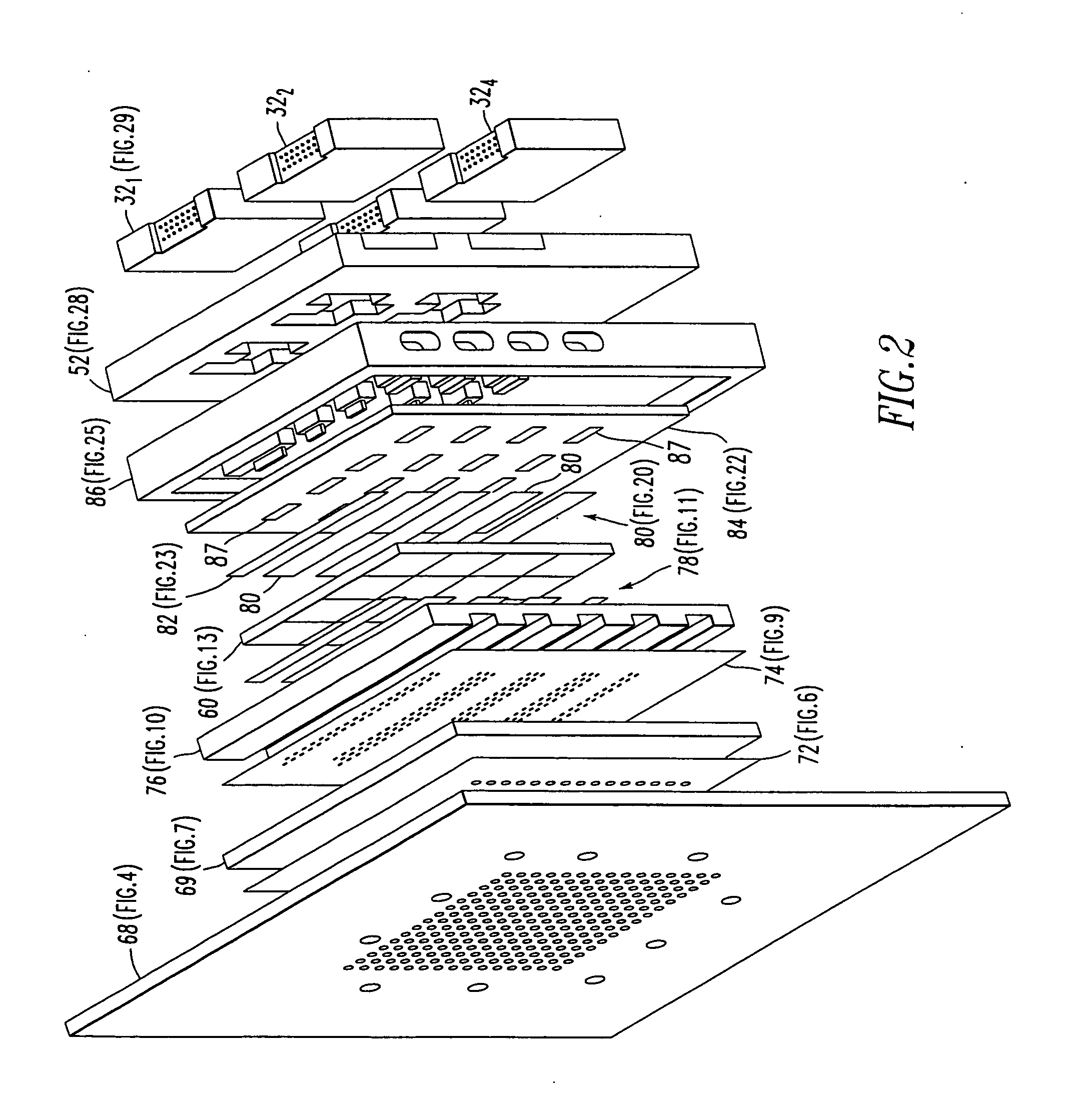
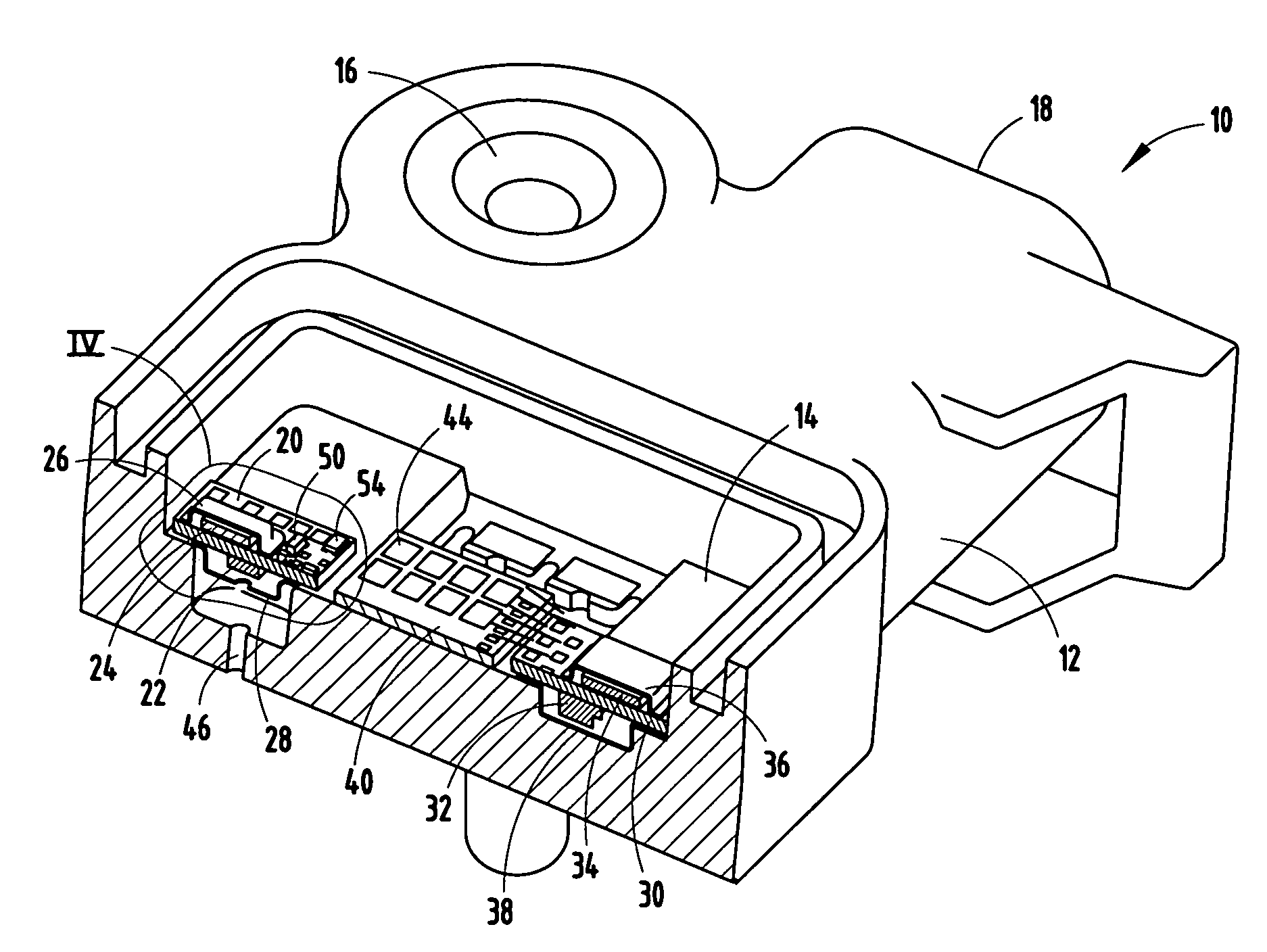
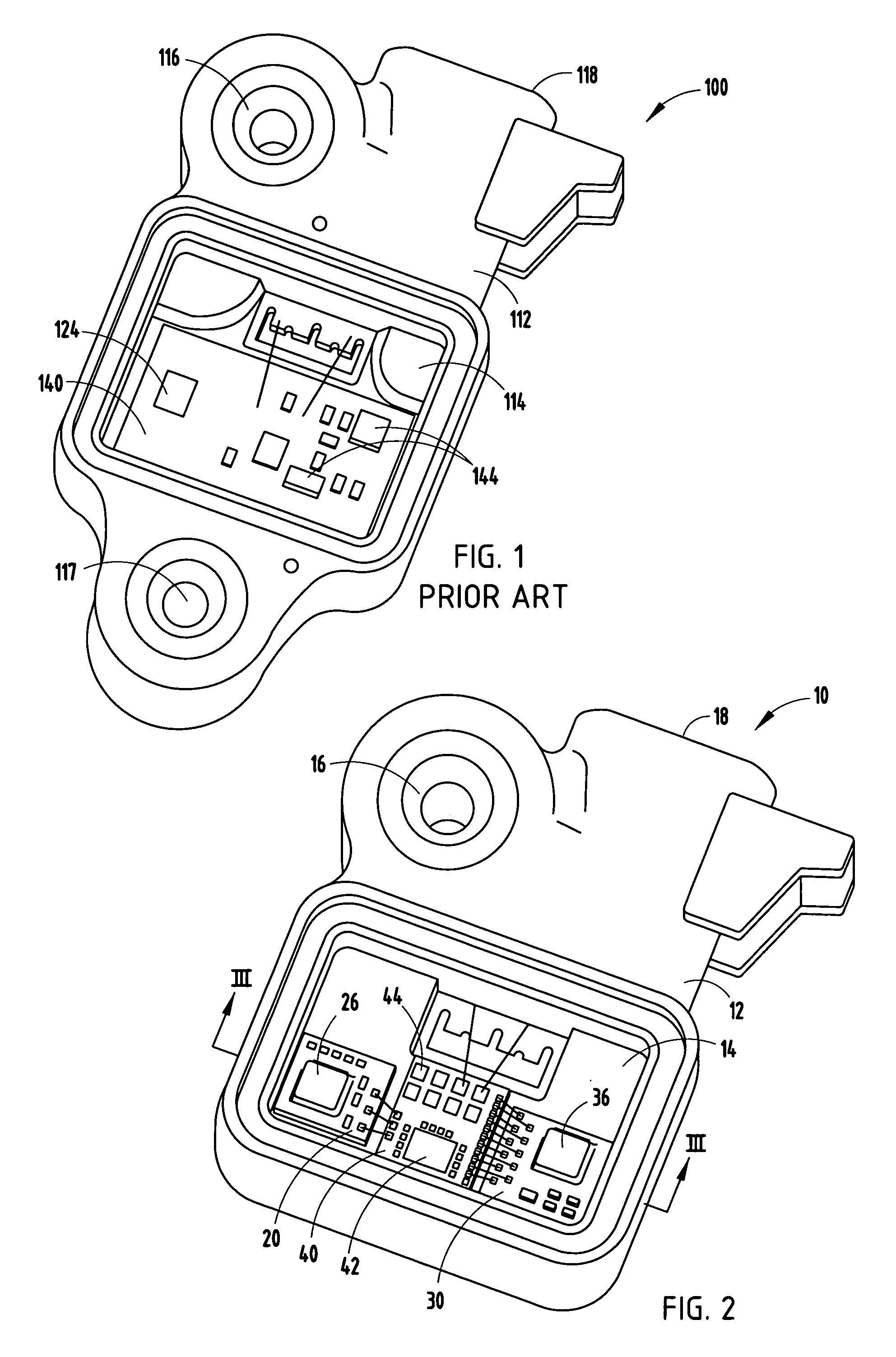
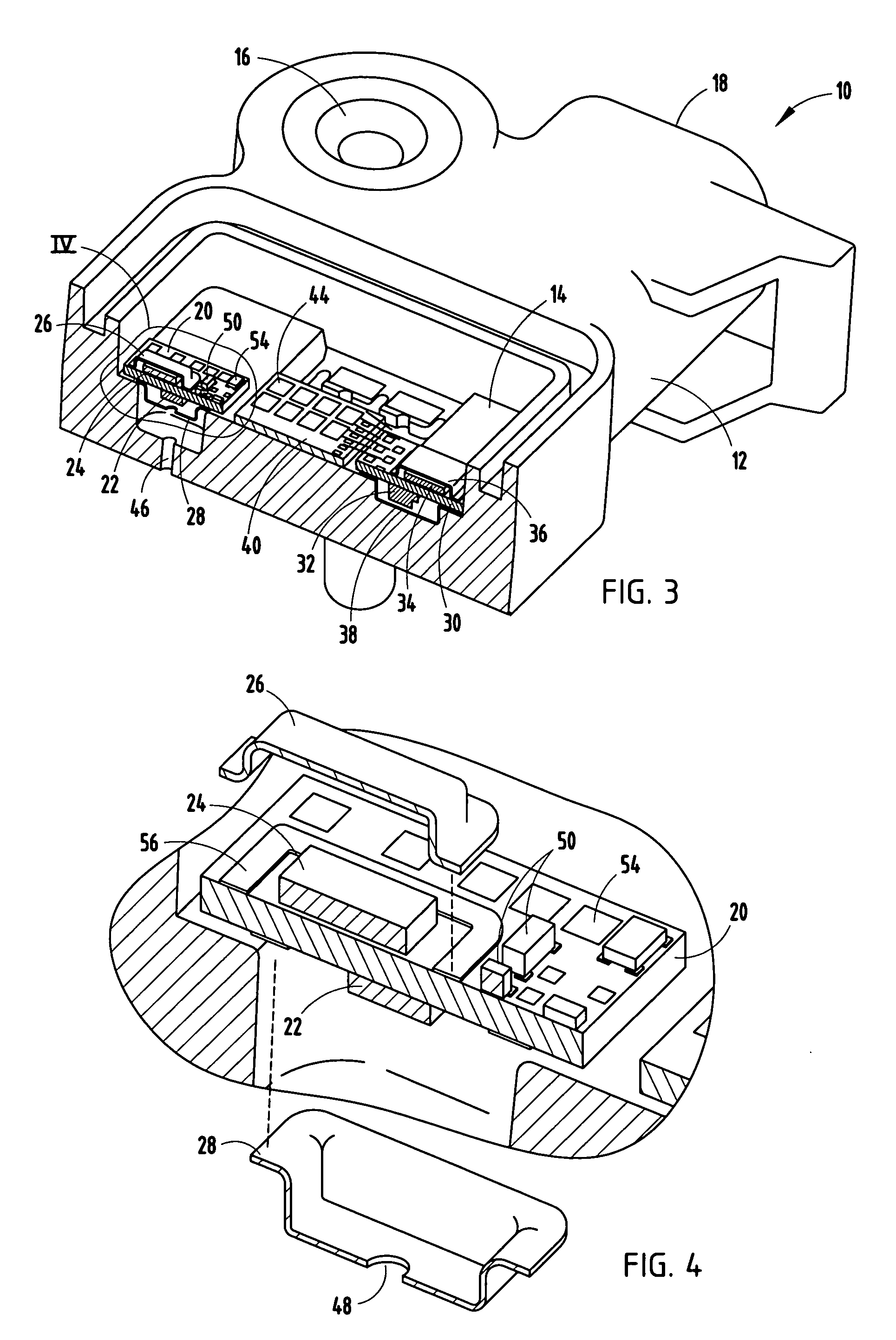
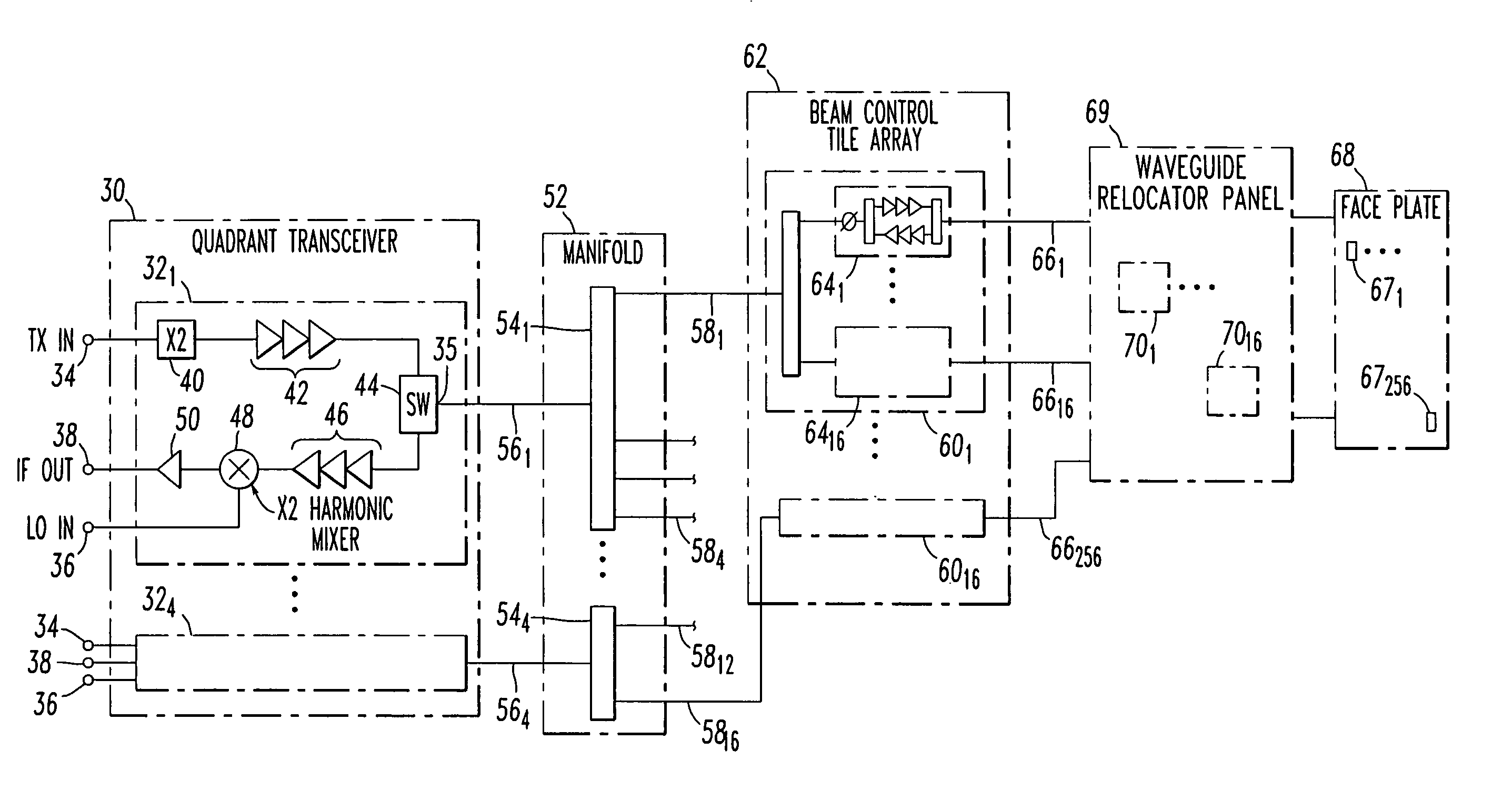
Low profile active electronically scanned antenna (AESA) for ka-band radar systems
InactiveUS20050146479A1Space is requiredPrevent RF leakageRadiating element housingsAntenna arrays manufactureTransceiverRadar systems
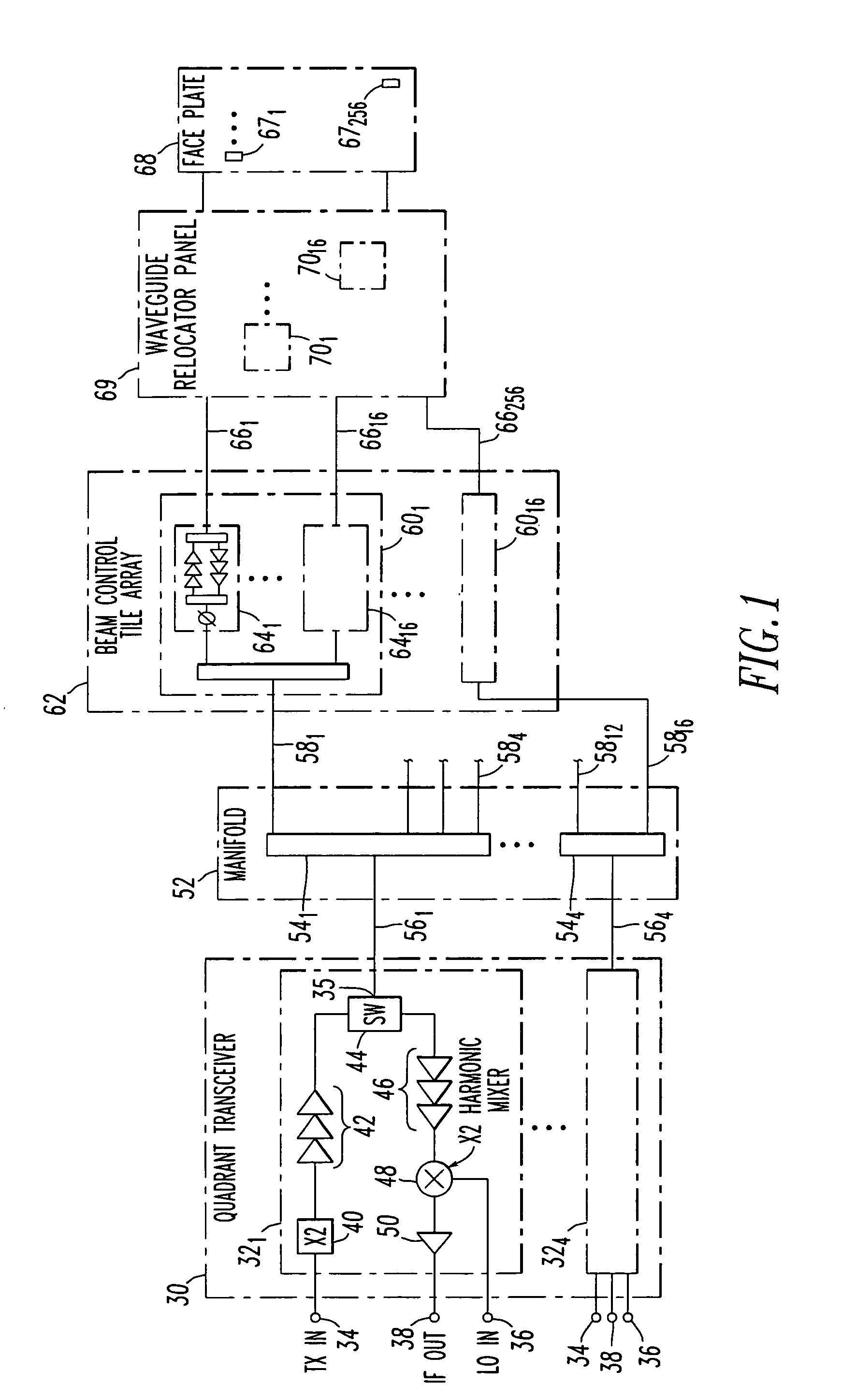
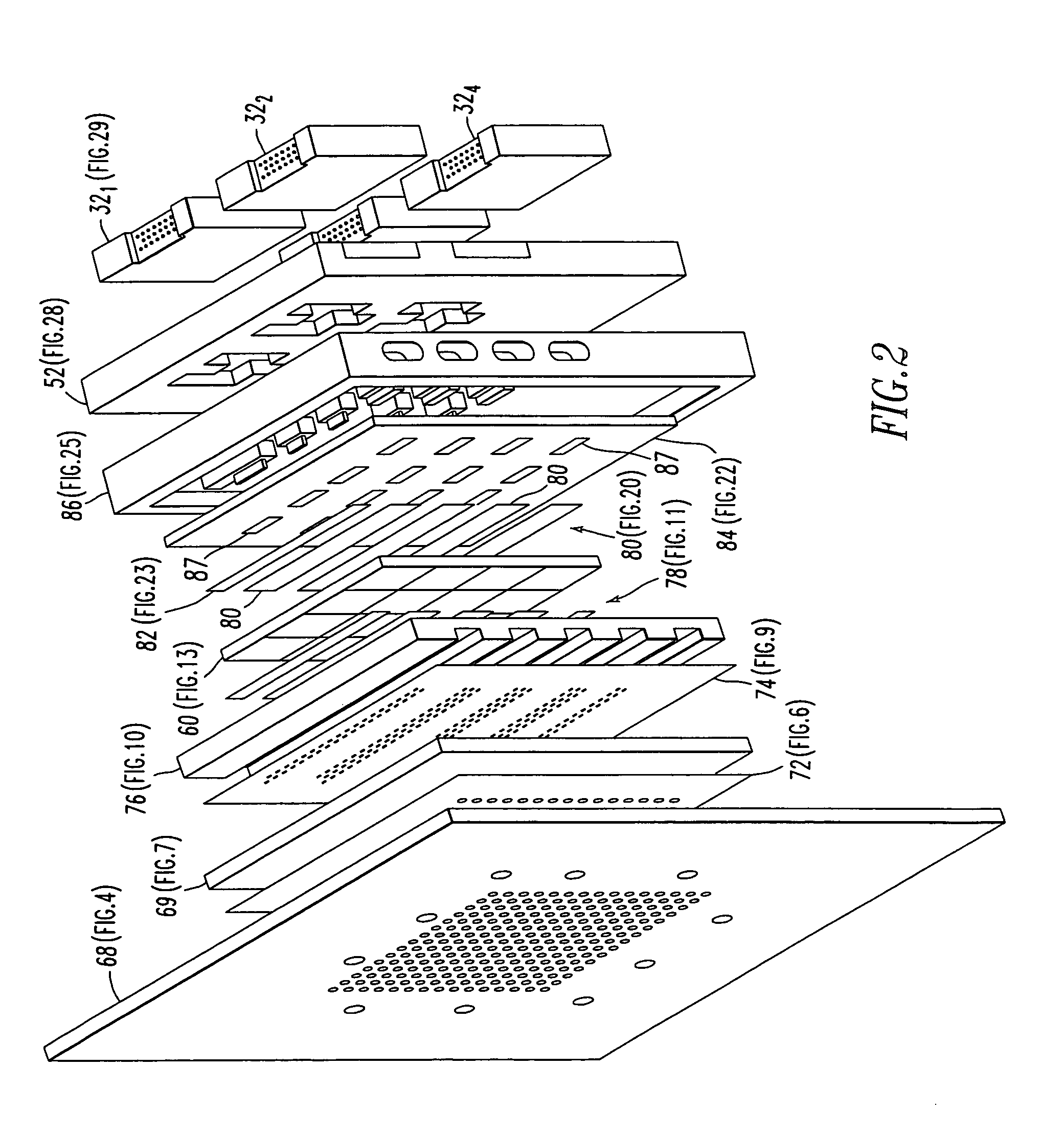
A vertically integrated Ka-band active electronically scanned antenna including, among other things, a transitioning RF waveguide relocator panel located behind a radiator faceplate and an array of beam control tiles respectively coupled to one of a plurality of transceiver modules via an RF manifold. Each of the beam control tiles includes a respective plurality of high power transmit / receive (T / R) cells as well as dielectric waveguides, RF stripline and coaxial transmission line elements. The waveguide relocator panel is preferably fabricated by a diffusion bonded copper laminate stack up with dielectric filling. The beam control tiles are preferably fabricated by the use of multiple layers of low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) material laminated together. The waveguide relocator panel and the beam control tiles are designed to route RF signals to and from a respective transceiver module of four transceiver modules and a quadrature array of antenna radiators matched to free space formed in the faceplate. Planar type metal spring gaskets are provided between the interfacing layers so as to provide and ensure interconnection between mutually facing waveguide ports and to prevent RF leakage from around the perimeter of the waveguide ports. Cooling of the various components is achieved by a pair of planar forced air heat sink members which are located on either side of the array of beam control tiles. DC power and control of the T / R cells is provided by a printed circuit wiring board assembly located adjacent to the array of beam controlled tiles with solderless DC connections being provided by an arrangement of “fuzz button” electrical connector elements.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Low Temperature Co-Fired Ceramic (LTCC) Tape Compositions, Light-Emitting Diode (LED) Modules, Lighting Devices and Methods of Forming Thereof
The present invention provides LTCC (low temperature co-fired ceramic) tape compositions and demonstrates the use of said LTCC tape(s) in the formation of Light-Emitting Diode (LED) chip carriers and modules for various lighting applications. The present invention also provides for the use of (LTCC) tape and LED modules in the formation of lighting devices including, but not limited to, LED devices, High Brightness (HB) LED backlights, display-related light sources, automotive lighting, decorative lighting, signage and advertisement lighting, and information display lighting.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
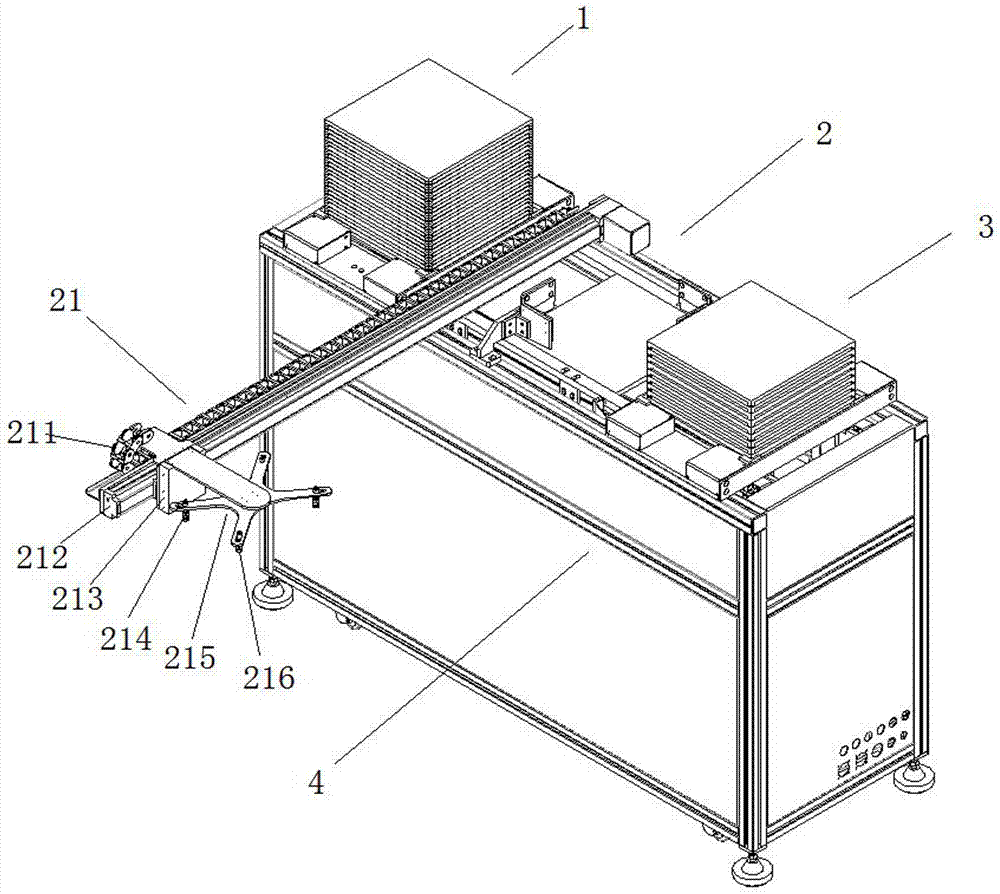
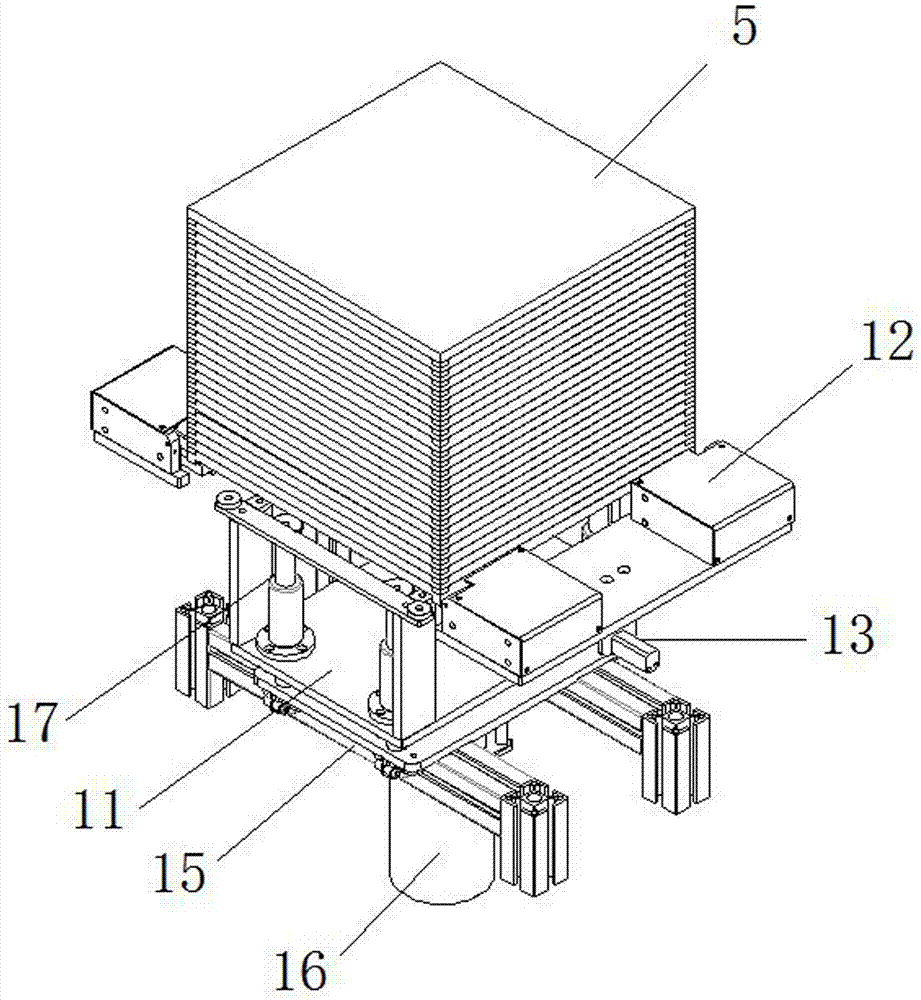
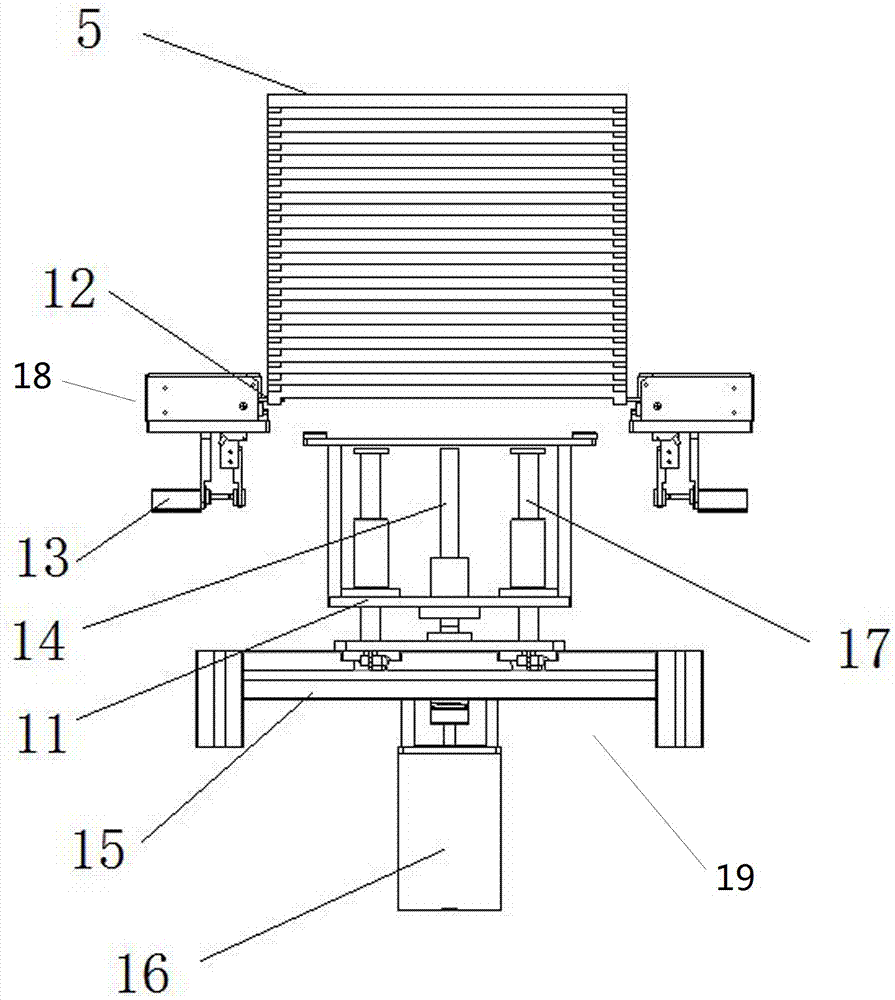
Universal type automatic loading and unloading system of bottom tool separation method based on conveyor belt
ActiveCN105438841AShort run pathImprove transport efficiencyConveyorsStacking articlesEngineeringCo-fired ceramic
The invention discloses a universal type automatic loading and unloading system of a bottom tool separation method based on a conveyor belt, and relates to the technical field of loading and unloading devices and high temperature co-fired ceramic processing devices. The universal type automatic loading and unloading system comprises a bottom tray separation mechanism, a locating and material taking mechanism, a tray bottom collection mechanism, trays, a sensor and a controller which are sequentially arranged on a rack, wherein the bottom tray separation mechanism comprises a three-station jacking device and a tray clamping device; the locating and material taking mechanism comprises a double-station jacking and locating device and a loading and unloading mechanical hand; the tray bottom collection mechanism comprises a double-station jacking and clamping device; and the bottom tray separation mechanism, the locating and material taking mechanism, the tray bottom collection mechanism and the sensor are connected with the controller. Through the adoption of the system, the continuity of the processing process and flexibility of loading and unloading can be improved, the loading and unloading system is a modularized standard single machine and can be matched with processing devices of products and raw ceramics of various types, the integration level is high, the loading and unloading location accuracy is high, the takt is compact, and the universality is high.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
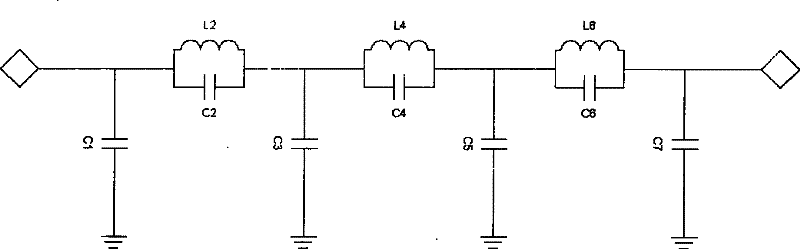
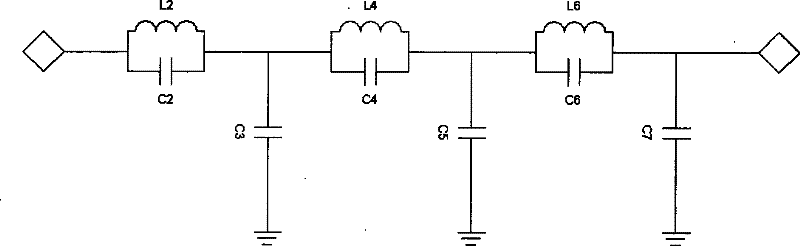
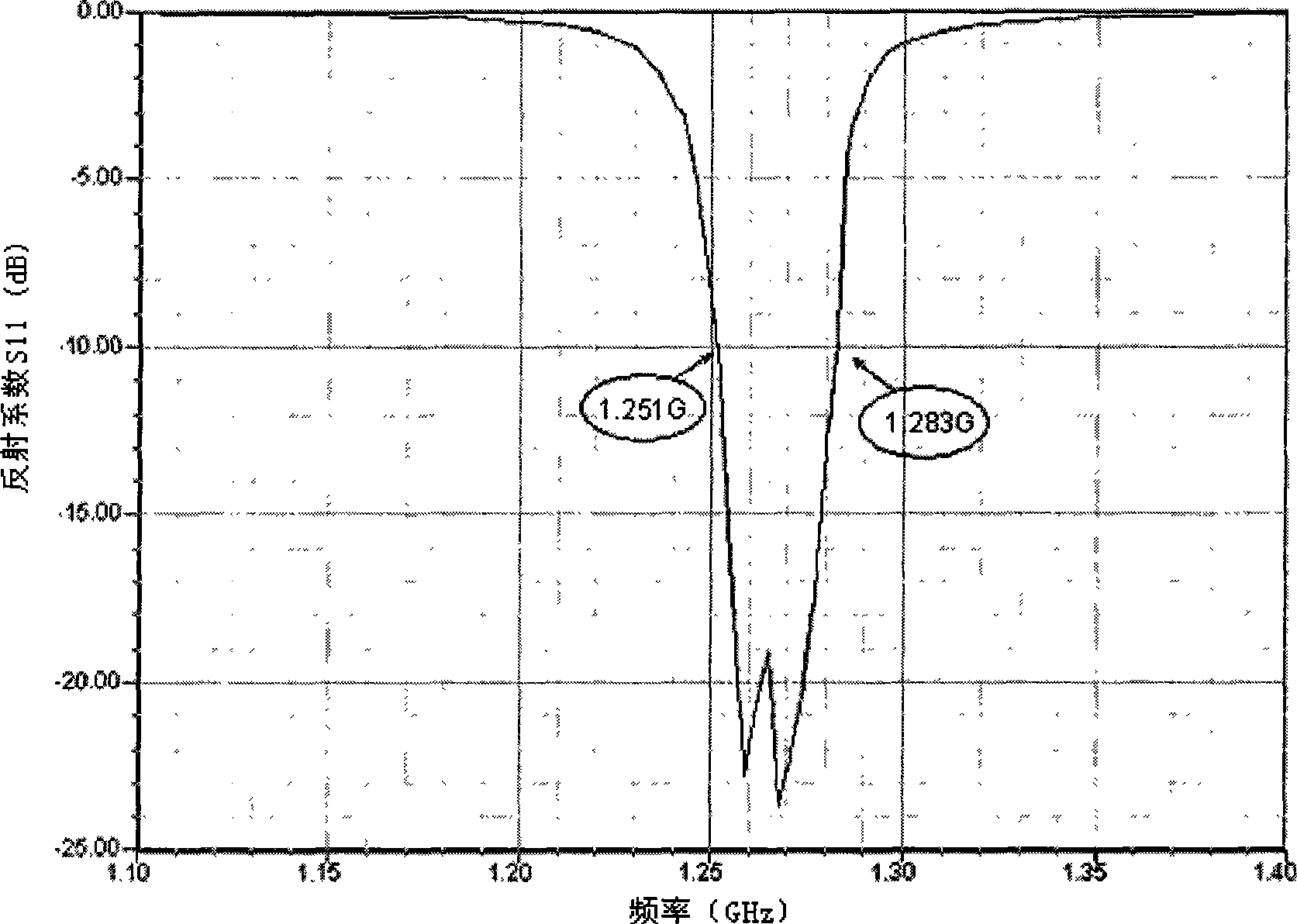
LTCC (Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramic) lowpass filter
InactiveCN102354777ASmall sizeLow insertion lossMultiple-port networksWaveguide type devicesLow-pass filterHarmonic
The invention discloses an LTCC (Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramic) lowpass filter which comprises an input end and an output end, wherein the input end is connected with input ends of the first pair of LC parallel harmonic oscillators (L2, C2), output ends of the first pair of LC parallel harmonic oscillators are connected with input ends of the second pair of LC parallel harmonic oscillators (L4, C4), output ends of the second pair of LC parallel harmonic oscillators are connected with input ends of the third pair of LC parallel harmonic oscillators (L6, C6), and output ends of the third pair of LC parallel harmonic oscillators are connected with the output end of the lowpass filter; parallel grounding capacitors C3 are arranged between connecting points of the first pair of LC parallel harmonic oscillators and the second pair of LC parallel harmonic oscillators and ground, parallel grounding capacitors C5 are arranged between connecting points of the second pair of LC parallel harmonic oscillators and the third pair of LC parallel harmonic oscillators and the ground, and parallel grounding capacitors C7 are arranged between connecting points of the third pair of LC parallel harmonic oscillators and the ground. The filter adopts a standard encapsulation structure, has the advantages of small volume, low cost, good frequency selecting property, good temperature stability and the like and is favorable to massive production.
Owner:西安瓷芯光电科技有限公司
Low-temperature sintering Ti-base microwave medium ceramic material and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101186496ALower sintering temperatureHigh dielectric constantCeramicsMicrowaveDielectric loss
The invention discloses a Ti-based microwave medium ceramics material by low-temperature sintering. The Ti-based microwave medium ceramics material takes rutile TiO2 as a main phase. The general formula of the prescription of the invention is that: (AxM2x)(NyTi1-y)1-3xO2, (BxM3x)(NyTi1-y)1-4xO2, (CxMx)(NyTi1-y)1-2xO2 or (1-m) TiO2-mBi2Ti4O11, wherein, the A is one of bivalent ions such as Zn<2+>, Cu<2+>, Ni<2+>, the B one of univalent ions such as Li<+>, the C one of trivalent ions such as Al<3+>, Fe<3+>, M is one of pentavalent ions such as Nb<5+>, Ta<5+>, Sb<5+>, N one of quadrivalent ions such as Zr< 4+ >, Sn< 4+ >, Mn< 4+ >; the X is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.25, the Y more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.5, the m more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.15, the n is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 2. The microwave medium ceramics material by low-temperature sintering has the advantages of high dielectric constant, low dielectric loss, wide covering range of temperature coefficient of resonant frequency, low sintering temperature, simple preparation technique and adjustable temperature coefficient of resonant frequency according to materials. The invention can be used for Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramics System (LTCC system) and used for producing microwave devices such as multi-media resonators, filters, etc.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
LED light sources for image projection systems
ActiveUS20050174544A1High temperature operationLighting heating/cooling arrangementsLighting elementsDisplay deviceElectrical connection
In accordance with the invention a light source for an image projection system comprises one or more LEDs packaged for high temperature operation. Advantageously, the LED die are disposed on a package comprising a ceramic coated metal base including one or more underlying thermal connection pads, and underlying electrical connection pads, each LED die thermally coupled through the metal base to a thermal connection pad and electrically coupled to electrical connection pads. The LED can be mounted directly on the metal of the base or on a thin coating of electrical insulator on the metal. Arrays of LED die thus packaged are advantageously fabricated by the low temperature co-fired ceramic-on-metal technique (LTTC-M) and can be referred to as LTTC-M packaged arrays. The LEDs are advantageously mounted in an array of cavities having tapered sides to reflect light from the LEDs. The high temperature LED light sources can substitute for HID lamps in a variety of front and rear projection systems and displays. They are particularly useful for rear projection systems.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP
LTCC lamination microstrip patch antenna
InactiveCN101510630AHigh bandwidthImprove stabilityRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaRadio reception
The invention discloses an LTCC-stacked microstrip patch antenna, pertains to the antenna technical field and relates to the LTCC (low temperature co-fired ceramic) technology, in particular to a low profile microstrip patch antenna applied to receiving radio. The microstrip patch antenna comprises three layers of LTCC substrates: the first layer of substrate is provided with a coaxial feeding hole, the upper surface thereof is a first radiation metal patch and the lower surface thereof is a reflection plate; the second layer of substrate is evenly provided with air holes; and the upper surface of the third layer of substrate is a second radiation metal patch. In addition, the microstrip patch antenna also comprises a coaxial feeding needle which is inserted into the coaxial feeding hole from the bottom to be connected with the first radiation metal patch on the first layer of substrate and be insulated with the reflection plate. The first, second and third layers of LTCC substrates form an integrity after passing through an LTCC stack and isostatic pressing technology from the bottom up and co-fire is carried out to the integrity at low temperature so as to form another integrity. The microstrip patch antenna can effectively widen the band width of a microstrip antenna, intensify the coupling between two radiation patches and improve the stability and reliability of the antenna.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
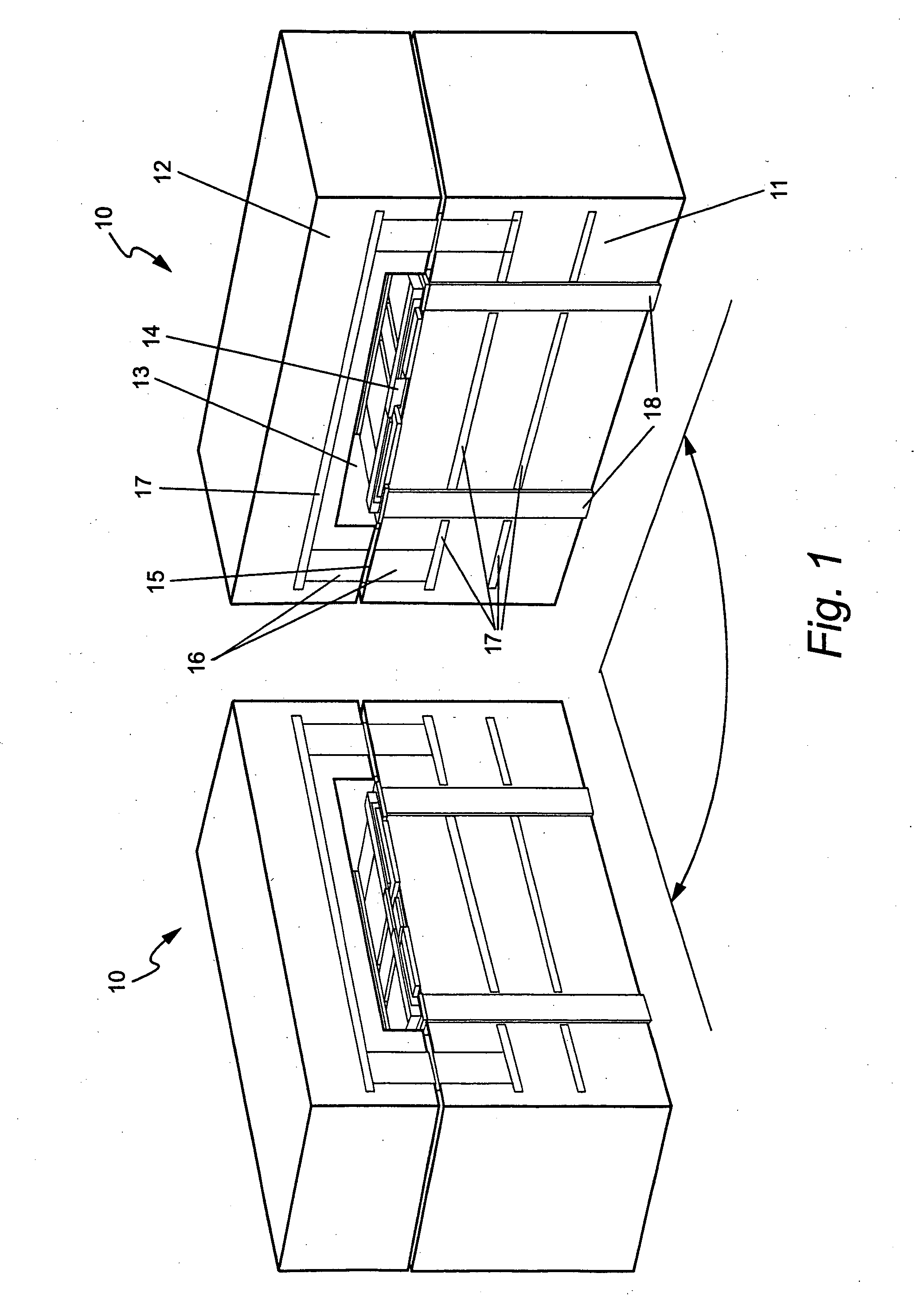
Phased array antenna using (MEMS) devices on low-temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) substrates
InactiveUS7012327B2Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricElectrical connection
Owner:FOR NAT RES INITIATIVES
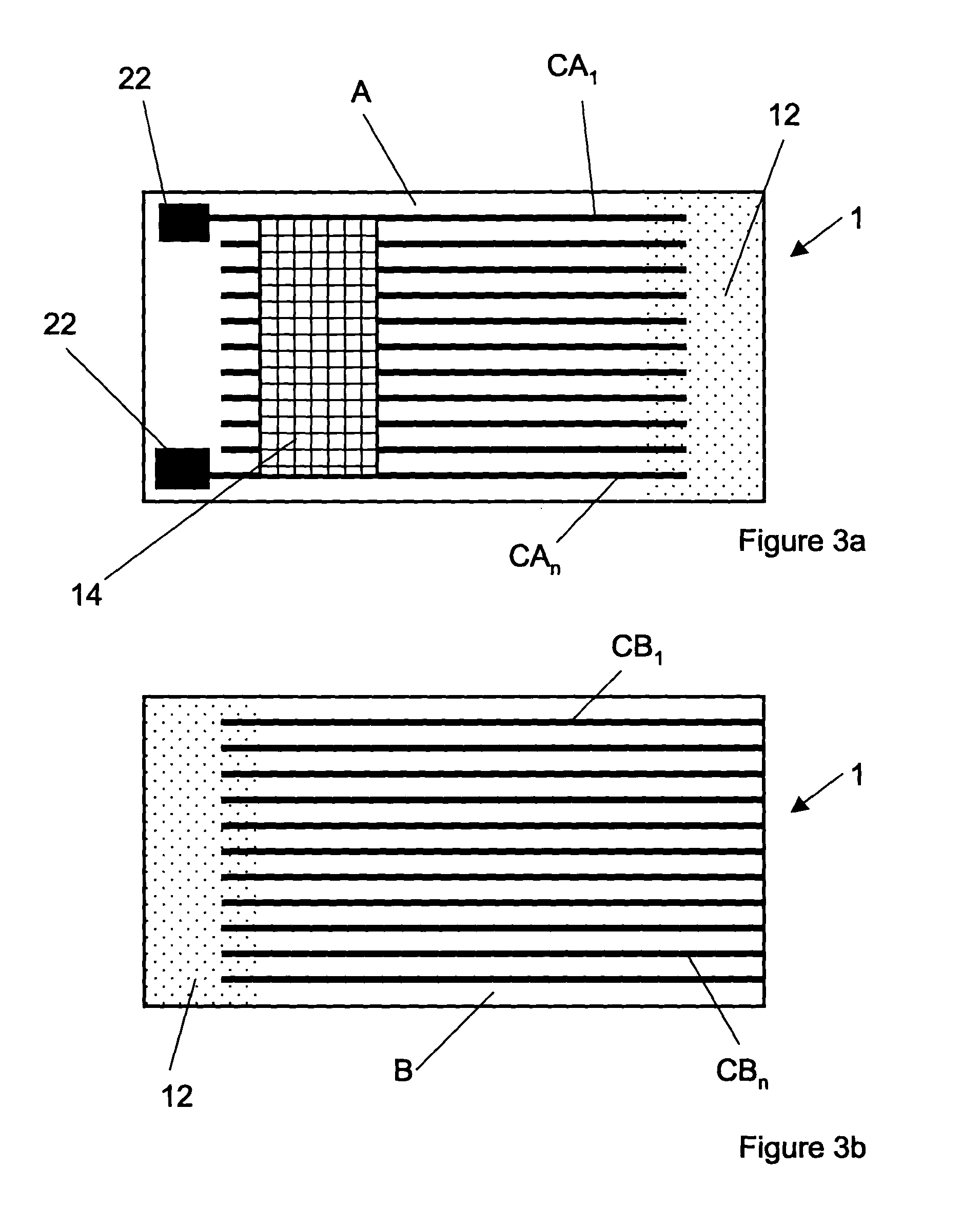
Sensor module
ActiveUS7331212B2Compact costAcceleration measurement using interia forcesMeasurement apparatus componentsSignal processing circuitsEngineering
A sensor module is provided having a compact housing containing a sensor. A low temperature co-fired ceramic substrate is located on the housing. The sensor and signal processing circuitry are located on the low temperature co-fired ceramic substrate. The sensor module further includes a metal shield substantially encapsulating the sensor.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Low profile active electronically scanned antenna (AESA) for Ka-band radar systems
InactiveUS6975267B2Space is requiredRadiating element housingsAntenna arrays manufactureTransceiverRadar systems
A vertically integrated Ka-band active electronically scanned antenna including, among other things, a transitioning RF waveguide relocator panel located behind a radiator faceplate and an array of beam control tiles respectively coupled to one of a plurality of transceiver modules via an RF manifold. Each of the beam control tiles includes a respective plurality of high power transmit / receive (T / R) cells as well as dielectric waveguides, RF stripline and coaxial transmission line elements. The waveguide relocator panel is preferably fabricated by a diffusion bonded copper laminate stack up with dielectric filling. The beam control tiles are preferably fabricated by the use of multiple layers of low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) material laminated together. The waveguide relocator panel and the beam control tiles are designed to route RF signals to and from a respective transceiver module of four transceiver modules and a quadrature array of antenna radiators matched to free space formed in the faceplate. Planar type metal spring gaskets are provided between the interfacing layers so as to provide and ensure interconnection between mutually facing waveguide ports and to prevent RF leakage from around the perimeter of the waveguide ports. Cooling of the various components is achieved by a pair of planar forced air heat sink members which are located on either side of the array of beam control tiles. DC power and control of the T / R cells is provided by a printed circuit wiring board assembly located adjacent to the array of beam controlled tiles with solderless DC connections being provided by an arrangement of “fuzz button” electrical connector elements.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
77GHz millimeter wave radio frequency device and using method thereof
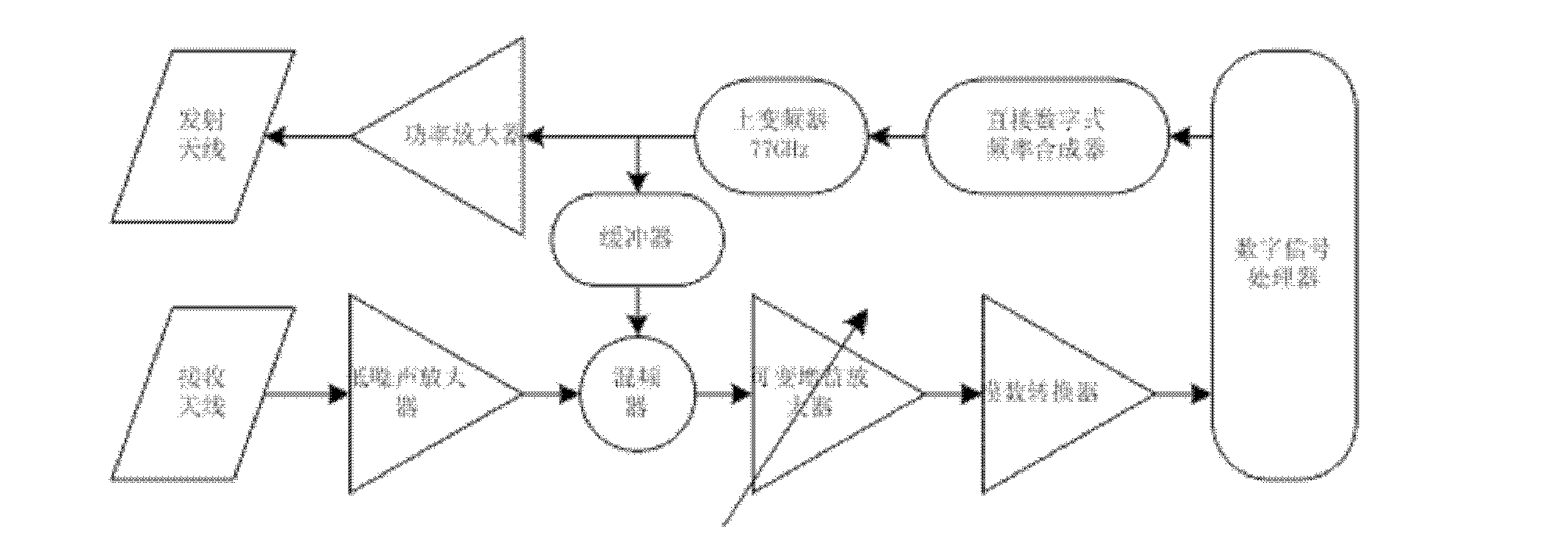
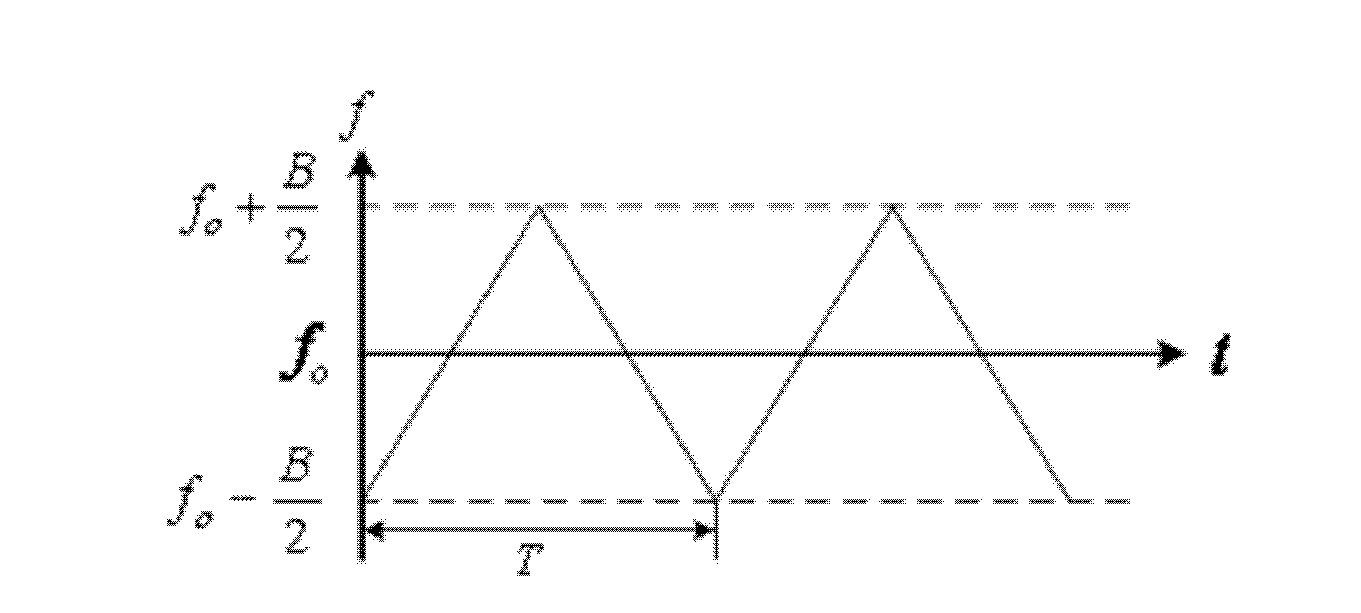
The invention provides a 77GHz millimeter wave radio frequency device and a using method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of millimeter wave radars. The 77GHz millimeter wave radio frequency device comprises a digital signal processor, a direct digital frequency synthesizer, an up-converter, a power amplifier, a buffer, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna, a low noise amplifier, a frequency mixer at a receiving terminal, a variable gain amplifier and a demodulating analog-to-digital converter. The 77GHz millimeter wave radio frequency device has the advantages that the 77GHz millimeter wave radio frequency device can be widely applied to millimeter wave range-and-speed measuring radar systems, and 77GHz is adopted as a working frequency band of a millimeter wave radar and combined with a phased-array antenna technology that low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) is used as a substrate to manufacture each micro-strip patch antenna serving as an antenna unit; the direct digital frequency synthesizer is adopted and combined with an up-conversion technology to generate linear frequency modulated continuous waves; and a plurality of transmitter units are adopted andcombined with the phased-array antenna technology to realize horizontal scanning of millimeter wave beams.
Owner:苏州煜瑛微电子科技有限公司
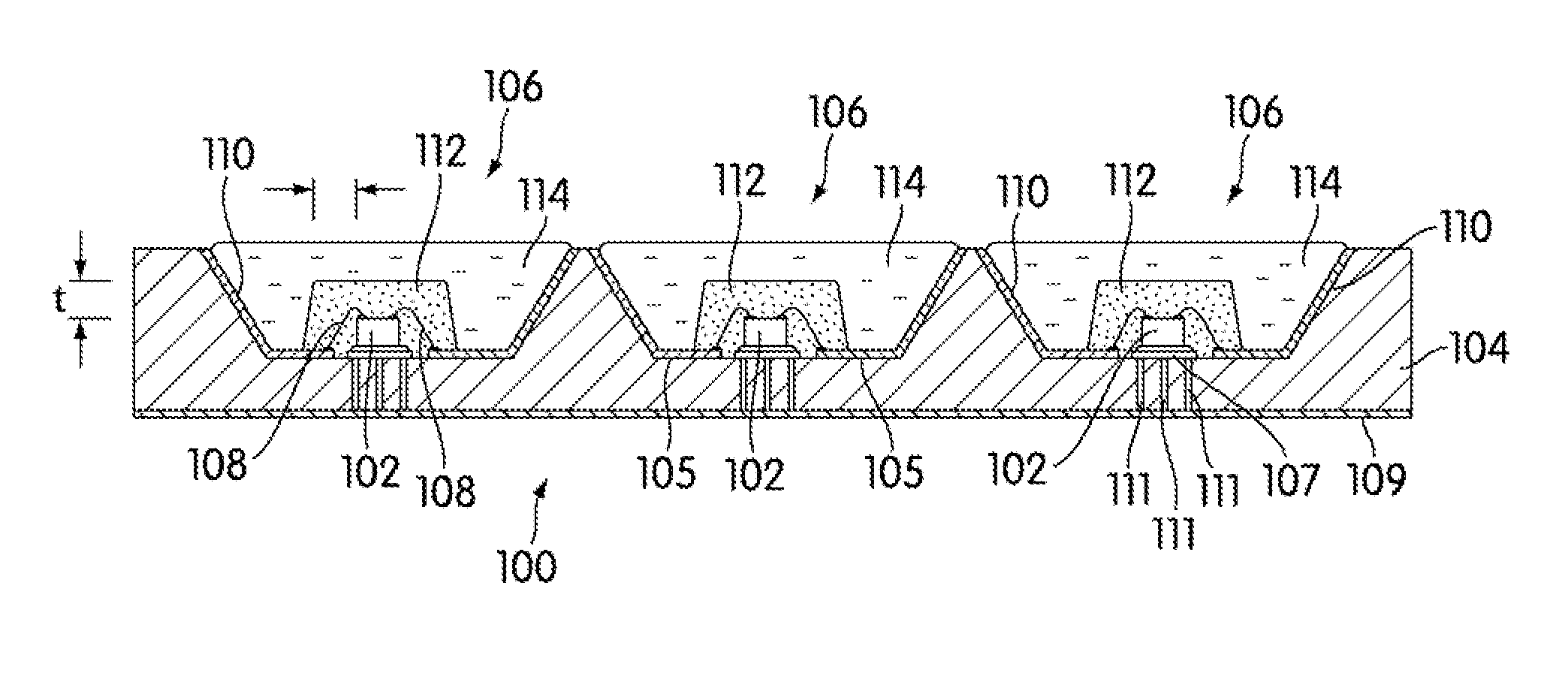
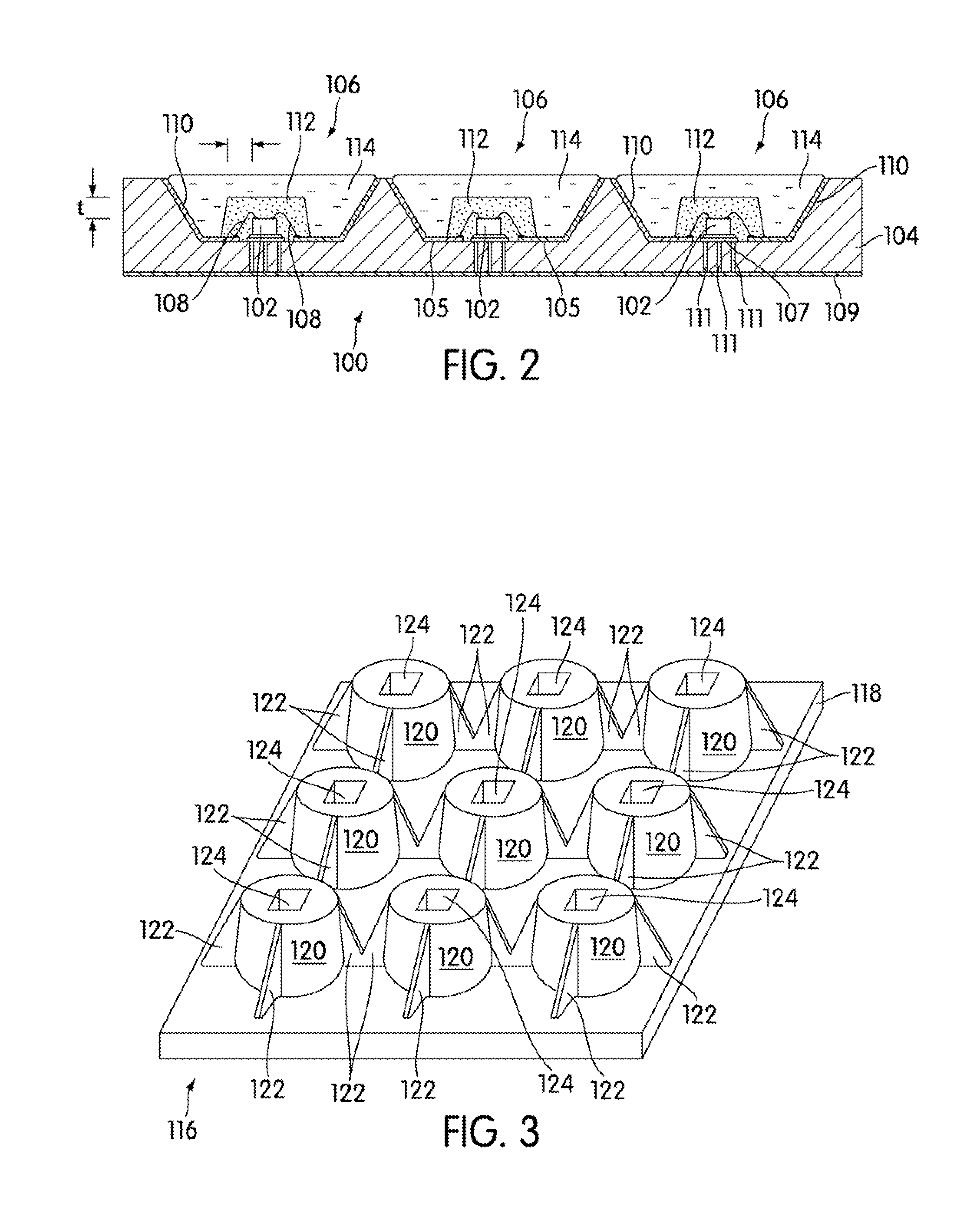
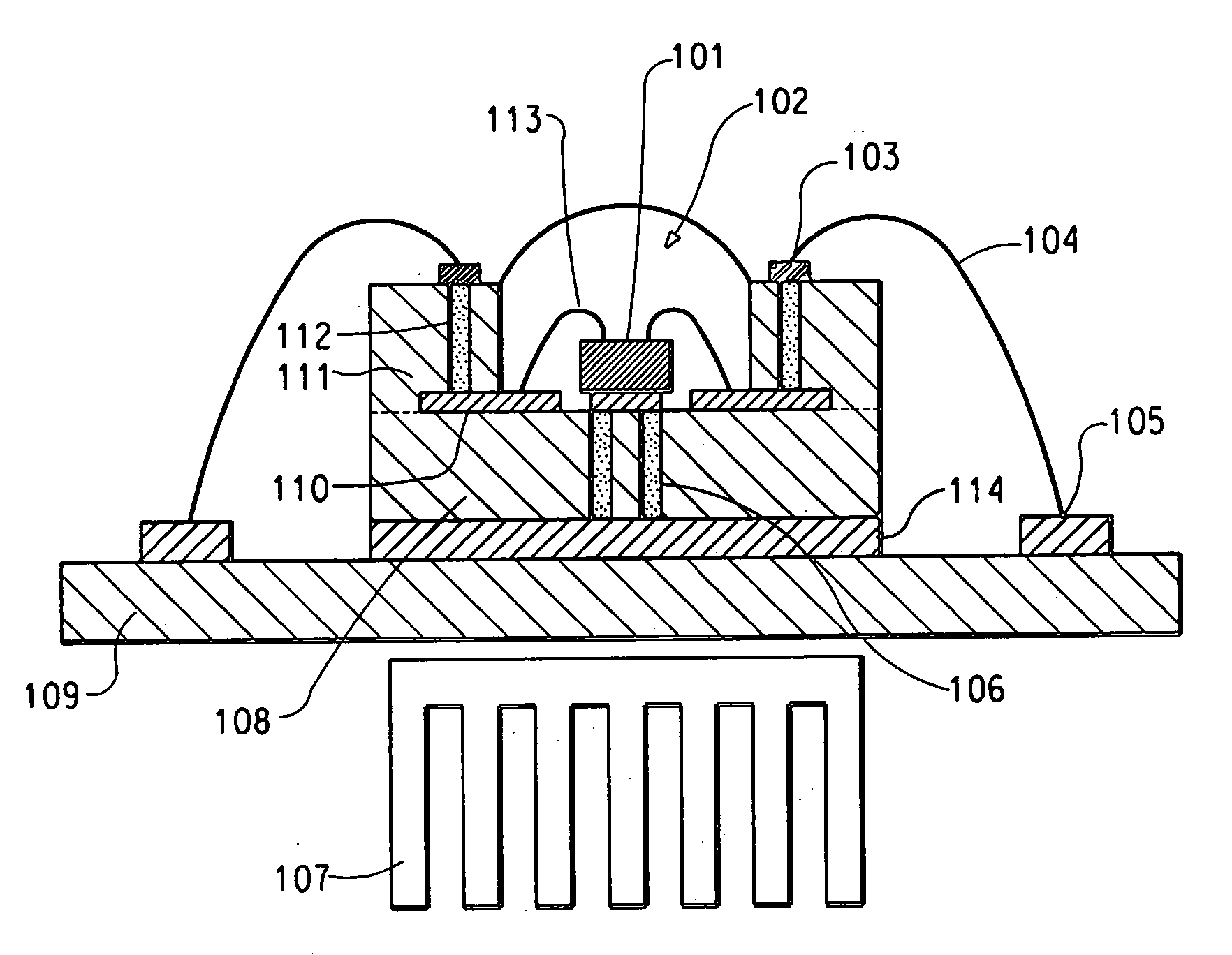
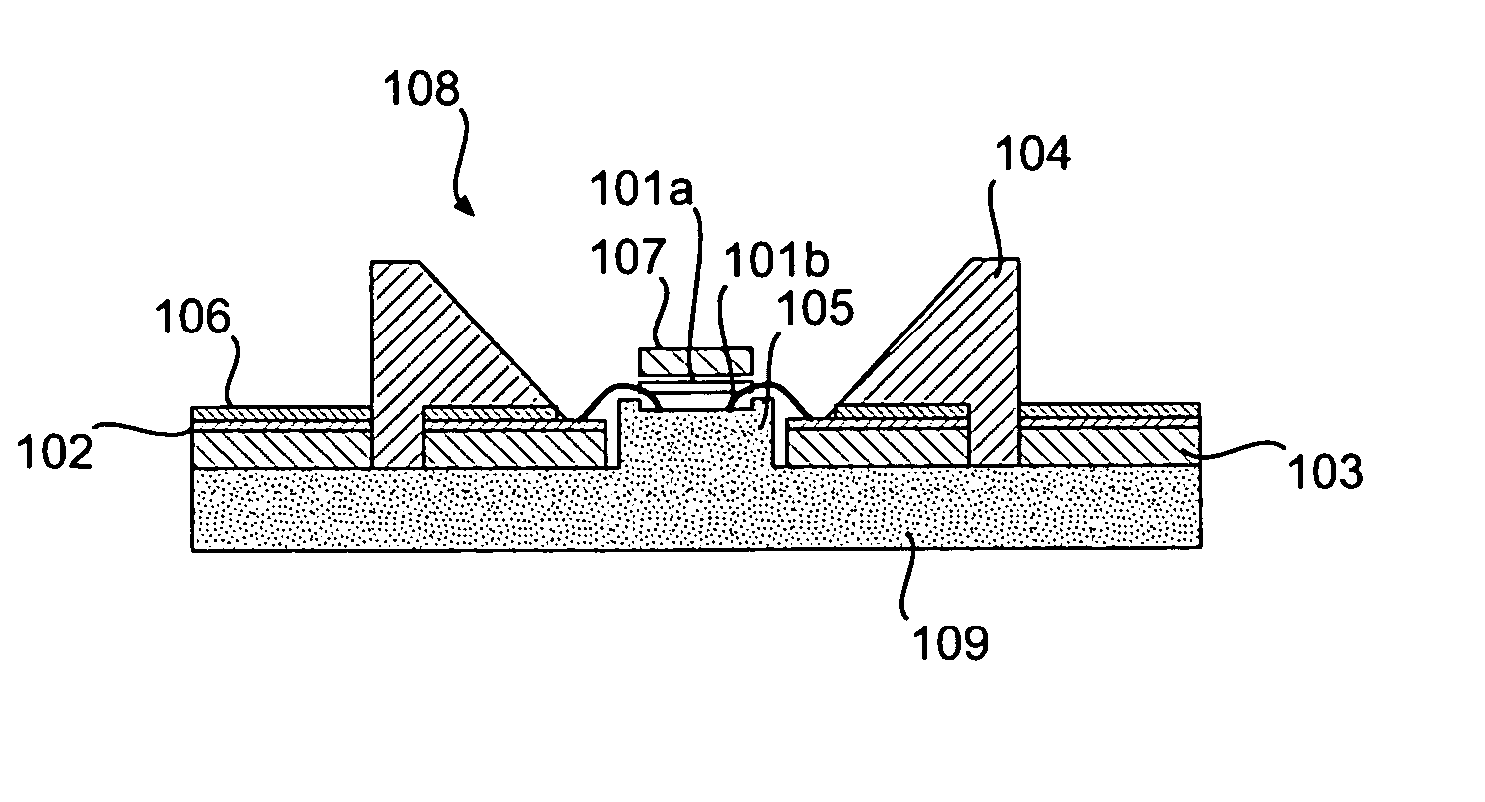
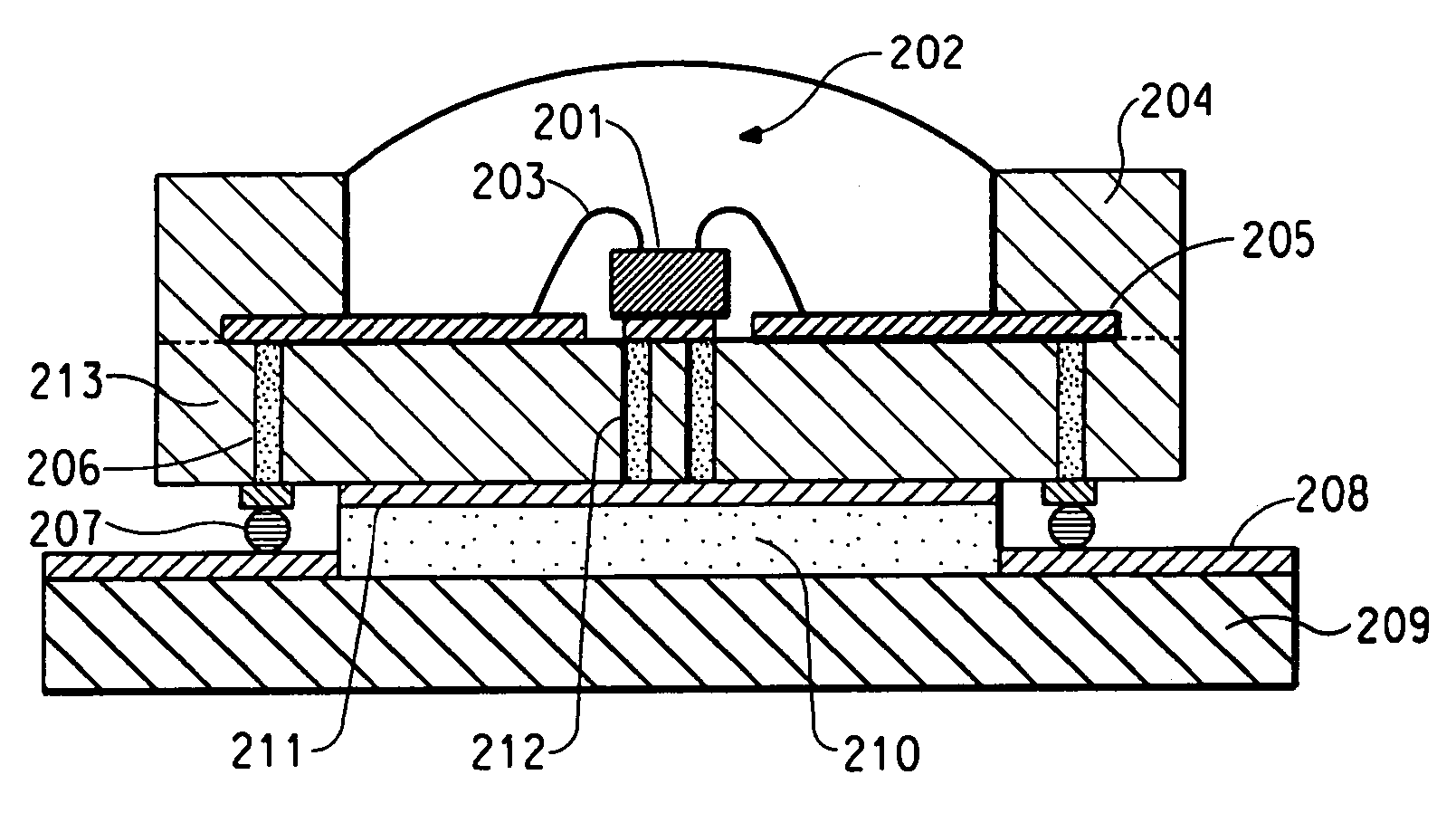
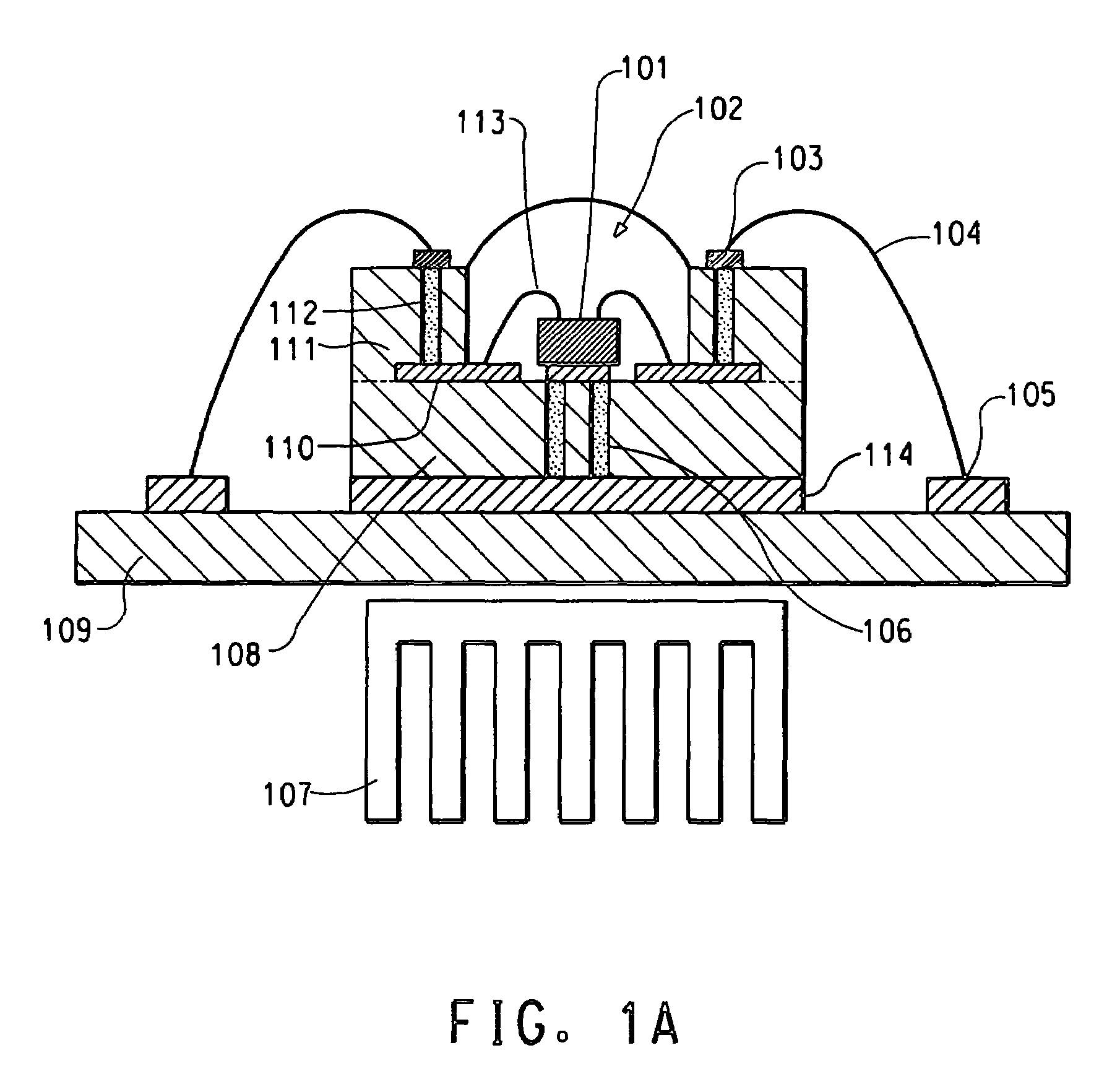
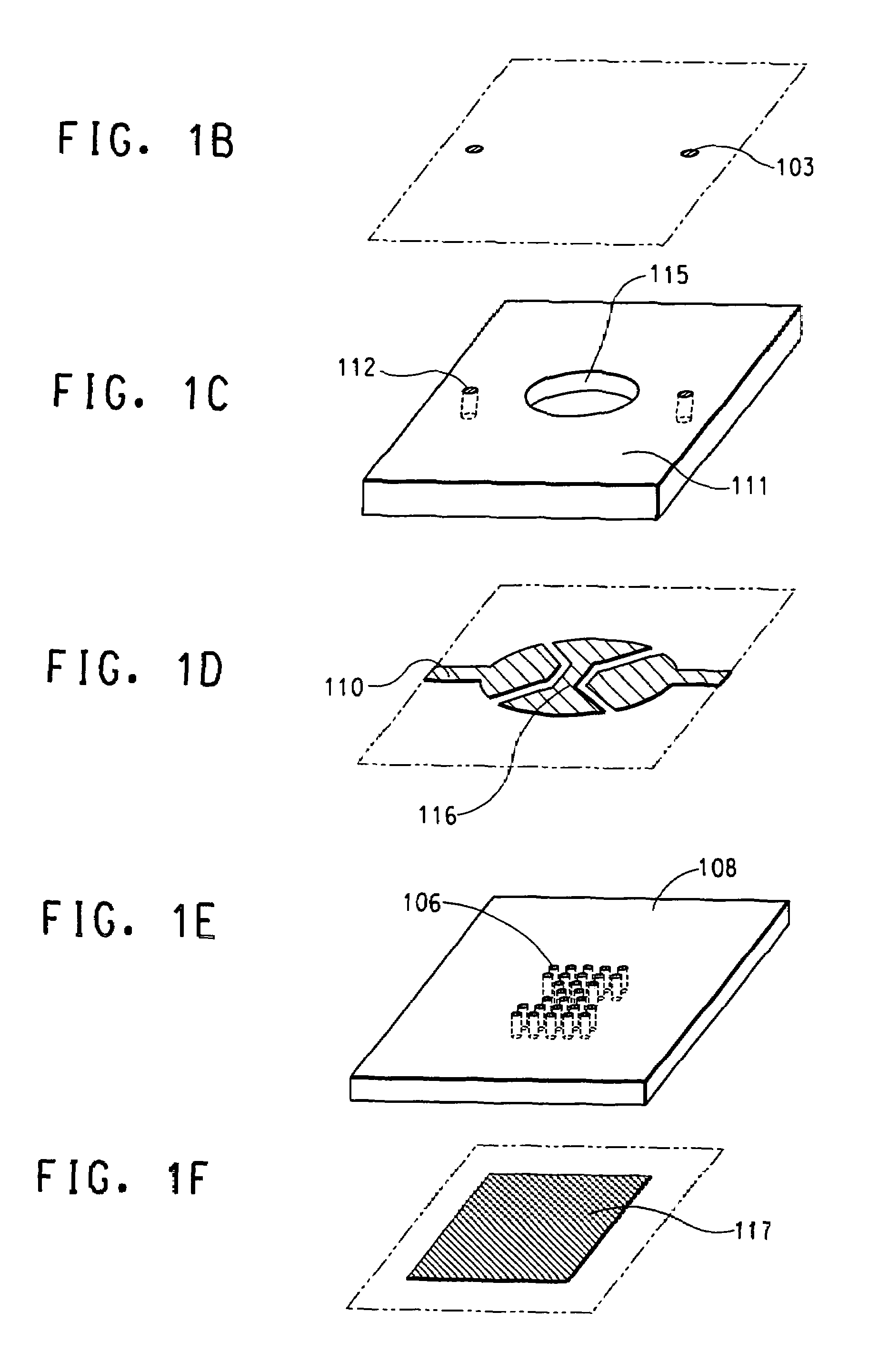
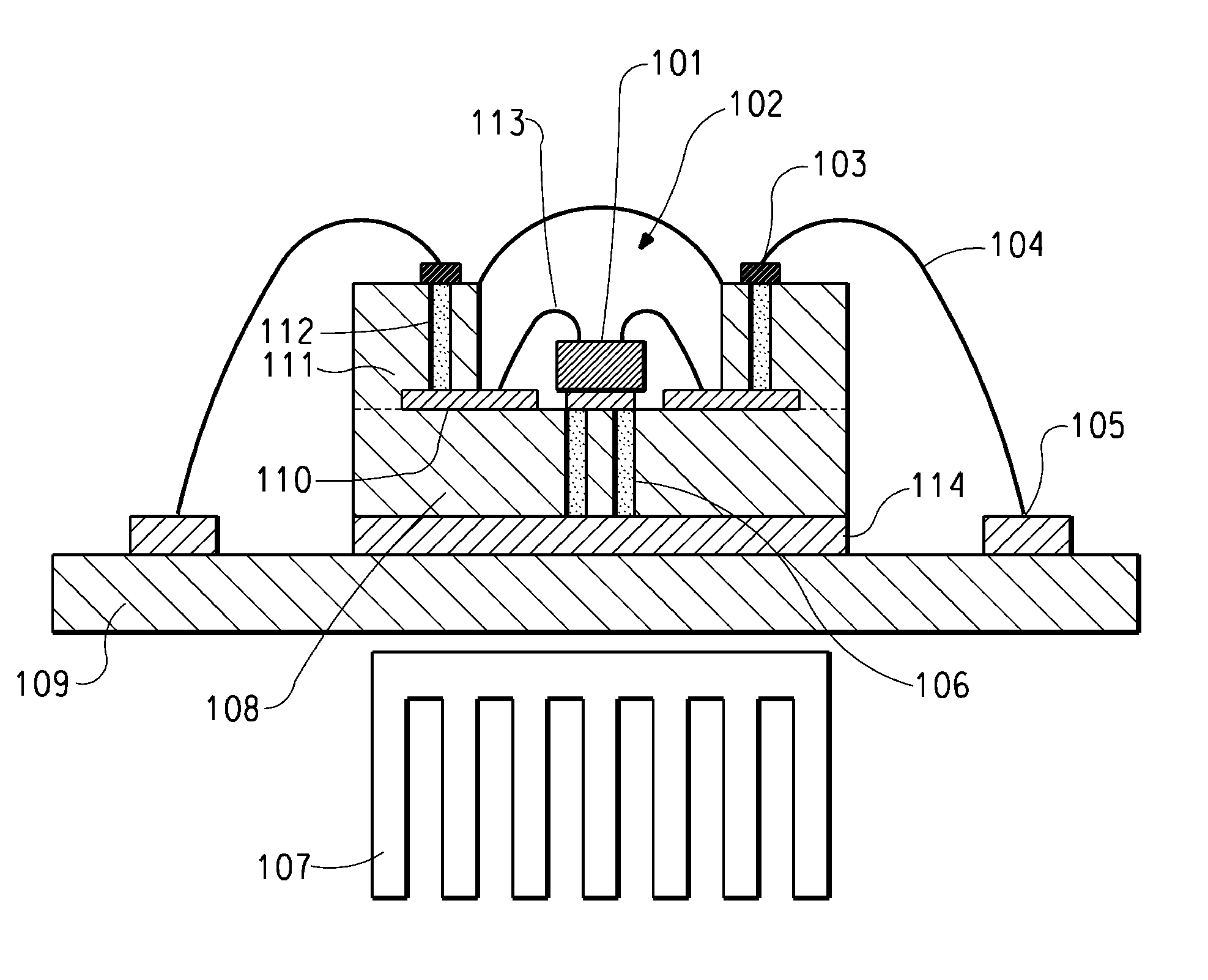
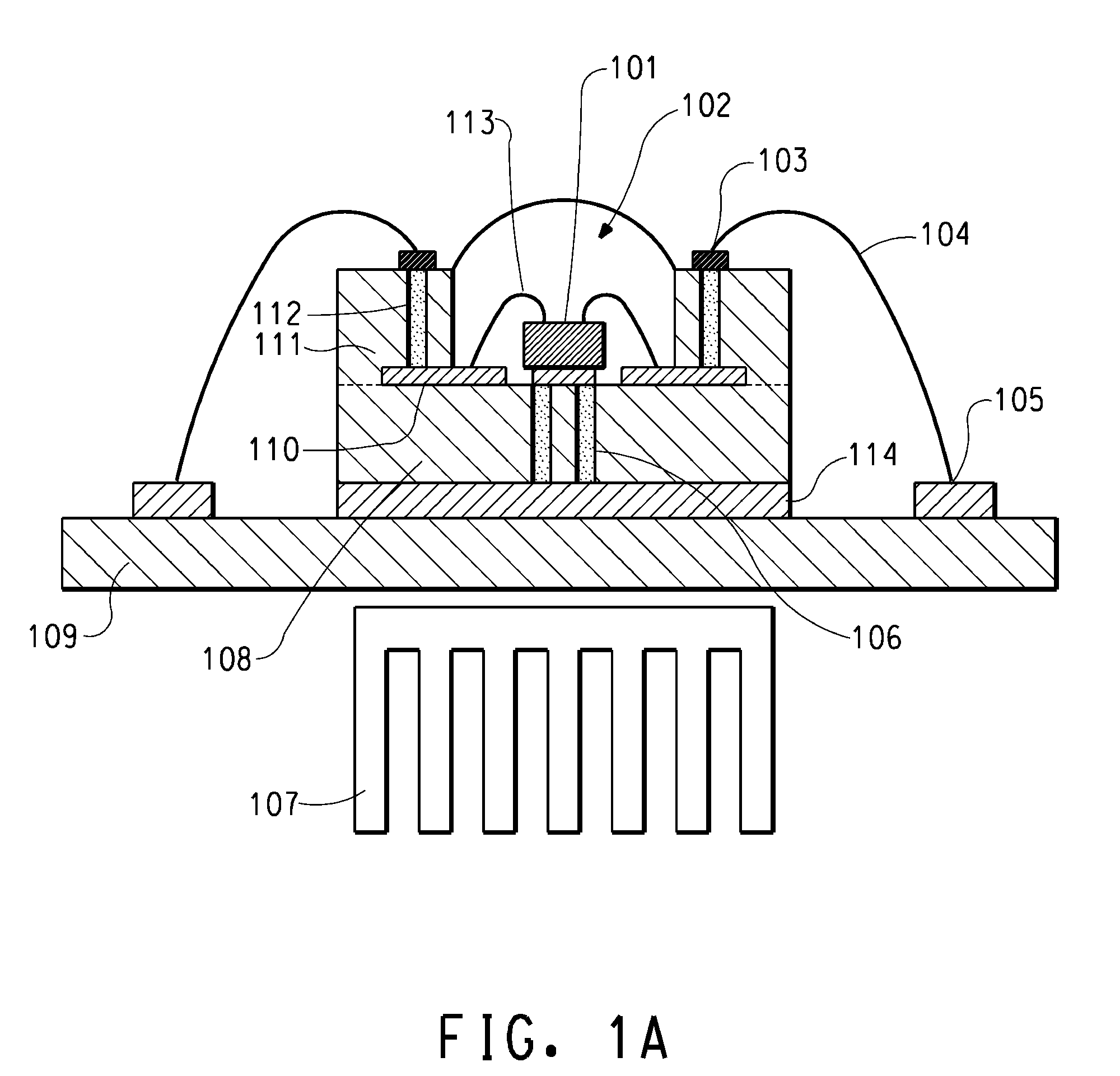
Light emitting device
ActiveUS8461613B2Maximizing numberPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesElectrical conductorPhosphor
A light emitting device comprises: a plurality of light emitting diodes and an insulating (low temperature co-fired ceramic) substrate with an array of recesses each for housing a respective one of the light emitting diodes. The substrate incorporates a pattern of electrical conductors that is configured for connecting the light emitting diodes in a selected electrical configuration and to provide at least two electrical connections on the floor of each recess. Light emitting diodes can be electrically connected to the electrical connections by at least one bond wire or by flip chip bonding. Each recess is filled with a transparent material to encapsulate each light emitting diode. The transparent material can incorporate at least one phosphor material such that the device emits light of a selected color and / or color temperature.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
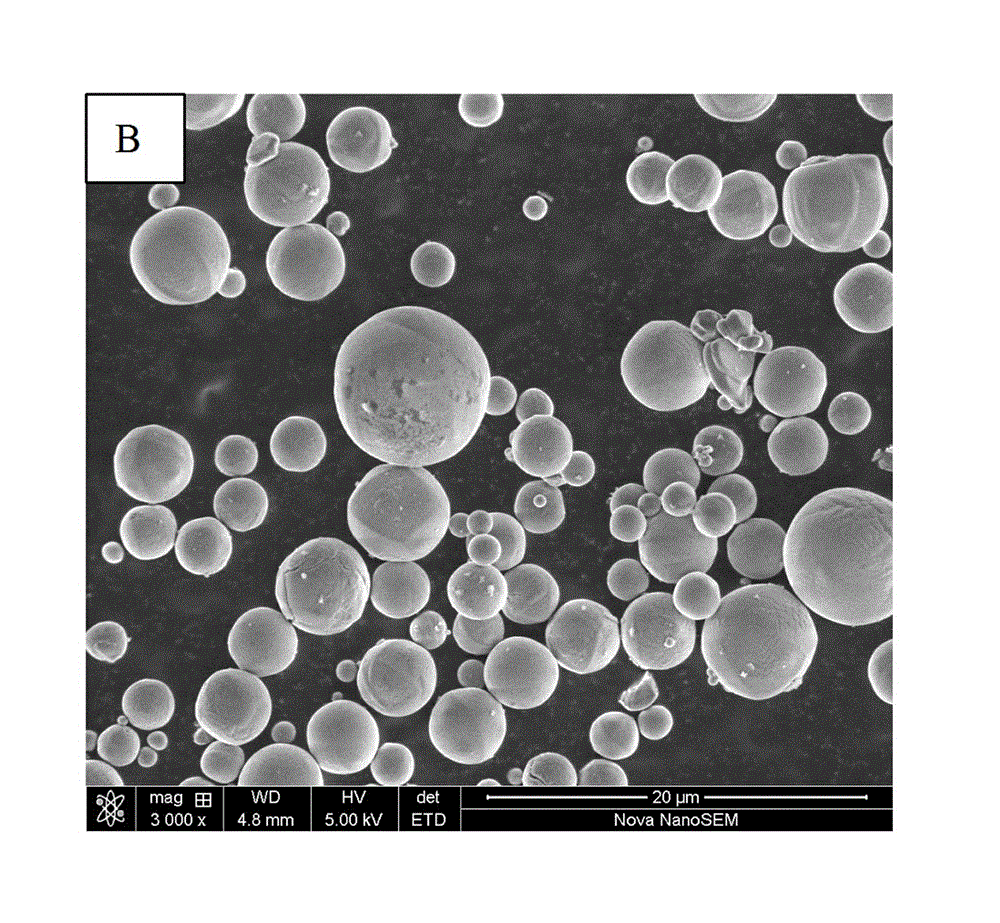
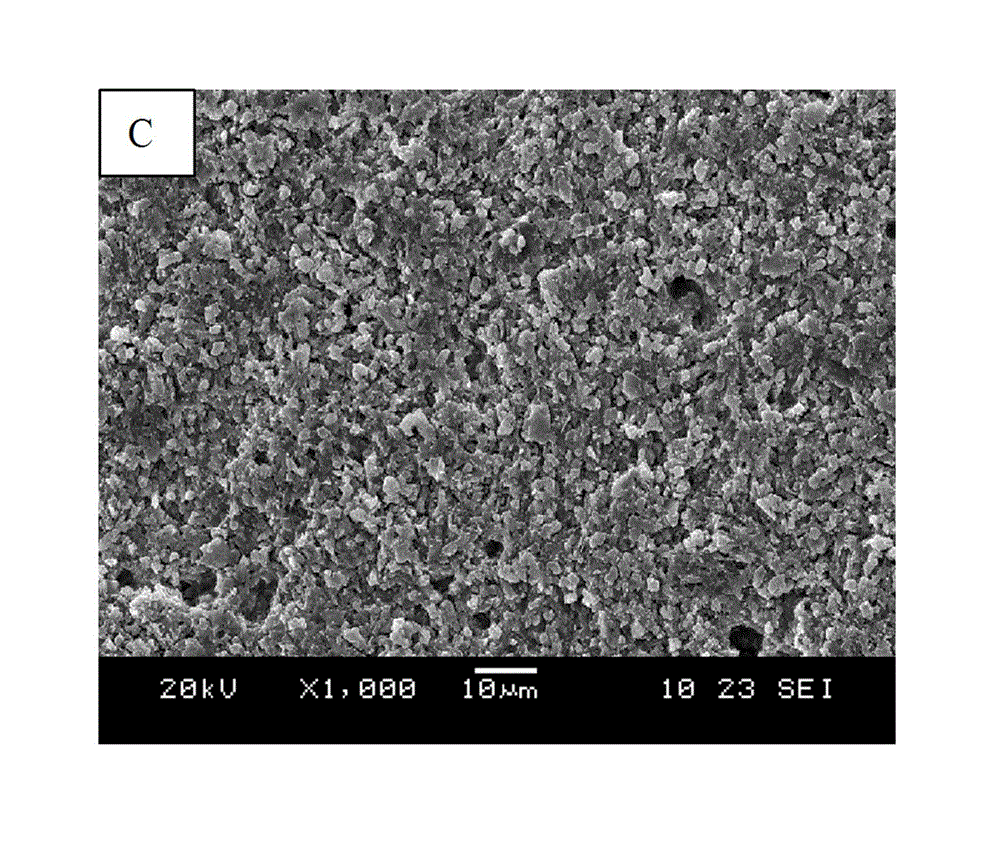
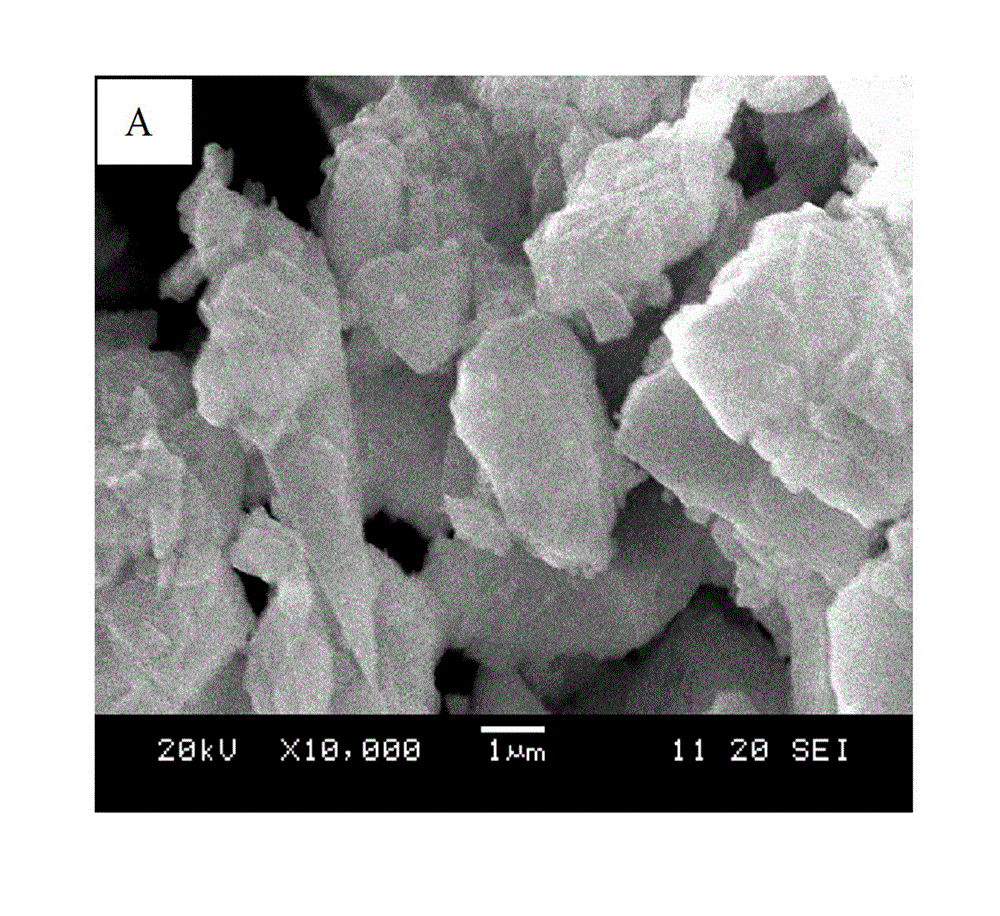
Borosilicate glass-spherical alumina low temperature co-fired ceramic green tape and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a borosilicate glass-spherical alumina low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) green tape and its preparation method. The green tape is composed of a glass-ceramic composite material and a casting medium. Specifically, the glass-ceramic composite material consists of borosilicate glass and spherical alumina. The casting medium consists of a mixed solvent, a monomer binder, a plasticizer and a dispersing agent. The low temperature co-fired ceramic green tape prepared in the invention has a level and smooth surface, a solid content up to 88-92wt%, and a firing shrinkage rate of 9-11%. The difference between the sintering shrinkage rate of each direction is small. And the green tape can achieve wiring co-firing with Au, Ag and other low melting point metals at 850DEG C. The raw material tape sintered ceramic body provided in the invention has excellent dielectric properties. Under the condition of less than 10GHz, the dielectric constant (epsilon r) of 7-8, the dielectric loss (Tan delta) is less than 2*10<-3>, and effectively solves the anisotropy problem of traditional LTCC green tape sintering shrinkage.
Owner:凤阳凯盛硅材料有限公司
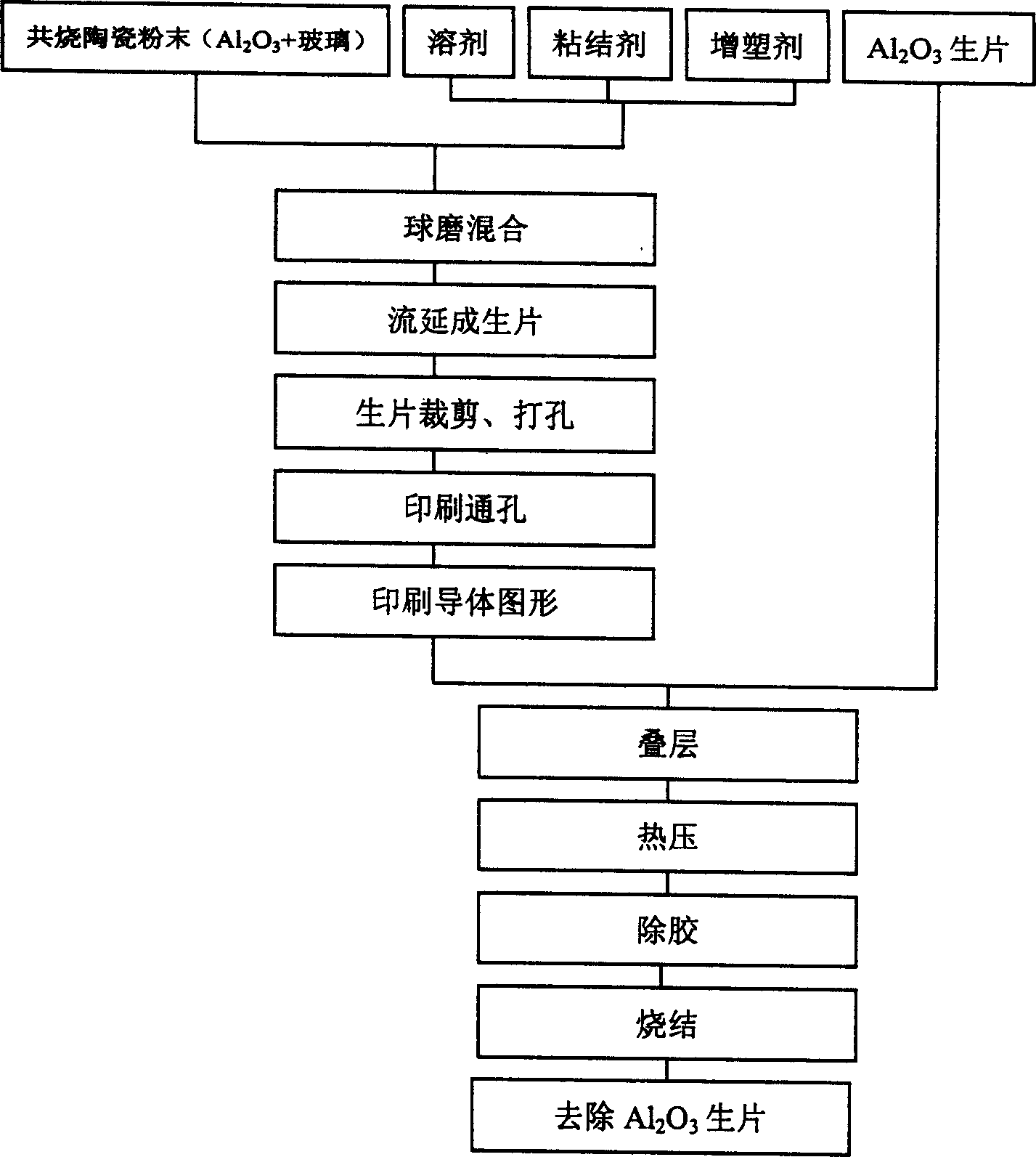
Process for preparing zero-shrinkage low-temp, co-fired ceramic multi-layer baseplate
InactiveCN1477687AImprove routing accuracyImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorCo-fired ceramic
The present invention relates to a process for preparing zero-contractibility low-temp. cosintered ceramic multi-layer baseplate. Before the baseplate is sinerted, a pair of Al2O3 ceramic raw pieces is respectively pressed on the upper and lower surface of the baseplate blank, then the above-mentioned material is undergone the processes of hot-pressing, removing adhesive and sintering treatment so as to can obtain the invented product material. It can provide accurate conductor pattern for packaging process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
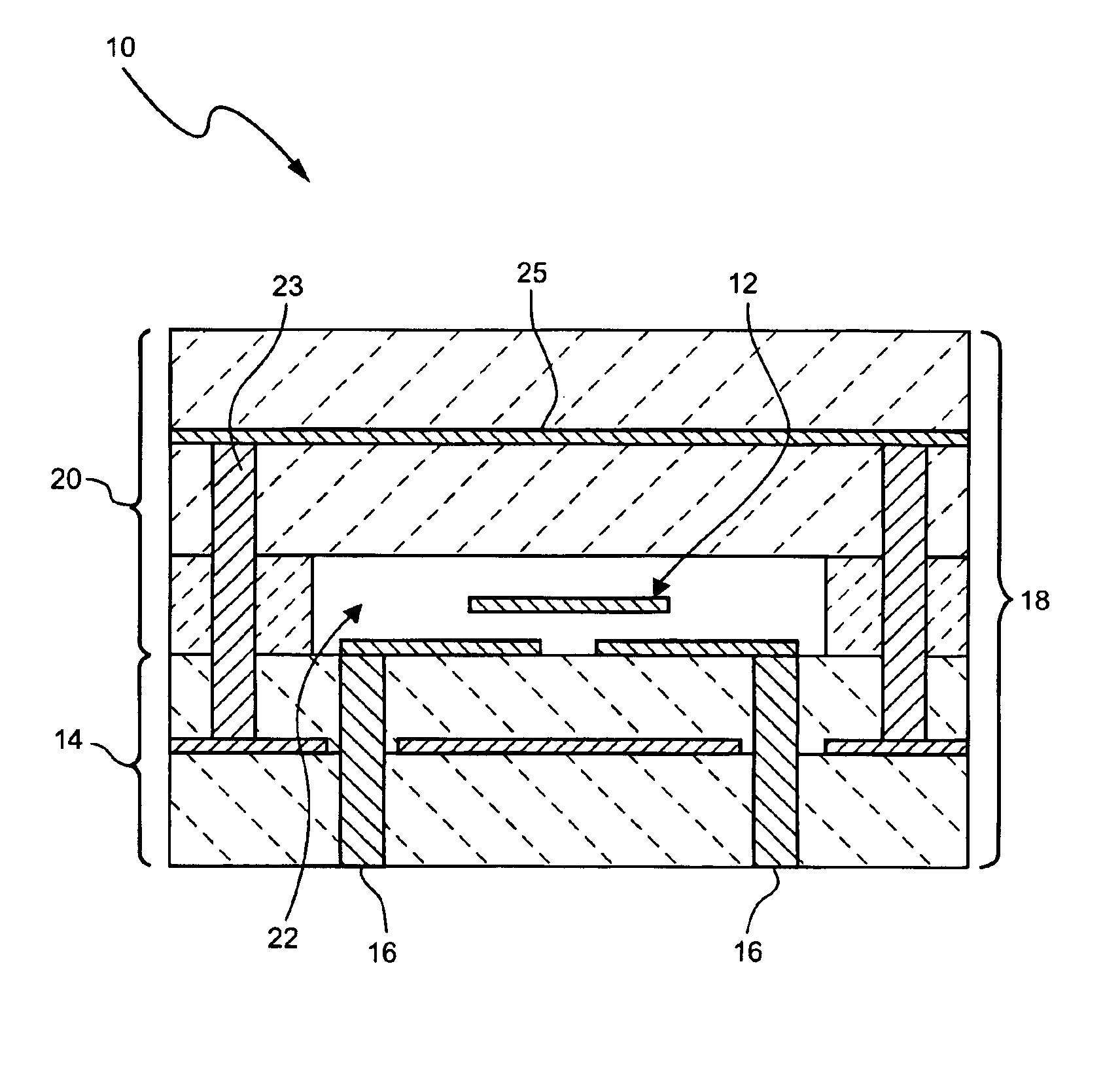
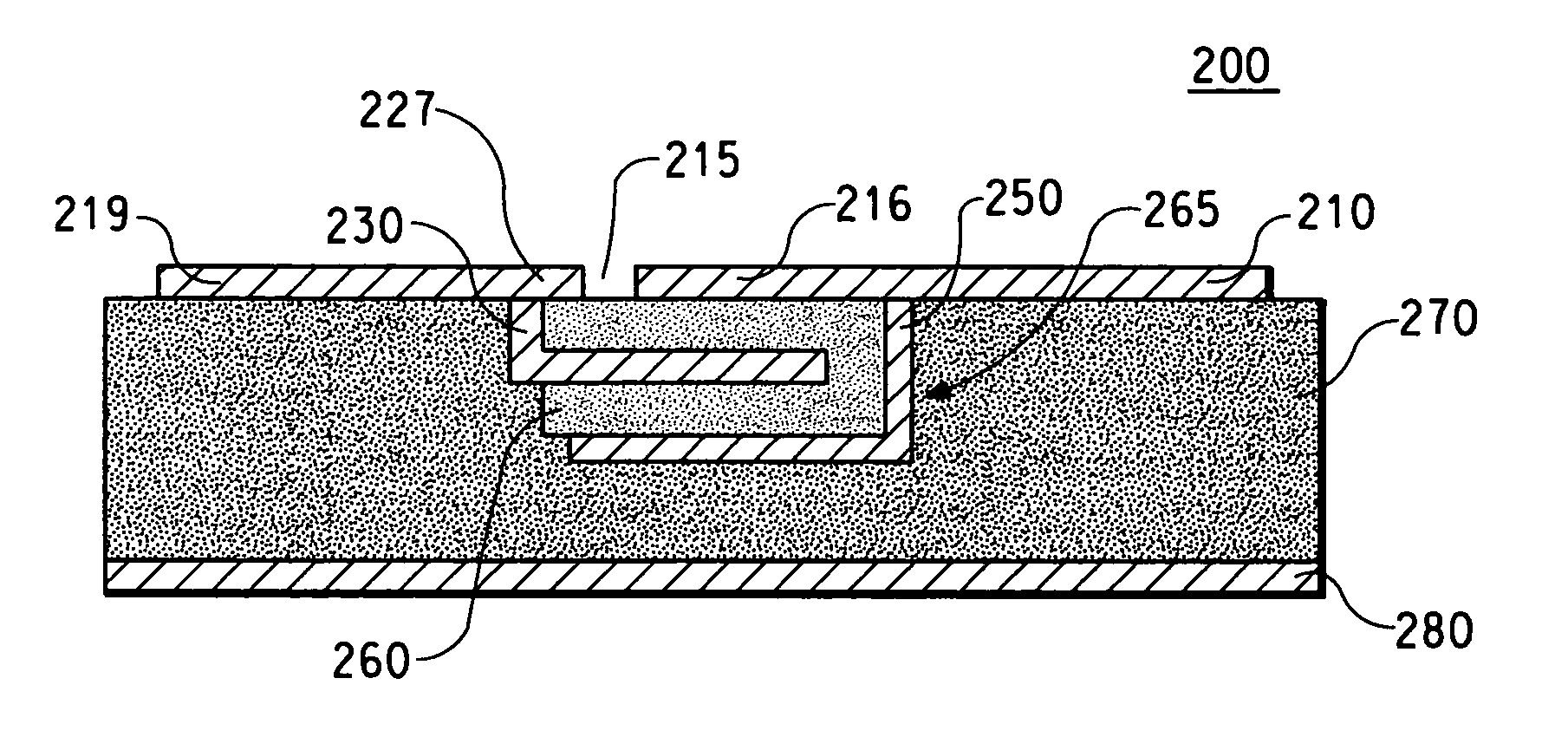
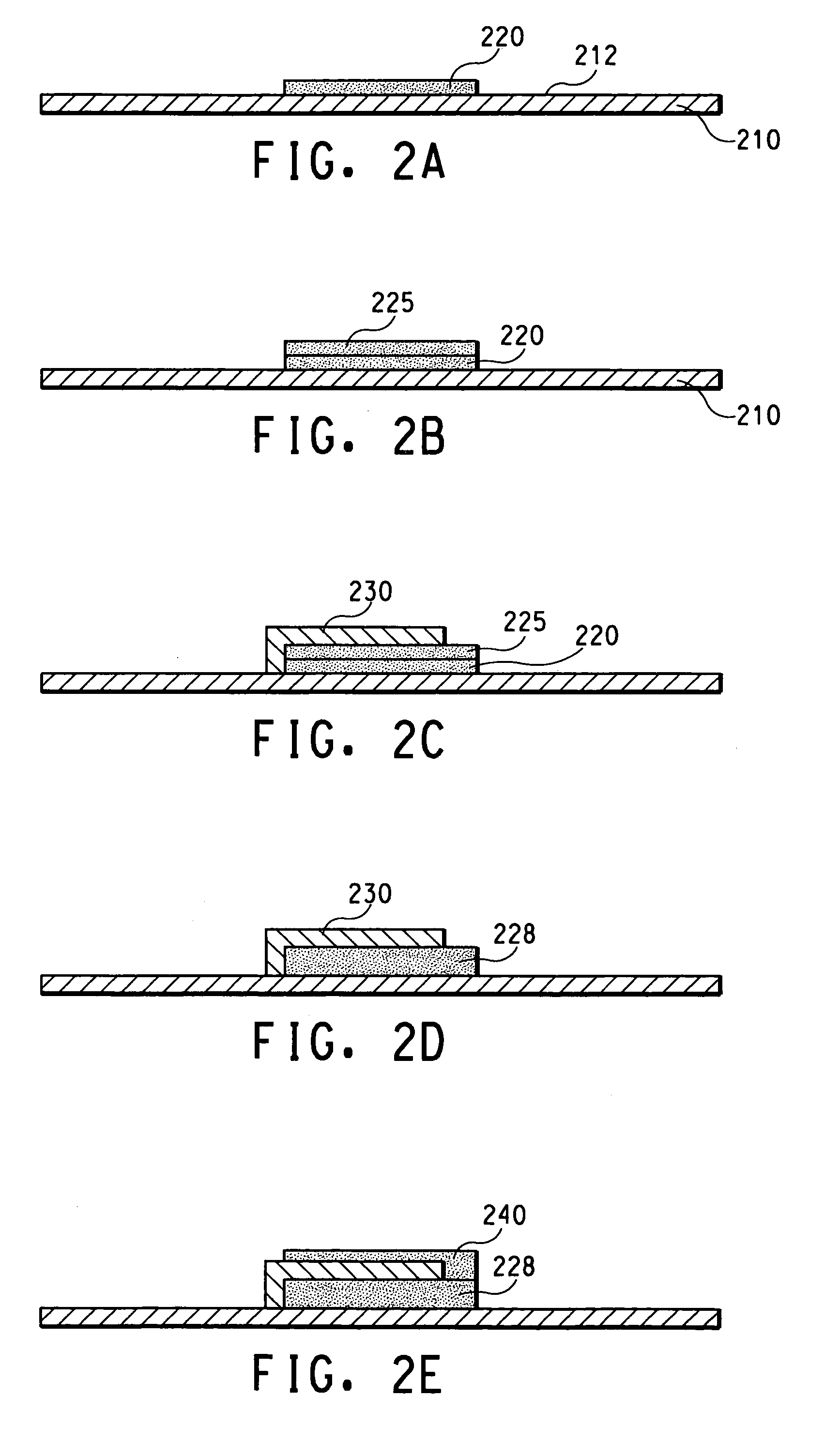
Co-fired ceramic capacitor and method for forming ceramic capacitors for use in printed wiring boards
InactiveUS7072167B2Increase capacitance densityAnti-noise capacitorsFixed capacitor electrodesDielectricCeramic capacitor
A capacitor structure is fabricated by forming a pattern of first dielectrics over a foil, forming first electrodes over the first dielectrics, and co-firing the first dielectrics and the first electrodes. Co-firing of the dielectrics and the electrodes alleviates cracking caused by differences in thermal coefficient of expansion (TCE) between the electrodes and the dielectrics. Co-firing also ensures a strong bond between the dielectrics and the electrodes. In addition, co-firing allows multi-layer capacitor structures to be constructed, and allows the capacitor electrodes to be formed from copper.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
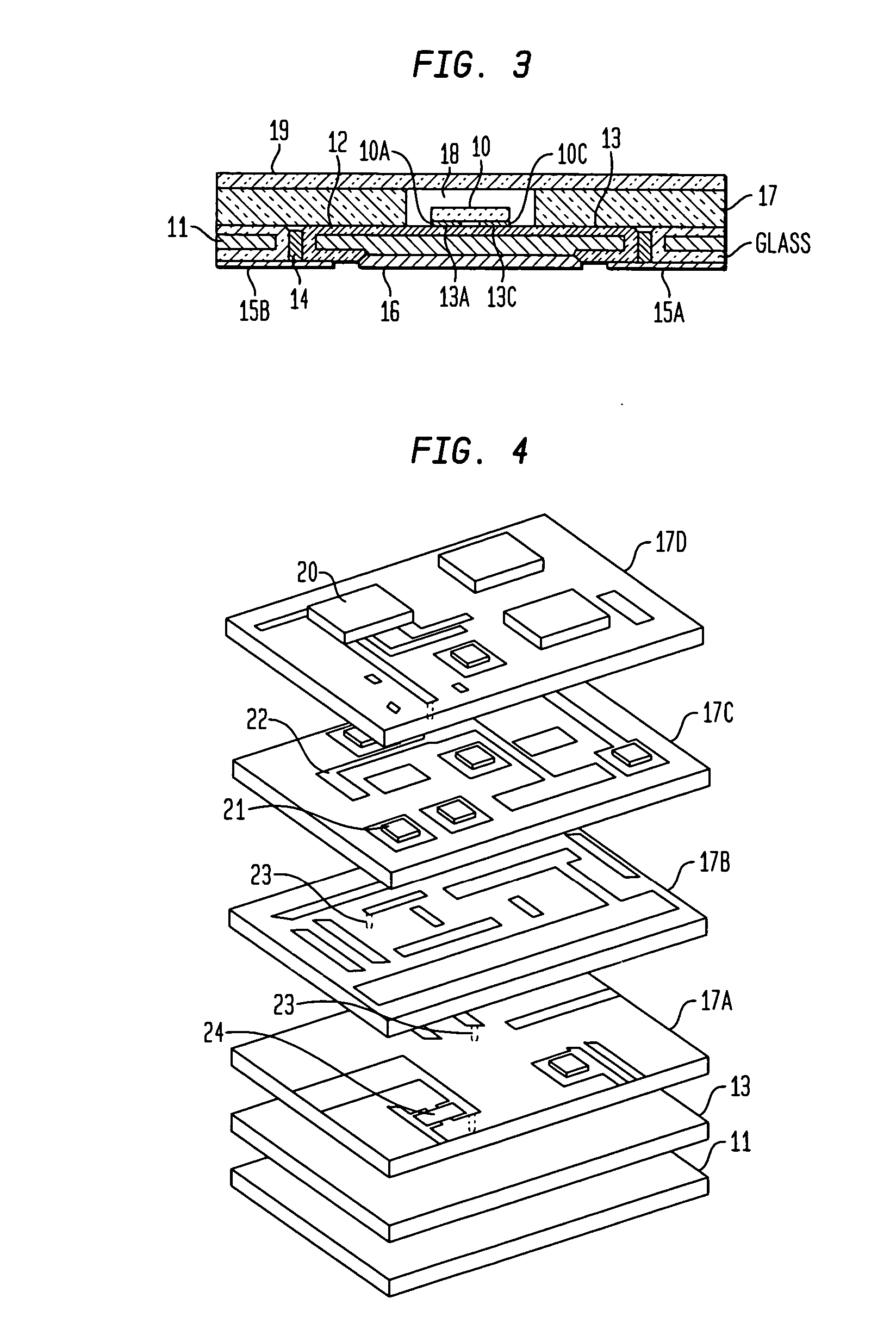
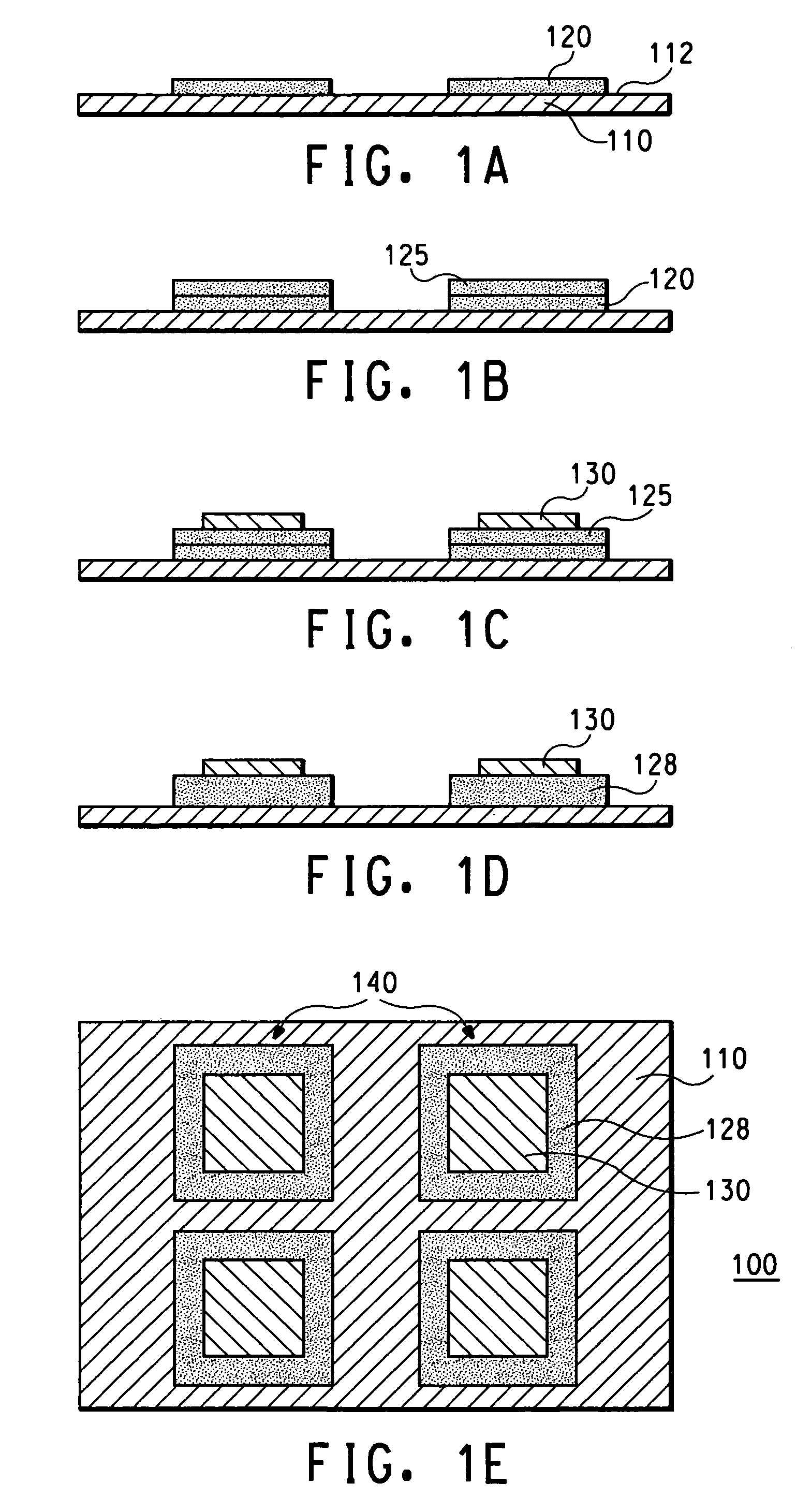
Semiconductor package including low temperature co-fired ceramic substrate
ActiveUS6879034B1Minimal profileEliminates formation of undesirableSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageCo-fired ceramic
A semiconductor package comprising a low temperature co-fired ceramic substrate defining opposed top and bottom surfaces. The substrate comprises at least two stacked ceramic layers and electrically conductive patterns which extend between the layers and along the top surface of the substrate. Mounted to the top surface of the substrate and electrically connected to the conductive patterns is at least one semiconductor die. A plurality of leads extend at least partially about the substrate in spaced relation thereto. Each of the leads defines opposed top and bottom surfaces, the semiconductor die being electrically connected to at least one of the leads. A package body at least partially encapsulates the substrate, the semiconductor die and the leads such that at least a portion of the bottom surface of each of the leads is exposed in the package body.
Owner:AMKOR TECH SINGAPORE HLDG PTE LTD
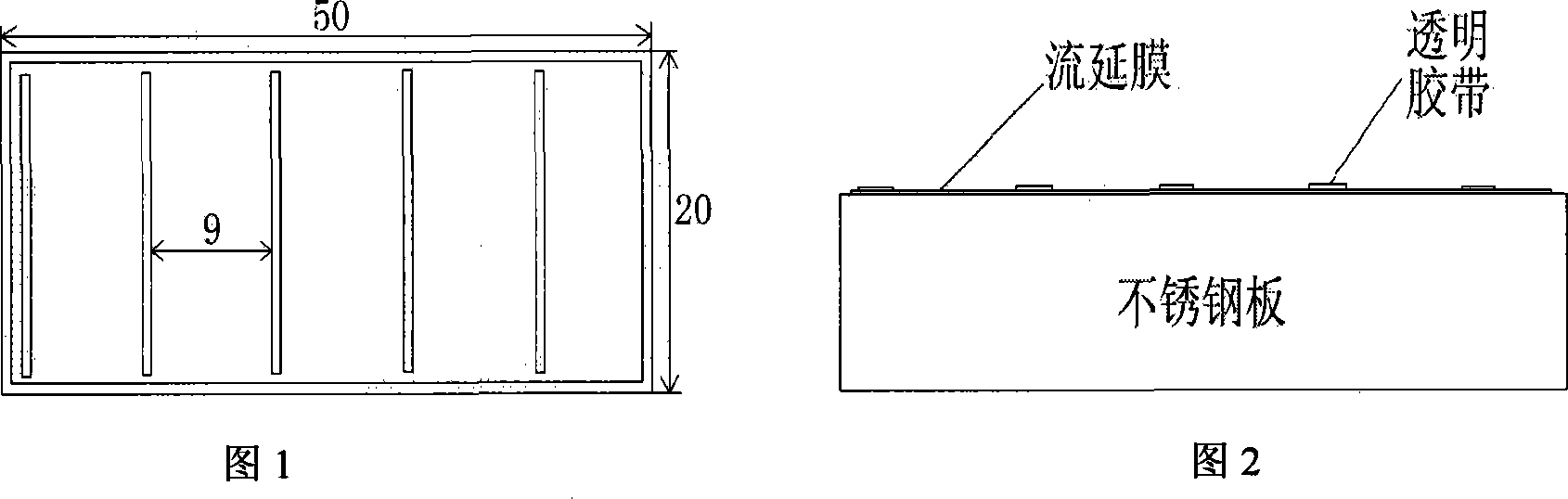
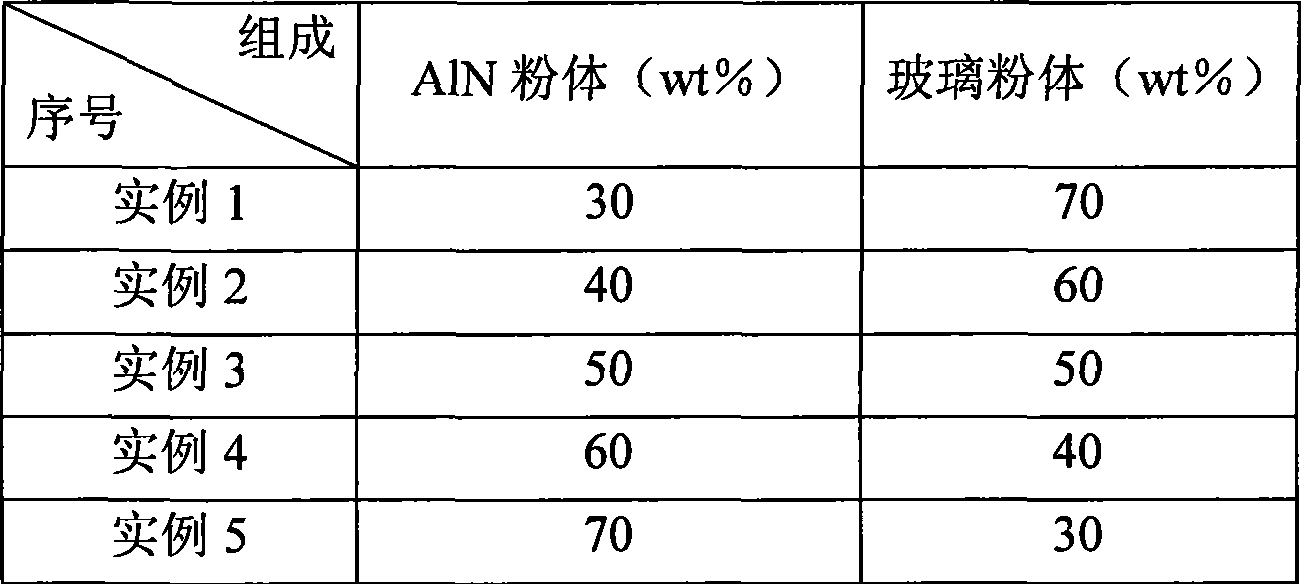
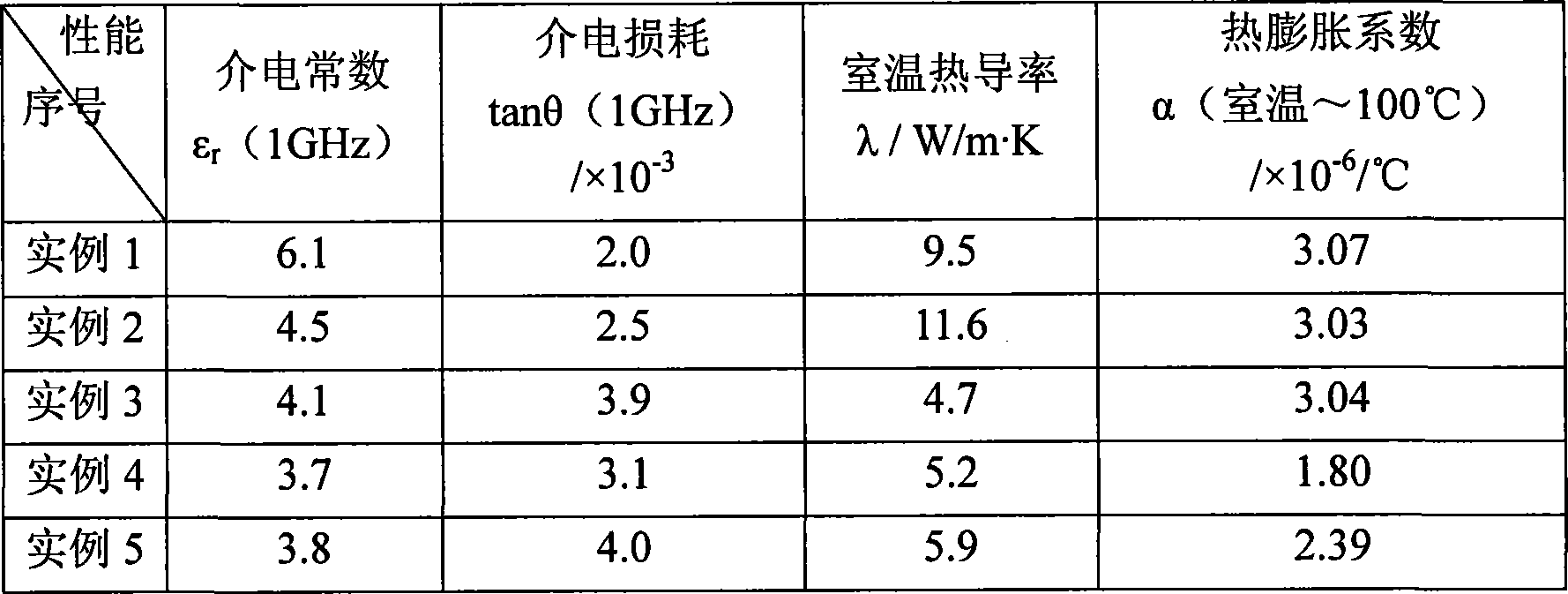
Aluminum nitride/borosilicate glass low-temperature co-fired ceramic substrate material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101100367AImprove performanceImprove thermal conductivityCircuit susbtrate materialsCo-fired ceramicProcess conditions
This invention relates to electronic baseplate by low-temperature co-sintering of aluminium nitride / borosilicate glass. This baseplate is composed of: AlN 30-70%; oxides 30-70%. Said oxides are then composed (by mol percentages) of: SiO2 8-12%, B203 18-24%, ZnO 45-60%, Al203 3-8%, Li20 3-8%. This inventive product has excellent comprehensive properties, its heat conductivity is increased from that of prior art product 2-5 W / m.K to 10W / m.K. It can be used in more greater power devices with excellent dielectric property. This invention has also advantages of: easily available raw materials, low cost, simple process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com