Microbacterium barkeri XJ and method for preparing steviol by microbacterium barkeri XJ
A technology of Microbacillus pasteurii and steviol, which is applied in the field of steviol glycoside or rubus glycoside conversion by microorganisms or enzymes, and the preparation of steviol can solve the problems of limited source of helicase and high price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0034] Preparation of Microbacterium pasteurianum powder or enzyme powder: Use conventional liquid or solid fermentation culture and enzyme separation methods to obtain bacteria powder or enzyme powder.
[0035] For example, the preparation of bacterial powder includes fermentation of bacteria, separation of fermentation broth, emulsification of bacterial sludge and vacuum freeze-drying of emulsion. The enzyme powder fermented by the enzyme produced by Microbacterium pasteurianus is frozen and then vacuum-dried for 30 h at a vacuum degree of 1-5 Pa.
[0036] The material used in the present invention is the transformation substrate: steviol glycoside and rubusoside can be purchased from Changsha Guangming Food Chemical Company, and can also be prepared from stevia rebaudiana or rubus cotyledons by common extraction methods.
Embodiment 1
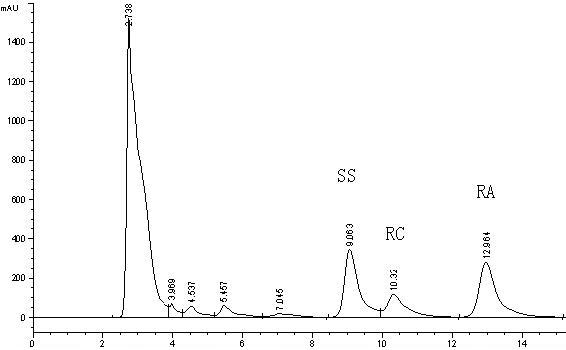
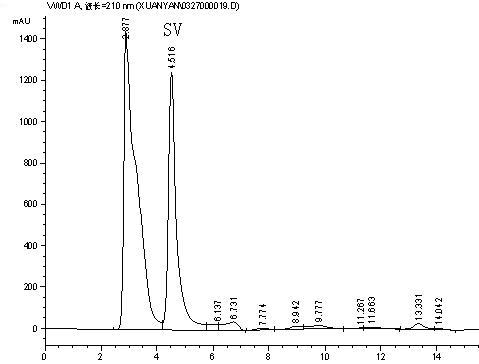
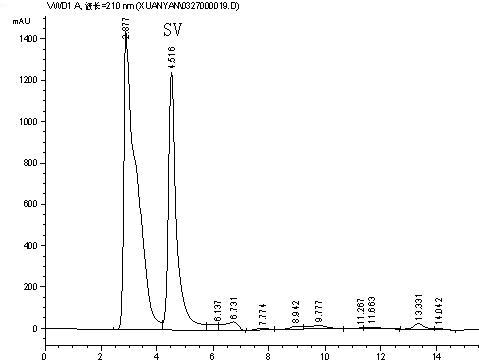
[0039] Prepare 1% (W / W), pH 7.5 steviol glycoside conversion substrate (steviol glycoside: water = 1::99 (W / W), the preparation method is the same below), insert 1% (V / V) Pasteur Microbial The bacillus liquid was cultured dynamically at 37°C and 220 r / min for 3 days. After the cultivation, the bacteria were removed by centrifugation at 5000 rpm. The supernatant was flocculated and precipitated to remove impurities, the macroporous resin was adsorbed and separated, and the eluent was crystallized and purified to obtain high-purity steviol with a purity of about 95%. The conversion rate of stevioside was 90%.
Embodiment 2
[0041] 1% (W / W), pH 6.5 steviol glycoside substrate in a 500 mL transformation bottle, add 10% (W / W) enzyme solution, and transform at 37°C for 2 days. After separation and purification, steviol with a purity of about 95% is obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com