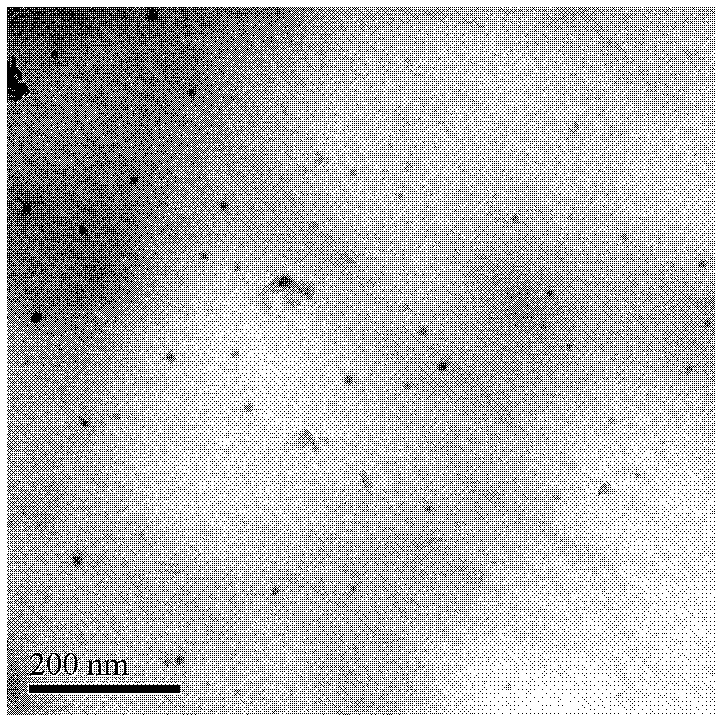Heat resistant aluminum alloy conductor material and preparation method thereof
An aluminum alloy conductor, heat-resistant technology, applied in the direction of metal/alloy conductor, cable/conductor manufacturing, metal rolling, etc., can solve the problems of unproven beneficial effect of heat resistance, difficulty in continuous production, reduction of electrical conductivity, etc. , to reduce production costs, inhibit recrystallization, and improve heat resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Using industrial pure aluminum ingots with a purity greater than 99.7% (where Fe<0.15%, Si<0.05%), Al-11.34% Zr master alloy, Al-4.7% Er master alloy and Al-5.0% Fe master alloy as raw materials, first Put industrial pure aluminum into a melting furnace to melt, keep the alloy liquid at 750°C-760°C, add aluminum-zirconium master alloy, aluminum-erbium master alloy and aluminum-iron master alloy, so that the mass percentage of each element is: zirconium is 0.06%, erbium is 0.29%, iron is 0.12%, silicon is 0.03%, the sum of impurity elements such as titanium, vanadium, chromium, manganese is 0.0058%, and aluminum is the balance. After the intermediate alloy is completely melted, stir, lower the alloy melt to 730°C and keep it warm, then carry out stirring, refining, standing, and slag removal in sequence, and obtain the heat-resistant aluminum alloy conductor material through continuous casting and rolling, wherein the rolling temperature is 530°C °C, the finish rolling t...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Using industrial pure aluminum ingots with a purity greater than 99.7% (where Fefigure 1 It is the transmission electron microscope observation structure of the alloy of Example 2. It can be seen from the figure that there are nano-scale second phases distributed on the matrix of the alloy material. Compared with the solid solution state, the presence of microalloying elements in this form has an impact on the conductivity of the alloy. The impact is much smaller, and at the same time, the heat resistance of the material can be greatly improved.
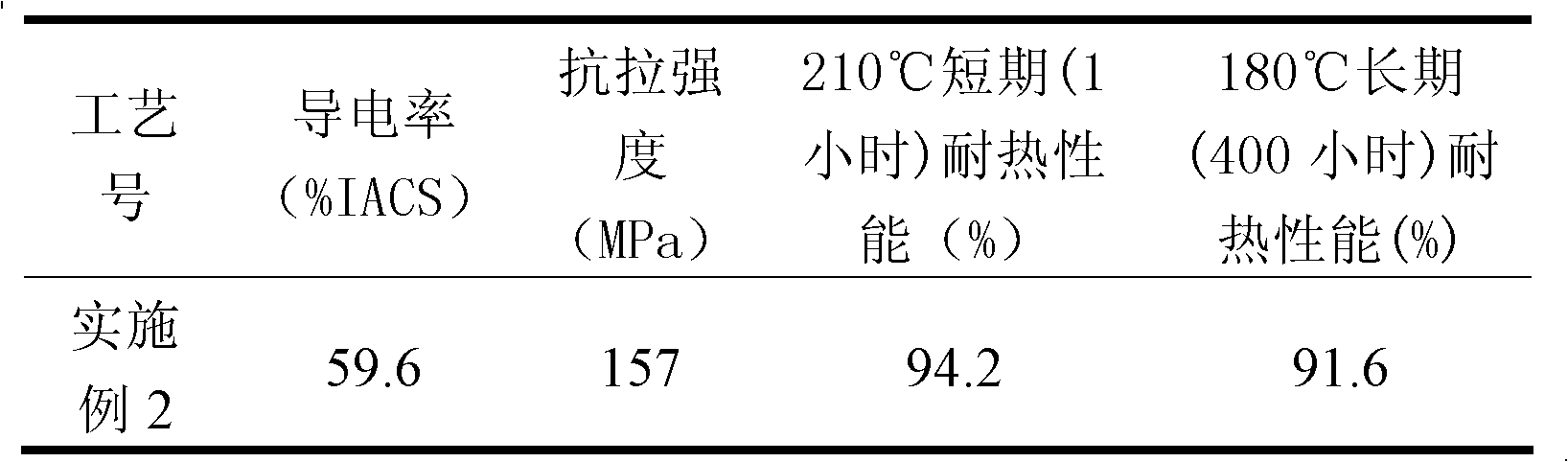
[0027] Table 2 Evaluation table of comprehensive performance of heat-resistant aluminum alloy conductor material
[0028]
Embodiment 3
[0030] Using industrial pure aluminum ingots with a purity greater than 99.7% (where Fe<0.15%, Si<0.05%), Al-11.34% Zr master alloy, Al-4.7% Er master alloy and Al-5.0% Fe master alloy as raw materials, first Put industrial pure aluminum into a melting furnace to melt, keep the alloy liquid at 750°C-760°C, add aluminum-zirconium master alloy, aluminum-erbium master alloy and aluminum-iron master alloy, so that the mass percentage of each element is: zirconium is 0.15%, erbium 0.15%, iron 0.16%, silicon 0.03%, the sum of titanium, vanadium, chromium, manganese and other impurity elements is 0.063%, aluminum is the balance. After the intermediate alloy is completely melted, stir, lower the alloy melt to 730°C and keep it warm, then carry out stirring, refining, standing, and slag removal in sequence, and obtain the heat-resistant aluminum alloy conductor material through continuous casting and rolling, wherein the rolling temperature is 480°C °C, the finish rolling temperature i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com