Method for fixing protein on surface of polydimethylsiloxane
A polydimethylsiloxane and surface immobilization technology, which is applied in material inspection products, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of complex protein types and quantities, unstable operation, poor specificity, etc., and achieves good specificity, The effect of improving sensitivity and increasing protein quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
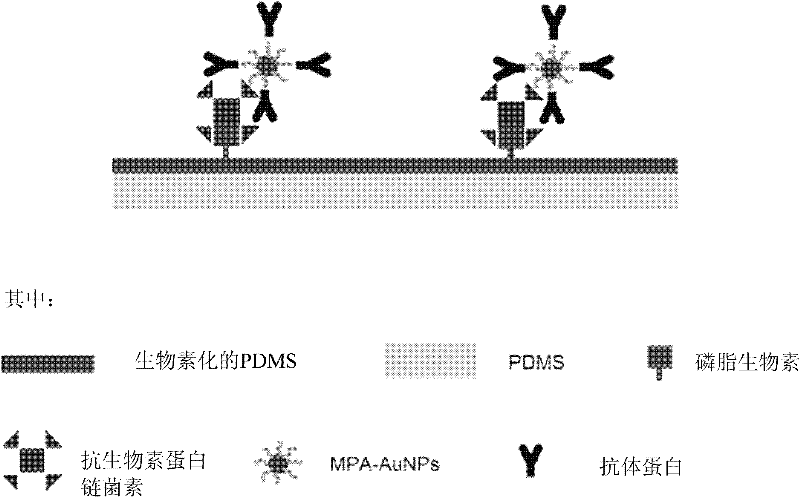
[0035] In this example, the low-density lipoprotein apoB 100 antibody mAb LDL-10 / 17 (purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA, USA)) was used as the protein to be immobilized, and the protein to be immobilized was immobilized on the PDMS surface according to the following method, immobilized The schematic diagram of the protein is as figure 1 Shown:
[0036] (1) Form a layer of biotinylated PDMS thin film on the surface of 60mm×60mm PDMS support layer. That is, add 10 microliters of 5 mg / mL phospholipid biotin in chloroform solution to the PDMS prepolymer / n-hexane (mass ratio is 1:2, and the quality of the PDMS prepolymer / n-hexane solution is 1 g), and then coat the The surface of the PDMS support layer was cured at 80°C for 20 minutes to form a layer of biotinylated PDMS film.
[0037] (2) In order to prevent the non-specific adsorption of protein on the surface of biotinylated PDMS film, use 10mmol / L pH 7.4 phosphate buffer solution (DPBS) containing 0.1wt% β-D-dodecyl-N-maltos...
Embodiment 2
[0043] In this example, alpha-fetoprotein antibody (purchased from American Research Products (Belmont, MA, USA)) was used as the protein to be immobilized.
[0044] (1) Form a layer of biotinylated PDMS thin film on the surface of 60mm×60mm PDMS support layer. That is, add 2 microliters of 5 mg / mL phospholipid biotin in chloroform solution to the PDMS prepolymer / n-hexane (mass ratio is 1:2, the mass ratio of PDMS prepolymer / n-hexane is 1 g), and then coat the PDMS The surface of the support layer was cured at 80°C for 20 minutes to form a layer of biotinylated PDMS film.
[0045] (2) In order to prevent non-specific adsorption of proteins on the surface of biotinylated PDMS, soak with 10mmol / L pH 7.4 phosphate buffered saline solution (DPBS) containing 0.2wt% β-D-dodecyl-N-maltose Biotinylate the PDMS surface for 5 min.
[0046] (3) In order to specifically bind streptavidin to the biotin group, soak the biotinylated PDMS surface with 200 μg / mL streptavidin in DPBS for 30 m...
Embodiment 3
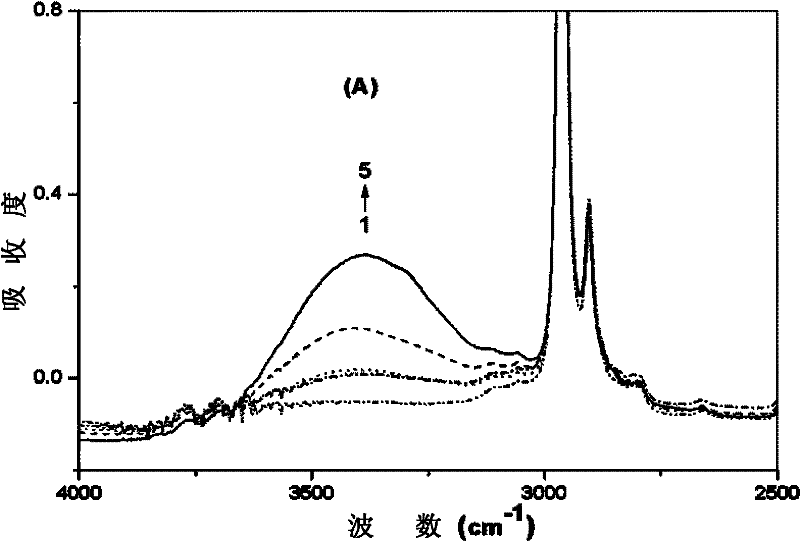
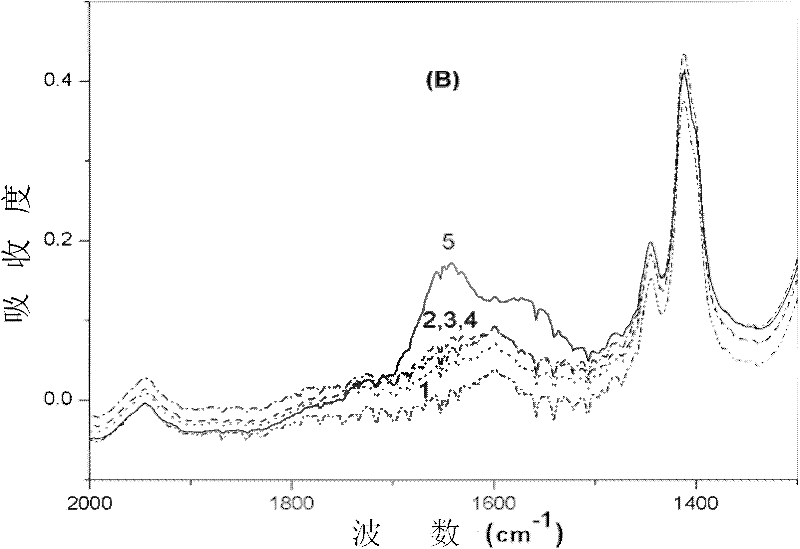
[0051] In this example, the intrinsic PDMS film and the modified PDMS film in Example 1 were characterized by FTIR / R760 infrared spectrometer (equipped with ATR components) ( Figure 2A-2B ). The spectrum (curve 1) of the intrinsic PDMS film is at 3386cm -1 There is no absorption peak nearby, and the spectrum (curve 2) of the PDMS thin film treated by DPBS solution is at 3386cm -1 There is an obvious broad absorption peak nearby, which indicates that the nonionic surfactant β-D-dodecyl-N-maltose molecule with many hydroxyl groups is adsorbed onto the PDMS surface. Compared with the PDMS film treated with DPBS solution, the spectrum (curve 3) of the PDMS film treated with the DPBS solution containing streptavidin is at 3386cm -1 There were no obvious changes nearby, which indicated that the surfactant β-D-dodecyl-N-maltose effectively prevented the non-specific adsorption of streptavidin on the PDMS surface. However, when the biotinylated PDMS film was modified with streptav...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com