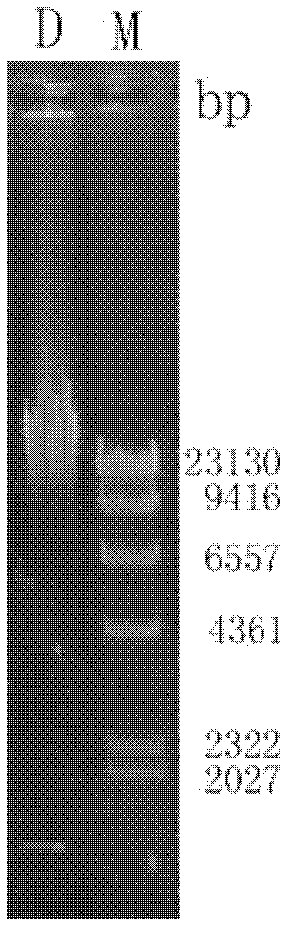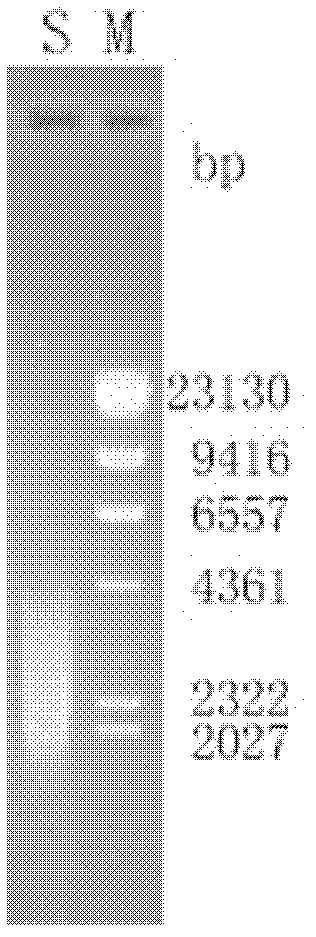Lipase for treating oil pollutants as well as encoding gene and application thereof
A technology that encodes a gene and lipase, which is applied in the field of lipase, can solve the problem of low efficiency of lipase gene expression, achieve high-efficiency expression, and improve the effect of expression activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1: the construction of activated sludge DNA library
[0024] 1. Extraction of activated sludge DNA
[0025] Sludge was collected from a food sewage treatment plant, and was properly diluted as a sample for DNA extraction. 12000r·min -1 Centrifuge for 5 minutes to collect samples, resuspend and wash once in TE, add lysozyme to a final concentration of 100 μg ml -1 , 37°C water bath for 2 hours. Add 5M NaCl to adjust the final concentration to 0.5M, mix well and add 40 μl of proteinase K and 20% SDS (final concentration is 0.5-1%), 37°C overnight or 50°C water bath for 3h until the solution is viscous and clear. Add 1 / 3 volume of saturated NaCl and shake vigorously for 15s, then 12000r·min -1 Centrifuge for 5 minutes, collect the supernatant into a sterilized centrifuge tube, add 0.6V isopropanol to mix and precipitate, 12000r·min -1 The precipitate was collected by centrifugation, washed with 70% ethanol, dried and dissolved in 400 μl sterilized deionized...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2: Screening and sequence analysis of lipase gene
[0036]The clones in the DNA library were cultured in LB liquid medium for 12 hours, after appropriate dilution, spread on the primary screening plate evenly coated with 2 drops of olive oil on the surface, cultured at 37°C for 24 hours, and selected on the plate The grown strains were inserted into the re-screened liquid medium, cultured at 37°C for 36 hours, and then the content of olive oil in each fermentation broth was determined. The strain with the strongest degradation ability to olive oil was selected, and the plasmid was extracted to sequence the inserted sequence. The lipase gene was named lipN, and the vector was named puc-lipN.
[0037] The sequencing results were compared with the NCBI Genbank database, and the results showed that no sequence homologous to the gene sequence was found in the database, which should be a new sequence. After the analysis of the lipase gene lipN, the possible codin...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Expression of lipase gene in yeast cells
[0040] 1. Construction of expression vector
[0041] Primers lipNF (ACTG AATTCATGTCCTATGTACCGTTCAG) and lipNR (ACTGCGGCCG CCTACCAGTGGGTCGTACCAA) were designed with EcoR I and Not I restriction sites respectively, and the plasmid puc-lipN was used as a template to amplify the lipase with EcoR I / Not I restriction sites Gene lipN, the PCR product was digested with EcoR I / Not I, and the 1.4 kb fragment was recovered, ligated with the same double digested pPIC9K (Invitrogen, USA), transformed into E.coli DH5α, and obtained the recombinant plasmid pPIC9K-lipN. The recombinant plasmid was verified by EcoRI / Not I double enzyme digestion. Enzyme digestion verification map such as image 3 shown.
[0042] 2. Prepare DNA for transformation
[0043] Linearize pPIC9k-lipN with Sal I or Sac I or Bgl II. For yeast cells, the transformant obtained by linearization with Sal I or Sac I has a His+Mut+ phenotype; the transformant ob...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com