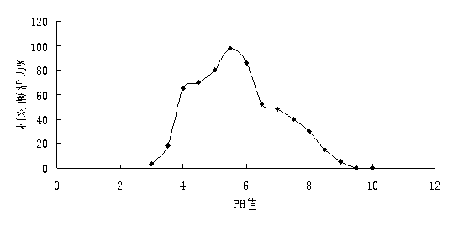
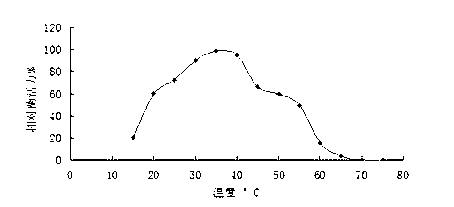
Laccase for biological treatment of papermaking wastewater and encoding gene as well as expression and application of encoding gene
A technology for papermaking wastewater and laccase, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as inability to completely eliminate wastewater, and achieve the effect of improving expression vitality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1 : Construction of activated sludge DNA library
[0023] 1. Extraction of activated sludge DNA
[0024] Sludge was collected from a papermaking wastewater treatment plant, and was properly diluted as a sample for DNA extraction. 12000 rpm -1 Collect samples by centrifugation for 5 min, resuspend in TE and wash once, then add lysozyme to a final concentration of 100 μg·ml -1 , 37 ℃ water bath for 2 hours. Add 5 M NaCl to adjust the final concentration to 0.5 M, mix well, add 40 μl proteinase K and 20% SDS (final concentration is 0.5-1%), and store at 37 °C overnight or in a water bath at 50 °C for 3 h until the solution is viscous and clear. Add 1 / 3 volume of saturated NaCl, shake vigorously for 15 s, 12000 r·min -1 Centrifuge for 5 min, collect the supernatant into a sterilized centrifuge tube, add 0.6 V isopropanol to mix and precipitate, 12000 r min -1 The precipitate was collected by centrifugation, washed with 70% ethanol, dried and dissolved in 40...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 : Screening and sequence analysis of laccase genes
[0035] The clones in the DNA library were cultured and preserved separately, and the positive clones and the highly efficient laccase-producing transformants were screened.
[0036] Primary Screening Medium
[0037]Bavendamm's reaction medium: add tannic acid to the PDA solid medium to make the final concentration 0.4 mmol l / L;
[0038] Oxidation zone assay medium: Add guaiacol to PDA solid medium to make the final concentration 0.04%.
[0039] Re-screening medium
[0040] 200 g of potatoes, 20 g of glucose, 3 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 1.5 g of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 1 g of yeast extract, 1 000 mL of distilled water, boil and filter, after cooling, divide into 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks, each bottle Inject 50 mL of culture medium.
[0041] Enzyme-producing basal medium
[0042] Glucose 30 g, sodium nitrate 2 g, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.5 g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate tri...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3 : Expression of laccase gene in yeast cells
[0051] 1. Construction of expression vector
[0052] Digest puc-LacN with EcoRI / NotⅠ, recover the exogenous fragment, insert it into the Pichia pastoris constitutive expression vector pGAPZaA (Invitrogen, USA) with the correct reading frame, connect and transform E. coli DH5α, the recombinant plasmid pGAPZaA-LacN was obtained. The recombinant plasmid was verified by EcoRI / NotI double enzyme digestion.
[0053] 2. Preparation of competent cells for electroporation
[0054] In a 50 ml centrifuge tube containing 5 ml YPD, culture yeast cells for 30 overnight; take 30~50 ul of the overnight culture, inoculate a 250 ml shake flask containing 50 ml of fresh medium, grow overnight until OD600=1.3~1.5 ;Collect the cells by centrifugation at 1500 g at 4°C for 5 min, and suspend the cells with 50 ml of pre-cooled sterile water; centrifuge as above, and suspend the cells with 25 ml of pre-cooled sterile water; Suspen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com