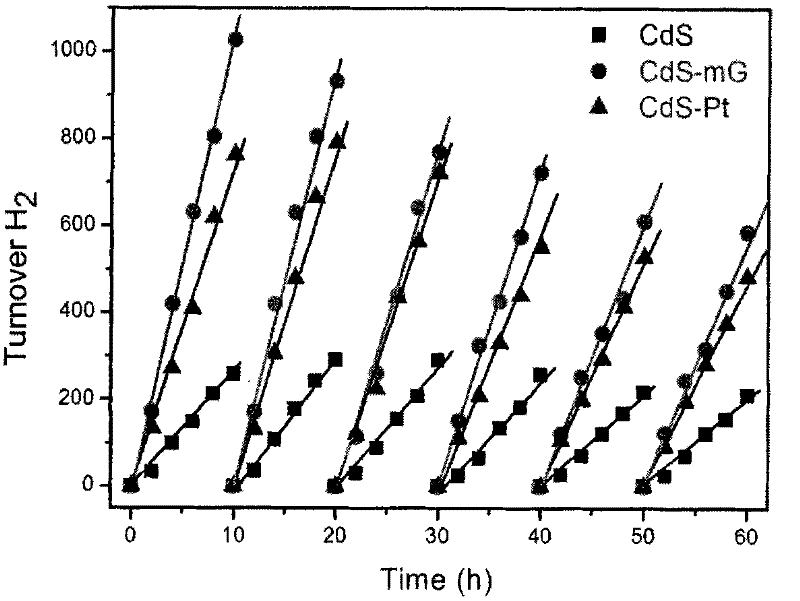
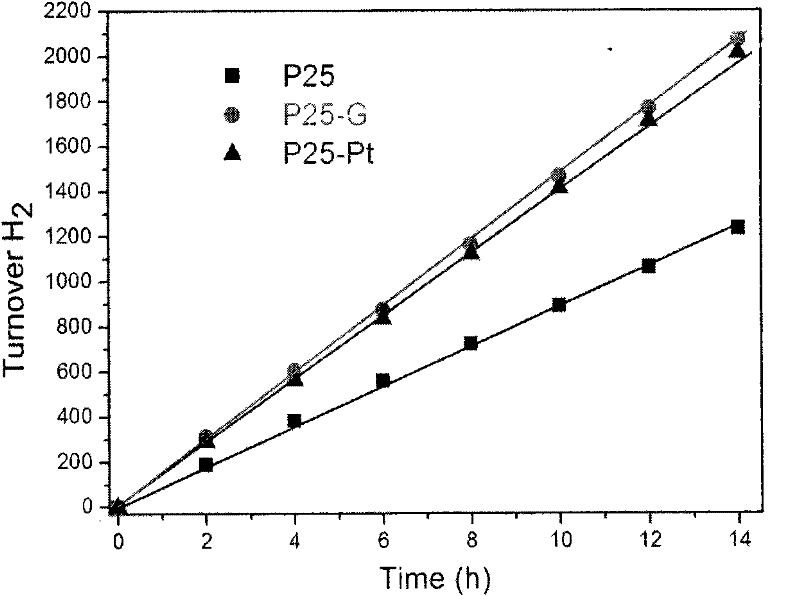
Preparation method of a novel catalyst for hydrogen production by photolysis of water without precious metals
A technology of photolysis of water to produce hydrogen and photocatalyst, which is applied in the field of photocatalysis technology and environmental science, can solve the problems of expensive precious metals, difficult to recycle, and unfriendly environment, and achieve the effects of low cost, increased efficiency, and promoted effective separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: 2 mg of sulfonated graphene is dispersed in 20 mL of deionized water for 30 min, and 6 mL of 0.1 mol / L CdCl is added dropwise 2 solution, stirred for 2 hours, then added dropwise 10mL of 0.05mol / L Na 2 S solution, and stirred for 3 hours, filtered and washed several times, and dried in a vacuum environment at 70°C.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2: Disperse 2 mg of graphene oxide in a mixed solvent of 20 mL of water and 10 mL of ethanol, and oscillate ultrasonically for 1 hour to make the dispersion uniform. Then add 200 mg of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (P25, Degussa, Germany), fully stir for 2 hours, put it into a 50 mL stainless steel reaction kettle, heat at 120 ° C for 3 h, filter and wash it for many times, and put it in a vacuum environment of 70 ° C dry.
Embodiment 3
[0024] Embodiment 3: the preparation method of simple CdS nanoparticle is as embodiment 1, the CdCl of 6mL 0.1mol / L 2 solution, stirred for 2 hours, then added dropwise 10mL of 0.05mol / L Na 2 S solution, and stirred for 3 hours, filtered and washed several times, and dried in a vacuum environment at 70°C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com