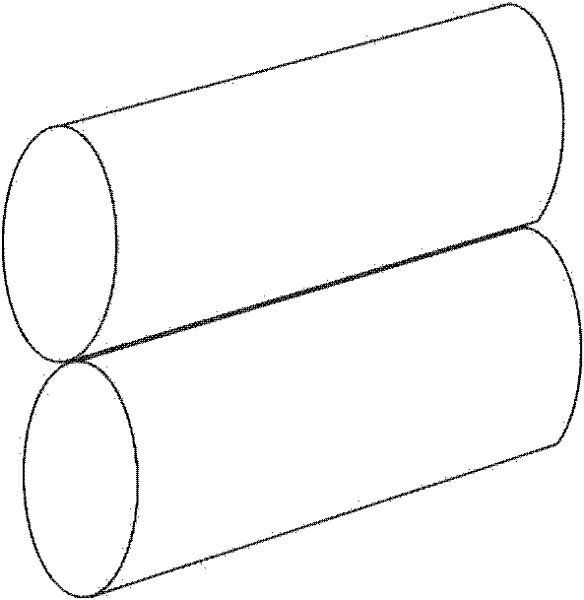
Side-pumped optical fiber structure and manufacturing method thereof
A technology for pumping optical fibers and manufacturing methods, which is applied in the direction of cladding optical fibers, manufacturing tools, and glass manufacturing equipment. Smaller area, improved pumping efficiency, and better operability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
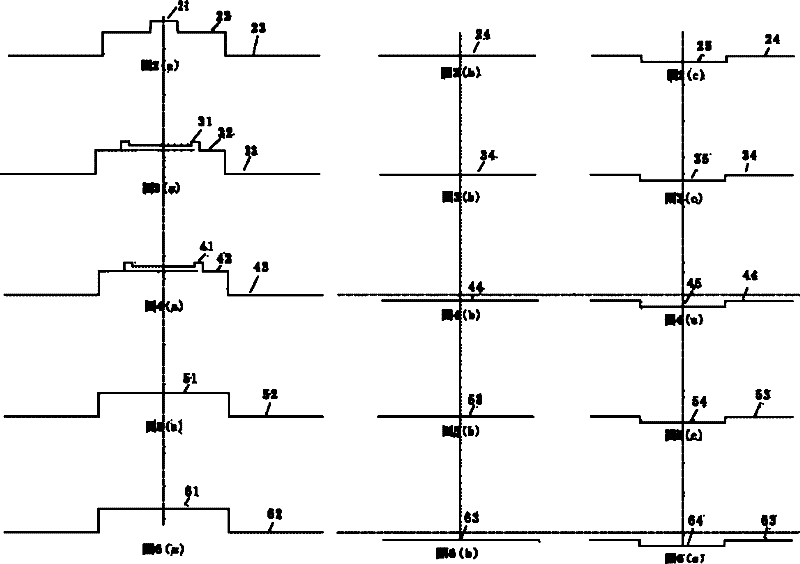
[0066] like Figure 2(a) ~ Figure 2(c) As shown, the refractive index distribution of the active optical fiber of this embodiment is shown in FIG. 2( a ), which is divided into three layers, and the core 21 is made of ytterbium-doped silica glass, which has the highest refractive index. Surrounding the core 21 is an annular inner cladding 22 of quartz glass doped with aluminum. The inner cladding 22 has a lower refractive index than the core 21 , and the difference between the two is 0.0007. The outermost outer cladding layer 23 is made of high-purity quartz glass, whose refractive index is lower than that of the inner cladding layer 22, and the difference between the two refractive indices is 0.004. Passive optical fiber 24 can be a single high-purity quartz glass material, and its refractive index is 1.4575, as shown in Figure 2 (b); it can also be a high-purity quartz glass material with a small amount of fluorine element doping 25, and its refractive index is 1.4572, as s...
Embodiment 2
[0082] like Figure 3(a) ~ Figure 3(c)As shown, other structures of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 1, the only difference lies in the refractive index distribution and size parameters of the active optical fiber. As shown in Fig. 3 (a), this active optical fiber is also divided into three layers of core 31, inner cladding 32 and outer cladding 33, the refractive index of the center of the core 31 is uniform, and the refractive index of the edge of the core 31 is higher than that of the center of the core 31. The index is slightly higher, and the refractive index difference Δ between the two is 0.0002. This design can make the Gaussian energy distribution of the fiber core 31 expand to the edge of the fiber core 31 under high power working conditions, so that the laser energy is relatively evenly distributed in the fiber core 31 region, avoiding the fiber core 31 region. Central energy density is too high. like Figure 3(b) and 3(c) As shown, the refrac...
Embodiment 3
[0085] like Figure 4(a) ~ Figure 4(c) As shown, in this embodiment, the refractive index distribution of the active fiber is the same as that of the active fiber in Embodiment 2. The only difference is its passive optical fiber 44 . The refractive index of the passive optical fiber 44 is 1.4570, which is slightly lower than the refractive index of the glass material of the outer cladding 43 of the active optical fiber. The center of the passive optical fiber can also be a glass material with more fluorine element doping 45, and its refractive index is slightly 1.4565. . In this embodiment, the diameters of the active fiber and the passive fiber are both 250 μm. Wherein, the diameter of the core 41 of the active optical fiber is 25 μm, the numerical aperture of the inner cladding 42 relative to the core 41 is 0.02, and the numerical aperture of the outer cladding 43 relative to the inner cladding 42 is 0.04.
[0086] The preparation method of this embodiment is also the sam...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com