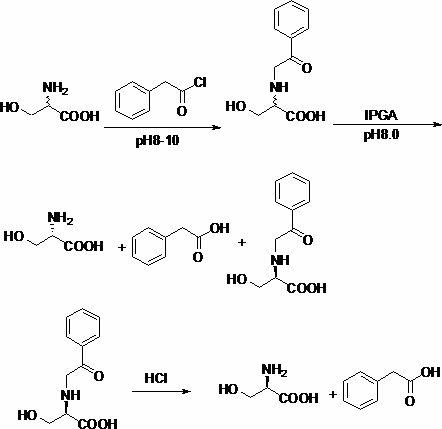
Chemical-enzymatic method for preparing D-serine
A technology of serine and phenylacetylserine, which is applied in the field of chemical-enzymatic preparation of D-serine, can solve the problems of poor selectivity and the optical purity of D-serine cannot meet the quality requirements, so as to reduce the process cost, easy to obtain the source, and high The effect of optical activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1: Preparation of DL-N-phenylacetylserine
[0021] 42g (0.4mol) of DL-serine and 40g (1.0mol) of NaOH were dissolved in 400ml of water, then cooled to 0°C in an ice bath, and 64ml (0.48mol) of phenylacetyl chloride was added dropwise. The rate of addition is controlled, and the temperature of the reaction solution does not exceed 5°C. After the dropwise addition, the stirring reaction was continued for 12h. The reaction solution was adjusted to a pH of about 1-2, filtered with suction, the solid was washed twice with water, and dried to obtain 86 g of DL-N-phenylacetylserine with a yield of 96.4%.
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2: DL-N-phenylacetylserinase-catalyzed hydrolysis
[0023] Add 66.9g (0.3mol) of DL-N-phenylacetylserine to 600ml of water, adjust the pH to 8.0 with ammonia water until completely dissolved, add 13g of immobilized penicillin acylase, and stir for 28 hours at room temperature. After the reaction was completed, the immobilized penicillin acylase was removed by suction filtration. CuSO was added to the filtrate 4 ·5H 2 O 18.8g, suction filtration, remove L-serine copper complex. The filtrate was adjusted to pH 1-2 with concentrated hydrochloric acid, filtered with suction, the solid was washed with cold water, and dried to obtain 32 g of D-N-phenylacetylserine with a yield of 47.8%.
Embodiment 3
[0024] Example 3: D-serine preparation
[0025] Add 32g of D-N-phenylacetylserine into 200ml of 6mol / L hydrochloric acid, acidify at 100°C for 8h, and add 10g of activated carbon for decolorization. Concentrate the decolorized solution to 40 ml, extract three times with ethyl acetate (40ml×3), adjust the pH of the aqueous layer to 5.8 with ammonia water, let stand overnight at 0-5°C, filter and wash the filter cake with a small amount of deionized water, and dry it 13.6 g of D-serine was obtained, the yield was 90%, and the ee measured by HPLC was 99.6%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com