Sintering ore cooling device and waste heat recovery system thereof
A technology for sintering and waste heat, which is applied in steam engine installations, waste heat treatment, lighting and heating equipment, etc. It can solve the problems of large one-time investment, large floor space, high operation and maintenance costs, and achieve the effect of high heat exchange efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
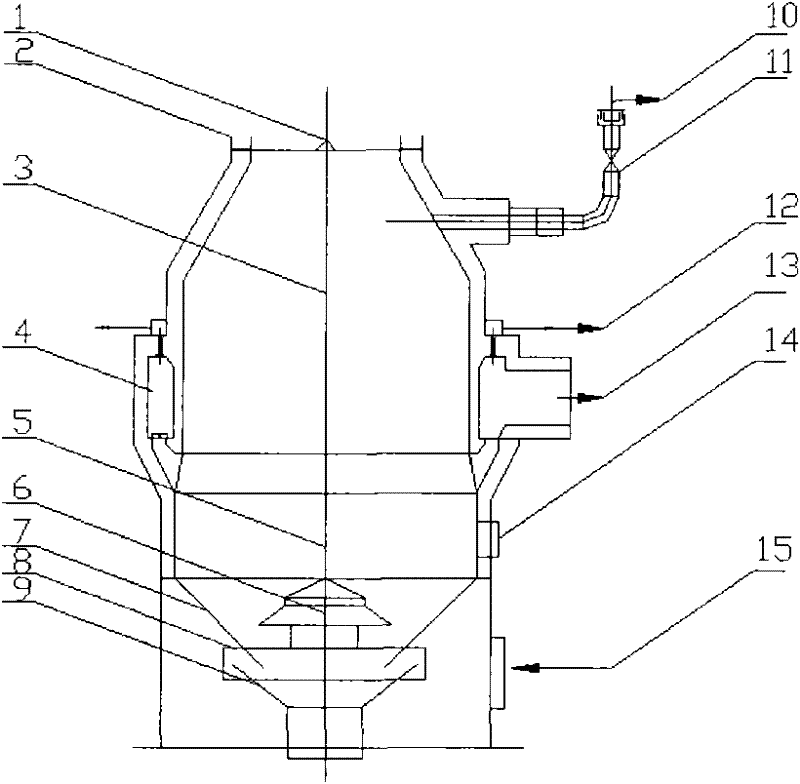
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
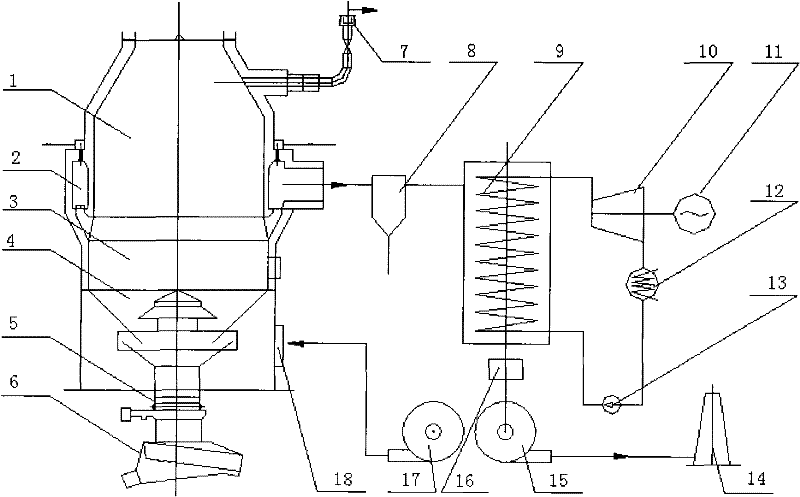
[0028] The temperature of the sinter leaving the sintering machine is 700-750°C. The design parameters are sintered ore 50t / h, 700℃. The heat dissipation of the cold ore furnace body is considered at 4%, and the cooling medium can obtain 7520kW of heat. 7520kW can drive 37054m of cold air at 20°C 3 / h heated to 550°C. The 550°C hot air heats the steam from the waste heat boiler to the design steam parameters and consumes 773kW. The cooled air is 500°C, which is used as the heat source of the waste heat boiler. 500°C air from waste heat boiler superheater and 235°C air from sintering machine 77111m 3 / h after mixing, it enters the evaporation part of the waste heat boiler, and heats water at 20°C to 2.5MPa saturated steam at 223.9°C. The 150°C medium after heat release is discharged into the atmosphere. The total air volume flowing through the heat exchanger is 114165m 3 / h.
[0029] The running time of the sintering machine and the cold ore furnace is 7680 hours (runni...
Embodiment 2
[0032]The temperature of sinter leaving the sintering machine is considered to be 500-600°C. The design parameters are sintered ore 50t / h, 550℃. The heat dissipation of the cold ore furnace body is considered at 4%, and the heat that can be recovered by sintering is 4472kW. Use 300°C sintering waste gas to increase the cold air from 20°C to 150°C and send it to the cold ore furnace to recover the heat of sintering ore. The required air volume is 45,000 cubic meters per hour. The heating surface of the waste heat boiler is divided into three parts. The first part raises the cold water from 20°C to 150°C to become hot water; the second part heats the 150°C hot water to the saturated steam temperature of 224°C under the pressure of 2.5MPa; the third part realizes steam superheating. Since the heat of sintered ore is not enough to realize the above process, 3278kW of additional heat is required, and 3380Nm3 / h of blast furnace gas of 3500kJ / Nm3 is required.
[0033] Cold air an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com