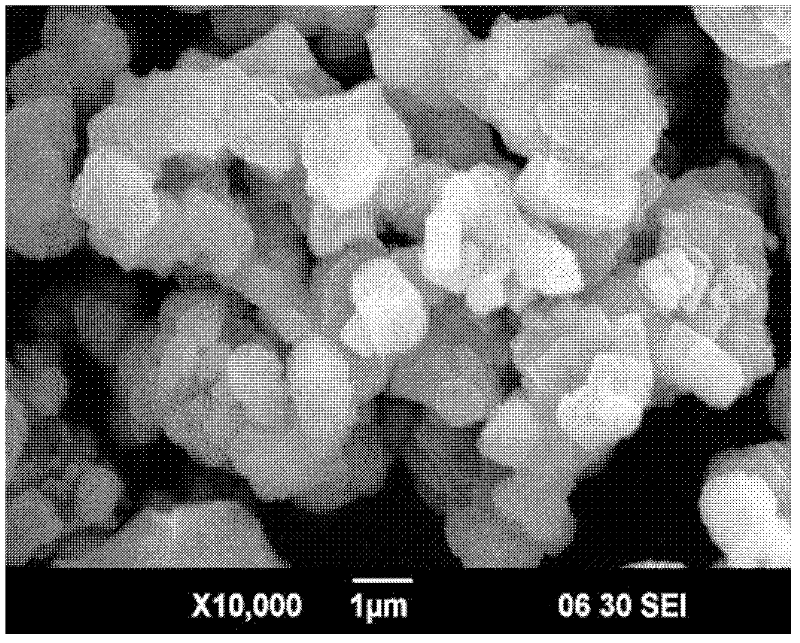
Preparation method of LiFePO4 lithium ion battery powder
A lithium-ion battery, PO4 technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of long synthesis cycle, large drying shrinkage, etc., achieve short reaction time, complete particles, and improve electrical properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] 1) Analytical pure LiOH·H 2 O and NH 4 h 2 PO 4 with FeC 2 o 4 2H 2 O according to Li:PO 4 : Fe = 3: 1: 1 molar ratio is added to deionized water, and after sealing, it is placed on a constant temperature heating magnetic stirrer and stirred to prepare Fe 2+ Solution A with a concentration of 0.2mol / L;
[0018] 2) Press LiOH·H 2 O and FeC 2 o 4 2H 2 The mass ratio of O mass sum and citric acid is 1: 0.5 in solution A, add analytically pure citric acid (C 6 h 8 o 7 ·H 2 (0), magnetic stirring under normal temperature evenly obtains solution B;
[0019] 3) Add activated carbon to solution B at a molar ratio of Fe:C=1:4, and stir magnetically at room temperature to obtain solution C;
[0020] 4) adjusting the pH value of solution C to 8.0 to obtain a reaction solution;
[0021] 5) Pour the reaction solution into an ultrasonic hydrothermal kettle, seal the hydrothermal kettle, and put it into a temperature-pressure dual-control ultrasonic hydrothermal react...
Embodiment 2
[0024] 1) separate analytically pure Li 2 CO 3 and NH 4 h 2 PO 4 with FeC 2 o 4 2H 2 O according to Li:PO 4 : Fe = 1: 3: 0.5 molar ratio is added to deionized water, sealed and placed on a constant temperature heating magnetic stirrer to stir to prepare Fe 2+ Solution A with a concentration of 0.1mol / L;
[0025] 2) Press Li 2 CO 3 and FeC 2 o 4 2H 2 The sum of O mass and citric acid are 1: 1.5 mass ratios in solution A, add analytically pure citric acid (C 6 h 8 o 7 ·H 2 (0), magnetic stirring under normal temperature evenly obtains solution B;
[0026] 3) Add activated carbon to solution B at a molar ratio of Fe:C=1:5, and stir magnetically at room temperature to obtain solution C;
[0027] 4) adjusting the pH value of solution C to 3.0 to obtain a reaction solution;
[0028] 5) Pour the reaction solution into an ultrasonic hydrothermal kettle, seal the hydrothermal kettle, and put it into a temperature-pressure dual-control ultrasonic hydrothermal reactor ...
Embodiment 3
[0031] 1) Analytical pure LiOH·H 2 O and NH 4 h 2 PO 4 with FeC 2 o 4 2H 2 O according to Li:PO 4 : The molar ratio of Fe=0.5:12:2 is added into deionized water, sealed and placed on a constant temperature heating magnetic stirrer to stir and prepare Fe 2+ Solution A with a concentration of 0.5mol / L;
[0032] 2) Press LiOH·H 2 O and FeC 2 o 4 2H 2 The sum of O mass and citric acid is 1: 2 solution B;
[0033] 3) Add activated carbon to solution B at a molar ratio of Fe:C=1:1, and stir magnetically at room temperature to obtain solution C;
[0034] 4) adjusting the pH value of solution C to 5.0 to obtain a reaction solution;
[0035] 5) Pour the reaction solution into an ultrasonic hydrothermal kettle, seal the hydrothermal kettle, and put it into a temperature-pressure dual-control ultrasonic hydrothermal reactor for reaction. The hydrothermal temperature is controlled at 220°C, the pressure is controlled at 5.0MPa, and the ultrasonic power Control at 1000w, reac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com