Peanut development gene, and application and detection method thereof
A peanut and gene technology, applied in the field of agricultural biology, can solve problems such as insufficient research depth, and achieve the effect of simple experimental design, good versatility, and high degree of automation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
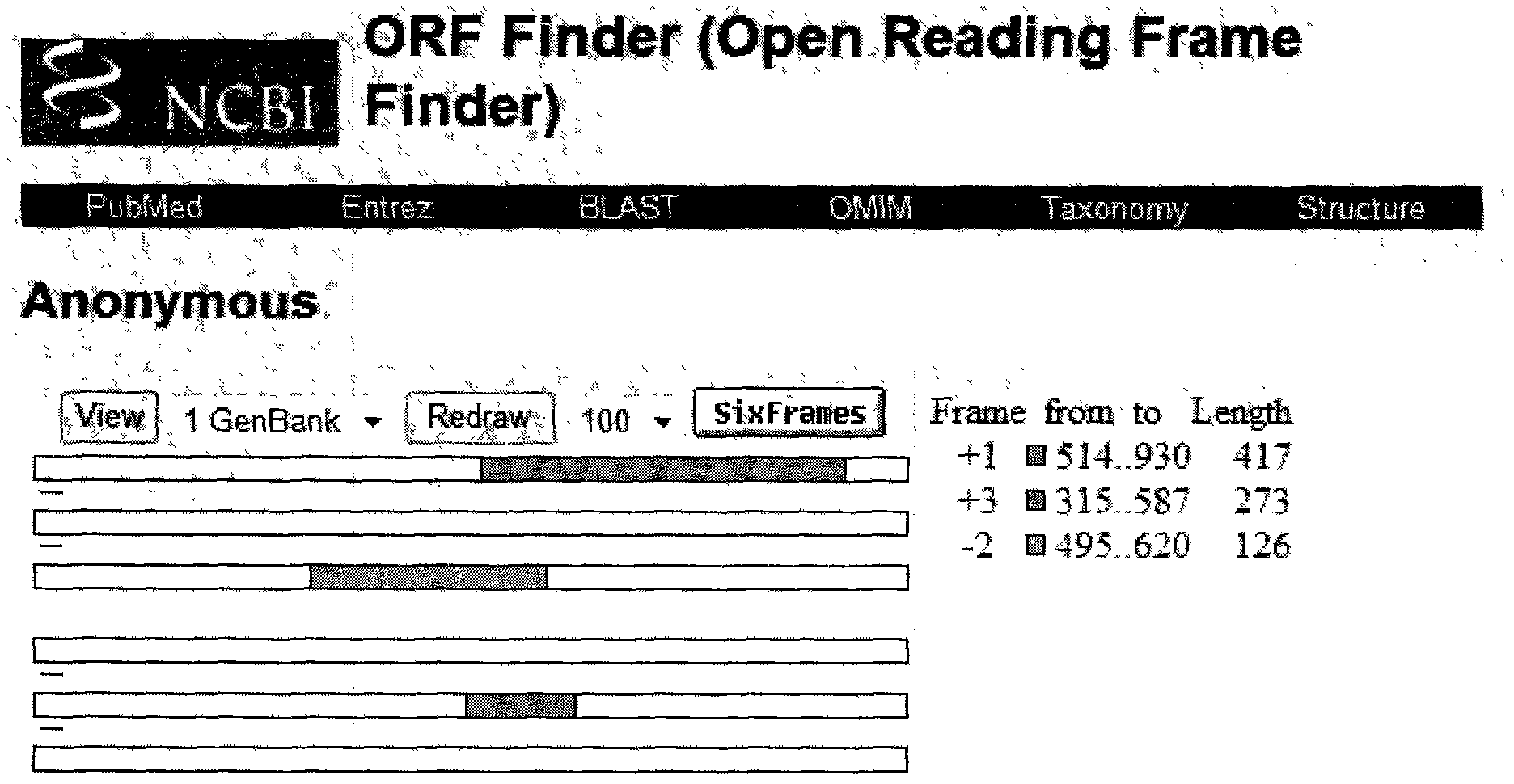
[0023] Example 1: Acquisition of peanut growth and development gene Ah56
[0024] 1. Extraction of total RNA from peanut tissue
[0025] Experimental preparation: All utensils used need special treatment. High-temperature-resistant instruments and utensils were baked at 200°C for 8 hours, and other utensils were soaked in 0.1% DEPC for 12 hours, and then removed by autoclaving to remove DEPC. The solution reagents are treated with 0.1% DEPC (sterilized after 12 hours at 37°C), and the reagents that are not resistant to high temperature are directly treated with DEPC-H 2 O preparation. Total RNA was extracted according to the operation requirements of GIBCOL's Trizol Reagent, and the specific steps were as follows:
[0026] 1) Take the young peanut leaves and grind them into powder in liquid nitrogen, then add 1 ml of Trizol solution for every 50 mg of tissue to grind, and note that the total volume of the sample should not exceed 10% of the volume of the Trizol used.
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2: A method for detecting the function of peanut growth and development gene Ah56 using fluorescent quantitative PCR technology
[0072] Follow the steps below to check:
[0073] Total RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis
[0074] Extract the total RNA of peanut leaves, with reference to the test method in Example 1, reverse transcription process:
[0075]
[0076] The system was placed at 37°C for 15 minutes, and the cDNA product was stored at -20°C.
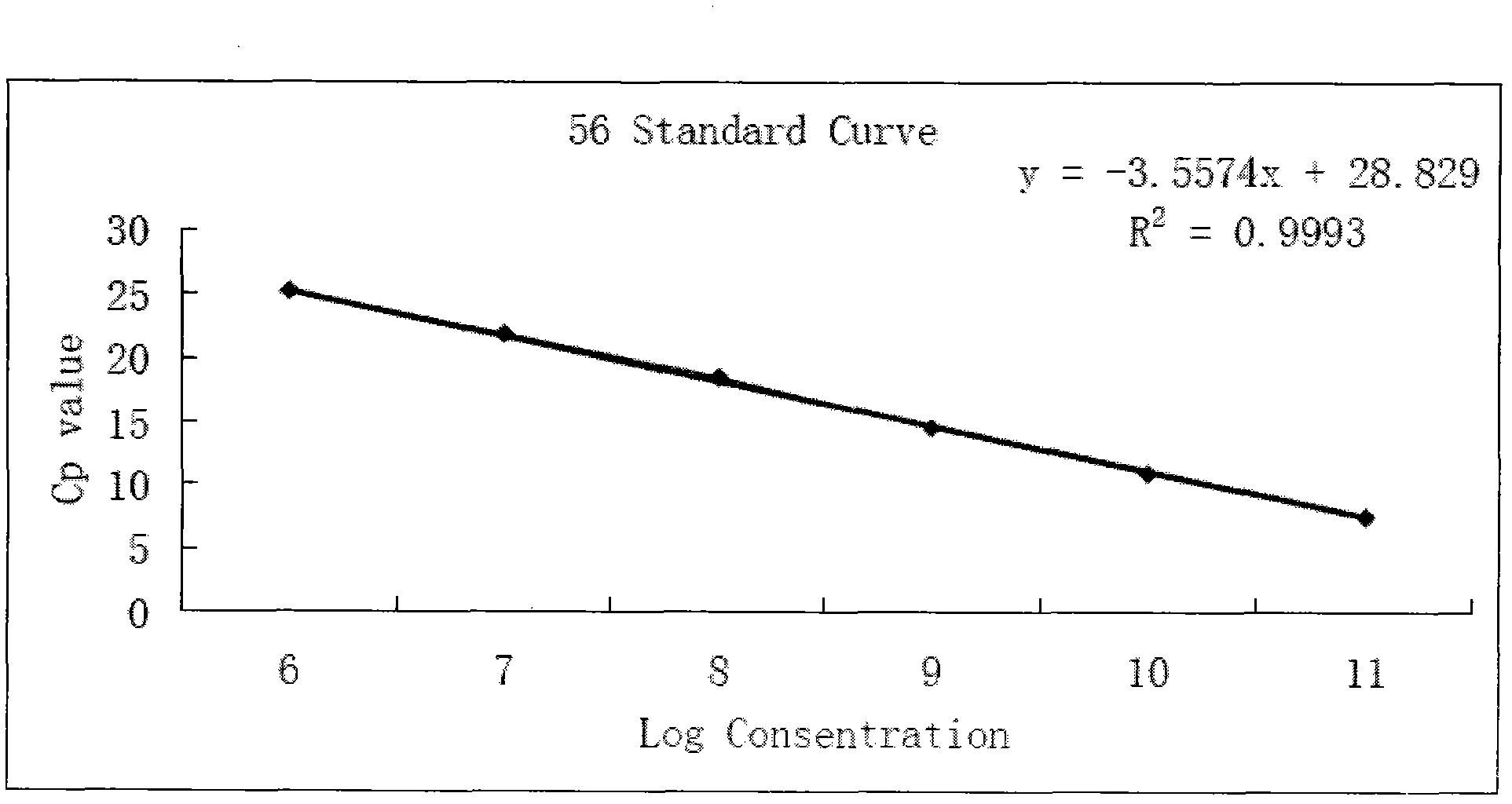
[0077] Drawing of standard curve
[0078] Design a pair of PCR primers according to the cloned gene fragment: Ah56f-4 and Ah56r-4, extract the total RNA of peanut seed coat, reverse transcribe it into cDNA, use it as a template, carry out PCR amplification, recover the amplified product, and convert the PCR product Connect with pMD-18, then transform Escherichia coli DH5α, after colony PCR identification, a large number of positive clones are amplified, the plasmid is extracted, the obtained plasmid is dil...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3: A method for detecting the specific expression of peanut growth and development gene Ah56 by using fluorescent quantitative PCR technology
[0090] In order to detect the specific differential expression of peanut growth and development gene Ah56, two varieties, Zhongkai 111 and Zhonghua 4, were selected and carried out in a constant temperature culture room. After soaking the seeds of the above varieties in tap water overnight, they were planted in plastic pots of the same size, two in each pot, and the cultivation carrier was common soil, and 10 pots of each variety were sown. For normal culture, samples were taken at different growth stages of peanuts, and the sampling parts were roots, stems, and leaves, which were stored in a -80°C refrigerator after being treated with liquid nitrogen. Total RNA was extracted from peanut seed coat and reverse transcribed into cDNA. (method is with embodiment 1 and 2).
[0091] Adopt the detection method described in th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com