Single-fiber device
A device and single-fiber technology, applied in the field of single-fiber devices, can solve the problems of loss of optical power and receiving sensitivity of optical devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
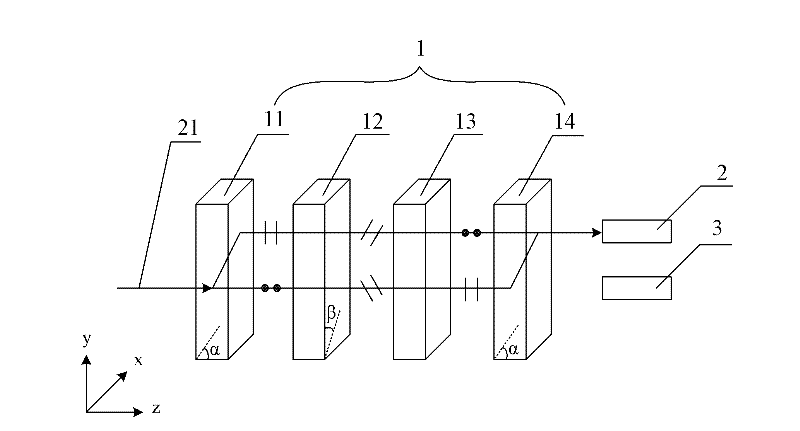
[0024] An embodiment of the present invention provides a single-fiber device, such as figure 2 As shown, it includes a first photodiode 2 (Photo Diode, PD) for receiving incident light 21 and a laser diode 3 (Laser Diode, LD) for emitting outgoing light, and also includes: The same wavelength splitter 1 in the forward direction, including the first birefringent plate 11, the half-wave plate 12, and the 45° Faraday rotation arranged in sequence along the positive direction (ie, the positive direction of the z-axis) and perpendicular to the positive direction (ie, the z-axis) sheet 13 and the same second birefringent sheet 14 as the first birefringent sheet 11; the angle between the optical axis of the first birefringent sheet 11 and the positive direction (ie, the positive direction of the z-axis) is α, 0°<α <90°; the angle between the e-axis of the half-wave plate 12 and the main section of the first birefringent plate 11 (ie, the zy plane) is β, β=67.5° or β=22.5°.
[0025]...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Based on the first embodiment, the embodiment of the present invention provides a single-fiber device, such as Figure 4 As shown, it also includes: a transceiver die 4 (Transistor Outline, TO), which is used to package the first photodiode 2 and the laser diode 3 together. The structure and principle of the same wavelength splitter 1 are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here. Preferably, the angle α between the optical axis of the first birefringent sheet and the positive direction is α=47.85°, so that the incident light is deviated by a relatively large distance.
[0031] Realize the single-fiber bidirectional device that encapsulates LD and PD in the same TO, and through the above-mentioned same-wavelength splitter, the separation of receiving and transmitting optical paths can be realized. Compared with the existing technology, there is no need to use partial transmission and partial reflection filters. In this way, theoretical lossless t...
Embodiment 3
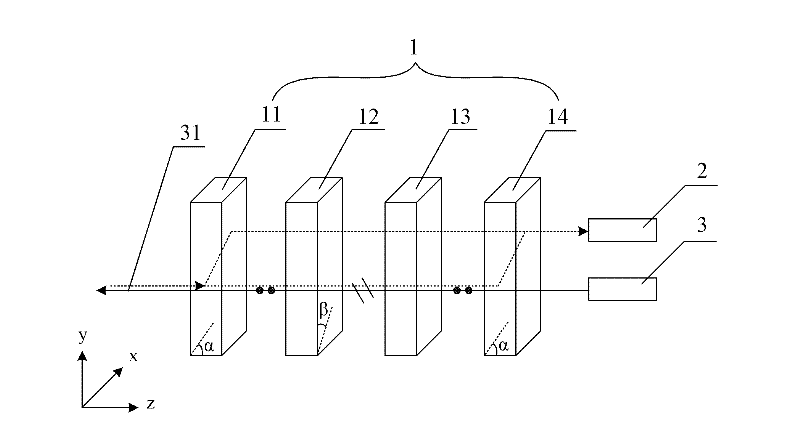
[0033] Based on the first embodiment, the embodiment of the present invention provides a single-fiber device, such as Figure 5 As shown, it also includes: a reflector 5 arranged on the incident light path between the first photodiode 2 and the same-wavelength beam splitter 1, used to reflect the incident light passing through the same-wavelength beam splitter 1, so that the first photodiode 2 Receive incident light; the first receiving die 22 is used to package the first photodiode 2 ; the emitting die 32 is used to package the laser diode 3 . The structure and principle of the same wavelength splitter 1 are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0034]The same wavelength single-fiber bidirectional optical device (Bi-Direction Optical Sub-Assembly, BOSA) is realized, and through the above-mentioned same wavelength splitter, the separation of receiving and transmitting optical paths can be realized. Compared with the prior art, there is no need to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com