Method for producing cellulose fiber-containing resin material
A technology of cellulose fibers and resin materials, which is applied in the field of thermoplastic resins, can solve the problems of undocumented organic solvent treatment methods, etc., and achieve the effect of improving heat resistance and tensile strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
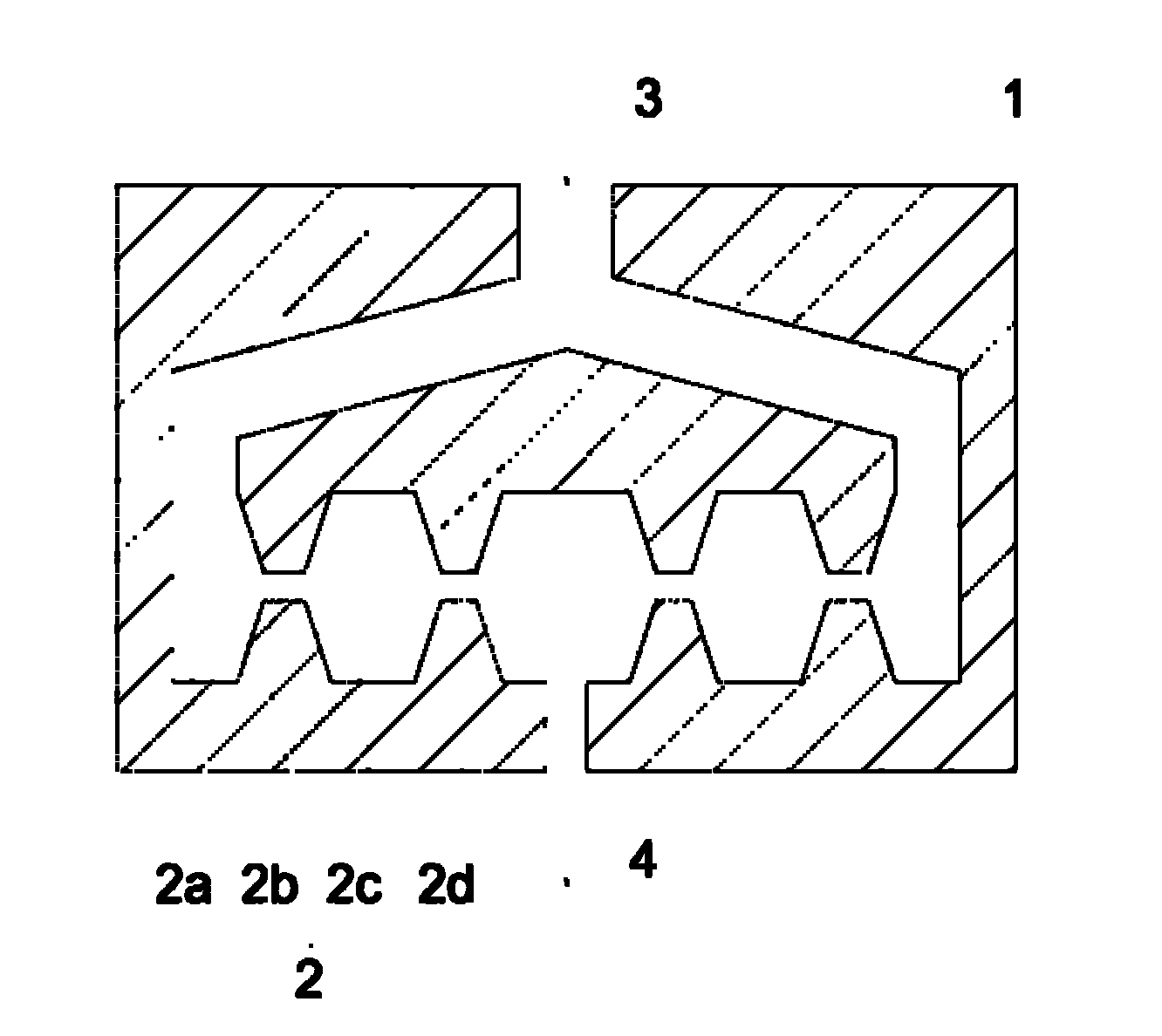
Image
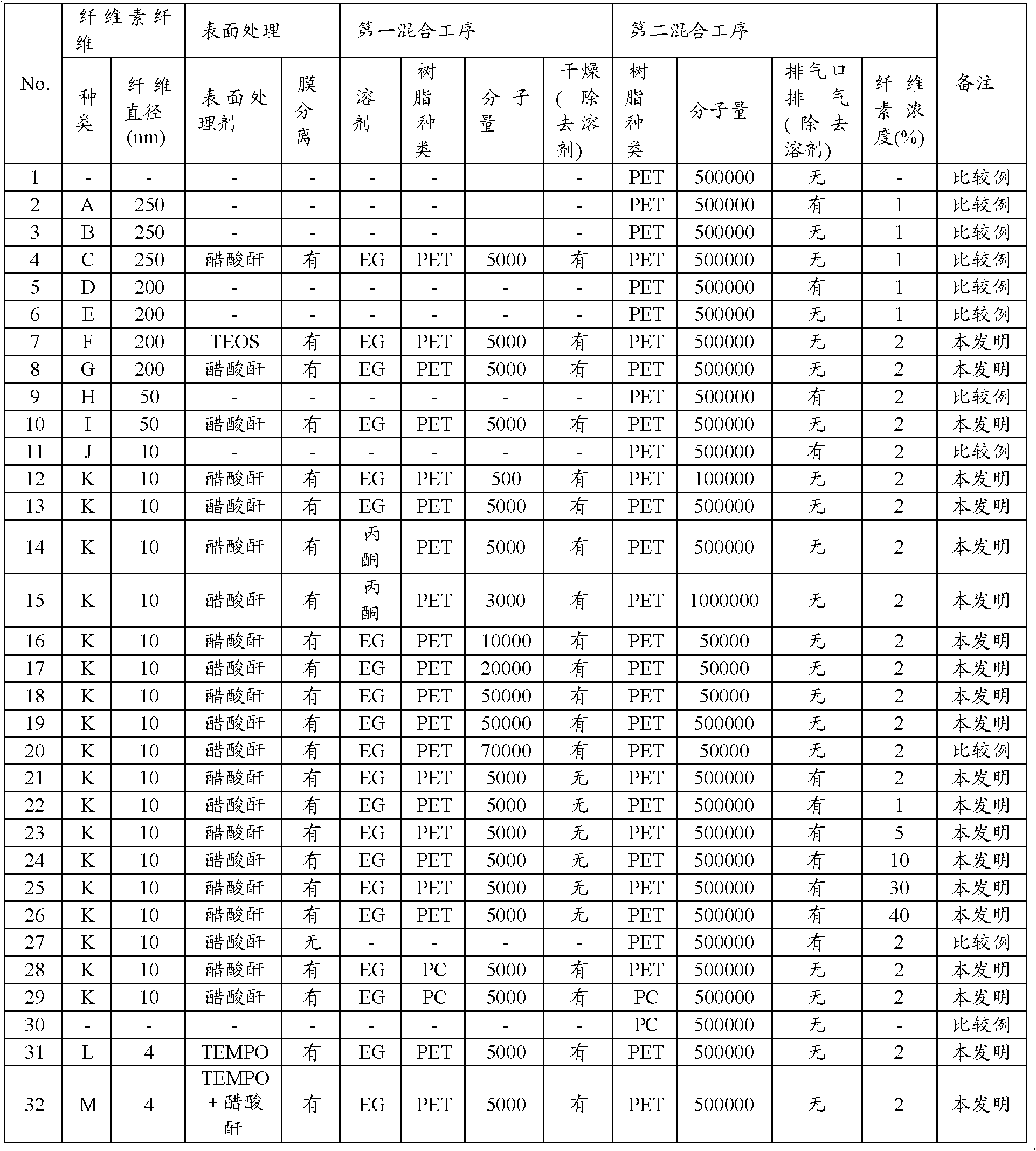
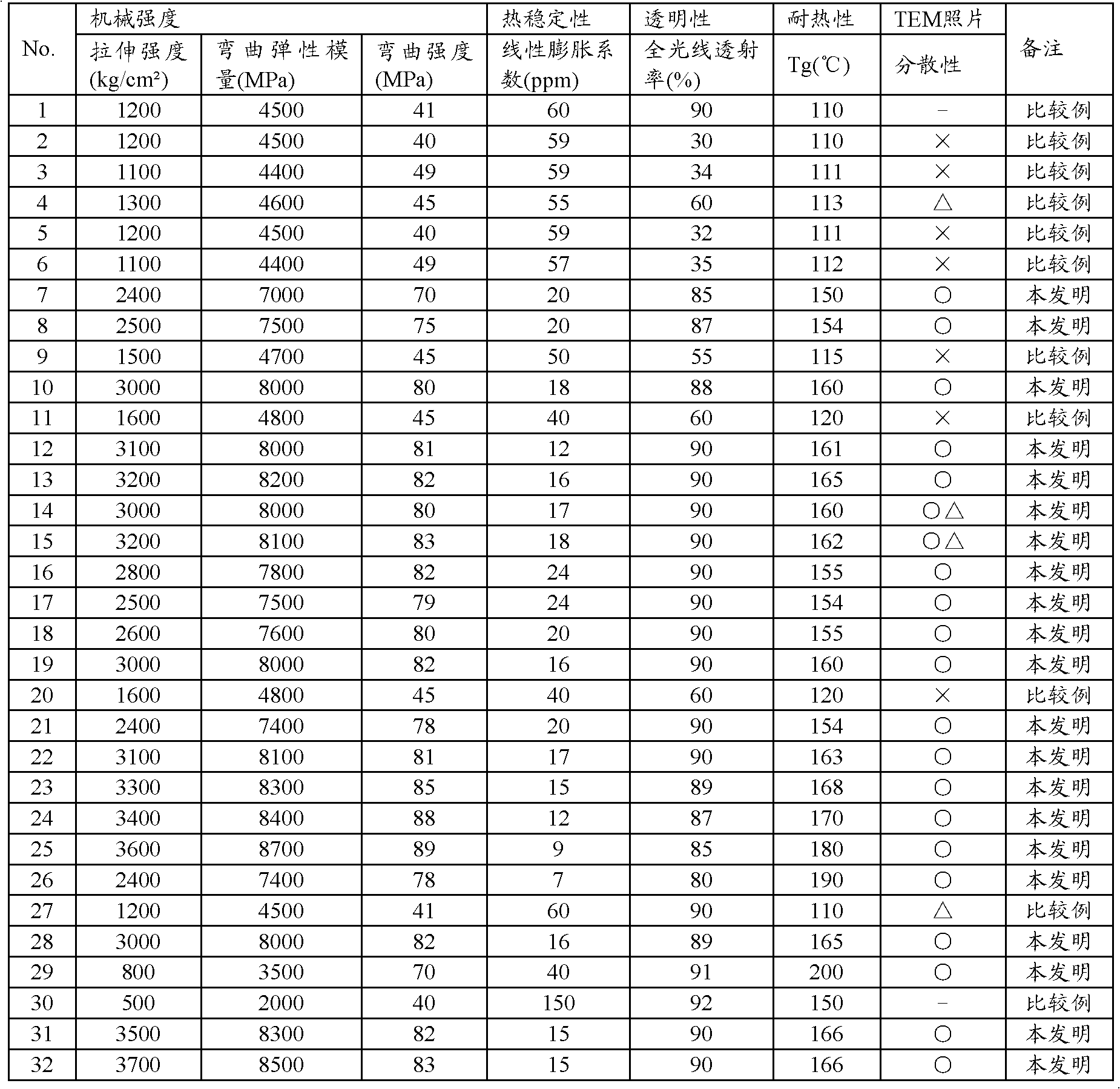
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0237]
manufacture example 1
[0244] A sample produced in the same manner as in Comparative Example 1 was set as cellulose fiber D except that the number of revolutions of Comparative Example 1 was changed to 10,000 revolutions / minute, and the spinning was performed for 15 minutes. It was confirmed that the fiber was spun into an average fiber diameter of 200 nm and microfibrillated.
manufacture example 2
[0246] The aqueous dispersion of cellulose fibers D produced in Production Example 1 was filtered, washed with pure water, and dried at 70° C. to obtain cellulose fibers E.
[0247] Add 5 parts by mass of cellulose fiber E to 100 parts by mass of ethanol and 1 part by mass of pure water to disperse it, and add 5 parts by mass of tetraethoxysilane to the dispersion over 60 minutes while stirring at 50°C The mixture was then further stirred for 2 hours. The obtained cellulose fibers were confirmed to have an average fiber diameter of 200 nm from the results of observation with a scanning electron microscope. Let the obtained sample be cellulose fiber F.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com