A building formwork material
A technology of building formwork and glass fiber, which is applied in the field of new building formwork materials, can solve the problems of inconvenient construction and transportation, heavy weight, insufficient toughness, etc., achieve excellent mechanical properties and processing performance, facilitate transportation and construction, and reuse many times. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
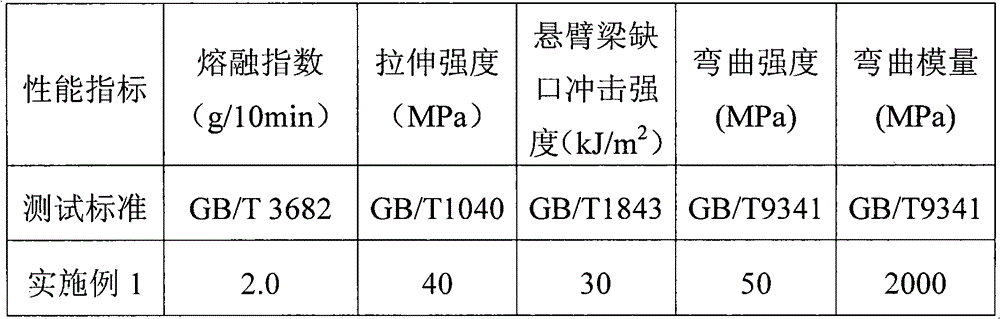
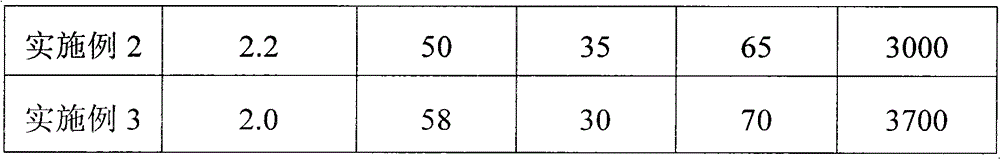
Examples
Embodiment 4
[0032] A preparation method of a novel building formwork material, comprising the following steps:
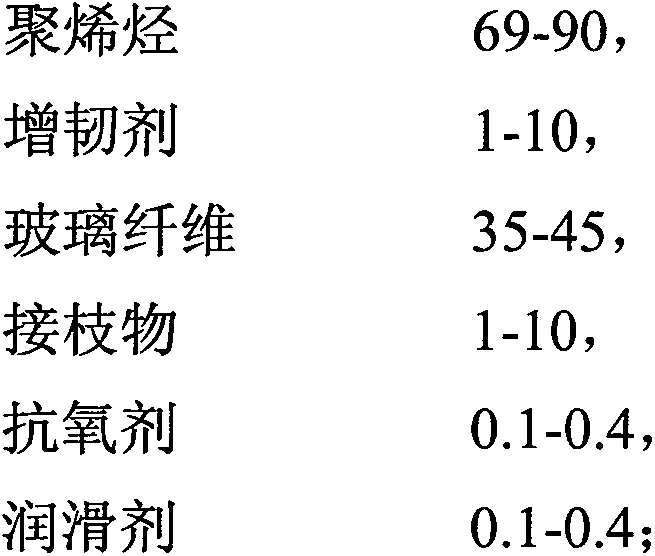
[0033] 50 parts by weight of polypropylene, 10 parts by weight of toughening agent EPDM, 45 parts by weight of E-glass fiber, 10 parts by weight of grafted maleic anhydride grafted polypropylene, 0.4 parts by weight of antioxidant DSTDP and lubrication 0.4 parts by weight of calcium stearate;
[0034] The polypropylene, toughening agent, graft, antioxidant and lubricant are weighed according to the proportion and then added to the high-speed mixer and mixed evenly. The mixed material is fed into the twin-screw extruder by a precisely metered feeder At the same time, glass fiber is added from the glass fiber inlet according to the above ratio, and is sheared and kneaded at high speed by twin-screw, extruded by machine head, drawn, air-cooled, pelletized, dried and packaged to obtain the new building formwork material .
Embodiment 5
[0036] A preparation method of a novel building formwork material, comprising the following steps:
[0037] 90 parts by weight of polyethylene, 1 part by weight of toughening agent ethylene-propylene copolymer, 5 parts by weight of C-glass fiber, 1 part by weight of grafted maleic anhydride grafted polyethylene, 1680.1 parts by weight of antioxidant and lubricant N.N 0.1 parts by weight of '-ethylene bis stearamide;
[0038] The polyethylene, toughener, graft, antioxidant and lubricant are weighed according to the proportion and then added to the high-speed mixer and mixed evenly. The mixed material is fed into the twin-screw extruder by a precisely metered feeder At the same time, glass fiber is added from the glass fiber inlet according to the above ratio, and is sheared and kneaded at high speed by twin-screw, extruded by machine head, drawn, air-cooled, pelletized, dried and packaged to obtain the new building formwork material .
Embodiment 6
[0040] A preparation method of a novel building formwork material, comprising the following steps:
[0041] 25 parts by weight of polypropylene, 50 parts by weight of polyethylene, 5 parts by weight of toughening agent ethylene-octene copolymer, 3 parts by weight of propylene-butene copolymer, 35 parts by weight of C-glass fiber, graft bismaleyl 7 parts by weight of imine, 10100.1 parts by weight of antioxidant, 1680.2 parts by weight of antioxidant and 0.2 parts by weight of lubricant calcium stearate, 0.15 parts by weight of N.N'-ethylene bis stearamide;
[0042] The polyolefin, toughener, graft, antioxidant and lubricant are weighed according to the proportion and then added to the high-speed mixer and mixed evenly. The mixed material is fed into the twin-screw extruder by a precisely metered feeder At the same time, glass fiber is added from the glass fiber inlet according to the above ratio, and is sheared and kneaded at high speed by twin-screw, extruded by machine head,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com