Novel polytetrafluoroethylene aqueous dispersion
A technology of polytetrafluoroethylene and dispersion, which is applied in the direction of textile, coating, fiber treatment, etc., can solve the problems of untaught water-soluble salt, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing yield and output
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0063] Preparation method of polytetrafluoroethylene dispersion
[0064] A typical aqueous dispersion polymerization process for the preferred PTFE polymer is to pass TFE gas into a reaction kettle containing heated fluorinated surfactant, paraffin wax and deionized water. A chain transfer agent may also be added if desired to reduce the molecular weight of the PTFE. The free radical initiator solution was added and additional TFE was added to maintain pressure as the polymerization proceeded. The heat evolved by the reaction was removed by circulating cooling water in the reactor jacket. After several hours, the feeds were stopped, the autoclave was evacuated and purged with nitrogen, and the native dispersion in the autoclave was transferred to a cooling vessel. The paraffin was removed and the aqueous dispersion was isolated and stabilized with nonionic surfactants.
[0065] The aqueous fluoropolymer dispersion of the present invention may be referred to as a stabilize...
Embodiment
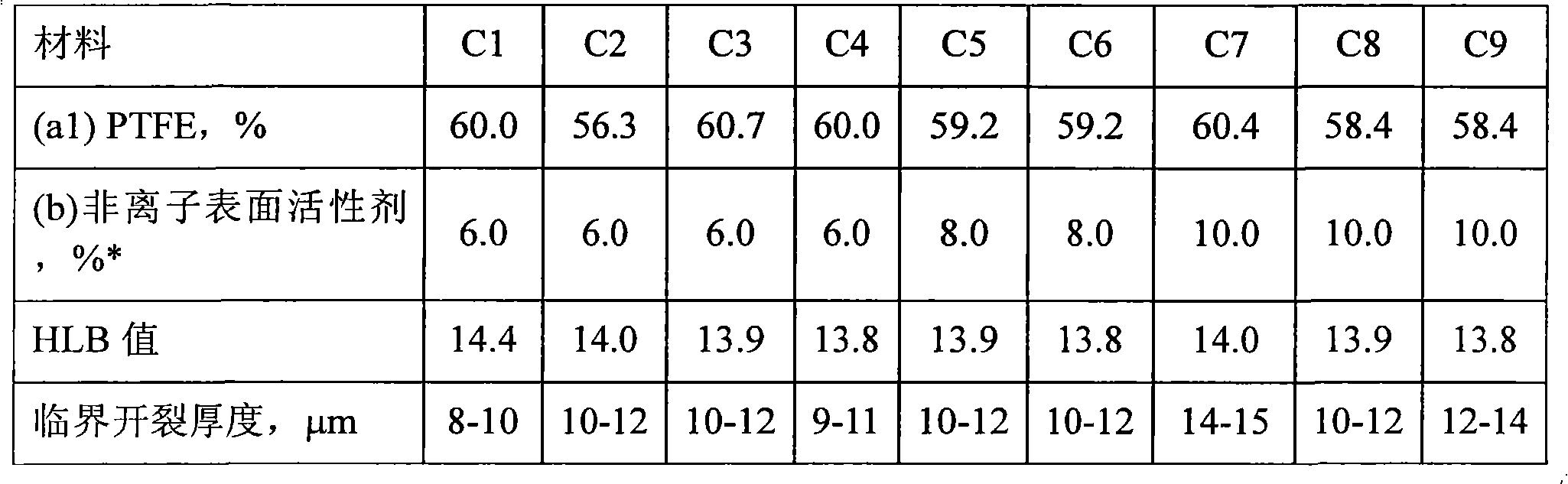
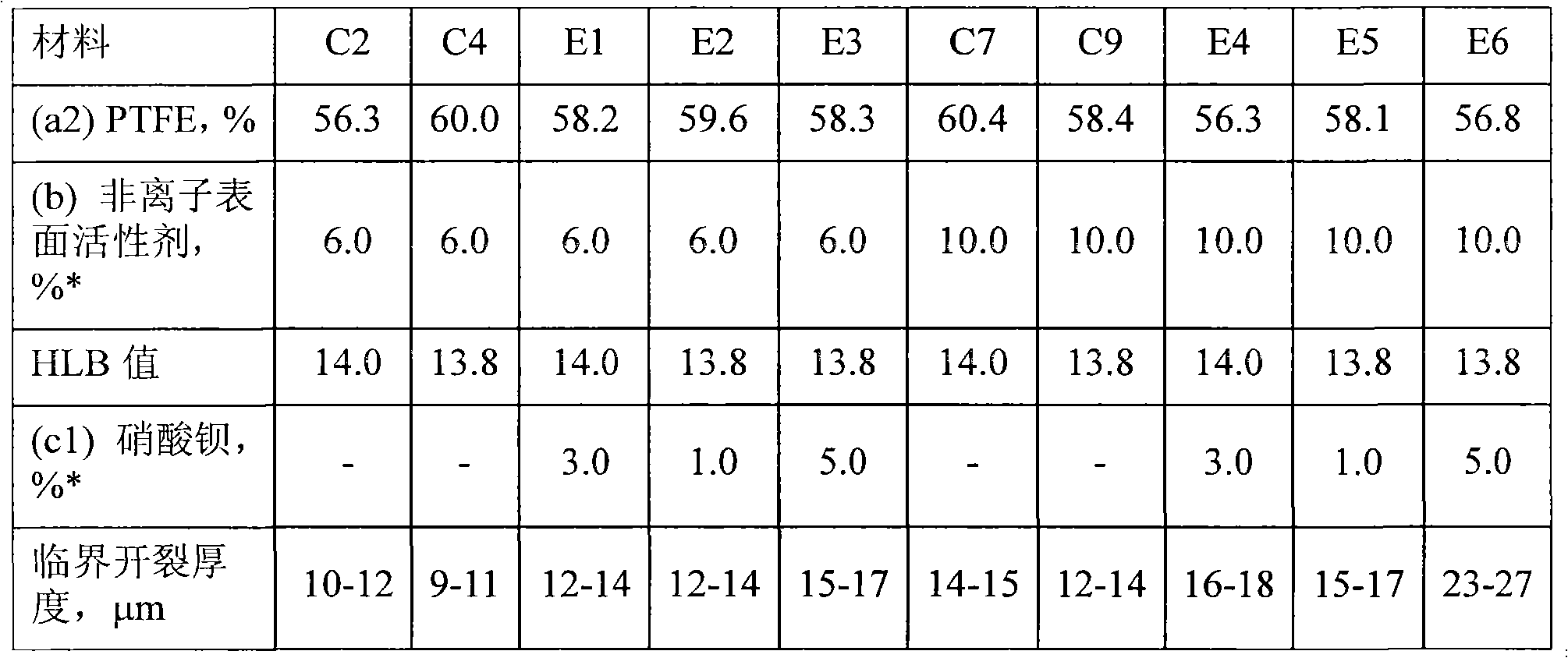
[0135] The abbreviation "E" means "Example", "C" means "Comparative Example", and the number following it indicates in which example the aqueous dispersion was prepared. All examples and comparative examples were prepared and tested in the same way. Percentages are by weight unless otherwise indicated.
[0136] Material
[0137] (a1) PTFE: A primary dispersion comprising about 41 to about 43% by weight of core / shell PTFE having an average particle size of 270 nm was mixed with component (b) and concentrated according to the procedure described below to obtain The final aqueous dispersion has a solids content of from about 50 to about 60% by weight.
[0138] (a2) PTFE: The primary dispersion comprising about 41 to about 43% by weight of PTFE has an average particle size of 220 nm, the dispersion is mixed with component (b) and concentrated according to the following steps to obtain a final particle size of about 50 to about 60% by weight solids content aqueous dispersion. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com