Heat sink for electronic device, and process for production thereof
A technology for electronic equipment and manufacturing methods, applied in metal processing equipment, chemical instruments and methods, cooling/ventilation/heating transformation, etc., can solve problems such as rising material costs, and achieve the effect of excellent thermal conductivity and thin thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
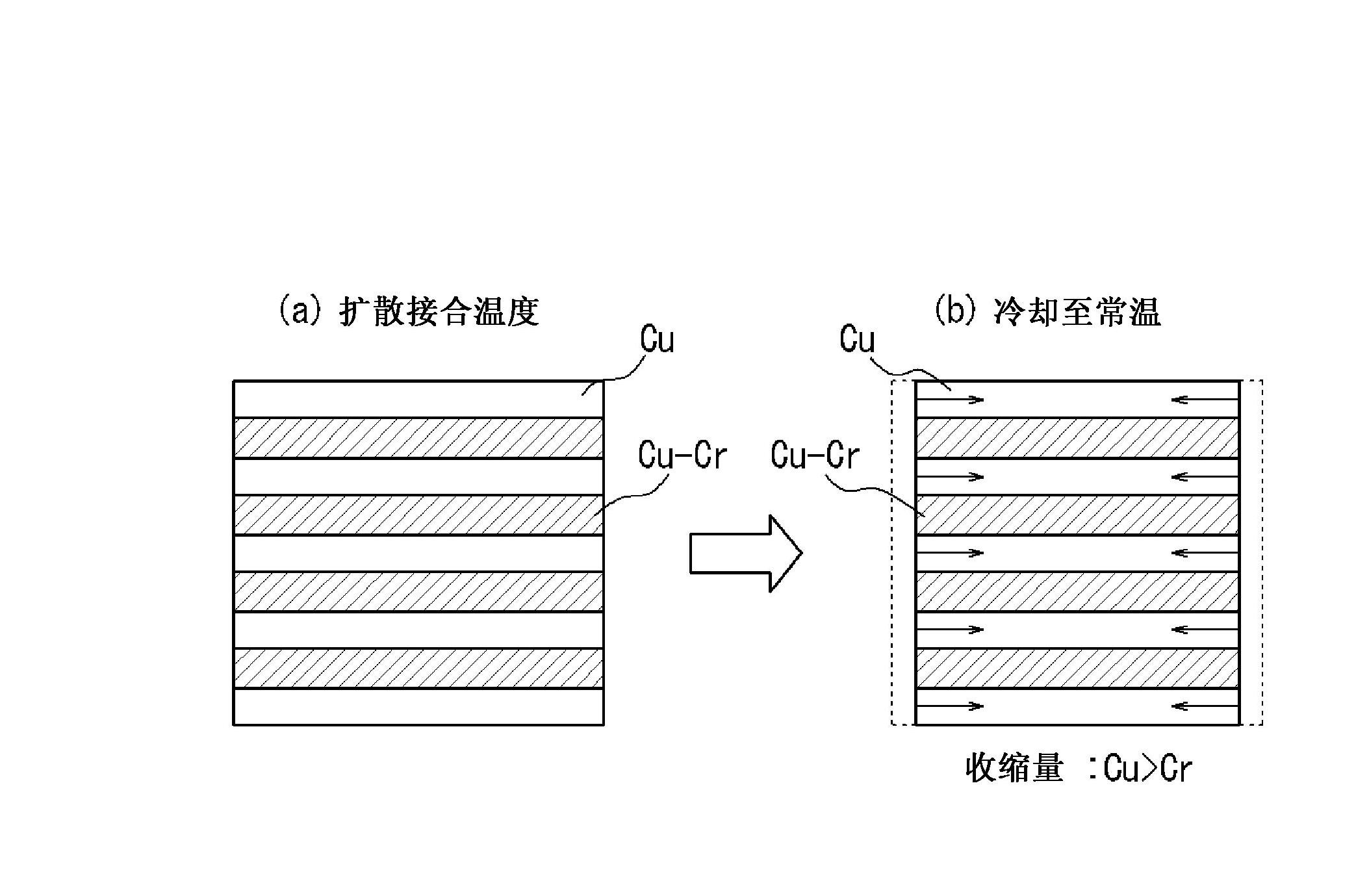
[0097] The Cr-Cu alloy sheet was cold-rolled and cross-rolled so that the rolling ratio in both rolling directions was the same, and the thickness was reduced to 0.05mm (rolling ratio: 98.3%), thereby obtaining a Cr-Cu alloy sheet . A size of 65 mm square was cut out from this rolled plate. Two sheets of the rolled Cr-Cu alloy plate are stacked to form 4 layers and 5 sheets of pure copper (the same size as the Cr-Cu alloy material and thickness: 0.1mm) are stacked according to the pure copper sheet (1 sheet), The order of Cr-Cu alloy plates (2 stacked into a group) is alternately stacked, passed through a spark plasma sintering (SPS) device [DR. And diffusion bonding was carried out under the condition of a pressure of 20 MPa to obtain a Cr-Cu alloy / Cu laminated body.
[0098] It was confirmed that the thermal conductivity in the thickness direction was 230 W when the test piece cut out from the obtained diffusion bonded plate was heat-treated at 600°C (holding time: 120 min...
Embodiment 2
[0103] The Cr-Cu alloy plate is cold rolled to a thickness of 0.10mm (rolling rate: 96.7%) to obtain a Cr-Cu alloy plate. The rolled Cr-Cu alloy plate is 4 pieces, and the pure copper plate (1 sheets) and Cr—Cu alloy plates (one sheet) were stacked alternately in this order, and a Cr—Cu alloy / Cu laminate was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1.
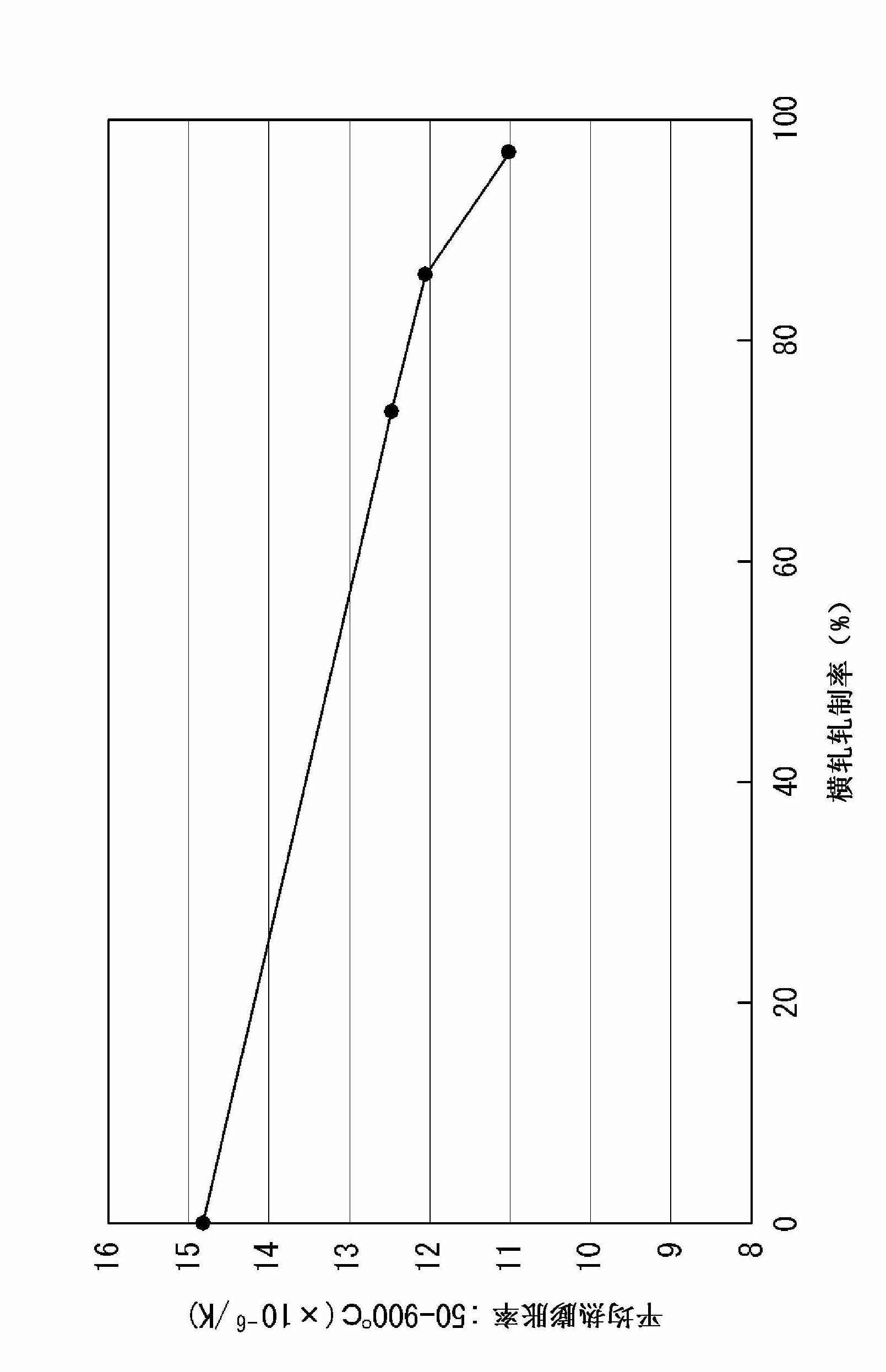
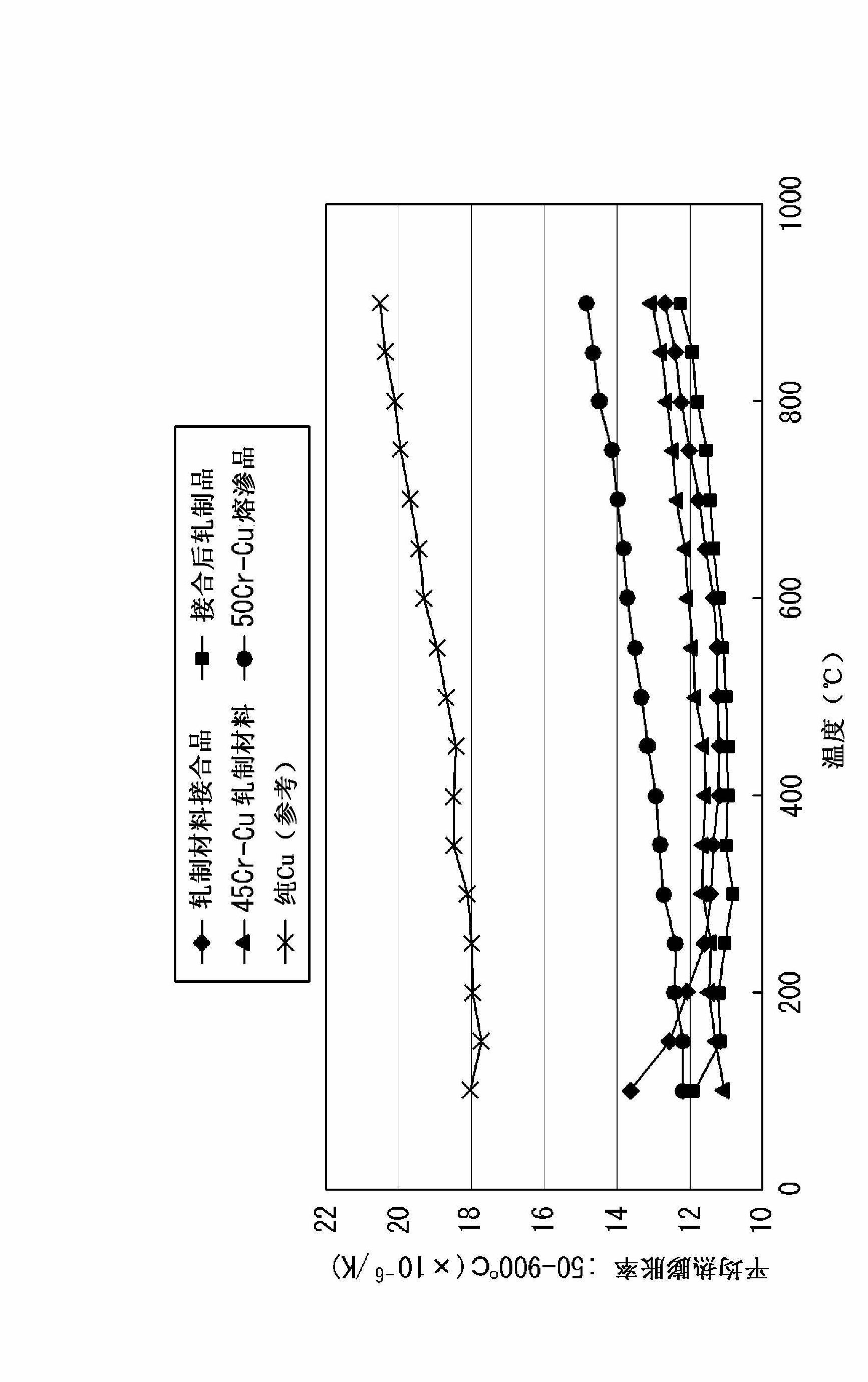
[0104]It was confirmed that the thickness The thermal conductivity in the direction is 230W / mK, and the thermal conductivity in the surface direction is 298W / mK, which has excellent heat dissipation. In addition, the average thermal expansion rate at 50~900°C is 12.5×10 -6 / K, and still obtain a thermal expansion rate that does not hinder the brazing joint.
Embodiment 3
[0106] The Cr-Cu alloy plate is cold rolled to a thickness of 0.15mm (rolling rate: 95.0%) to obtain a Cr-Cu alloy plate. The rolled Cr-Cu alloy plate is 4 pieces, and the pure copper plate (1 sheets) and Cr—Cu alloy plates (one sheet) were stacked alternately in this order, and a Cr—Cu alloy / Cu laminate was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1.
[0107] It was confirmed that the thickness The thermal conductivity in the direction is 195W / mK, and the thermal conductivity in the surface direction is 280W / mK, which has excellent heat dissipation. In addition, the average thermal expansion rate at 50~900°C is 11.6×10 -6 / K, and still obtain a thermal expansion rate that does not hinder the brazing joint.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Long trail | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com