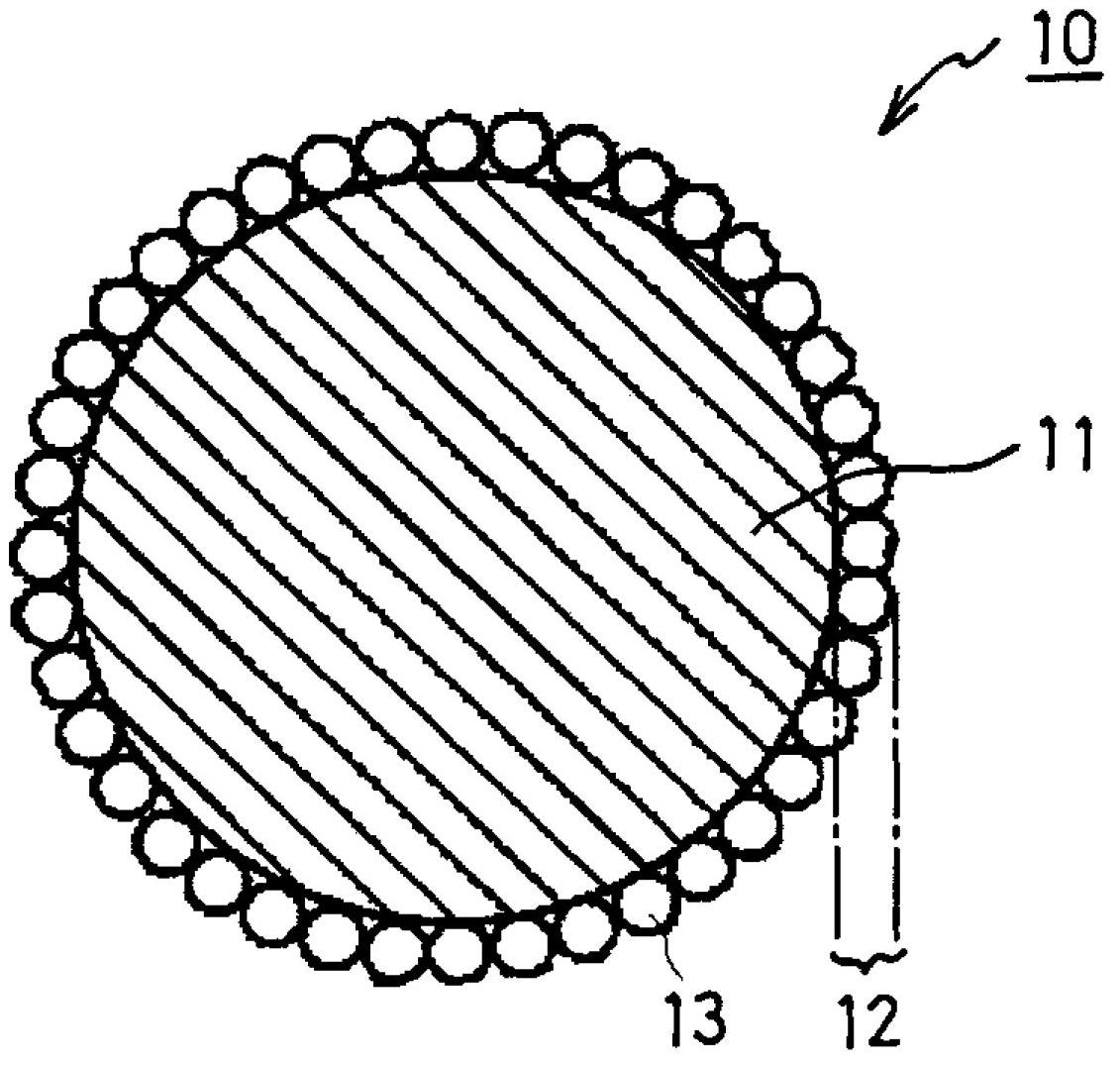
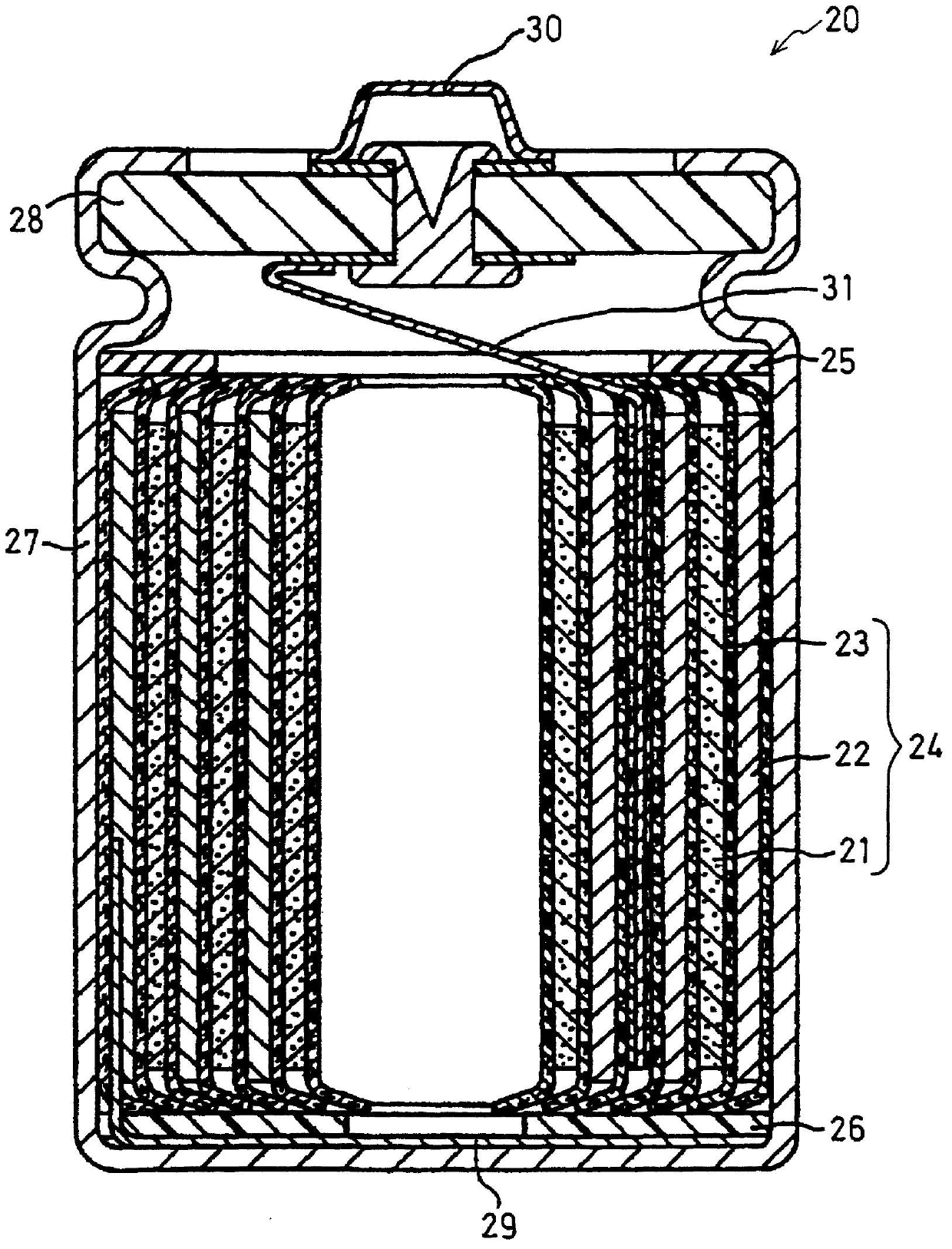
Positive electrode active material particles for lithium ion secondary battery, positive electrode using said positive electrode active material particles, and lithium ion secondary battery
A positive active material, secondary battery technology, applied in the direction of secondary batteries, battery electrodes, lithium batteries, etc., can solve the problems of reduced battery capacity, reduced battery cycle characteristics, internal short circuit, etc., to improve cycle characteristics and rate characteristics. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0133] (1) Production of positive electrode active material particles
[0134] Lithium hydroxide monohydrate, ferrous oxalate dihydrate, and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate were dry mixed at a molar ratio of 1:1:1.
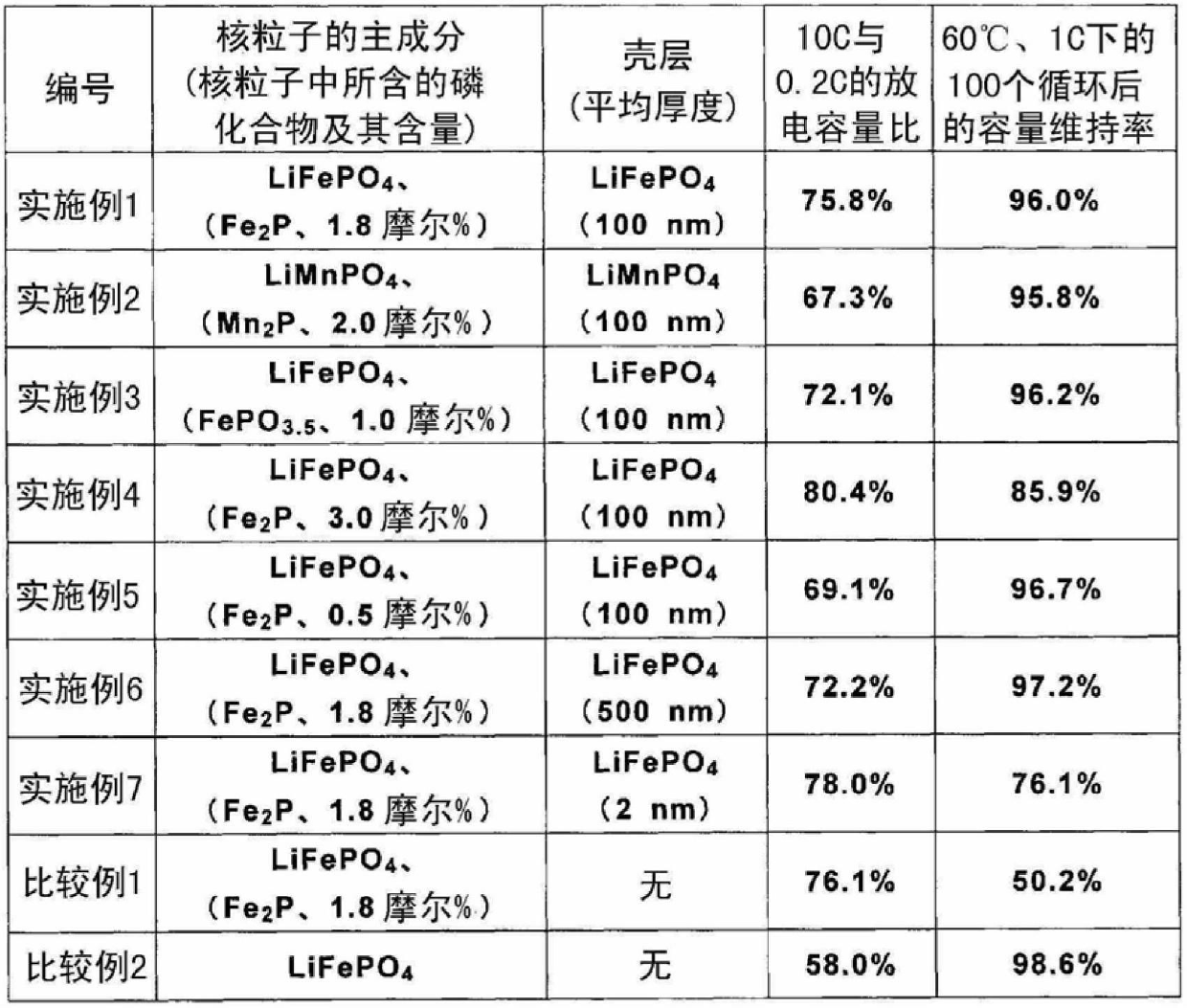
[0135] Next, the obtained mixture was fired at 800° C. for 24 hours in an Ar atmosphere to obtain core particles a1. The core particle a1 is made of olivine-type LiFePO 4 and Fe 2 P formation, Fe relative to the total moles of both 2 The content ratio of P was 1.8 mol%.
[0136] Fe in nuclear particle a1 2 The ratio of P was determined by XRD as follows.
[0137] After the mixture of the core particle a1 and the epoxy resin is coated on the surface of the metal plate and dried, the cross section of the core particle a1 is exposed by FIB (Focused Ion Beam) processing. Next, micro-area X-ray diffraction analysis is performed on the cross-sectional portion of the nuclear particle a1. Fe 2 P / LiFePO 4 The peak intensity ratio of , from the intensity ratio thus o...
Embodiment 2
[0157] (Production of positive electrode active material particles)
[0158] Mix lithium hydroxide monohydrate, manganese (II) oxalate dihydrate, and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate in a molar ratio of 1:1:1. Next, the obtained mixture was fired at 800° C. for 24 hours in an Ar atmosphere to obtain core particles b1. The core particle b1 is composed of olivine-type LiMnPO 4 and Mn 2 P formation, Mn relative to the total moles of both 2 The content ratio of P was 2.0 mol%. Mn in nuclear particle b1 2 The ratio of P is compared with the Fe in the core particle a1 in Example 1 2 The P content was measured in the same manner.
[0159] On the other hand, lithium hydroxide monohydrate, manganese (II) chloride tetrahydrate, and phosphoric acid were dissolved in distilled water at a molar ratio of 1:1:1 to prepare an aqueous precursor solution. The obtained precursor aqueous solution was atomized at 500° C. by a spray pyrolysis method, and dried to obtain precursor fine particles...
Embodiment 3
[0162] A core particle c1 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the firing temperature at the time of producing the core particle was changed from 800° C. to 600° C. The obtained nuclear particle c1 is made of LiFePO 4 and FePO 3.5 formed, FePO relative to the total moles of both 3.5 The content ratio of is 1.0 mol%. In addition, the average particle diameter of the core particles c1 is 1 μm. Mechanical alloying was performed in the same manner as in Example 1 except for using the thus obtained core particle c1 and fine particle a2 having an average particle diameter of 100 nm, thereby obtaining a positive electrode active material particle C having the fine particle a2 adhered to the surface of the core particle c1. The average thickness of the shell layer of the positive electrode active material particle C was 100 nm. Furthermore, except having used the obtained positive electrode active material particle C, it carried out similarly to Example 1, t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com