SAT (satisfiability) based method for bounded model checking (BMC) for propositional projection temporal logic (PPTL)
A technology of projected sequential logic and model detection, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of model detection method state space explosion, limited expression ability, etc., to achieve the effect of easy verification and improved efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
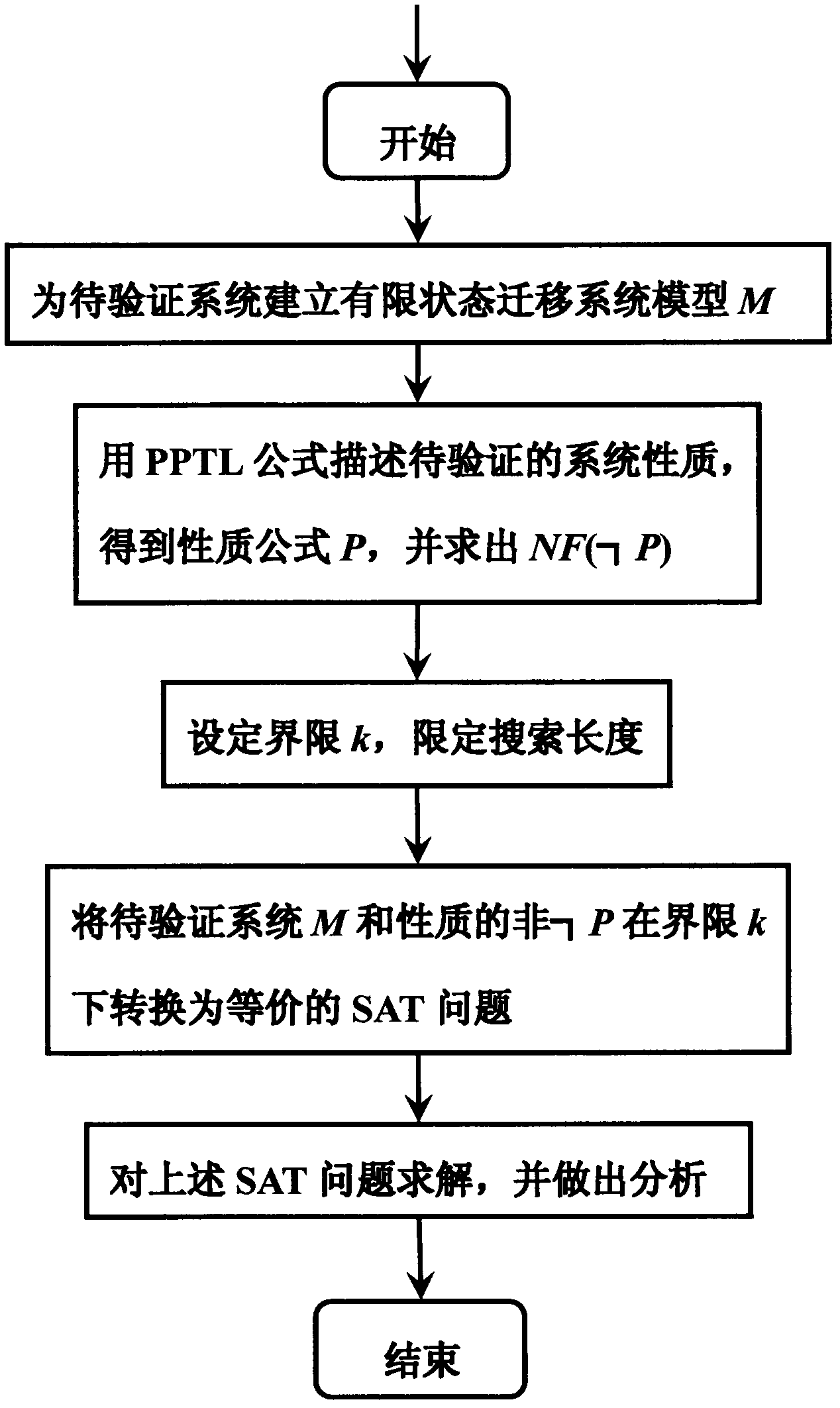
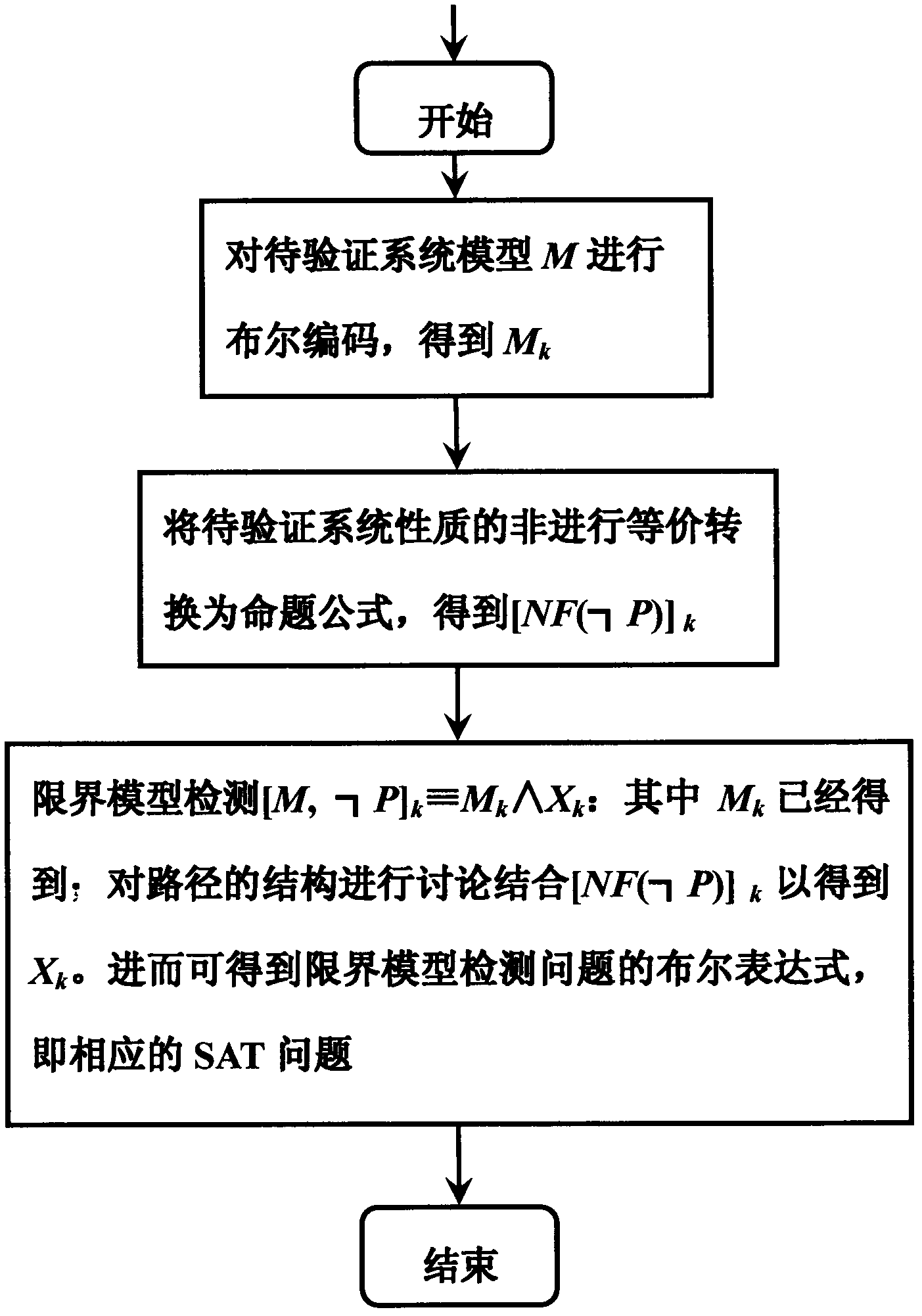
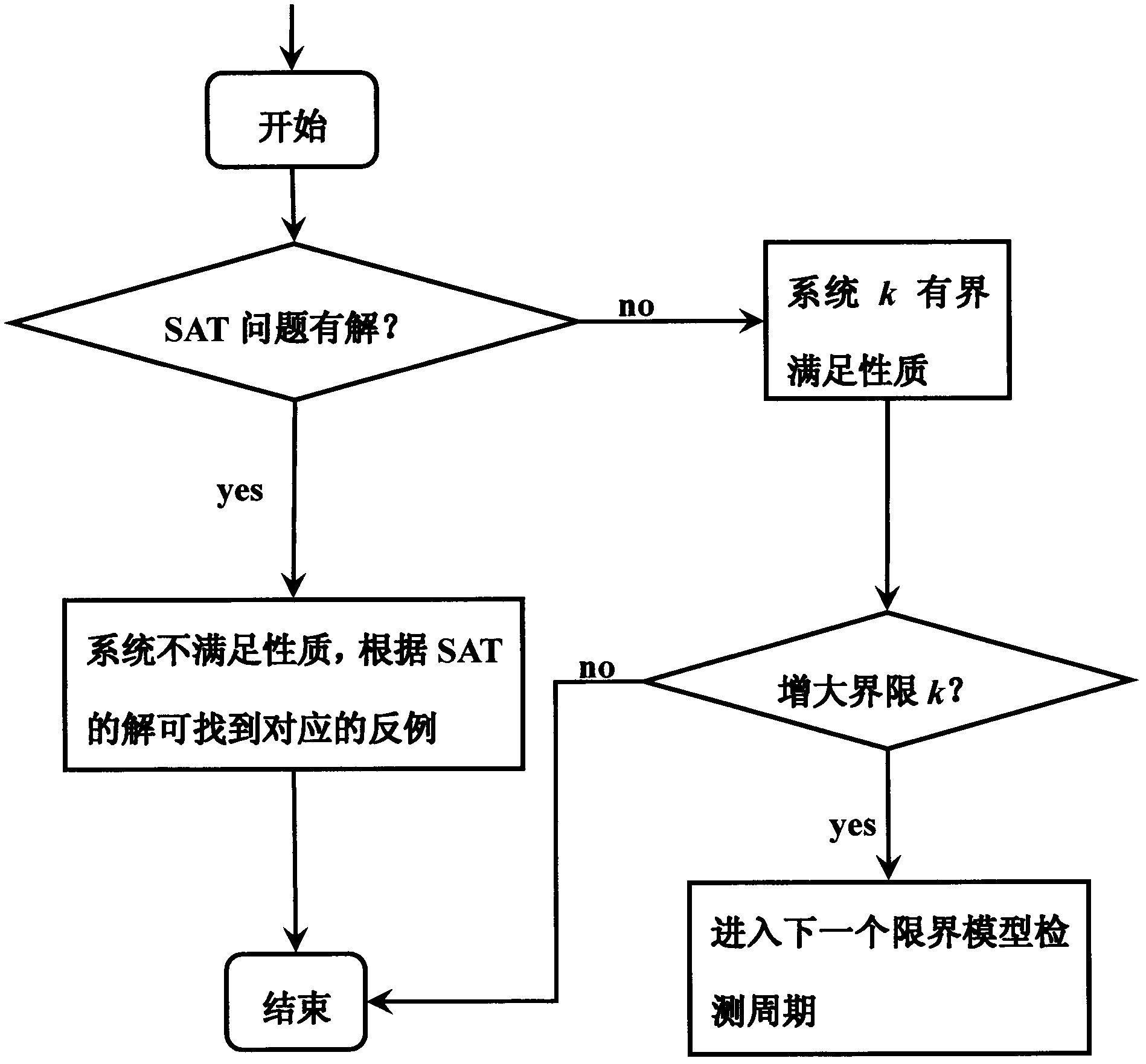
[0051] The invention is a SAT-based propositional projection temporal logic boundary model detection method, which uses the specification description language PPTL with regular expression ability to describe the properties of the system to be verified, and verifies the properties of the system to be verified through the detection method of the boundary model. During the verification process In this paper, the problem of bounded model detection is transformed into a SAT problem, and the solution of the SAT problem is used to judge whether the system to be verified is bounded and satisfies the property. The system to be verified is either a newly developed software system, or a newly developed hardware system, or a communication protocol, or an algorithm. The properties of the system to be verified are either safety-related or activity-related. The design and development process of these systems often need to expend huge manpower and material resources, therefore, before these n...
Embodiment 2
[0081] SAT-based propositional projection temporal logic boundary model detection method is the same as embodiment 1, such as figure 1 Shown, the present invention is described from another angle, and the present invention mainly comprises the following parts:
[0082] 1. System modeling
[0083] Analyze the system to be verified and establish a corresponding system model. During the modeling process, the system needs to be abstracted to a certain extent, and the established model should faithfully reflect the behavior of the system, and the scale should be compact. The invention establishes the Kripke structure model of the finite state transition system for the system to be verified. Firstly, the definition of the Kripke structure of the finite state transition system is given:
[0084] The Kripke structure M is a quadruple M=(S, I, T, L), where S is a finite state set; is the initial state set; is a set of transition relations, and conforms to the complete relation, ...
Embodiment 3
[0105] The SAT-based propositional projection temporal logic boundary model detection method is the same as that in Embodiment 1-2.
[0106] In a communication system, there are often situations where multiple users apply for the right to use the same channel at the same time, but the system will only authorize one user to use the channel at the same time. This is a typical shared resource allocation problem. Assuming that two users apply for the right to use the same channel at the same time, it can be modeled as a mutual exclusion system with two independent processes applying for a critical resource at the same time. The system M is a mutually exclusive system with two processes, and a Kripke structure model is established for M, such as Figure 4 (a), where x indicates that process A is in the critical section, and y indicates that process B is in the critical section. Consider the property P of the system: "neither process A nor process B is in the critical section" is a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com