Method for direct rapid detection and identification of banana-root nematode in soil or other media
A technology for banana perforating nematodes and soil, which is applied in the field of molecular biology detection and identification, and achieves the effects of high detection sensitivity and good purification effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1 Rapid detection and identification of the banana borer nematode from soil samples containing the banana borer nematode
[0030] Test materials: Banana perforator nematodes were collected from the rhizosphere soil of Anthurium anthurium, cultured and preserved on carrot callus in a 25°C incubator in our laboratory; the soil was collected from the rhizosphere soil of bananas in the field.
[0031] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0032] 1. Extraction of total DNA from mixed samples of banana borer nematode and soil
[0033] 1.1 Weigh 0.5 g of the above-mentioned field soil sample, put it into a 15 mL sterilized conical centrifuge tube, and add an equal weight of small glass beads with a diameter of 0.5 mm;
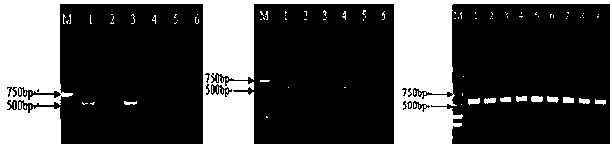
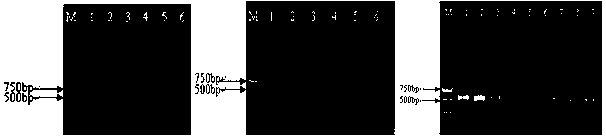
[0034] 1.2 The banana perforator nematodes were isolated from the carrot callus group where the nematode was cultivated, and 50, 5, 4, 3, 2 and 1 banana perforator nematodes were picked under the microscope and put into different soils ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 Rapid detection and identification of the banana borer nematode directly from the banana rhizosphere soil where the banana borer nematode disease occurred
[0056] Test materials: In this laboratory, the rhizosphere soil of Banana brasiliensis inoculated with the nematode and diseased in the greenhouse was potted.
[0057] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0058] Take about 500-1 000 g of the rhizosphere soil of the diseased Brazilian banana, mix it well, weigh 5 parts of 0.5 g soil (No. 1-5), and weigh 0.5 g of sterilized soil (No. In a sterilized centrifuge tube, add an equal weight of small glass beads with a diameter of 0.5 mm; other steps are the same as in Example 1, and the test results are shown in figure 2 . Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that the DNA of the brazilian rhizosphere soil infected with the banana nematode has the target fragment after PCR detection, while the soil DNA without the banana nematode does not detect...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3 Rapid detection and identification of the banana borer nematode from samples mixed with the substrate
[0060] Experimental material: The preparation and acquisition of the banana perforator nematode were the same as in Example 1, and the substrate was purchased from Guangzhou Fangcun Lvyuan Horticultural Plant Material Farm.
[0061] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0062] Weigh 0.5 g of matrix, put it into a 15 mL sterilized centrifuge tube, and add an equal weight of small glass beads with a diameter of 0.5 mm. Other steps are with embodiment 1. See the test results image 3 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com