HBV antisense inhibitors
一种反义、反义寡核苷酸的技术,应用在反义寡聚体领域,能够解决限制治疗效果、HBeAg血清转换率HBsAg损失率低等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
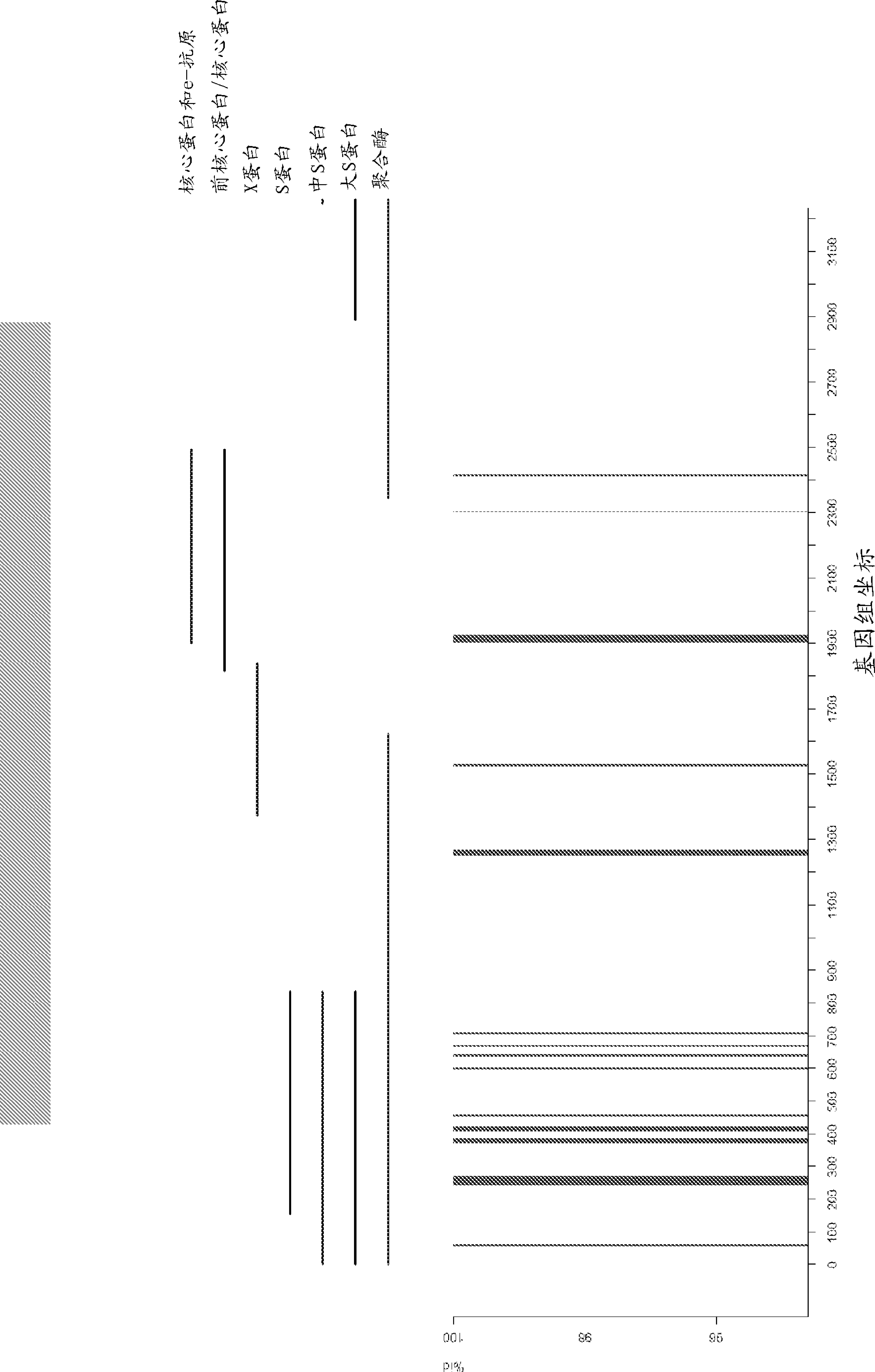
[0160] Example 1: Antisense inhibition of hepatitis B virus expression in HepG2 2.2.15 cells by LNA antisense oligonucleotides
[0161] Locked nucleic acid oligonucleotides were purchased from Exiqon. The total length of the LNA antisense oligonucleotides tested was 16 nucleotides, each had a 4LNA-8nt-4LNA motif, and each contained a central nucleotide (nt) gap segment with 8 consecutively linked 2'-deoxynucleotides. The nt gap segment in each 16-mer ASO is flanked by wing segments on both sides (5' and 3'). Each wing segment in each ASO has 4 consecutively linked nucleotides. Each nucleotide of each wing in each ASO has a locked nucleic acid (LNA) sugar modification. Every internucleotide linkage throughout every LNA antisense oligonucleotide is a phosphorothioate (P=S) linkage, although it is envisioned that certain nucleotides on certain ASOs of the invention Interlinkages can be linkages other than phosphorothioate, including phosphodiester linkages. The LNA motif f...
Embodiment 2
[0169] Example 2: Antisense inhibition of hepatitis B virus or SV40 T antigen expression in HepAD38 (Tet-HBV) cells by LNA antisense oligonucleotides
[0170] An HBV-targeting LNA antisense oligonucleotide was designed with the sequence GAGGCATAGCAGCAGG (SEQ ID NO: 16), which is complementary to the DNA sequence depicted in SEQ ID NO: 4 and GENBANK Accession No. U95551.1, incorporated herein as SEQ ID NO: 16. The total length of the LNA antisense oligonucleotide is 16 nucleotides with a 4-8-4 LNA motif, wherein the ASO has a central gap segment with 8 consecutively linked 2'- deoxynucleotides. The gap segments flank the wing segments on both sides (5' and 3'). Each wing segment has 4 consecutively linked nucleotides. Each nucleotide of each wing has a locked nucleic acid (LNA) sugar modification. Each internucleotide linkage throughout the LNA antisense oligonucleotide is a phosphorothioate (P=S) linkage. Each cytosine of the LNA antisense oligonucleotide is 5-methylcyt...
Embodiment 3
[0177] Example 3: Antisense inhibition of hepatitis B virus or SV40 T antigen expression in THT1 cells by LNA antisense oligonucleotides
[0178] The LNA antisense oligonucleotides described in Example 3 were evaluated for their ability to reduce HBV mRNA in THT1 cells (also called HepG2 2.2.15 cells). These cells were transfected by electroporation with 741 nM, 2,222 nM, 6,667 nM and 20,000 nM antisense oligonucleotides over a period of approximately 24 hours. RNA was isolated from cells and HBV mRNA levels were measured by quantitative real-time PCR. HBV mRNA levels were adjusted according to the total RNA content measured by RIBOGREEN. Data are shown in Table 4 expressed as percent inhibition of mRNA levels compared to untreated cells. As shown in Table 4, the LNA antisense oligonucleotides reduced HBV mRNA levels in a dose-dependent manner.
[0179] Table 4 The dose-dependent antisense suppression of HBV mRNA in HepG2 cells
[0180]
[0181] (B) Evaluation of anti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com