Engineered zinc finger proteins targeting plant genes involved in fatty acid biosynthesis
A technology of zinc finger protein and biosynthesis, applied in the field of engineered DNA binding domain, which can solve the problems of labor-intensive, time-consuming, inability to specifically target selected genes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0204] Example 1: Identification of target sequences in Brassica napus
[0205] 1.1 Target sequence identification
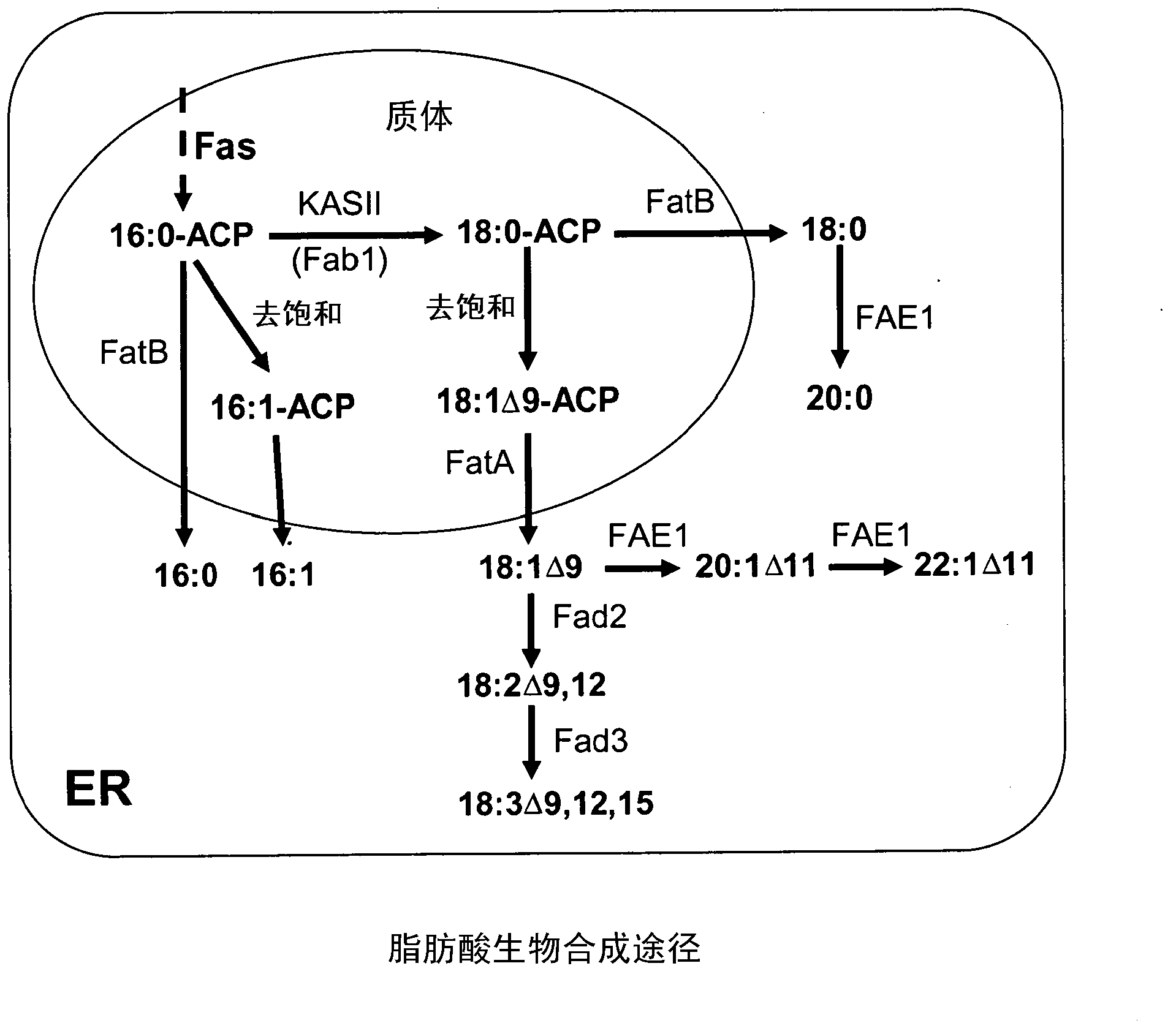
[0206] In this example, the endogenous DNA sequence encoding the native β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase II (KAS II) of Brassica napus (Brassica napus) was identified. These genes were selected as exemplary targets to demonstrate that transcriptional regulation by engineered zinc finger protein transcription factors (ZFP TFs) produces the desired modification of fatty acid biosynthesis and concomitant altered seed oil profile. The enzyme β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase II catalyzes the conversion of 16:0-ACP to 18:0-ACP and subsequent formation of oleic acid (Ohlrogge and Browse, 1995, The Plant Cell, 7:957-970). Reported β- The Arabidopsis fab1 mutation of ketoacyl-ACP synthase II resulted in a 65% decrease in enzyme activity accompanied by a 7% and 3% increase in stearic acid content in leaves and roots, respectively (Wu et al., 1994, Plant Physiology, 106:143- 150). Stab...
Embodiment 2
[0213] Example 2: Design of a ZFP DNA-binding domain specific to the β-ketoacyl-ACP synthetase II gene
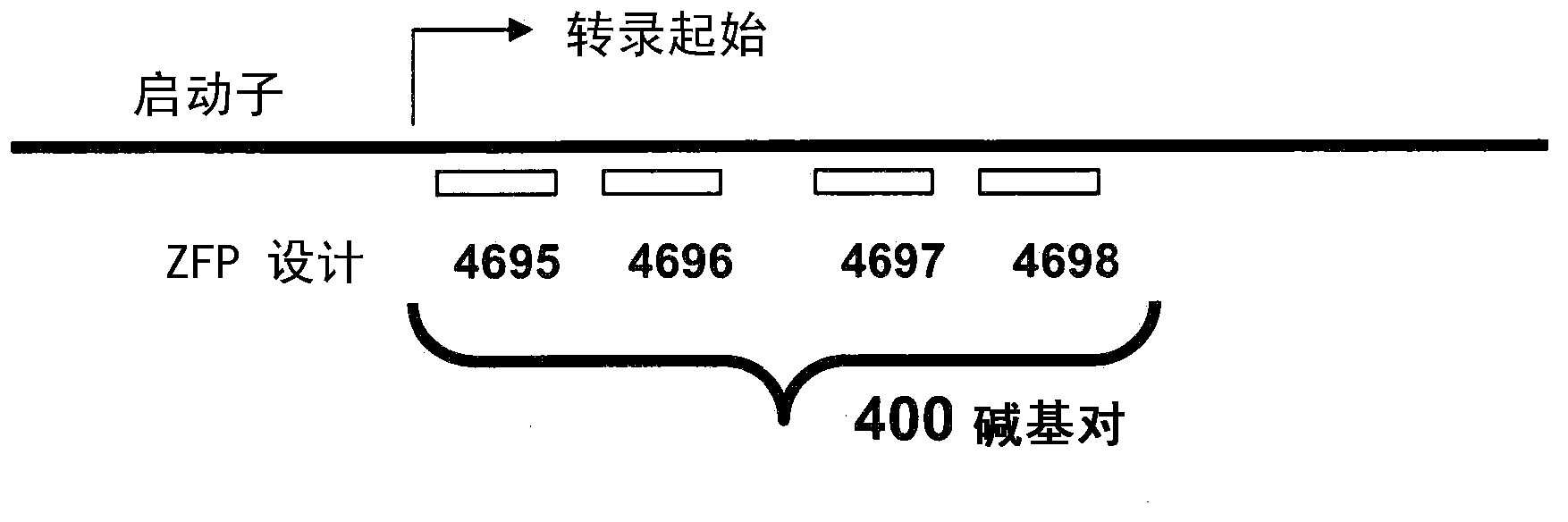
[0214] Zinc finger proteins were designed against various target positions in the promoter region and 5' untranslated and translated regions of the Brassica napus β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase II gene. see figure 2 . Recognition helices for representative ZFP designs are shown in Table 1. Target locations for zinc finger design are shown in Table 2.
[0215] Table 1: β-ketoacyl-ACP synthetase II zinc finger design
[0216]
[0217] Table 2: Target positions of β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase II zinc fingers
[0218]
[0219] β-ketoacyl-ACP synthetase II was designed to be incorporated into a zinc finger expression vector encoding a protein with at least one CCHC-binding finger. See US Patent Publication 2008 / 0182332. Specifically, the last finger in each protein has a CCHC structure (architecture).
[0220] The zinc finger coding sequences were then fused to sequences encod...
Embodiment 3
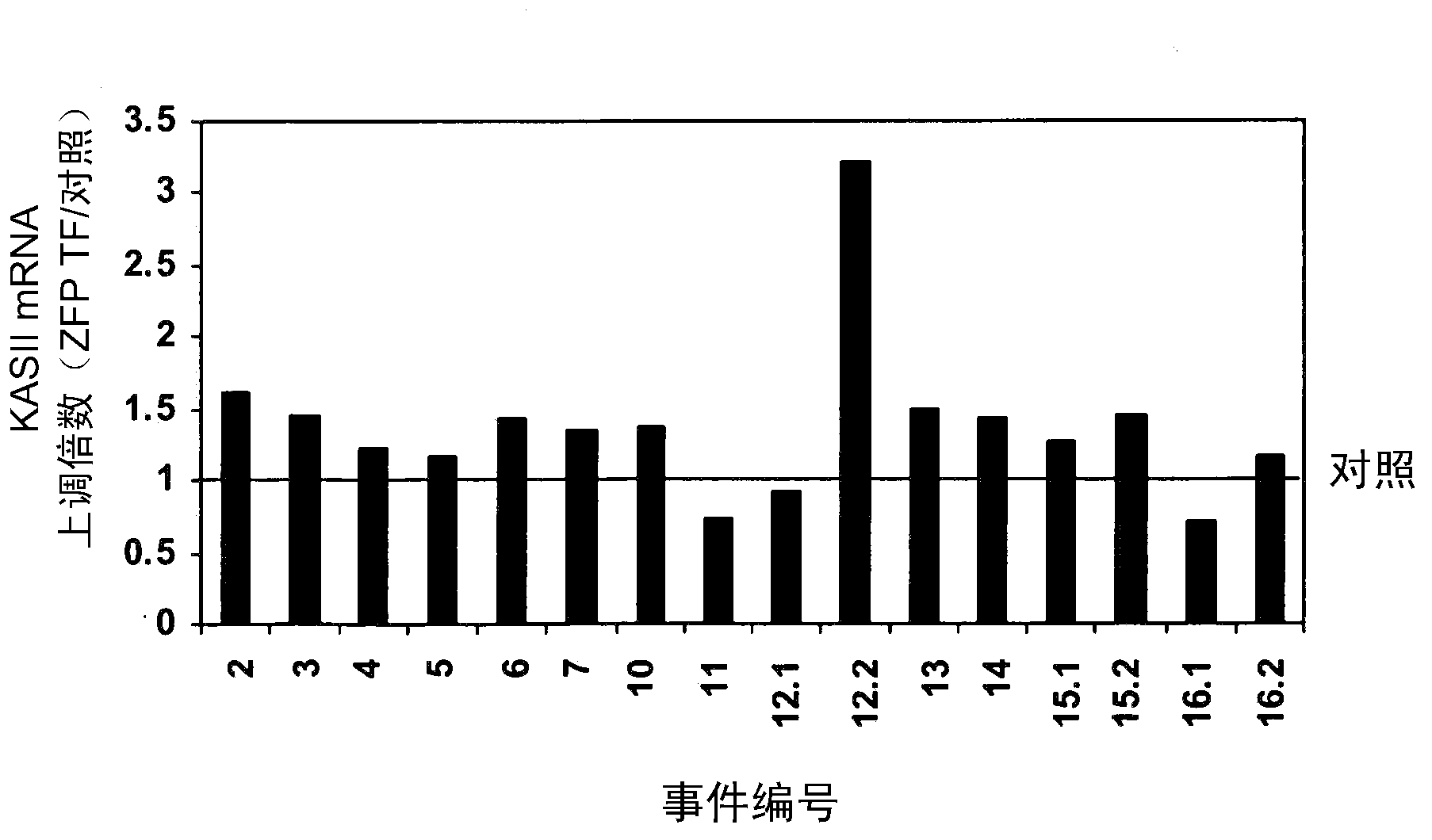
[0221] Example 3: ZFP TF mediates upregulation of the native β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase II gene in Brassica napus
[0222] To evaluate the function of the designed zinc finger proteins in plant cells, a method of expressing the proteins in living plant cells was employed. DNA encoding a zinc finger protein can be delivered to a plant cell under conditions where the DNA does not integrate into the genome of the plant cell. Thus, DNA molecules are transiently maintained in plant cells and serve as templates for gene expression. Alternatively, the DNA encoding the zinc finger protein can be delivered to the cell under conditions under which the DNA integrates into the genome of the plant cell. A transgenome of the zinc finger protein encoding gene is generated such that the DNA molecule is stably maintained in the plant cell and serves as a template for gene expression. Those skilled in the art can evaluate the function of these proteins in living plant cells by transiently or tra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com