Method for promoting rapid drying of dredged silt by microorganism
A technology for dredging sludge and microorganisms, which is applied in the field of rapid drying of dredged sludge promoted by microorganisms, which can solve the problems of long treatment period, prolonged treatment period of vacuum preloading method, and difficulty in achieving mud content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
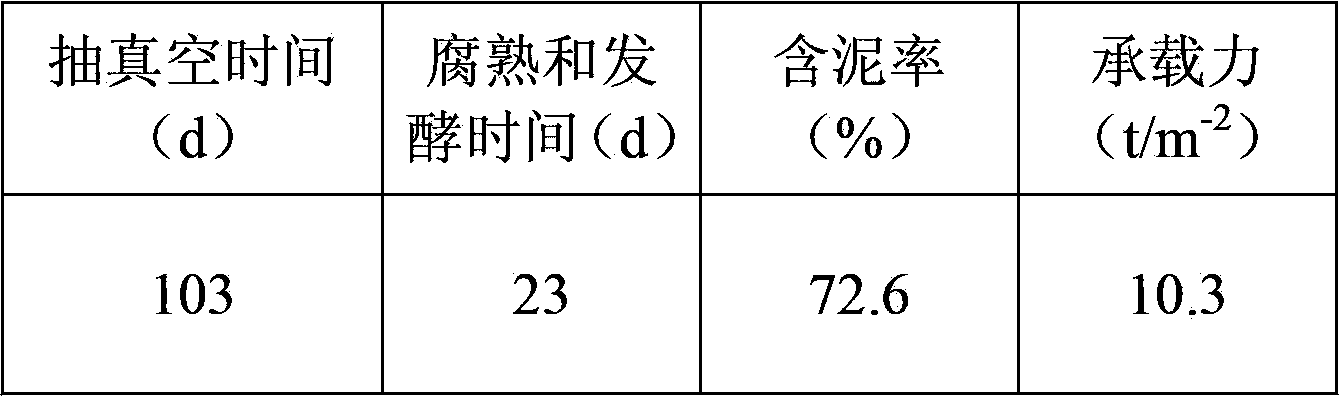
Embodiment 1
[0100] A method for rapid drying of dredged silt by microorganisms, using the following steps:
[0101] (1) Construct a drying pond with an internal size of 100m (length)×100m (width)×5m (depth) as a sludge storage yard, excavate 3m below the ground at a depth of 5m, pile up a cofferdam height of 2m, and have a total volume of about 50,000m 3 , 2 layers of sealing film are laid inside for anti-seepage treatment.
[0102] (2) Using water hyacinth, rice straw, and cow dung with a dry mass ratio of 1:1:0.2 as raw materials, a large anaerobic fermentation tank is used as a container to domesticate gas-producing microorganisms. The domestication temperature is 30°C and the solid-to-liquid ratio is 1: 5. The daily gas production was detected, and the fermentation broth was collected when the gas production reached its peak for 3 consecutive days.
[0103] (3) Repeat step (2), and regularly replace the fermented material in the fermenter with fresh substrate to maintain the microbi...
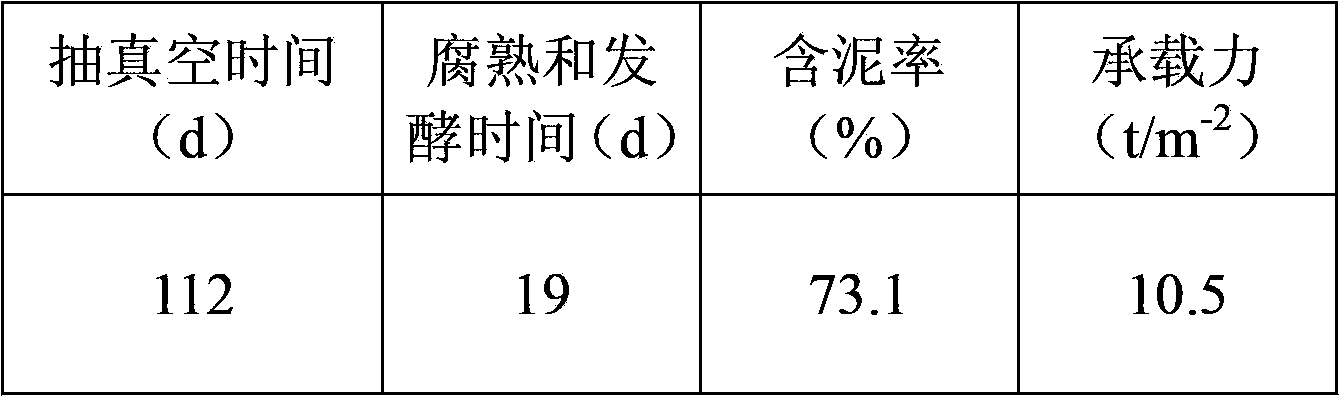
Embodiment 2
[0121] A method for rapid drying of dredged silt by microorganisms, using the following steps:
[0122] (1) Construct a drying pond with an internal size of 100m (length)×100m (width)×5m (depth) as a sludge storage yard, excavate 3m below the ground at a depth of 5m, pile up a cofferdam height of 2m, and have a total volume of about 50,000m 3 , 2 layers of sealing film are laid inside for anti-seepage treatment.
[0123] (2) Using water hyacinth, rice straw, and sheep manure with a dry mass ratio of 1.5:1:0.3 as raw materials, a large anaerobic fermentation tank is used as a container to domesticate gas-producing microorganisms. The domestication temperature is 30°C and the solid-to-liquid ratio is 1: 5. The daily gas production was detected, and the fermentation broth was collected when the gas production reached its peak for 3 consecutive days.
[0124] (3) Repeat step (2), and regularly replace the fermented material in the fermenter with fresh substrate to maintain the m...
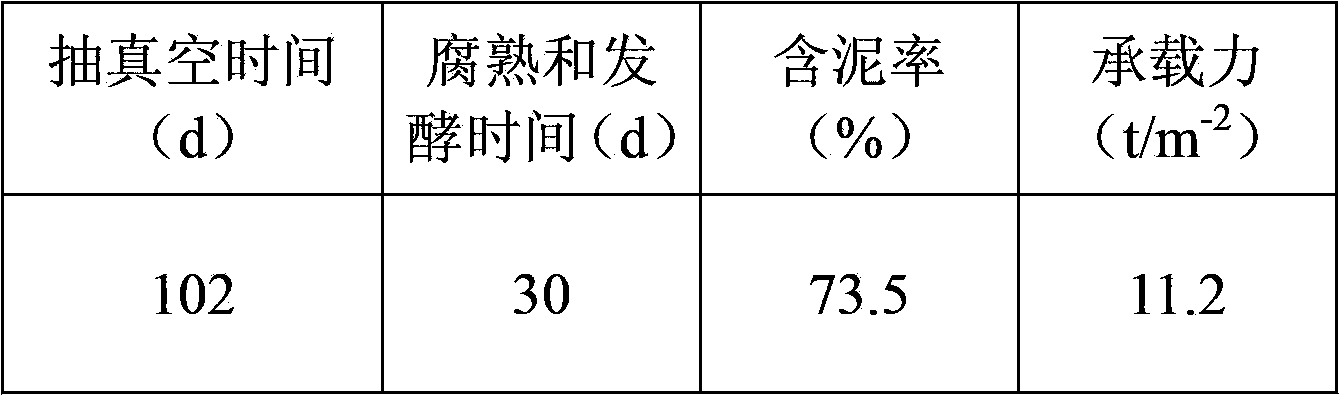
Embodiment 3
[0142] A method for rapid drying of dredged silt by microorganisms, using the following steps:
[0143] (1) Construct a drying pond with an internal size of 100m (length)×100m (width)×5m (depth) as a sludge storage yard, excavate 3m below the ground at a depth of 5m, pile up a cofferdam height of 2m, and have a total volume of about 50,000m 3 , 2 layers of sealing film are laid inside for anti-seepage treatment.
[0144] (2) Use straw, rice straw, and chicken manure with a dry mass ratio of 1.1:0.8:0.2 as raw materials, and use a large anaerobic fermentation tank as a container to domesticate gas-producing microorganisms. The domestication temperature is 30°C and the solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:5. . The daily gas production was detected, and the fermentation broth was collected when the gas production reached its peak for 3 consecutive days.
[0145] (3) Repeat step (2), and regularly replace the fermented material in the fermenter with fresh substrate to maintain the microbi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com