Preparation of polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) nano-fiber scaffold and application of PLGA nano-fiber scaffold to tissue engineering
A nanofiber, tissue engineering technology, applied in the preparation of PLGA nanofiber scaffolds, the application field in tissue engineering, can solve the problems of limiting scaffold/cell in vivo repair effect, difficult to achieve cell differentiation, uneven pore size distribution of cell scaffolds, etc. Achieve uniform distribution, large porosity and sufficient adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
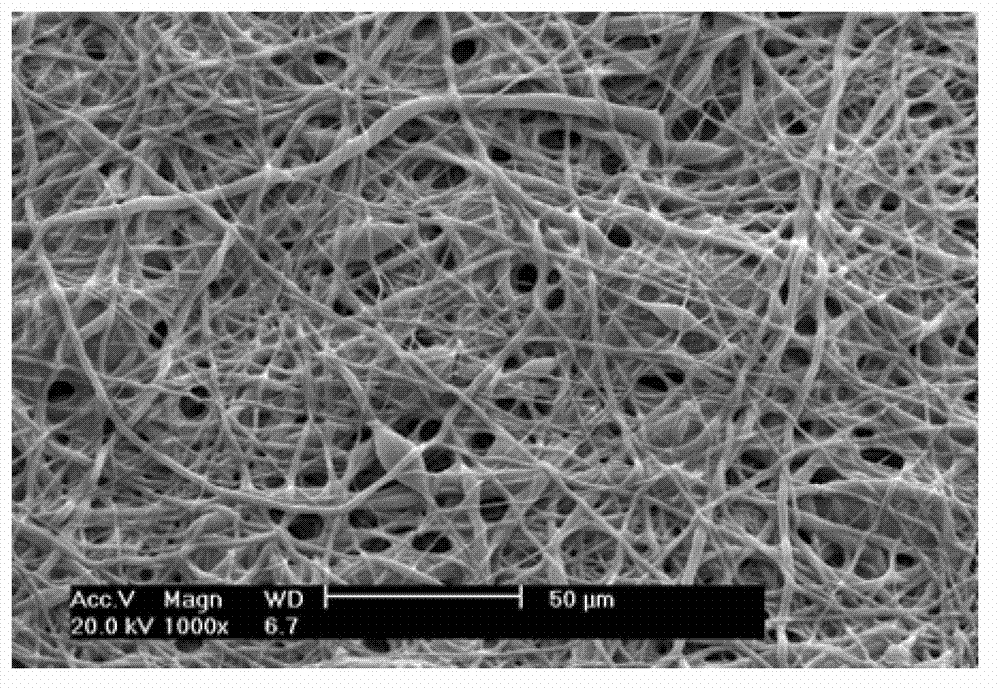
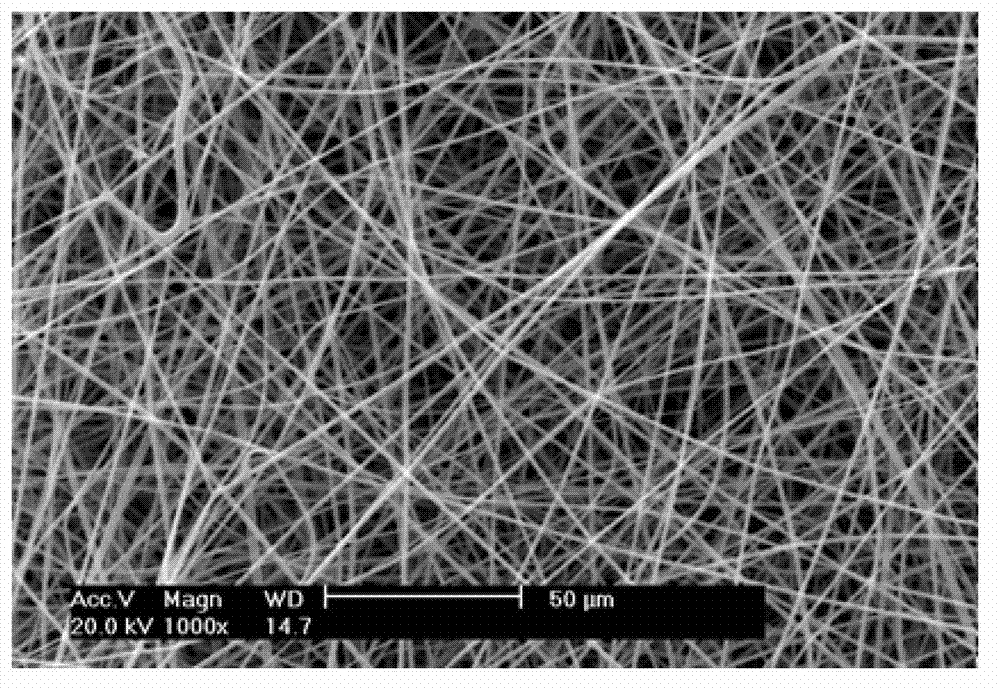
[0037] Prepare a solution of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer (PLGA, LA / GA=75 / 25, Mv=5000, Shandong Institute of Medical Devices) with a mass fraction of 5% in hexafluoroisopropanol as a solvent, and add 5ppm rhodamine B solution, placed in a magnetic stirrer and stirred evenly; using absolute ethanol as a solvent to prepare a polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) solution with a mass fraction of 5%, placed in a magnetic stirrer and stirred evenly; draw 0.5mL PLGA solution with a 25mL syringe and 15mL PVP solution, installed in two syringe pumps; cut a piece of tin foil according to the drum of the electrospinning receiving target, and fix it in the drum; open the drum to make it rotate, and adjust the rotation speed of the drum to 20r / min; High-voltage electricity, adjust the voltage intensity to 15KV, adjust the injection speed of PVP solution to 15mL / h, and the injection speed of PLGA solution to 0.5mL / h respectively, so that the two can eject filaments in the electrostatic fiel...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Prepare a solution of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer (PLGA, LA / GA=75 / 25, Mv=5000, Shandong Institute of Medical Devices) with a mass fraction of 20% in hexafluoroisopropanol as a solvent, and add 8ppm rhodamine B solution, placed in a magnetic stirrer and stirred evenly; using absolute ethanol as a solvent to prepare a polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) solution with a mass fraction of 20%, placed in a magnetic stirrer and stirred evenly; use a 25mL syringe to draw 15mL PLGA solution and 0.5 mL of PVP solution, installed in two syringe pumps; cut a piece of tin foil according to the drum of the electrospinning receiving target, and fix it in the drum; open the drum to make it rotate, and adjust the rotation speed of the drum to 100r / min. Turn on the high voltage, adjust the voltage intensity to 20KV, and adjust the injection speeds of the PVP solution and the PLGA solution to 15mL / h and 0.5mL / h respectively, so that the two respectively eject filaments in the electrosta...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Prepare a polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) (PLGA, LA / GA=75 / 25, Mv=5000, Shandong Institute of Medical Devices) solution with a mass fraction of 10% in hexafluoroisopropanol as a solvent, and add 10ppm Rhodamine B solution was placed in a magnetic stirrer and stirred evenly; a solution of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) with a mass fraction of 15% was prepared with absolute ethanol as a solvent, and placed in a magnetic stirrer and stirred evenly; draw 15mL with a 25mL syringe respectively PLGA solution and 3mL PVP solution are installed in two syringe pumps; cut a piece of tin foil according to the drum of the electrospinning receiving target, and fix it in the drum; open the drum to make it rotate, and adjust the rotation speed of the drum to 50r / min ; Turn on the high voltage, adjust the voltage intensity to 25KV, adjust the injection speed of the PVP solution and the PLGA solution to be 10mL / h, so that the two spray filaments in the electrostatic field respectively, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com