Triple cross-linking collagen, preparation method and uses thereof
A collagen and manufacturing method technology, applied in dental preparations, pharmaceutical formulations, dental prostheses, etc., can solve the problems of anti-enzyme decomposition that cannot meet expectations, low cross-linking degree, uneven cross-linking, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
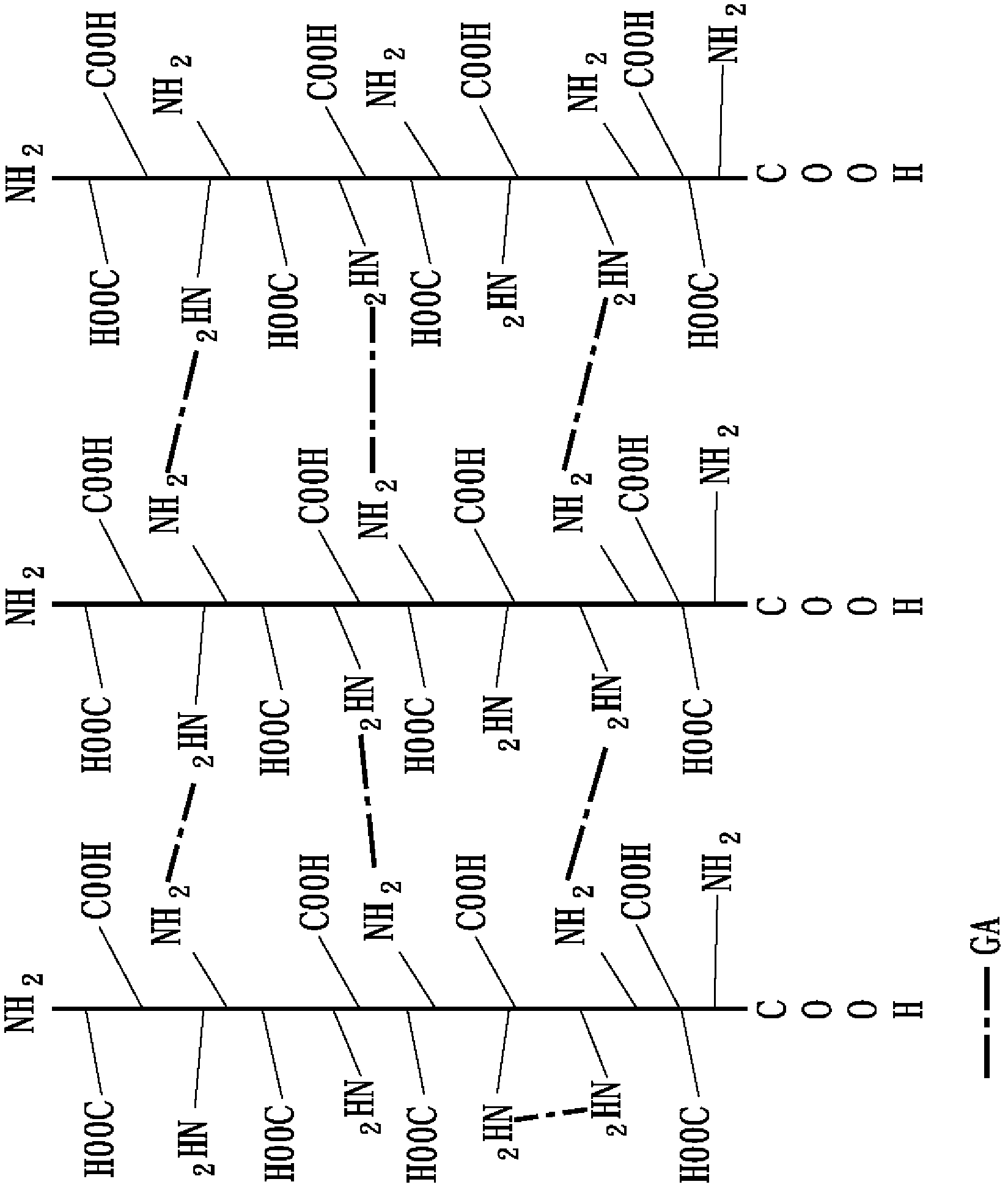
[0054] 1-1 Collagen fiber reorganization
[0055] Extract the pig-derived collagen solution from pig skin, mix this collagen solution with 0.2M, pH 11.2 phosphate buffer solution at a volume ratio of 9:1, and slowly stir for 6 hours at 25°C to Collagen fiber reorganization of collagen is performed. Next, the restructured collagen fibers were collected by centrifugation, and dispersed in 20 mM, pH 7 phosphate buffer solution to obtain a recombined collagen fiber solution with a concentration of about 2.7 mg / mL.
[0056] 1-2 The first cross-linking reaction
[0057] Glutaraldehyde, which belongs to the aldehyde crosslinking agent, is used as the primary crosslinking agent in this embodiment. Glutaraldehyde was added to the above recombinant collagen fiber solution with a concentration of about 2.7 mg / mL, and the final concentration of glutaraldehyde was 35 ppm. Next, stir slowly for 16 hours at 30°C and pH 7.2 to carry out the covalent cross-linking reaction between amine gro...
experiment example 1
[0066] 1-1 Cross-linking degree test
[0067] In this experimental example, trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (trinitrobenzenesulphonate, TNBS) reagent was used to analyze the cross-linking degree of triple cross-linked collagen fibers.
[0068]
[0069] Add 4 mg of lyophilized triple cross-linked collagen fibers to 1 ml of 0.1 M sodium bicarbonate solution (sodium bicarbonate solution) at pH 8.5, then add 1 ml of 0.5% TNBS solution by volume. At 40°C, react for 2 hours. After the reaction, 3 ml of 6N hydrochloric acid (HCl) was added, and the reaction was carried out at 60° C. for 1.5 hours. After the reaction was completed, after the reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, 5 ml of deionized water was added and mixed evenly. Take out 5ml of the mixed solution into a spiral test tube, add 10ml of ether, shake evenly and let it stand still, wait for the liquid to separate into layers, and then take out the upper layer of ether. Then, 10 ml of diethyl ether was added,...
Embodiment 2
[0081] 2-1 Collagen fiber reorganization
[0082] Same as the collagen fiber reorganization steps in Example 1.
[0083] 2-2 The first cross-linking reaction
[0084] Same as the first heavy cross-linking reaction step of Example 1.
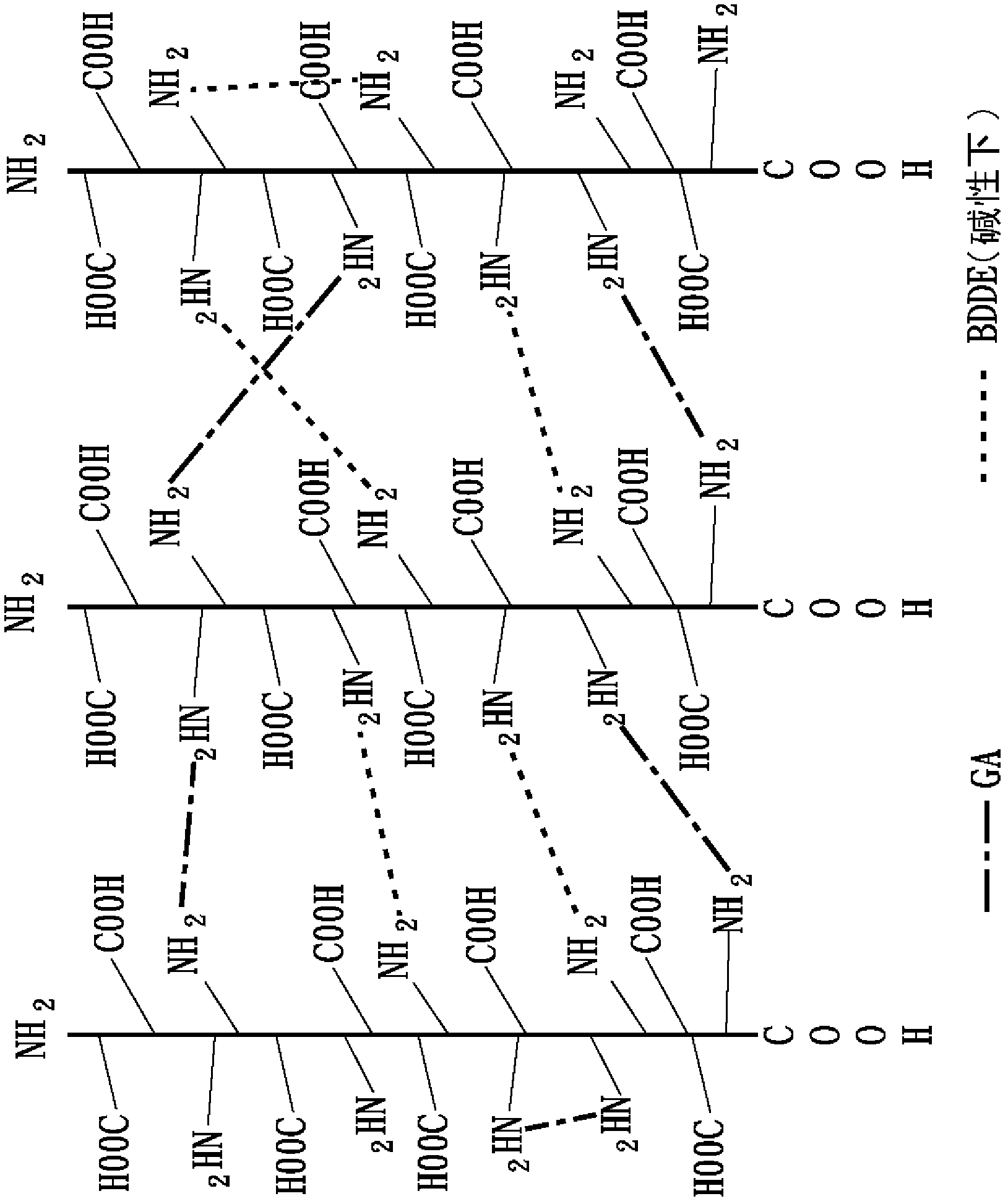
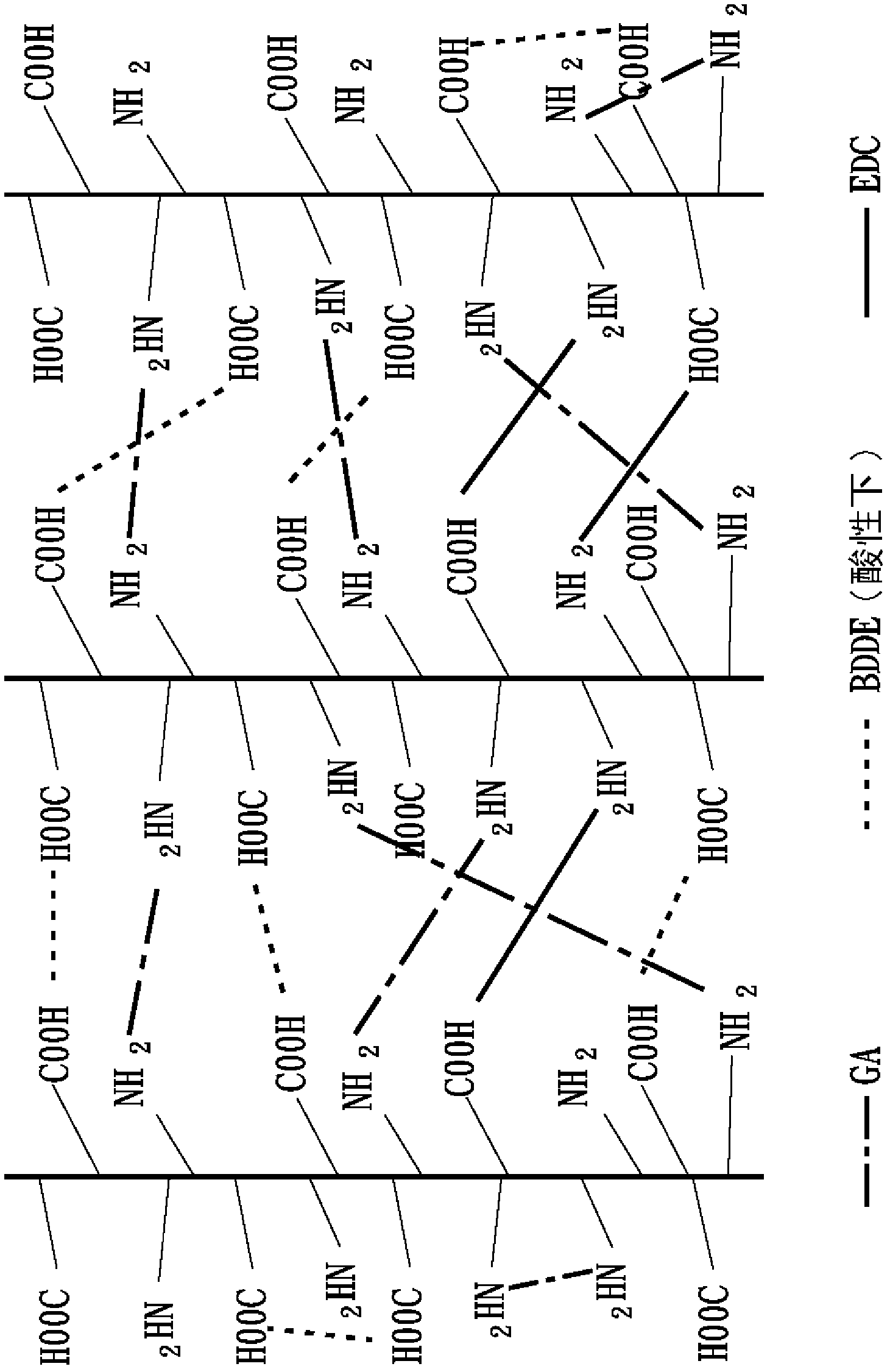
[0085] 2-3 The second cross-linking reaction
[0086] The second heavy cross-linking reaction in this embodiment is based on the imine cross-linking agent 1-ethyl-3-3-dimethylaminopropyl-carbodiimide (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl ) carbodiimide hydrochloride, EDC) as the second cross-linking agent in this embodiment, and also mix EDC with N-hydroxy-succinimide (N-hydroxysuccinimide, NHS) at a molar ratio of 5:1 to The second crosslinker mixture (EDC / NHS) of this example was formed. The first heavy cross-linked collagen collected by centrifugation was dispersed in 0.1M 2-morpholineethanesulfonic acid (MES) buffer solution (pH 5.5) to obtain a heavy cross-linked collagen fiber solution with a concentration of about 2.7mg / mL, Then add the s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com