Method for repairing cadmium-polluted soil/bottom mud using beta vulgaris var.cicla l
A technology of cadmium-contaminated soil and red beetroot, which is applied in the field of phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil/sediment, can solve the problems of secondary pollution, lower utilization value, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
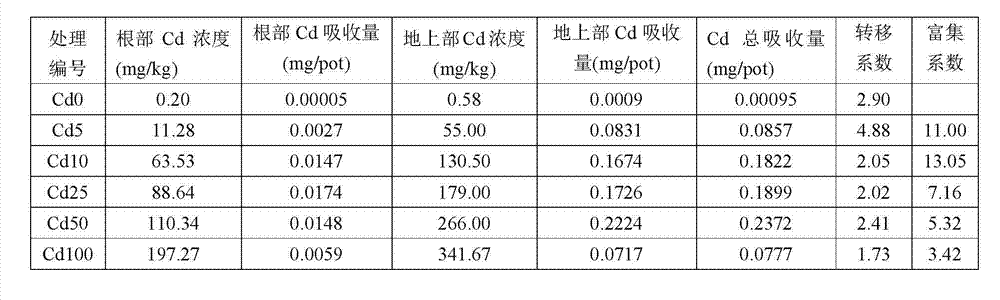
[0014] Embodiment 1 Pot concentration gradient experiment
[0015] The potting experiment site is in the greenhouse of the South Campus of Shenyang University. The site is located in the center of Shenyang. There are no pollution sources around the experimental site, and it is an area not polluted by heavy metals. It belongs to the humid and semi-humid warm temperate continental climate affected by the monsoon. The potting experiment soil was collected from the surface (0-20cm) soil of the non-polluted area in the Shenyang Ecological Station of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The soil type is meadow brown soil. 0.12 mg / kg, the mechanical composition of the soil is 21.4% sand, 46.5% silt and 32.1% clay.
[0016] In this experiment, 6 treatments were set up. The above-mentioned clean soil was used to make Cd-contaminated soil. 2 2.5H 2 O (analytical pure) form is mixed with pollutants, and the concentration of Cd is: 0 mg / kg (Cd0), 5 mg / kg (Cd5), 10 mg / kg (Cd10), 25 mg / kg (Cd...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2: the potted experiment of leaf with red spinach in dredging bottom mud
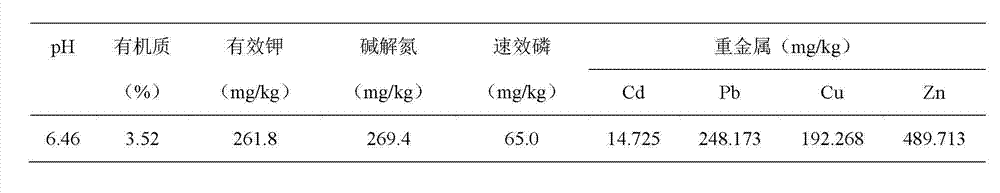
[0026] Bottom mud for test: The dredged bottom mud of Xiheqianmiaozi, Shenyang City, Liaoning Province was used, and its physical and chemical properties were measured by conventional agricultural analysis methods. Its basic physical and chemical properties are shown in Table 1:
[0027] Table 1 Basic physical and chemical properties of the tested sediment
[0028]
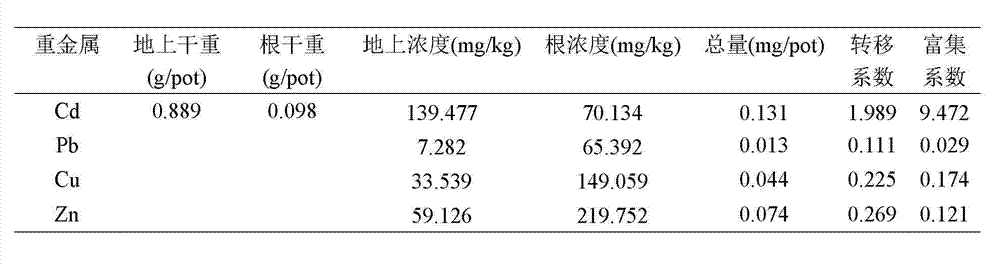
[0029] After the bottom mud was naturally air-dried, passed through a 2 mm sieve, mixed evenly, and put into plastic flower pots, each pot was filled with 1.5 kg of bottom mud, and urea (N 0.1 g / kg), potassium chloride (K 2 O 0.05 mg / kg), superphosphate (P 2 o 5 0.05g / kg), all treatments were repeated 3 times.
[0030] After sterilizing the seeds of red beetroot for leaves, grow seedlings in clean soil. When 4-6 true leaves grow, transplant the seedlings of red beetroot for leaves into the above-mentioned cadmium-c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com