Low-temperature sintered ceramic glazed tile and preparation method thereof
A low-temperature firing and ceramic glaze technology, applied in the field of building materials, can solve the problems of difficult utilization of tailings resources and high energy consumption for firing, and achieve the effects of shortening firing time, avoiding waste of resources and improving work efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
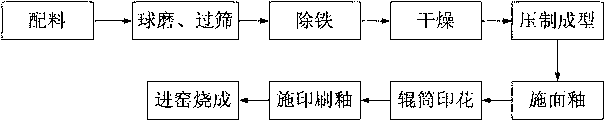
[0108] The preparation method of the ceramic glazed tile of described low-temperature firing comprises the following steps:
[0109] S1. Ingredients: Select raw materials of brick components used to prepare ceramic glazed bricks, including feldspar, clay, high-temperature sand, talc and lithium feldspar in lithium mine tailings. The component raw materials and contents of the bricks are as follows: Weight percent gauges include:
[0110] SiO 2 69.4%;
[0111] al 2 o 3 19.5%;
[0112] LiO 2 0.2%;
[0113] CaO 0.6%;
[0114] MgO 3.7%;
[0115] Na 2 O 1%;
[0116] K 2 O 5.5%;
[0117] Fe 2 o 3 0.2%;
[0118] TiO 2 0.1%.
[0119] S2. Ball milling, sieving, and iron removal: add water to mix with the raw materials of the adobe, send it to a ball mill for ball milling, and then sieve and remove iron.
[0120] S3. Drying: Spray-dry the adobe raw material after iron removal by using a spray drying tower to obt...
Embodiment 2
[0144] The preparation method of the ceramic glazed tile of described low-temperature firing comprises the following steps:
[0145] S1. Ingredients: Select raw materials of brick components used to prepare ceramic glazed bricks, including feldspar, clay, high-temperature sand, talc and lithium feldspar in lithium mine tailings. The component raw materials and contents of the bricks are as follows: Weight percent gauges include:
[0146] SiO 2 68.4%;
[0147] al 2 o 3 20.5%;
[0148] LiO 2 0.5%;
[0149] CaO 0.5%;
[0150] MgO 3.9%;
[0151] Na 2 O 1.4%;
[0152] K 2 O 4.3%;
[0153] Fe 2 o 3 0.4%;
[0154] TiO 2 0.1%.
[0155] S2. Ball milling, sieving, and iron removal: add water to mix with the raw materials of the adobe, send it to a ball mill for ball milling, and then sieve and remove iron.
[0156] S3. Drying: Spray-dry the adobe raw material after iron removal by using a spray drying tower to obt...
Embodiment 3
[0179] The preparation method of the ceramic glazed tile of described low-temperature firing comprises the following steps:
[0180] S1. Ingredients: Select raw materials of brick components used to prepare ceramic glazed bricks, including feldspar, clay, high-temperature sand, talc and lithium feldspar in lithium mine tailings. The component raw materials and contents of the bricks are as follows: Weight percent gauges include:
[0181] SiO 2 69.5%;
[0182] al 2 o 3 19.5%;
[0183] LiO 2 0.2%;
[0184] CaO 0.5%;
[0185] MgO 3.7%;
[0186] Na 2 O 1%;
[0187] K 2 O 5.3%;
[0188] Fe 2 o 3 0.2%;
[0189] TiO 2 0.1%.
[0190] Lithium feldspar (LiAlSi) in lithium mine tailings 4 o 10) as the brick adobe cooling material of the present invention can reduce the firing temperature of glazed tiles, shorten the cooling time of the biscuit firing cycle, and realize low-temperature fast firing. At the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com