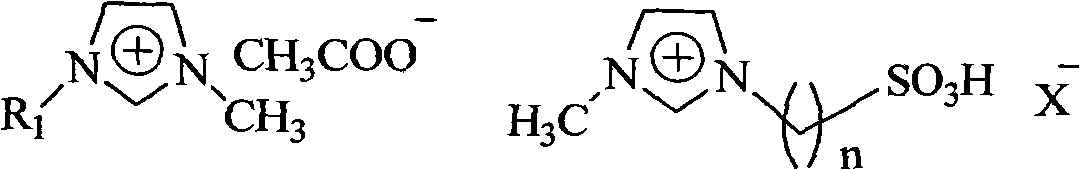Novel method for recovering calcium lactate by hydrolysis of waste polylactic acid material
A technology of polylactic acid material and calcium lactate, applied in the preparation of carboxylate, carboxylate/lactone, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems such as catalyst can not be reused, pollution, catalyst can not be reused reaction conditions, etc., Achieve the effect of overcoming the problem of non-reusability, easing reaction conditions, improving equipment corrosion and wastewater discharge problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
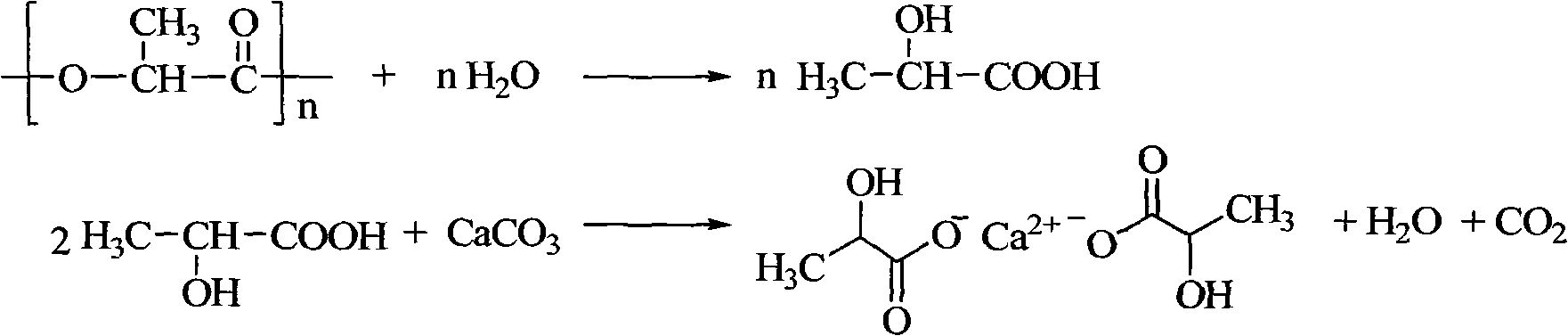
[0020] Example 1: Put 12.0g of waste PLA into an autoclave, add 6g of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazole acetate and 18g of water successively, stir and react at 130°C for 2h, after cooling down to room temperature, add certain Mass of CaCO 3 , filtered, after the filtrate was distilled under reduced pressure to remove water, a certain amount of absolute ethanol was added, filtered, the filter cake was calcium lactate, and the ionic liquid was recovered from the filtrate through reduced pressure distillation. The PLA hydrolysis rate is 93.9%, and the calcium lactate yield is 91.8%.
Embodiment 2
[0021] Example 2: The experimental conditions and steps are the same as in Example 1, except that 1-butyl-3-methylimidazole acetate is changed to 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazole acetate, and the PLA hydrolysis rate is 93.0%. Calcium lactate yield 91.7%.
Embodiment 3
[0022] Example 3: The experimental conditions and steps are the same as in Example 1, except that 1-butyl-3-methylimidazole acetate is changed to 1-octyl-3-methylimidazole acetate, and the PLA hydrolysis rate is 93.2%. Calcium lactate yield 91.3%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com