Method for preparing magnesium-silver hydrogen storage material
A hydrogen storage material, magnesium-silver technology, applied in the field of hydrogen storage materials, achieves the effects of fast hydrogen absorption and desorption, reduced consumption, and lower melting and annealing temperatures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
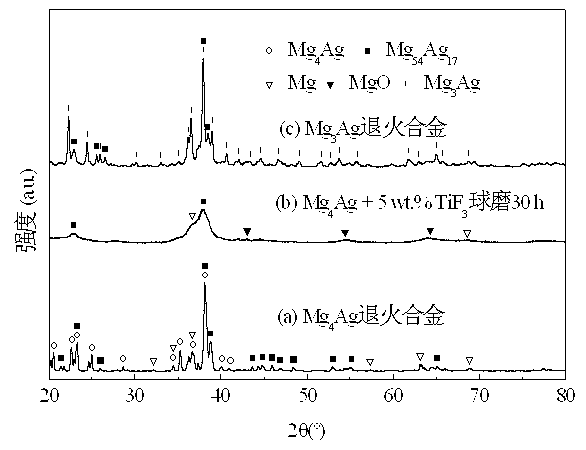
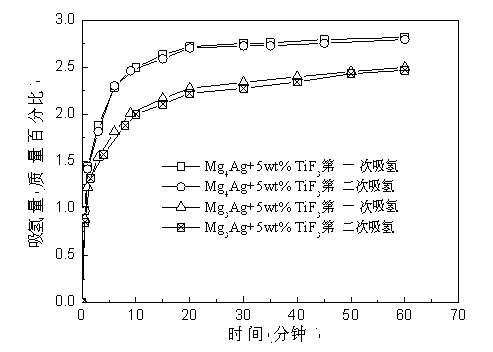
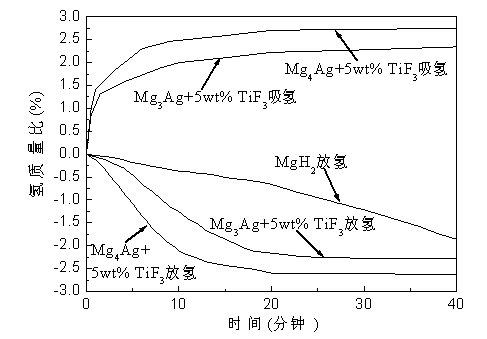
[0021] Example 1: Put a Mg block with a total weight of about 30 grams and a molar ratio of 4:1 (99% purity, add 8% more burn loss to the Mg block) and Ag sheet (99.5% purity) into a copper crucible , and then induction smelted twice under 15 KW power to obtain smelted Mg 4 Ag alloy, the alloy is annealed at 300 ℃ for 6 hours in a common vacuum annealing furnace, the alloy is composed of Mg 4 Ag, Mg 54 Ag 17 and a small amount of Mg heterogeneous composition (see figure 1 (a)). Use a grinder to remove the oxide skin on the surface of the annealed alloy, and then grind it into a 100-mesh alloy powder in a glove box, and add TiF to the alloy powder at 5wt.% of the magnesium-silver hydrogen storage material 3 (purity 99.9 wt.%) was ball milled for 30 h in a ball mill tank filled with 2 atm argon to obtain an amorphous alloy (see figure 1 (b)); where the ball-to-material ratio is 20:1, and the rotational speed of the ball mill is 300 rpm. The alloy po...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2: Put a Mg block with a total weight of about 30 grams and a molar ratio of 3:1 (99% purity, add 8% more burning loss to the Mg block) and Ag flakes (99.5% purity) into a copper crucible , and then induction smelted twice under 15 KW power to obtain smelted Mg 3 Ag alloy, the alloy is annealed at 300 ℃ for 6 hours in a common vacuum annealing furnace, the alloy is composed of Mg 3 Ag and Mg 54 Ag 17 phase composition (see figure 1 (c)). Use a grinder to remove the oxide skin on the surface of the annealed alloy, and then grind it into a 100-mesh alloy powder in a glove box, and add TiF to the alloy powder at 5wt.% of the magnesium-silver hydrogen storage material 3 (Purity 99.9 wt.%) Amorphous alloy was obtained by ball milling in a ball mill tank filled with 2 atm argon for 30 h; the ball-to-material ratio was 20:1, and the ball mill speed was 300 rpm. The alloy powder after ball milling was found to have good hydrogen storage perfor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com