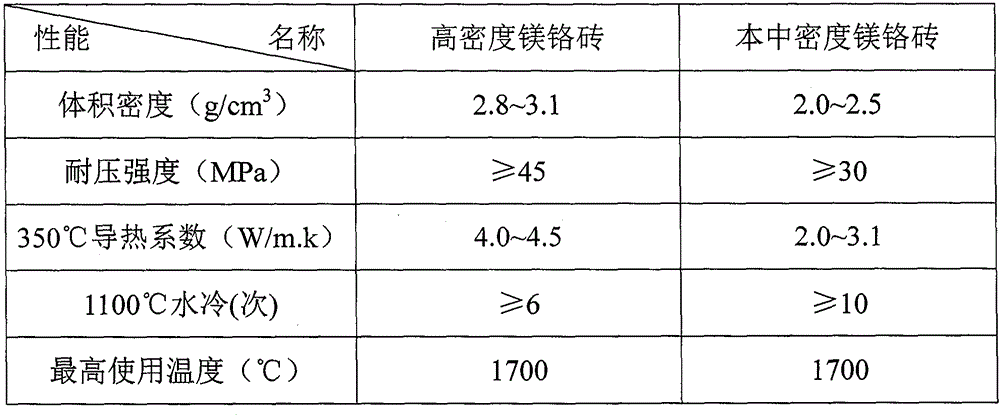
Medium-density magnesite-chrome brick for rotary kiln
A medium-density, magnesia-chrome brick technology, applied in the field of refractory materials, can solve problems such as increased heat dissipation of the kiln shell, thermal expansion of the shell, and increased heat consumption of clinker, so as to reduce energy and equipment power consumption and resist thermal shock Good performance and the effect of improving the working environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] The raw materials and parts by weight used in this embodiment are: 48 parts of magnesia of 0-5 mm, 22 parts of magnesia powder not larger than 180 mesh, 14 parts of chrome ore sand of 0-3 mm, 6 parts of chrome ore powder not larger than 180 mesh, 10 parts of 0-1mm magnesium oxide hollow spheres, 4 parts of industrial lignosulfonate solution with additional binder.
[0023] A method for preparing medium-density magnesia-chrome bricks for a rotary kiln comprises the following steps in sequence:
[0024] A. Ingredients: After mixing the granular material, lightweight aggregate and binder evenly in proportion, then add powder in proportion and stir to form a uniform material;
[0025] B. Forming: Add the homogeneous material formed in step A into the mold, and form it into a green body by vibrating on a vibrating press. The vibrating pressure is 30 tons, and the product density is 2.5g / cm 3 , the broken rate of the hollow ball is 12%;
[0026] C. Drying and firing: After ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] The raw materials and parts by weight used in this embodiment are: 25 parts of magnesia of 0-5 mm, 30 parts of magnesia powder not larger than 180 mesh, 20 parts of chrome ore sand of 0-3 mm, 5 parts of chrome ore powder not larger than 180 mesh, 20 parts of 0-5mm magnesium-aluminum hollow spheres, 6 parts of methyl cellulose solution as a binder.
[0030] A method for preparing medium-density magnesia-chrome bricks for a rotary kiln comprises the following steps in sequence:
[0031] A. Ingredients: After mixing the granular material, lightweight aggregate and binder evenly in proportion, then add powder in proportion and stir to form a uniform material;
[0032] B. Forming: Add the homogeneous material formed in step A into the mold, use a 300-ton press to form it, control the stroke, keep the product size fixed, and the product reaches a density of 2.2g / cm 3 , the crushing rate of lightweight aggregate is 10%;
Embodiment 3
[0036] The raw materials and parts by weight used in this embodiment are: 25 parts of magnesia of 0-5 mm, 26 parts of magnesia powder not larger than 180 mesh, 15 parts of chrome ore sand of 0-3 mm, 4 parts of chrome ore powder not larger than 180 mesh, 20 parts of 0-1mm magnesium-chromium hollow spheres, 10 parts of 0-3mm magnesium-calcium hollow spheres, and 8 parts of yellow dextrin melt as a binder.
[0037] A method for preparing medium-density magnesia-chrome bricks for a rotary kiln comprises the following steps in sequence:
[0038] A. Ingredients: After mixing the granular material, lightweight aggregate and binder evenly in proportion, then add powder in proportion and stir to form a uniform material;
[0039] B. Forming: Add the homogeneous material formed in step A into a mold with a fixed size, and vibrate it on a vibrating press to form a green body. The vibrating pressure is 30 tons, and the product density is 2.0g / cm 3 , the crushing rate of lightweight aggreg...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com