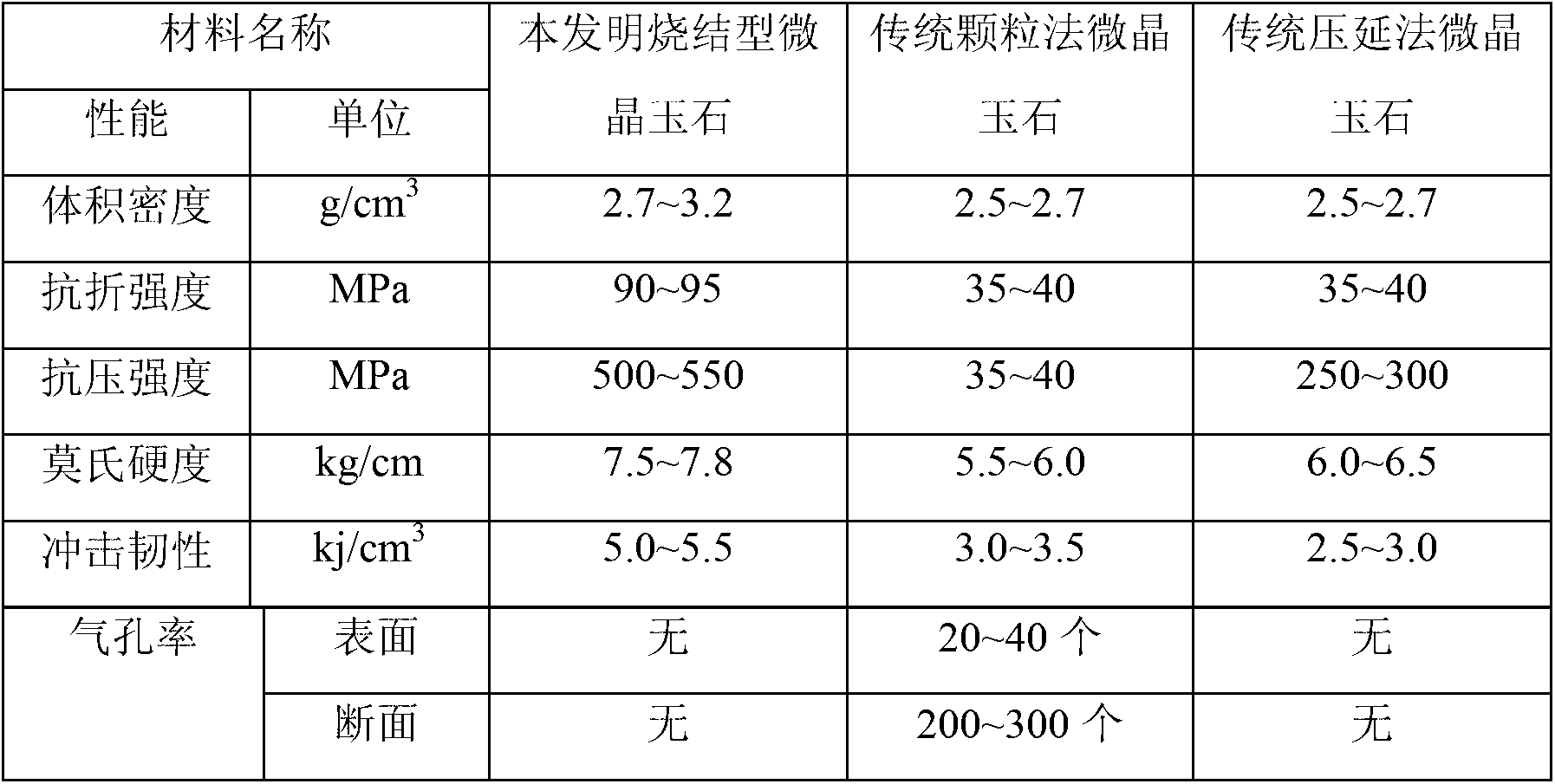
Pore-free sinter molding microcrystal jade and manufacturing technology
A technology of microcrystalline jade and sintering molding, which is applied in the field of microcrystalline jade, can solve the problems of high material brittleness, lack of diversification, difficult processing and molding, etc., and achieve the effect of good toughness and strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] 1. Ingredients design: select the raw material ratio (by weight) according to the raw material composition, of which the main raw materials: 60 parts of quartz sand, 18 parts of calcite, 5 parts of fluorite, 3 parts of dolomite; auxiliary raw materials: 7 parts of alumina, 4 parts of sodium carbonate, 4 parts of potassium carbonate, 5 parts of zinc oxide, 2 parts of sodium nitrate. Stir the said raw materials through a mixer for 7 minutes to make them evenly mixed.
[0031] 2. High-temperature melting: evenly put the mixed raw materials into the high-temperature melting furnace, melt at 1470°C for 4 hours, and form qualified glass liquid through homogenization and clarification.
[0032] 3. Forming of semi-finished products: Qualified glass liquid is made into a glass sheet with a thickness of 4mm and a diameter of 130mm through the method of dripping, forming a qualified semi-finished product.
[0033] 4. Sintering molding:
[0034] a. Carry out heat treatment throug...
Embodiment 2
[0039] 1. Ingredients design: select the raw material ratio (by weight) according to the raw material composition, of which the main raw materials are: 55 parts of quartz sand, 10 parts of potassium feldspar, 23 parts of calcite, 5 parts of fluorite, and 3 parts of dolomite; auxiliary raw materials : 10 parts of sodium carbonate, 5 parts of zinc oxide, 2 parts of sodium nitrate. Stir the said raw materials through a mixer for 6 minutes to make them evenly mixed.
[0040] 2. High-temperature melting: evenly put the mixed raw materials into a high-temperature melting furnace, melt at 1490°C for 4 hours, and form qualified glass liquid through homogenization and clarification.
[0041] 3. Forming of semi-finished products: Qualified glass liquid is made into a glass sheet with a thickness of 6mm and a diameter of 120mm through the method of dripping, forming a qualified semi-finished product.
[0042] 4. Sintering molding:
[0043] a. Carry out heat treatment through sintering ...
Embodiment 3
[0048] 1. Ingredients design: select the raw material ratio (by weight) according to the raw material composition, of which the main raw materials: 70 parts of quartz sand, 25 parts of calcite, 4 parts of fluorite, 2 parts of dolomite; auxiliary raw materials: 6 parts of alumina, 5 parts of sodium carbonate, 10 parts of potassium carbonate, 5 parts of zinc oxide, 3 parts of sodium nitrate. Stir the said raw materials through a mixer for 5 minutes to make them evenly mixed.
[0049]2. High-temperature melting: evenly put the mixed raw materials into the high-temperature melting furnace, melt at 1450°C for 6 hours, and form qualified glass liquid through homogenization and clarification.
[0050] 3. Forming of semi-finished products: Qualified glass liquid is made into a glass sheet with a thickness of 2mm and a diameter of 100mm through the method of dripping, forming a qualified semi-finished product.
[0051] 4. Sintering molding:
[0052] a. Carry out heat treatment throug...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bulk density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com