Metal ceramic composite substrate and manufacturing method for same
A metal-ceramic composite and metal-ceramic technology, which is applied in printed circuit manufacturing, circuit substrate materials, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of poor bonding performance of metal-ceramic composite substrates, poor thermal conductivity of metal substrates, etc., and achieves easy control and improvement of manufacturing conditions. Thermal conductivity, simple operation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
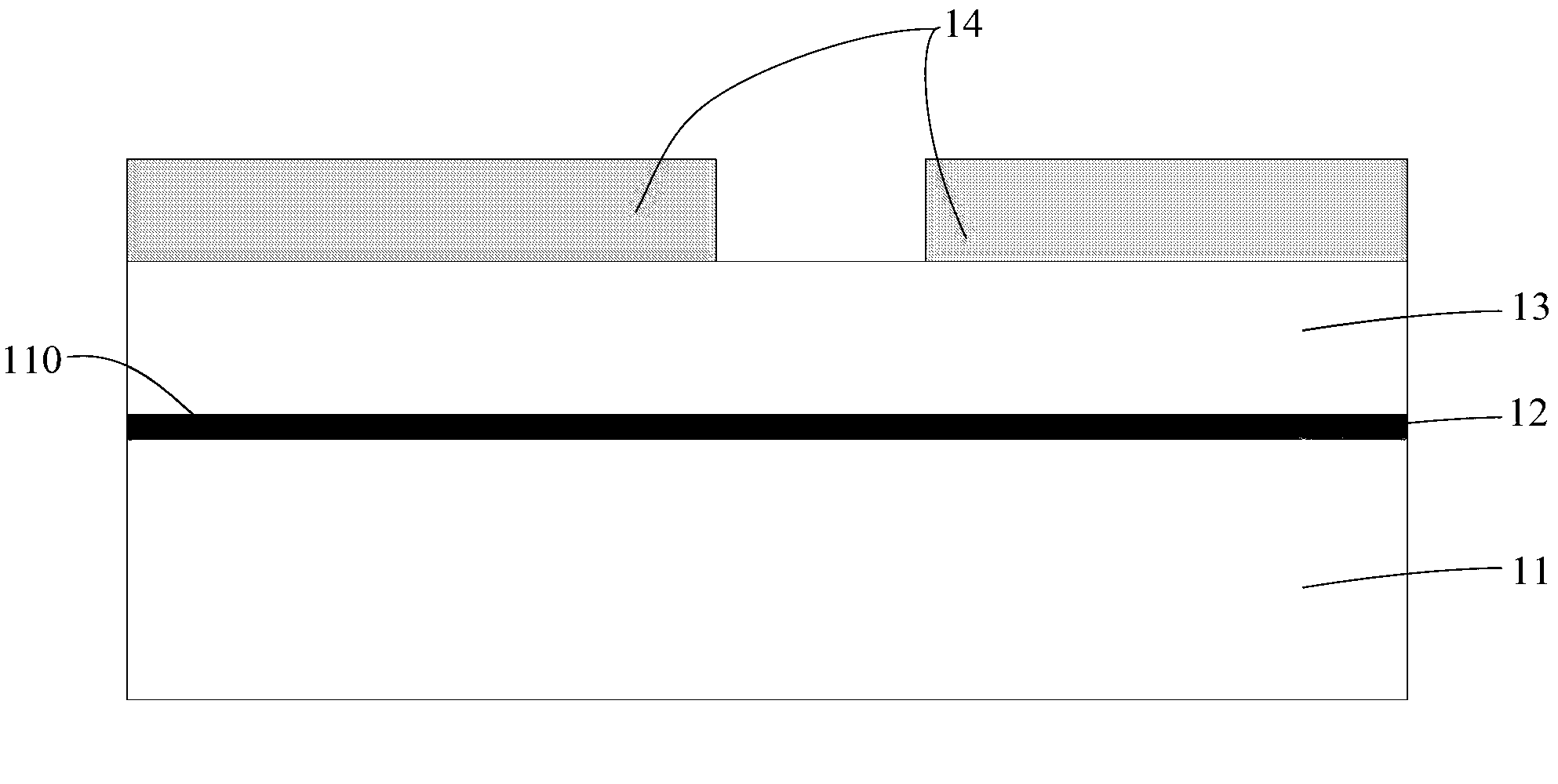
[0026] Please refer to figure 1 , the metal-ceramic composite substrate includes a metal base 11, a ceramic layer 13 disposed on the first surface 110 of the metal base 11, a metal circuit layer 14 disposed on the surface of the ceramic layer 13 away from the first surface 110, and a metal circuit layer 14 through the metal base 11 The metal-ceramic transition layer 12 is formed by injecting nitrogen on the first surface 110 and is connected to the ceramic layer 13. The ceramic layer 13 is composed of a ceramic film and is located between the metal-ceramic transition layer 12 and the metal circuit layer 14. The metal-ceramic transition layer 12 is a mixture of metal and metal nitride.
[0027] The material of the metal base 11 may be aluminum, aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy, titanium alloy, nickel alloy, steel and copper alloy, zinc alloy, lead or titanium-aluminum intermetallic compound and the like. When in use, the material of the metal matrix 11 can be selected according...
Embodiment 2
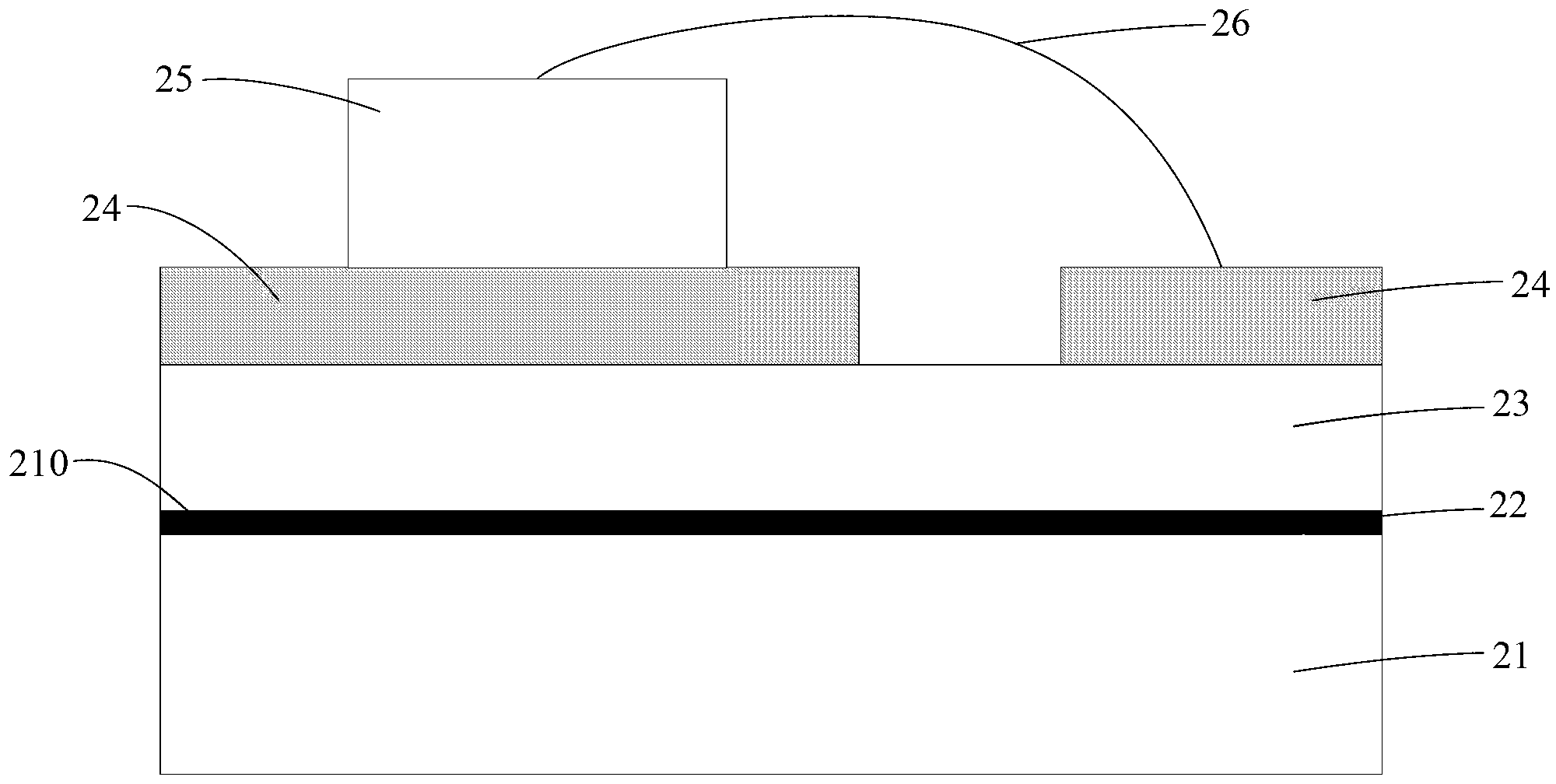
[0035] Please refer to figure 2, the metal-ceramic composite substrate includes a metal base 21, a ceramic layer 23 disposed on the first surface 210 of the metal base 21, a metal circuit layer 24 disposed on the surface of the ceramic layer 23 away from the first surface 210, and a metal circuit layer 24 through the metal base 21 The metal-ceramic transition layer 22 is formed by injecting nitrogen into the first surface 210 of the first surface 210 and is connected to the ceramic layer 23. The ceramic layer 13 is composed of a ceramic film and is located between the metal-ceramic transition layer 22 and the metal circuit layer 24. The metal-ceramic transition layer 22 is a mixture of metal and metal nitride.
[0036] The material of the metal base 21 may be aluminum, aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy, titanium alloy, nickel alloy, steel and copper alloy, zinc alloy, lead or titanium-aluminum intermetallic compound, and the like. During use, the material of the metal matrix 2...
Embodiment 3
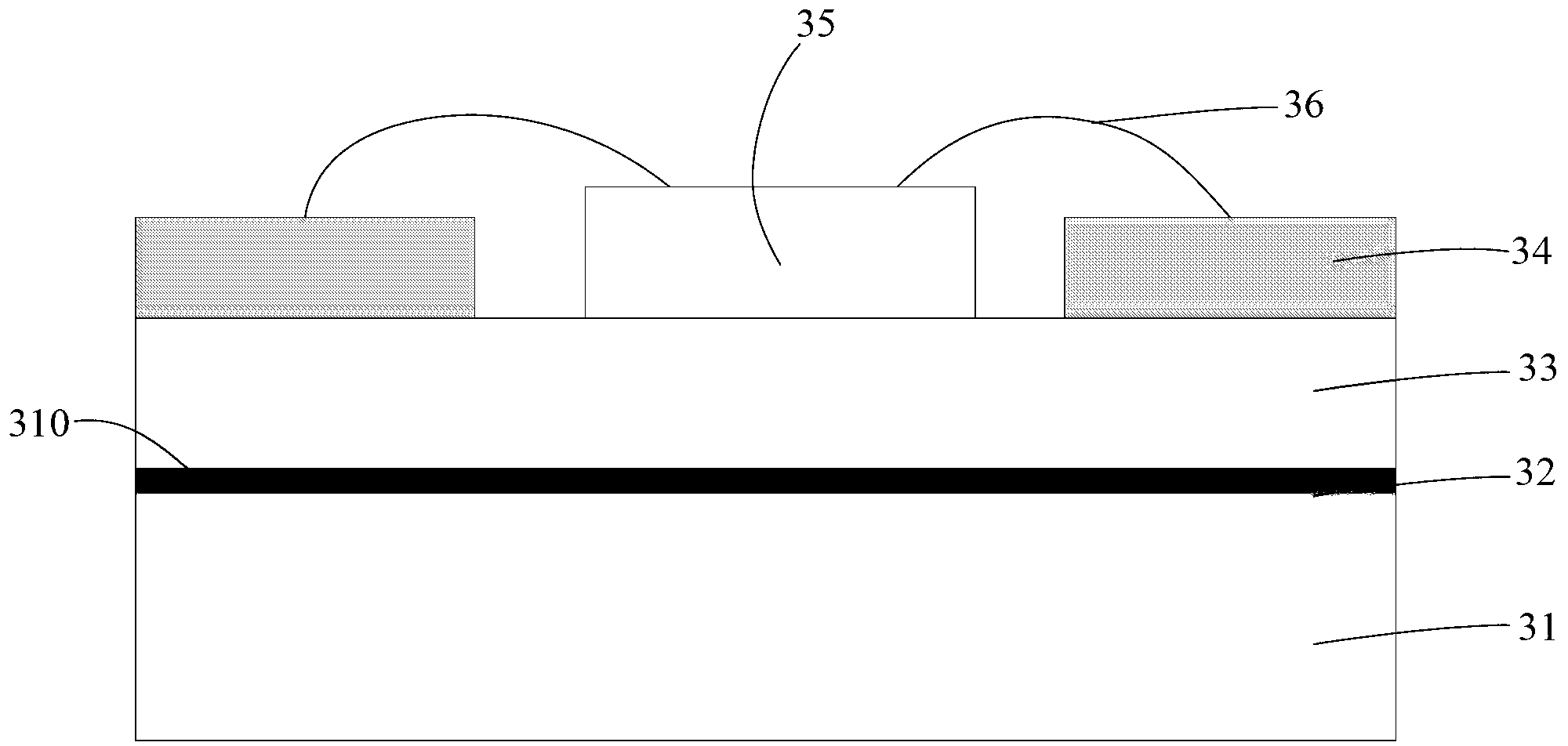
[0047] The difference between this embodiment and the second embodiment is:
[0048] The heating element 35 of this embodiment is installed on the ceramic layer 33, that is, the heating element 35 and the metal circuit layer 34 are arranged side by side on the ceramic layer 33 to form a circuit layer, so the ceramic layer 33 is located between the circuit layer and the circuit layer. between the cermet transition layers 32 .
[0049] The heating element 35 in this embodiment is a light-emitting diode with a horizontal electrode structure.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com