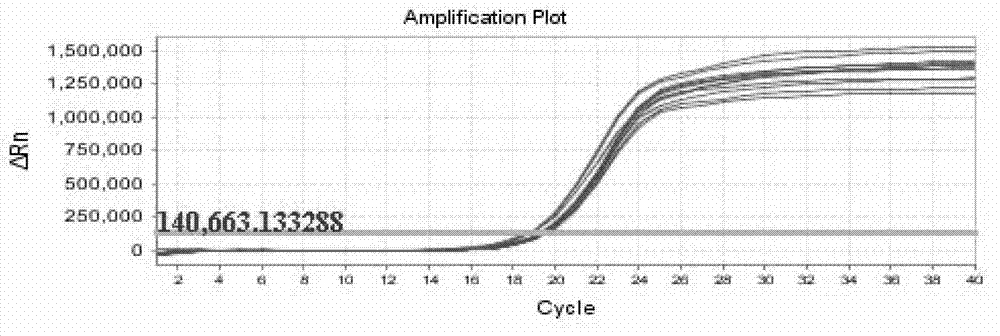
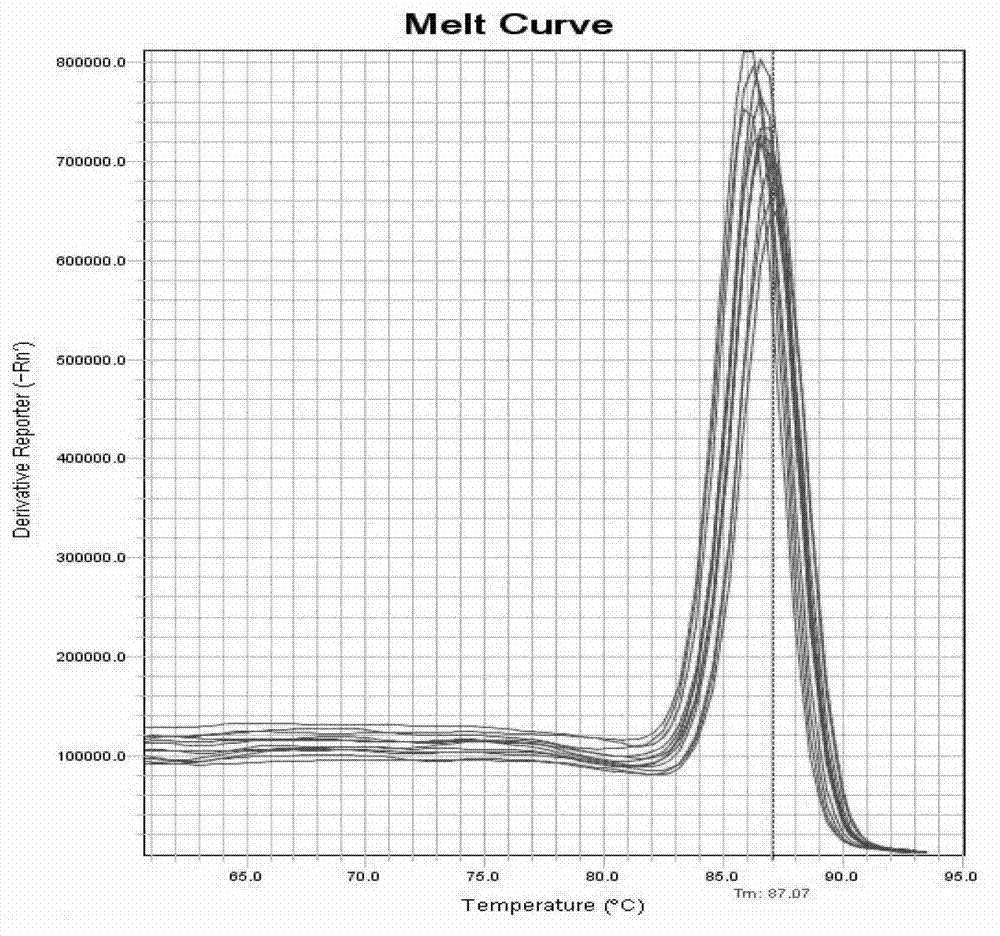
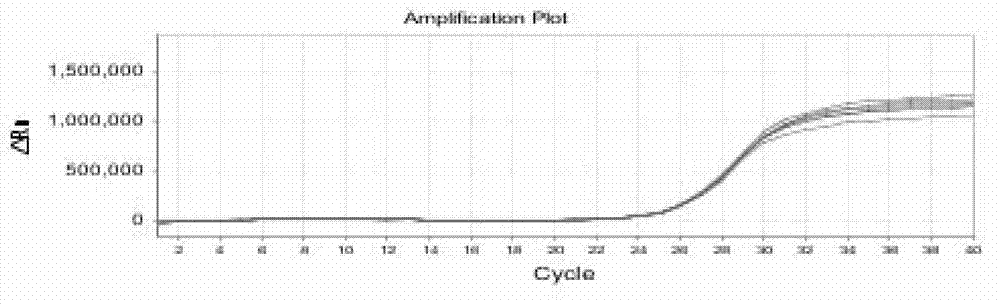
Method for detecting egg laying amount of insects by heat shock protein 90 gene
A technology of insect egg production and heat shock protein, applied in the field of detection of insect egg production with heat shock protein 90 gene, can solve the problems of time-consuming, labor-intensive and expensive, and achieve the effect of easy purchase, simple operation and wide source of materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1. Discovery of Heat Shock Protein 90 and its Encoding Gene for Detecting Insect Oviposition and Design of Special Primers
[0044] Studies have found that the heat shock protein 90 gene is a good molecular marker for detecting the amount of eggs laid by insects. Therefore, the present invention uses the expression of the heat shock protein 90 (heat shock protein 90) coding gene of the stinkbug to detect the production of the stinkbug. Egg volume.
[0045] The nucleotide sequence of the heat shock protein 90 coding gene of the stinkbug is sequence 1 in the sequence listing or sequence 1 in the sequence listing from the 2nd to 331st nucleotides at the 5' end, and the amino acid sequence of the protein is in the sequence listing Sequence 2 of .
[0046] The primers designed to amplify the coding gene according to the heat shock protein 90 coding gene of the stinkbug are as follows:
[0047] Upstream primer: GAAGGTGAGGATGATAAGCCCAA (SEQ ID NO: 3);
[0048] Downs...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2, the application of heat shock protein 90 or coding gene or special primers in detecting the amount of eggs laid by stinkbugs
[0050] The stink bug (Arma chinensis) adopted in the following experiments is recorded in Taxonomic and bionomic notes on Arma chinensis (Fallou) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae: Asopinae, Zootaxa, 3382: 41-52, 2012, the public can obtain from Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences Obtained) were divided into two groups according to the quality of food taken, 50 in each group:
[0051] Bacteria gnats eating artificial diet: stinkbugs fed artificial diet (27±1°C, 16:8(L:D), 75±5%RH) were fed with 160 μl of artificial diet per adult per day until the gnats fed artificial diet Stinkbugs die naturally;
[0052] The prey-feeding group of gnats: the gnats that feed on prey (27±1°C, 16:8(L:D), 75±5%RH) each pair of adults feeds one prey, every 7-15 days according to When the prey is eaten, the prey is replaced onc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com