A high-resolution sensing system for measuring the beat length and strain of polarization-maintaining optical fiber based on ofdr system
A polarization-maintaining optical fiber and high-resolution technology, applied in the field of distributed optical fiber sensors, can solve the problems of difficult polarization state or phase performance, unstable time and space changes of the optical fiber output polarization state, and avoid optical pulse width and data sampling. Rate limitation, fast signal processing and demodulation, effects of high spatial resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
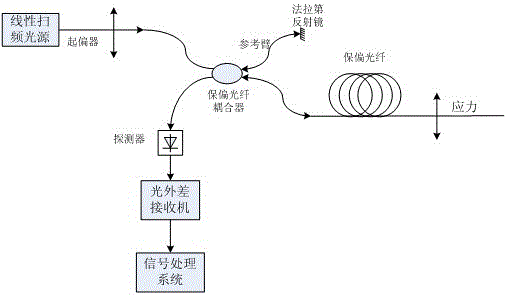
[0028] Such as figure 1 As shown, it is a schematic diagram of a high-resolution sensing system based on the OFDR system and Michelson interferometric structure to measure the beat length and stress or strain of polarization-maintaining optical fiber. It can be adjusted according to the measurement distance and the spatial resolution. The light generated by the linearly swept narrow-linewidth light source is converted into linearly polarized light by the fiber polarizer and injected into the polarization-maintaining fiber coupler; one output end of the fiber coupler is connected to the polarization-maintaining fiber used for strain testing, and the other end is connected to A section of polarization-maintaining fiber is used as a reference arm, and a mirror is attached to the end of the reference arm.
Embodiment 2
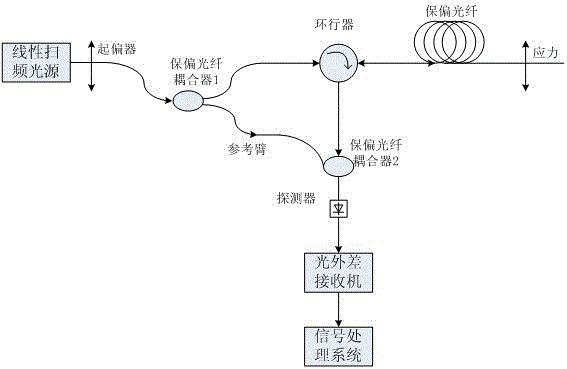
[0030] Such as figure 2 As shown, it is a schematic diagram of a high-resolution sensing system based on the OFDR system and the MZ interferometric structure using single-ended detection to measure the beat length and stress or strain of polarization-maintaining fibers. A section of polarization-maintaining fiber connected to the first polarization-maintaining fiber coupler as a reference arm is connected to the output end of the circulator through a second polarization-maintaining fiber coupler to generate interference, and a detector is used to detect the interference signal.
Embodiment 3
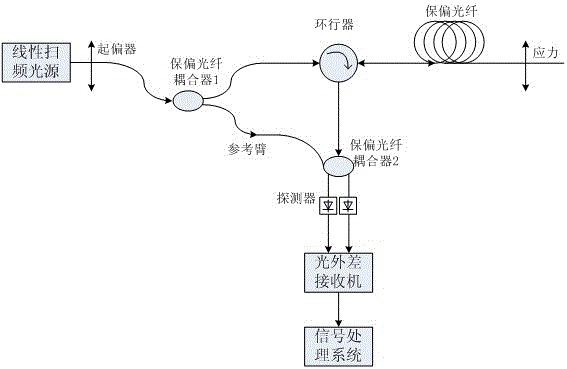
[0032] image 3 Shown is a schematic diagram of the dual-way balanced detection structure. When a point on the test polarization-maintaining fiber is strained, the beat length of this position will change, and the amount of change is proportional to the strain. At the same time, the Rayleigh backscattering signal generated at this position will propagate to the polarization-maintaining fiber coupler to mix and interfere with the optical signal returned by the reference arm, and output a beat frequency signal. The frequency of the beat frequency signal reflects the stress or strain position, and the magnitude of the beat frequency is the magnitude of the optical power at that point. The beat length at this time can be obtained by detecting the cycle of a certain polarization state optical power change, and finally the corresponding stress or strain can be obtained through the mapping model of the beat length and the change signal.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com