A Method for Predicting Retention Time in Gradient Elution Mode of Reversed-Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography
A reversed-phase high-efficiency liquid phase and retention time technology, applied in the field of liquid chromatography, can solve the problems of too many parameters and low practicability, and achieve the effect of simple prediction process and improved accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] Instrument: high performance liquid chromatography: Agilent1200HPLC. Equipped with online degassing device, its model is: G1379A DEGASSER serial#JP1321086; pump model: G1311AQuatPumpserial#DE33224312; G1313A ALS DE33223289; autosampler model: G1313A; UV-Vis detector model: G131413VWD.
[0092] Chromatographic column: reversed phase column model: SUPELCO C18, HPLC Column BL: 6580, 25 cm x 4.6 mm, 5 μm.
[0093] Conditions: room temperature 21-25°C, quantitative detection wavelength: 268nm; flow rate: 0.7ml / min.
[0094] Solvent: Gradient elution is done with two solvents. Solvent A: 0.1% formic acid aqueous solution; Solvent B: methanol.
[0095] Gradient elution conditions: injection volume: 10μl;
[0096] 1st order gradient elution condition: (0,20)→(2,10)→(17,100)→(20,100), where the abscissa represents the time (min), and the ordinate represents the volume fraction of the organic modifier (methanol) ( %).
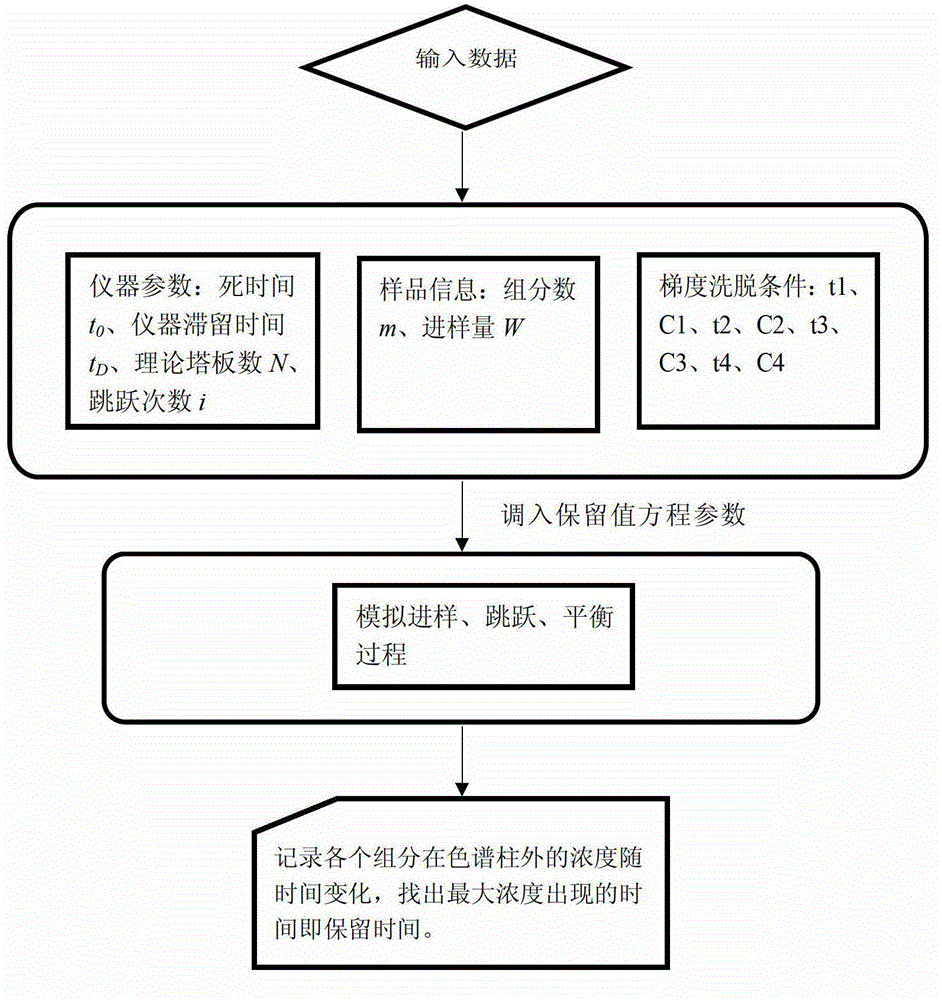
[0097] Determination of dead time of chromatographic ...
Embodiment 2
[0106] The process and condition of the present embodiment are identical with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0107] Elution condition: 2-step gradient elution condition: (0,20)→(2,20)→(22,40)→(30,65)→(32,65).
[0108] Selected compounds: sulfamethazine (SDD), sulfamethoxypyridazine (SMP) and sulfamethoxazole (SMZ).
[0109] (1) Determine the retention times of the three compounds under different isocratic conditions, as shown in the table below:
[0110]
[0111] The fitting results of the retention equation are shown in the table below:
[0112]
[0113] (2) Predict retention time.
[0114]
Embodiment 3
[0116] The process and condition of the present embodiment are identical with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0117] Elution conditions: 3-step gradient elution conditions: (0,20)→(2,20)→(8,28)→(18,28)→(28,78)→(32,78).
[0118] Selected compounds: sulfachloropyridazine (SCP), sulfaquinoxaline (SQ) and sulfachloropyrazine sodium (SPZ).
[0119] (1) Determine the retention times of the three compounds under different isocratic conditions, as shown in the table below:
[0120]
[0121]
[0122] The fitting results of the retention equation are shown in the table below:
[0123]
[0124] (2) Predict retention time.
[0125]
[0126] In summary, the above three examples have verified that the method can predict the retention time under any gradient condition with high precision, and the prediction process is simple.
[0127] Those skilled in the art can understand that the accompanying drawing is only a schematic diagram of a preferred embodiment, and the serial n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com