Material capable of controlling slow release of fertilizer
A technology of slow-release fertilizer and carbon material, applied in the field of new materials, materials for controlling slow-release of fertilizers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
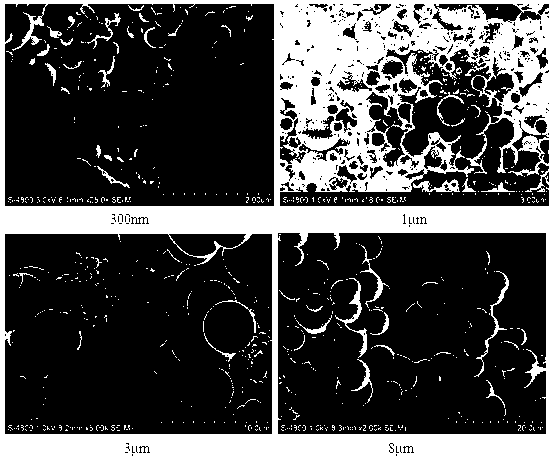
[0048] This example illustrates the synthesis method and synthesis results of carbon sphere materials.
[0049] 1) 300nm carbon spheres: configure 100mL of 0.5mol / L glucose solution, fully stir until the solution is clear, put it into a 150mL hydrothermal reaction kettle with a polytetrafluoroethylene lining, seal it, and conduct a hydrothermal reaction in an oven at 160°C for 5 hours, and the end After natural cooling, centrifuge at 15000r / min, the black carbon material was washed and centrifuged three times with purified water and ethanol respectively, and the final carbon material was obtained and dried in an oven at 80°C.
[0050] 2) 1μm carbon spheres: configure 100mL of 0.25mol / L starch solution, fully stir until the solution is clear, put it into a 150mL hydrothermal reaction kettle with a polytetrafluoroethylene lining, seal it, and conduct a hydrothermal reaction in an oven at 180°C for 5h, and the end After natural cooling, centrifuge at 15000r / min, the black carbon ...
Embodiment 2
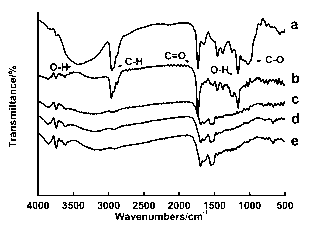
[0055] This example illustrates the superior structure of the synthetic carbon sphere material.
[0056] The carbon spheres of Example 1 were taken for infrared spectrum characterization. The result is as figure 2 As shown, the results show that carbon spheres are rich in carbon-oxygen bonds, as well as carbon-hydrogen bonds.
Embodiment 3
[0058] This example illustrates the specific steps for the synthesis of polyaspartic acid modified carbon sphere materials.
[0059] The 300nm carbon sphere obtained in Example 1 was taken, and the polyaspartic acid modified carbon sphere material was synthesized by the following steps.
[0060] Disperse 5 g of carbon spheres in 20 times the mass of deionized water, stir at high speed for 0.5 h to form a stable suspension, add 10 g of L-aspartic acid, 2 mL of 85% H 3 PO 4 Solution, 0.05g cross-linking agent N,N-methylenebisacrylamide, ultrasonically disperse at 200 watts for 1 hour, pass N 2 protection, then raised the temperature to 180°C for 1 hour, cooled to room temperature 25°C, washed with methanol and water three times each until neutral, and dried to obtain the intermediate product.
[0061] The obtained intermediate product was crushed, hydrolyzed for 0.5h under alkaline conditions, neutralized, and then the neutralized hydrolyzed solution was slowly poured into a s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com