A method for extracting d-ribose from fermentation broth using ion exchange and membrane separation technology
An ion exchange and fermentation broth technology, which is applied in the field of extracting D-ribose from fermentation broth by using ion exchange and membrane separation technology, can solve the problems of reduced membrane filtration speed, affected filtration effect, complicated operation steps, etc. The effect of reducing the extraction and separation steps, and the process is simple and reasonable
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
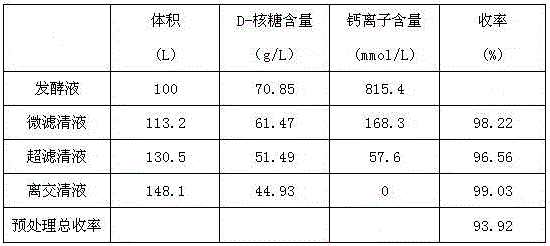
[0019] Pass 100L of D-ribose fermentation broth through a microfiltration membrane with a membrane pore size of 1000nm. The membrane entry pressure is 0.2MPa, the membrane exit pressure is 0.1MPa, and the operating temperature is 25°C. After the fermentation broth is concentrated 8 times, 25L of dialysis water is added. The microfiltrate passes through the ultrafiltration membrane with a membrane molecular weight cut-off of 5000, the operating pressure is 1.4MPa, and the operating temperature is 30-35°C. After the microfiltrate is concentrated 15 times, 25L of dialysis water is added. The filtrate passes through the 732-type cation exchange resin column at a flow rate of 2BV / H, and the effluent from the positive column is also directly connected to the 717-type anion-exchange resin column at a flow rate of 2BV / H. The ionized liquid is chromatographed by HZ-803 resin, the effluent is concentrated under reduced pressure, the temperature is controlled at 50-60°C, and the vacuum de...
Embodiment 2
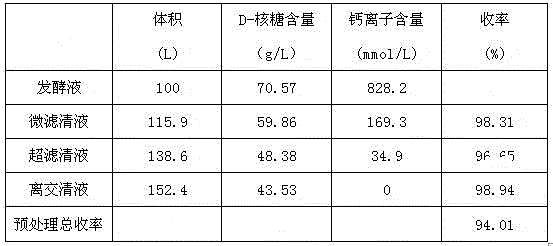
[0022] 100L of D-ribose fermentation broth passed through a microfiltration membrane with a membrane pore size of 500nm, the membrane entry pressure was 0.2MPa, the membrane exit pressure was 0.1MPa, and the operating temperature was 25°C. After the fermentation broth was concentrated 10 times, 25L of dialysis water was added. The filtrate passes through an ultrafiltration membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 2000, the operating pressure is 1.4 MPa, and the operating temperature is 30-35°C. After the microfiltrate is concentrated 15 times, 25 L of dialysis water is added. The ultrafiltrate passes through the 732-type cation exchange resin column at a flow rate of 2BV / H, and the effluent from the positive column is also directly connected to the 717-type anion-exchange resin column at a flow rate of 2BV / H. According to the follow-up extraction method in Example 1, after the D-ribose crystals were vacuum-dried, a total of 4.71Kg of D-ribose product was obtained. The purit...
Embodiment 3
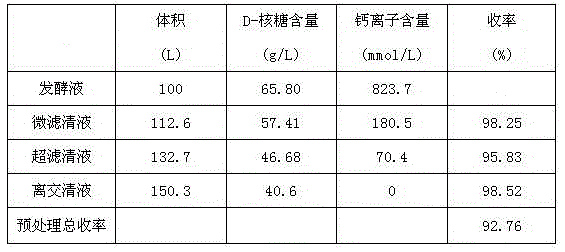
[0025] 100L of D-ribose fermentation broth passes through a microfiltration membrane with a membrane pore size of 200nm, the membrane entry pressure is 0.2MPa, the membrane exit pressure is 0.1MPa, and the operating temperature is 25°C. After the fermentation broth is concentrated 10 times, 30L of dialysis water is added. The microfiltrate passes through the ultrafiltration membrane with a membrane molecular weight cut-off of 1000, the operating pressure is 1.4MPa, and the operating temperature is 30-35°C. After the separation fluid is concentrated by 15 times, 30L of dialysis water is added. The filtrate passes through the 732-type cation exchange resin column at a flow rate of 2BV / H, and the effluent from the positive column is also directly connected to the 717-type anion-exchange resin column at a flow rate of 2BV / H. According to the subsequent extraction method in Example 1, after the D-ribose crystals were vacuum-dried, a total of 4.85 Kg of D-ribose product was obtained....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com