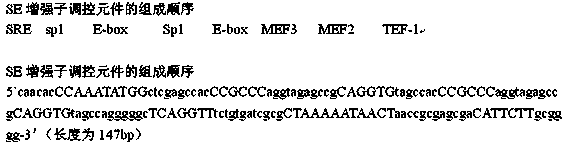An enhancer of myogenin (myog) gene
A technology of generating hormones and muscle cells, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as weak activity, and achieve the effects of diverse functions, obvious effects and simple production.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
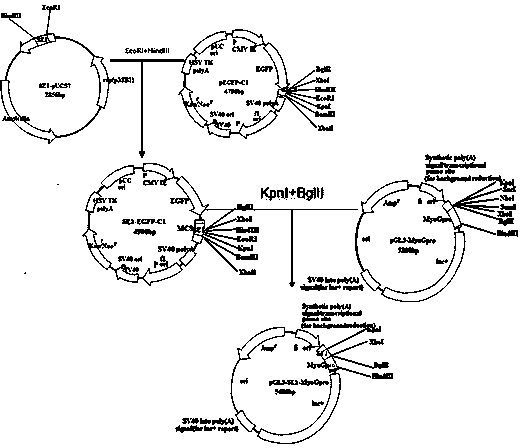
[0026] Example 1 Obtaining of pGL3-MyoGpro373
[0027] In the present invention, a nucleic acid sequence with a length of 2125 bp in the 5' end regulatory region of the MyoG gene is firstly obtained by PCR, and a method for analyzing the activity of the missing promoter fragment is used to obtain a nucleic acid sequence with a length of 373 bp and a relatively high muscle-specific promoter activity. The missing fragment of pGL3-MyoGpro373 (established through previous experiments, a vector that already exists in the laboratory).
[0028]
[0029] The steps for extracting genomic DNA with Tissue DNA Kit are as follows:
[0030] 1. Discard the culture medium, wash the cells 3 times with 4ml PBS, then digest the cells with 500μl trypsin, transfer the cells to a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 1000rpm for 5min at room temperature, and remove the supernatant thoroughly;
[0031] 2. Add 25ulOB protease, mix well, and treat in a water bath at 65°C for 5 minutes to completely lyse ...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2 Artificial synthesis of enhancer fragment "SE" and construction of expression vector
[0066] According to the preliminary bioinformatics analysis of MyoG natural promoter sequence and the sequence of promoter regulatory elements and the core sequences of some muscle-specific gene promoter regulatory elements found in bovine muscle cells, the present invention artificially designed and synthesized A muscle-specific enhancer sequence, which is linked to the 373 fragment of the pGL3-MyoGpro373 expression vector, can regulate the expression of the MyoG gene during the early differentiation of muscle cells by increasing the promoter activity of the MyoG gene (see figure 1 ). The gene expression regulatory elements contained in the enhancer sequence are E-box (Seq ID No: 2), SRE (Seq ID No: 3), KLF3 (Seq ID No: 4), E-box (Seq ID No: 5) , Sp1 (Seq ID No: 6), E-box (Seq ID No: 7), Sp1 (Seq ID No: 8), TEF-1 (Seq ID No: 9), and their nucleic acid sequence information...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Example 3 Analysis of MyoG promoter activity
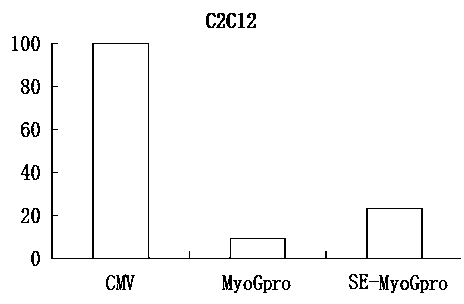
[0082] The promoter activity analysis was carried out by using the host cell transfection experimental method, so as to finally obtain the efficient and specific expression regulating the transcription of the bovine MyoG gene. It was found by double luciferase activity assay that the synthetic muscle enhancer increased the activity of MyoG promoter by about 2 times. Further studies have found that artificial synthetic muscle enhancers can increase the MyoG promoter activity in both the proliferation and differentiation stages of myoblasts ( image 3 and Figure 4 ).
[0083] Mouse C2C12 cells and bovine fibroblast cultures. When the growth density of cultured cells reaches about 80%-90%, discard the culture medium, rinse three times with PBS without calcium and magnesium ions, add 0.5ml of 0.25% trypsin for digestion, and place at 37°C for 1-2min. When 80% of the cells became rounded under the microscope, 5.5 ml of cell...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com