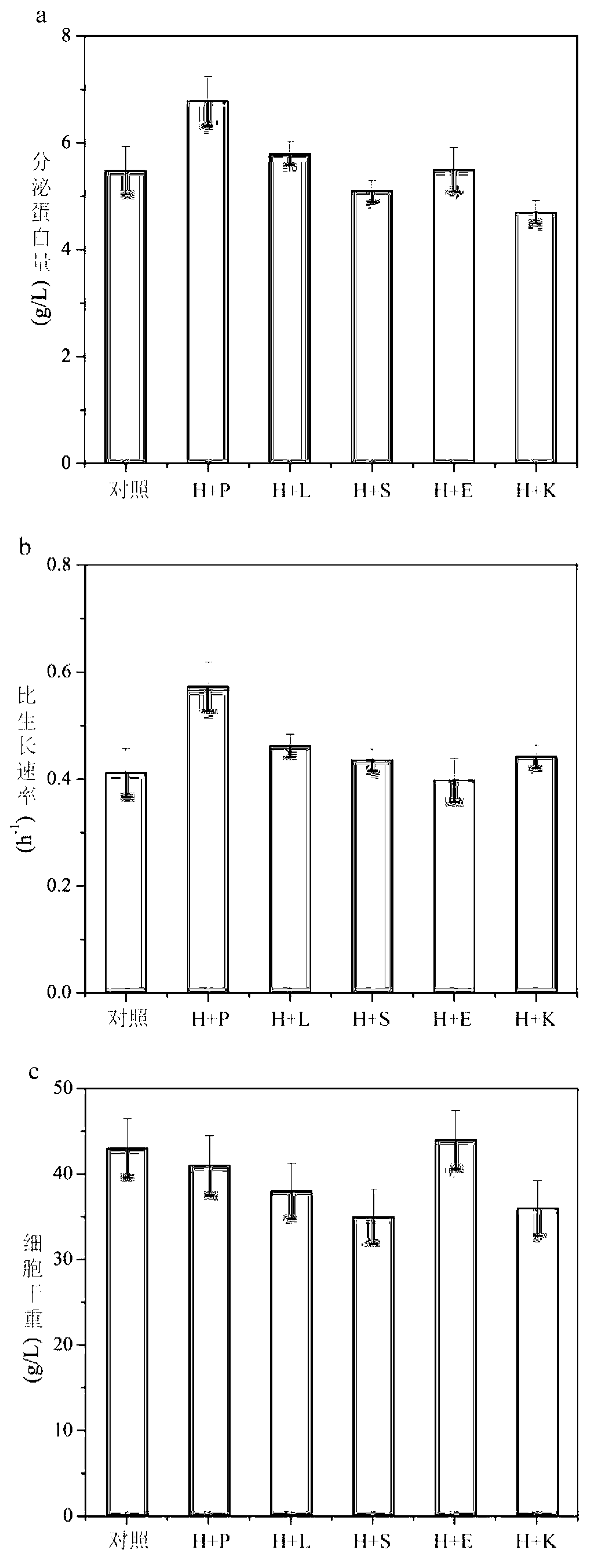
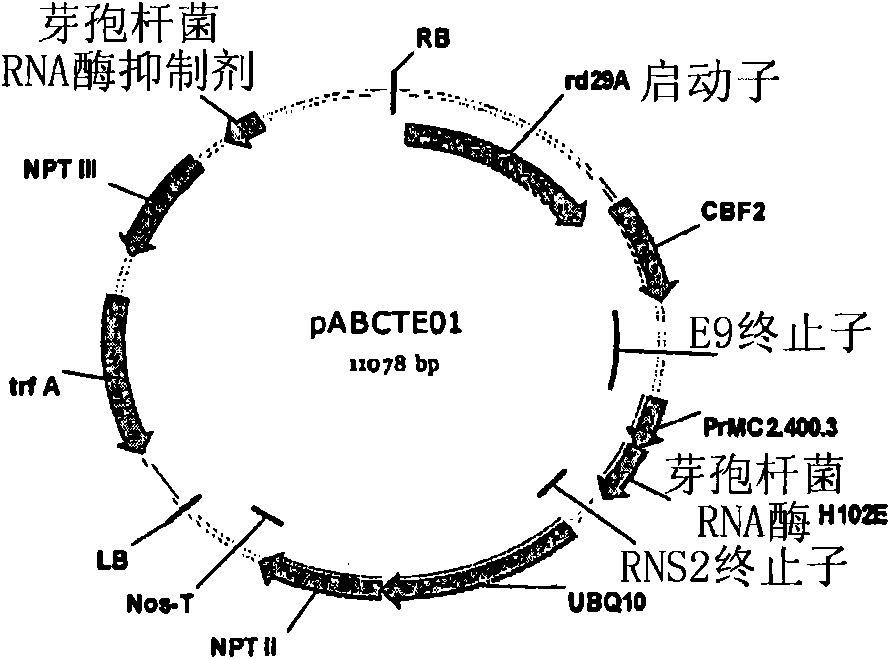
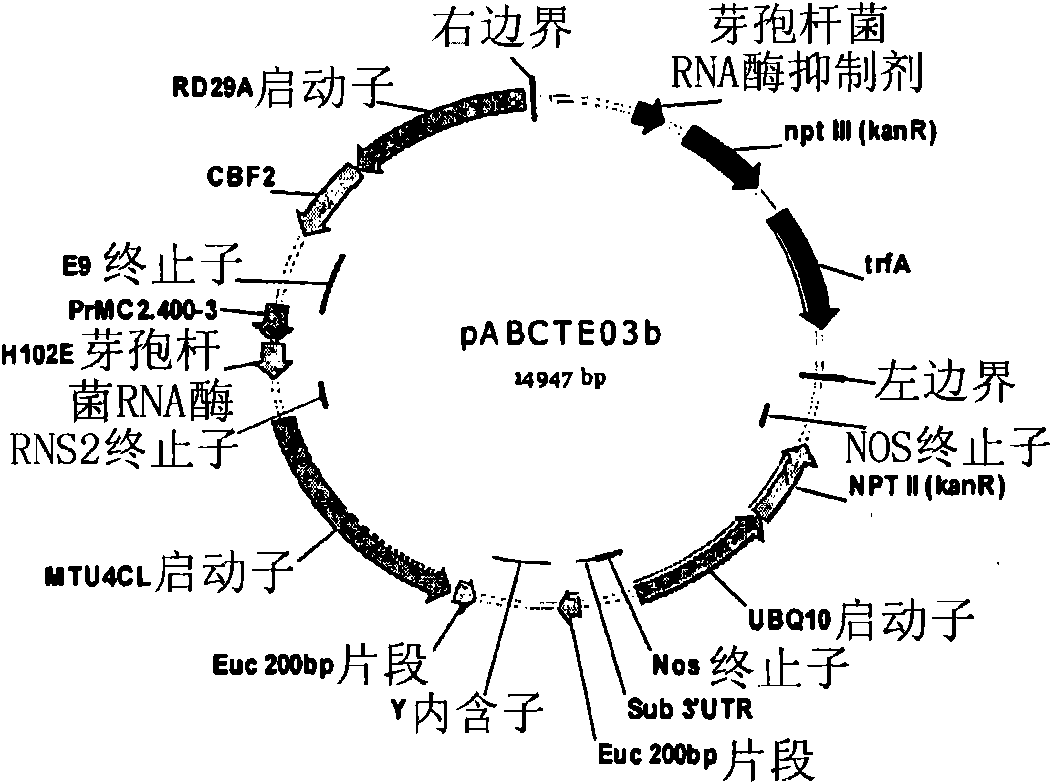
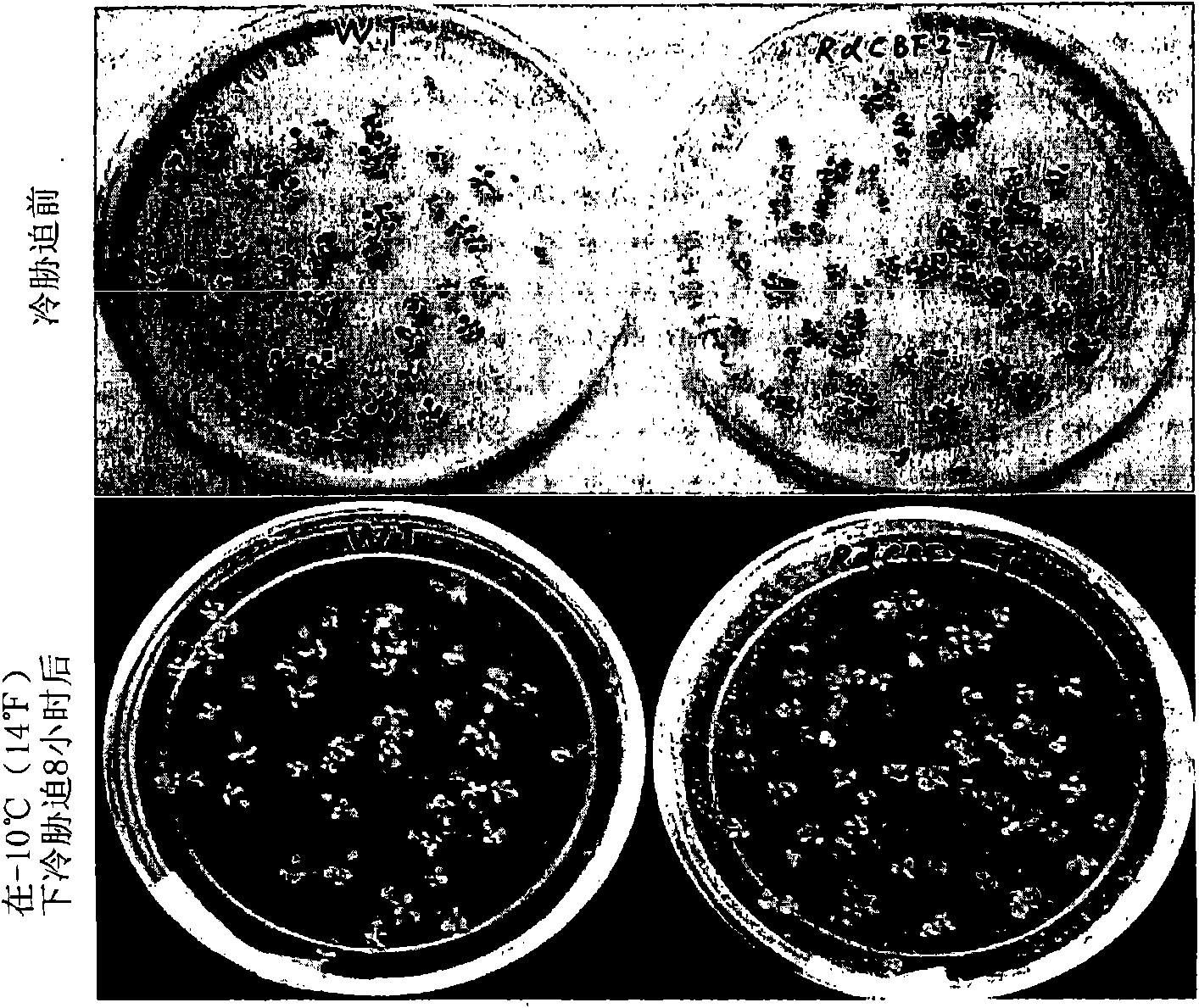
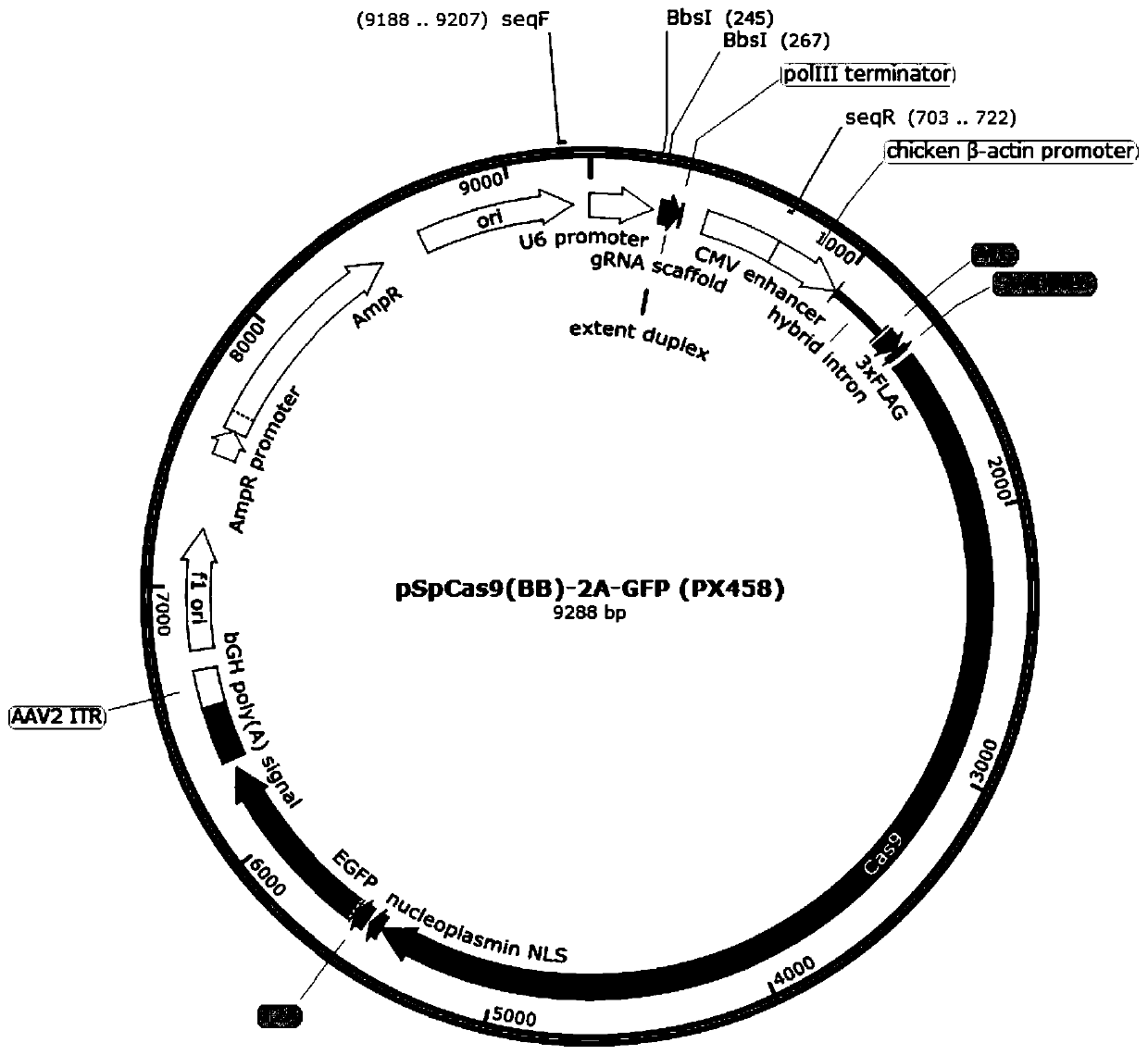
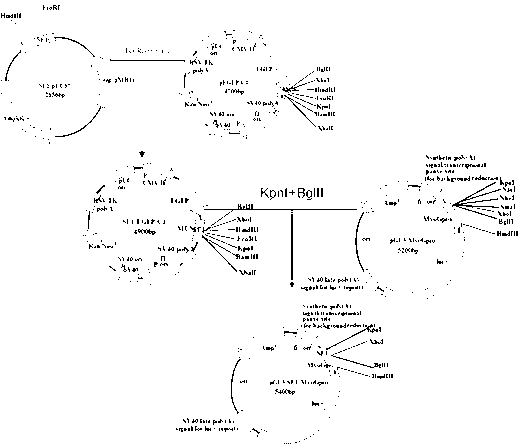
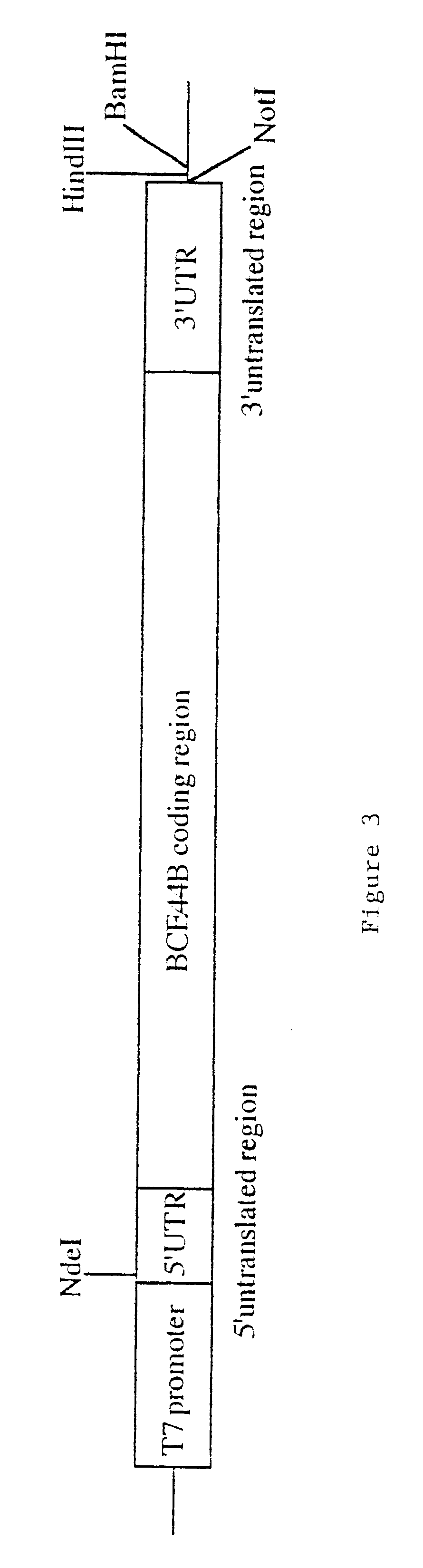
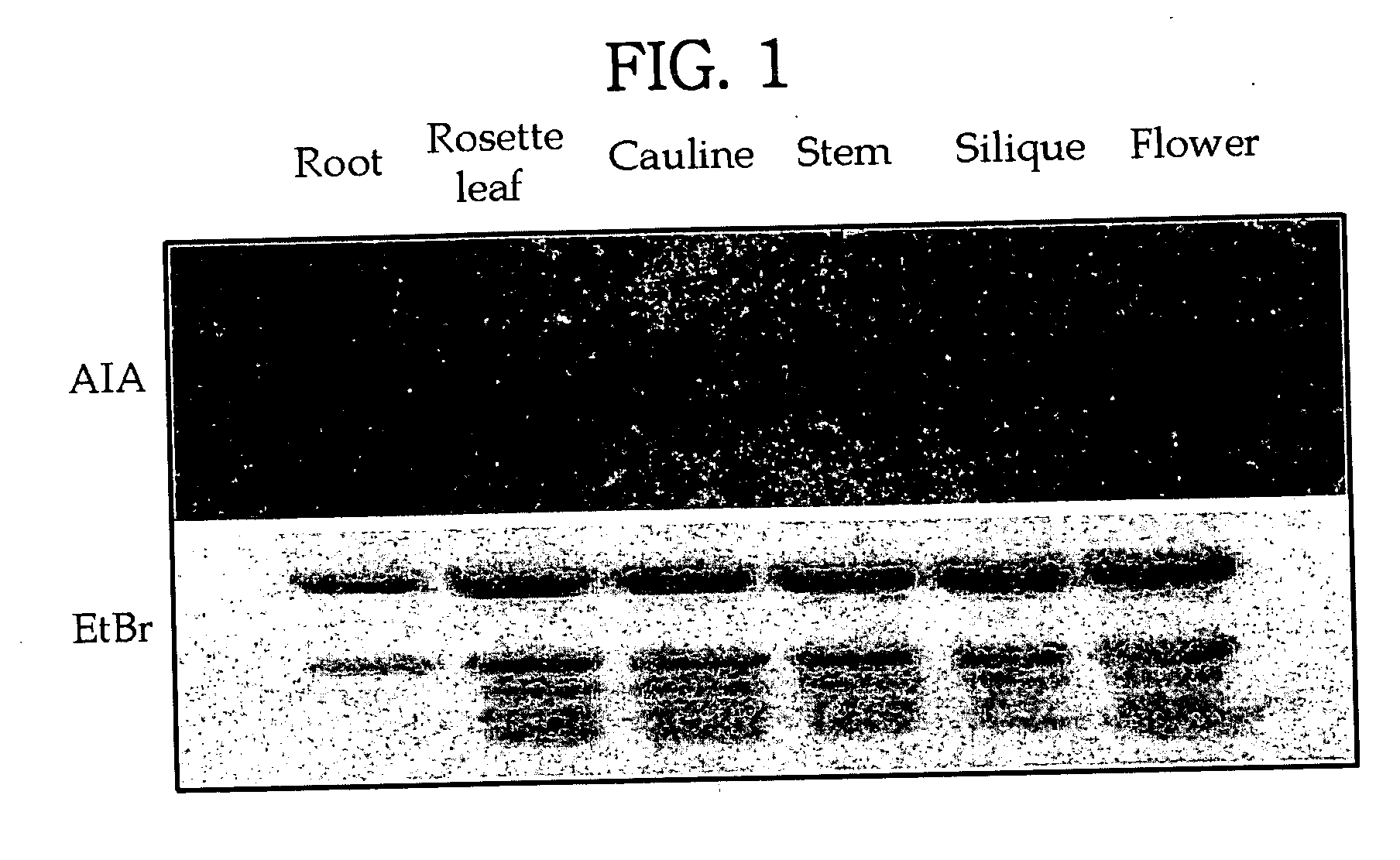
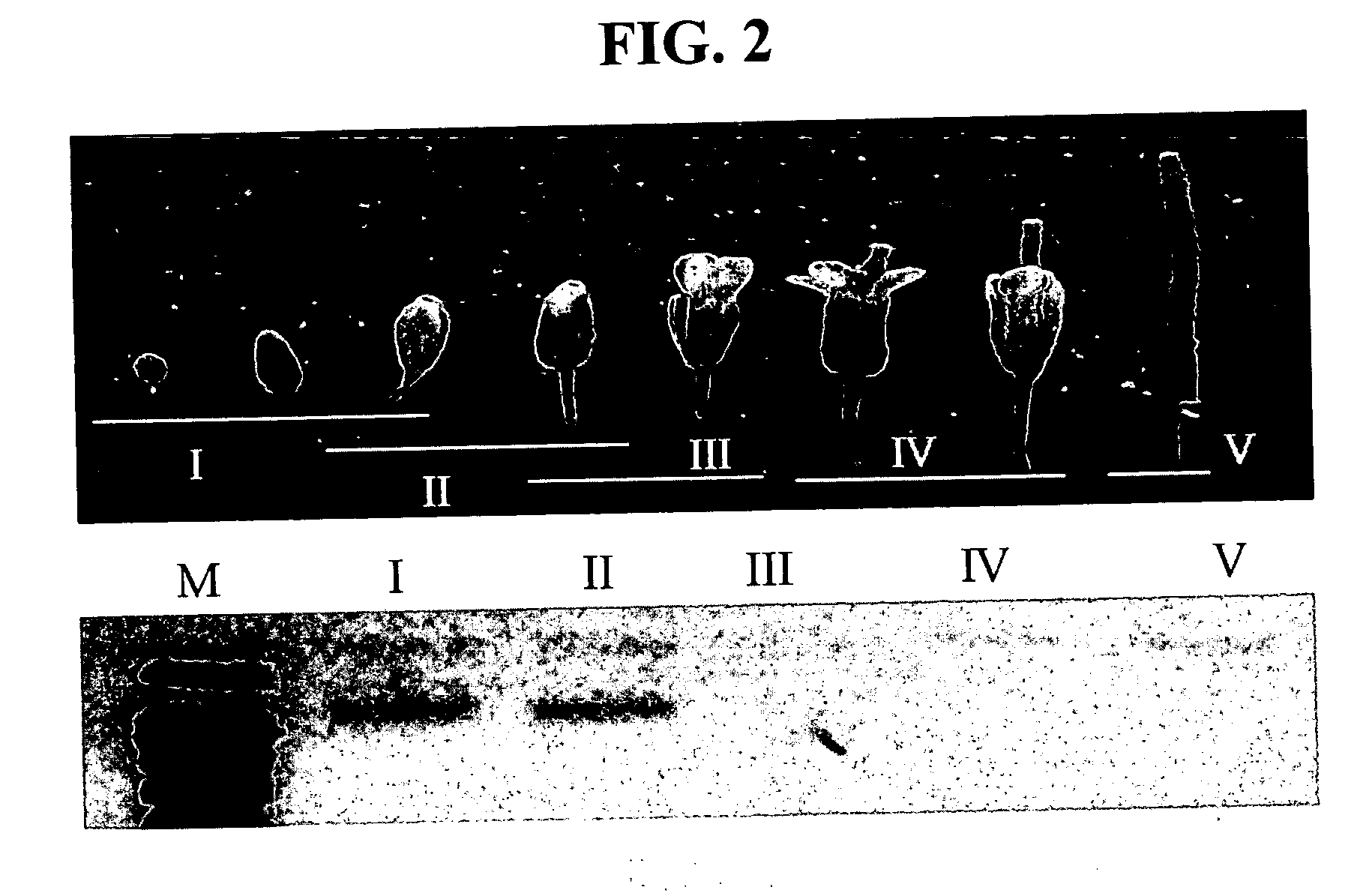
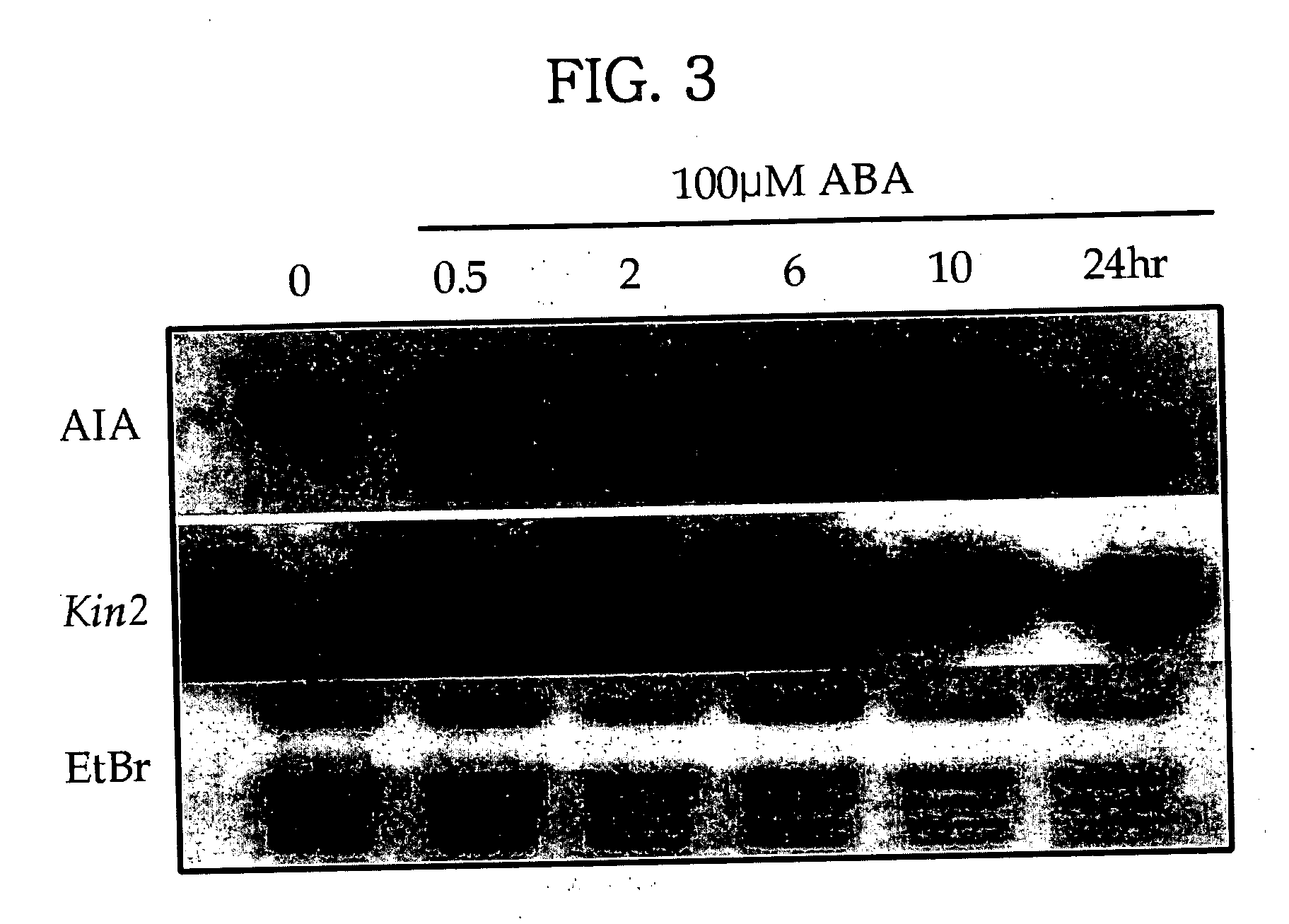
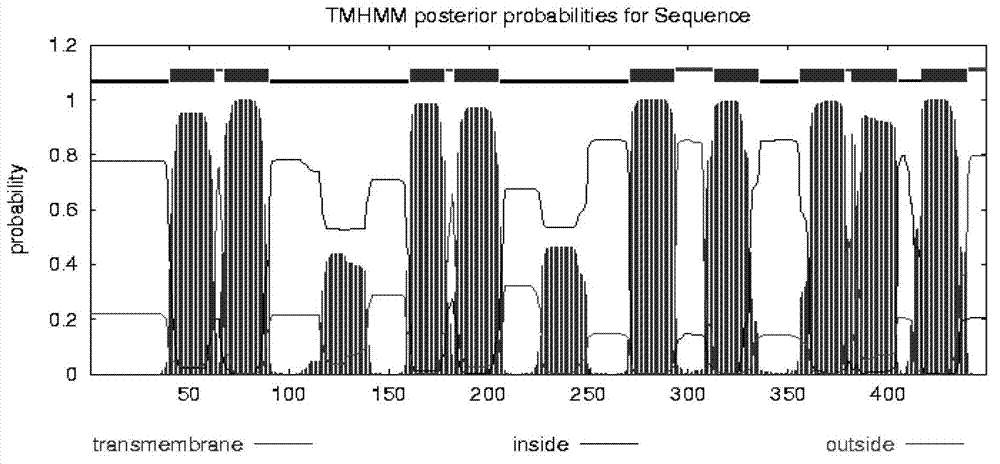
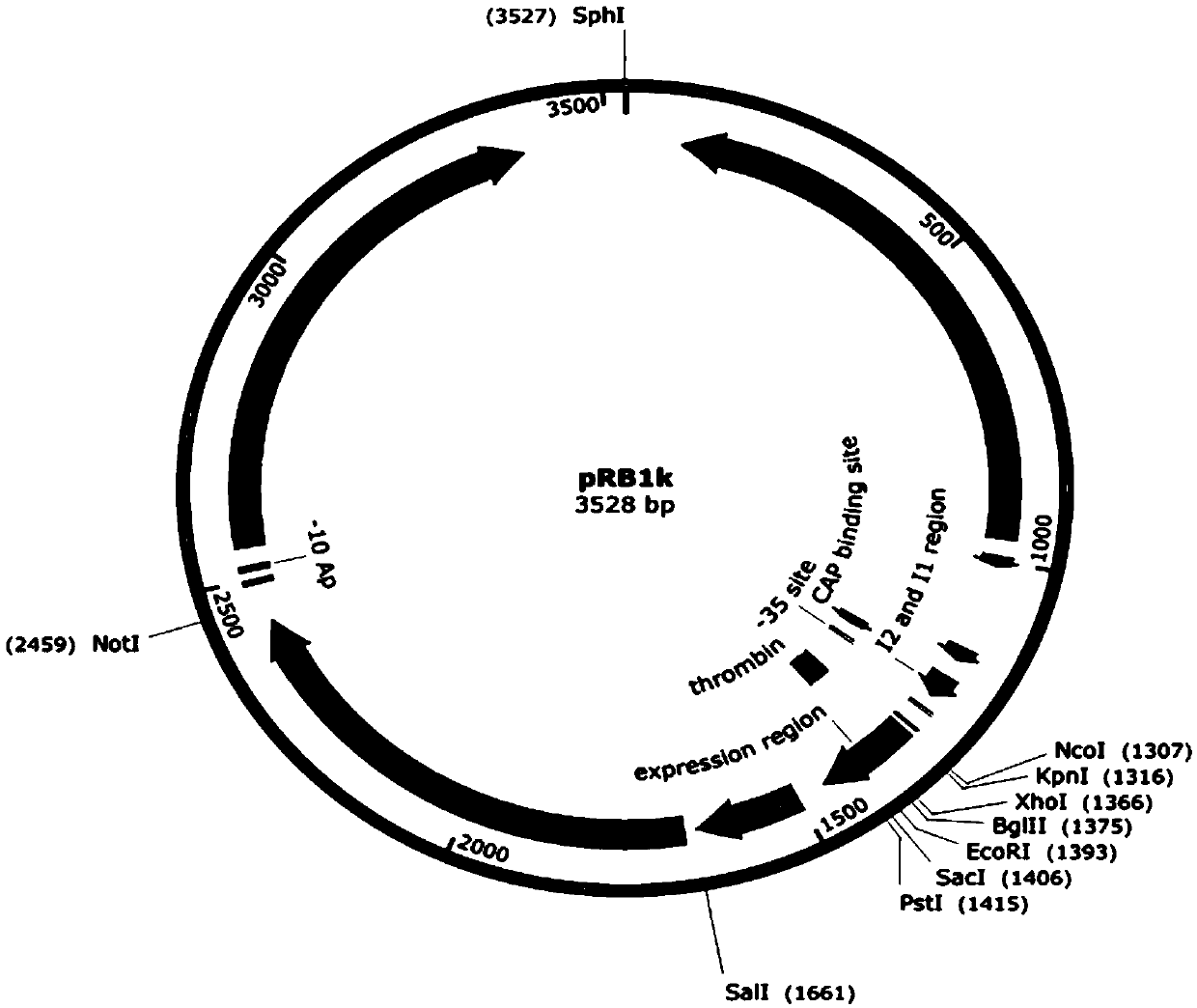
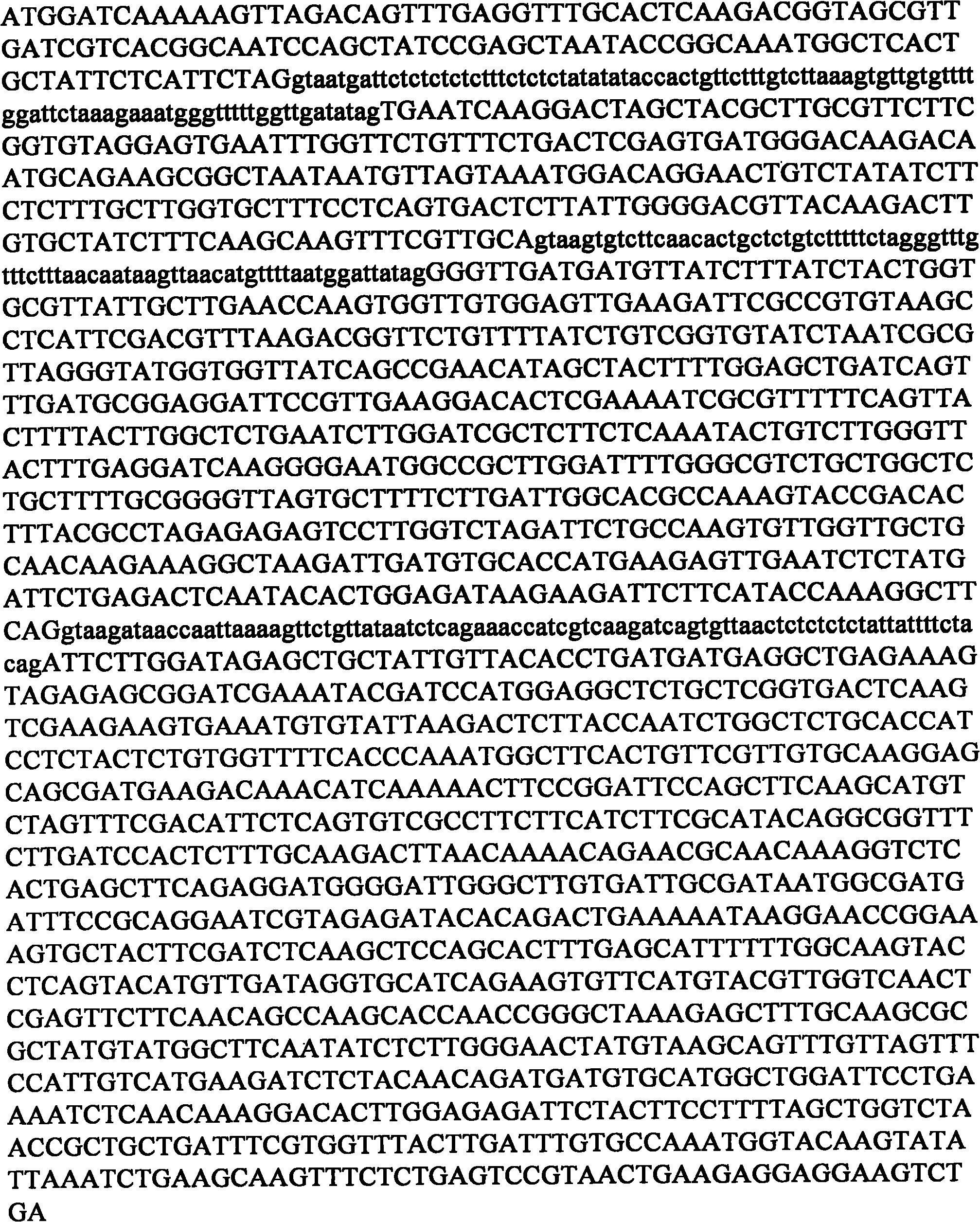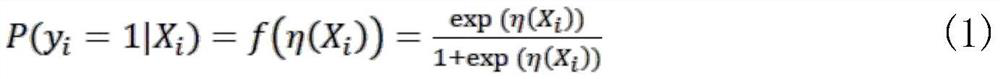Patents
Literature
52 results about "Genetic enhancement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetic enhancement refers to the use of genetic engineering to modify a person's nonpathological human traits. In contrast, gene therapy involves using genetic engineering to alter defective genes or insert corrected genes into the body in order to treat a disease.
Methods for alzheimer's disease treatment and cognitive enhancement
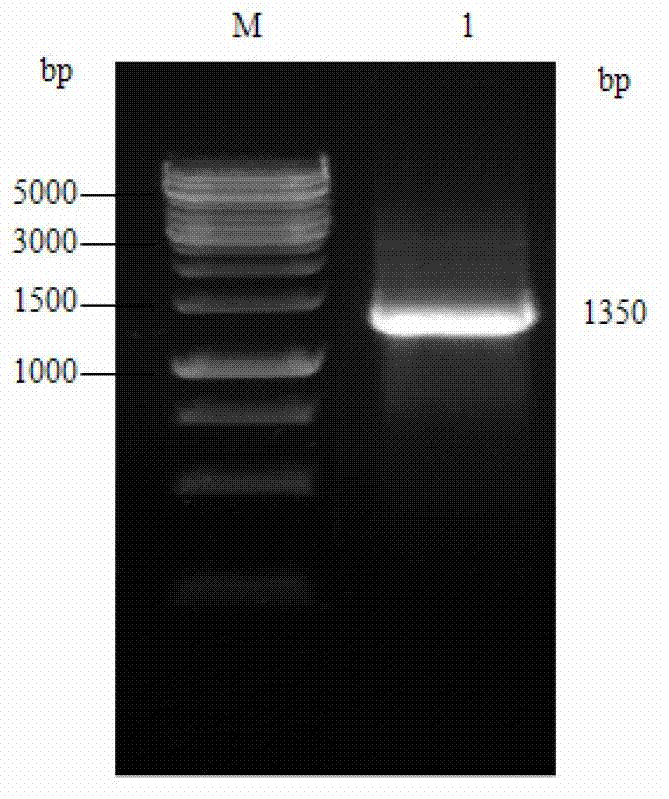
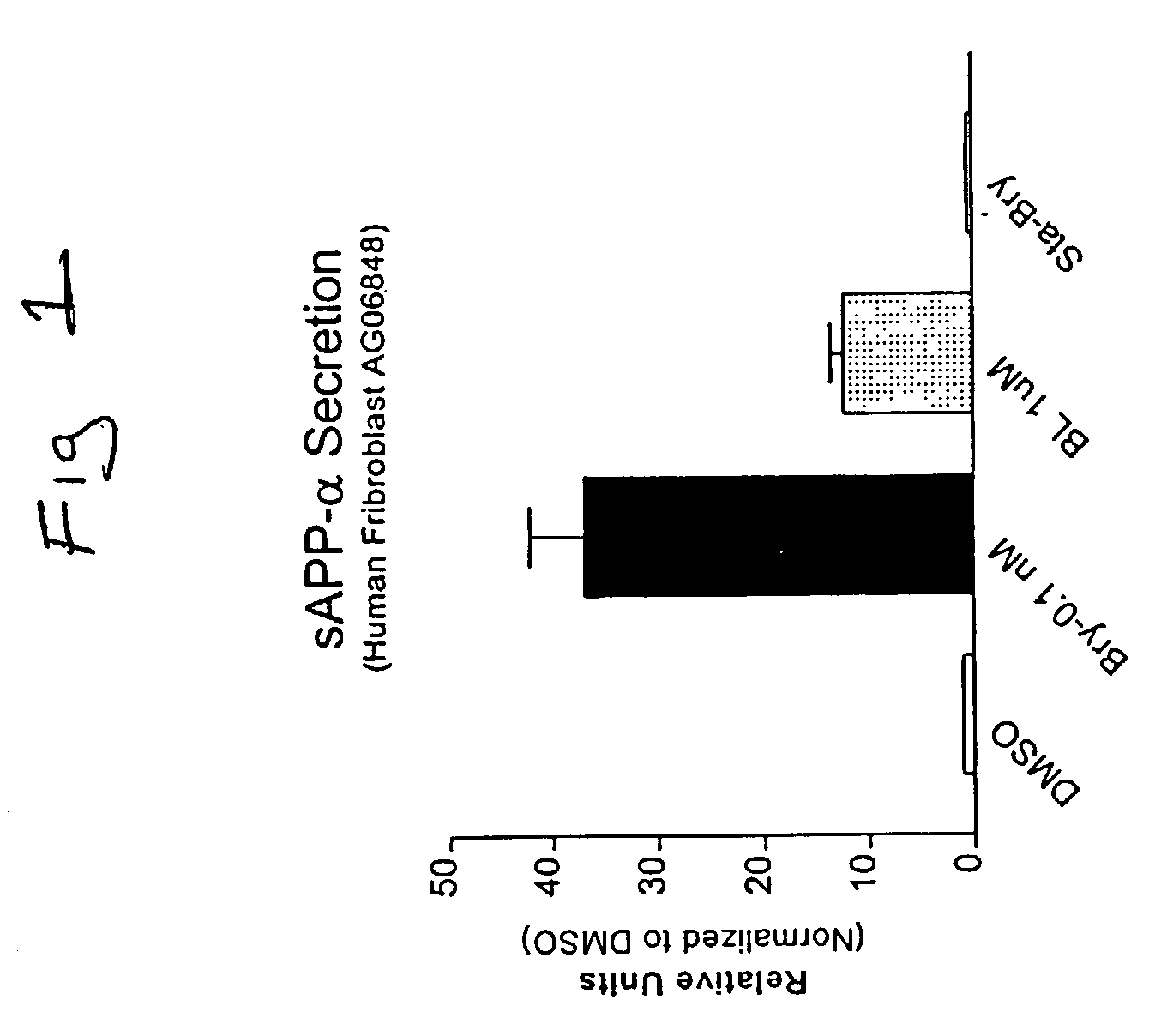
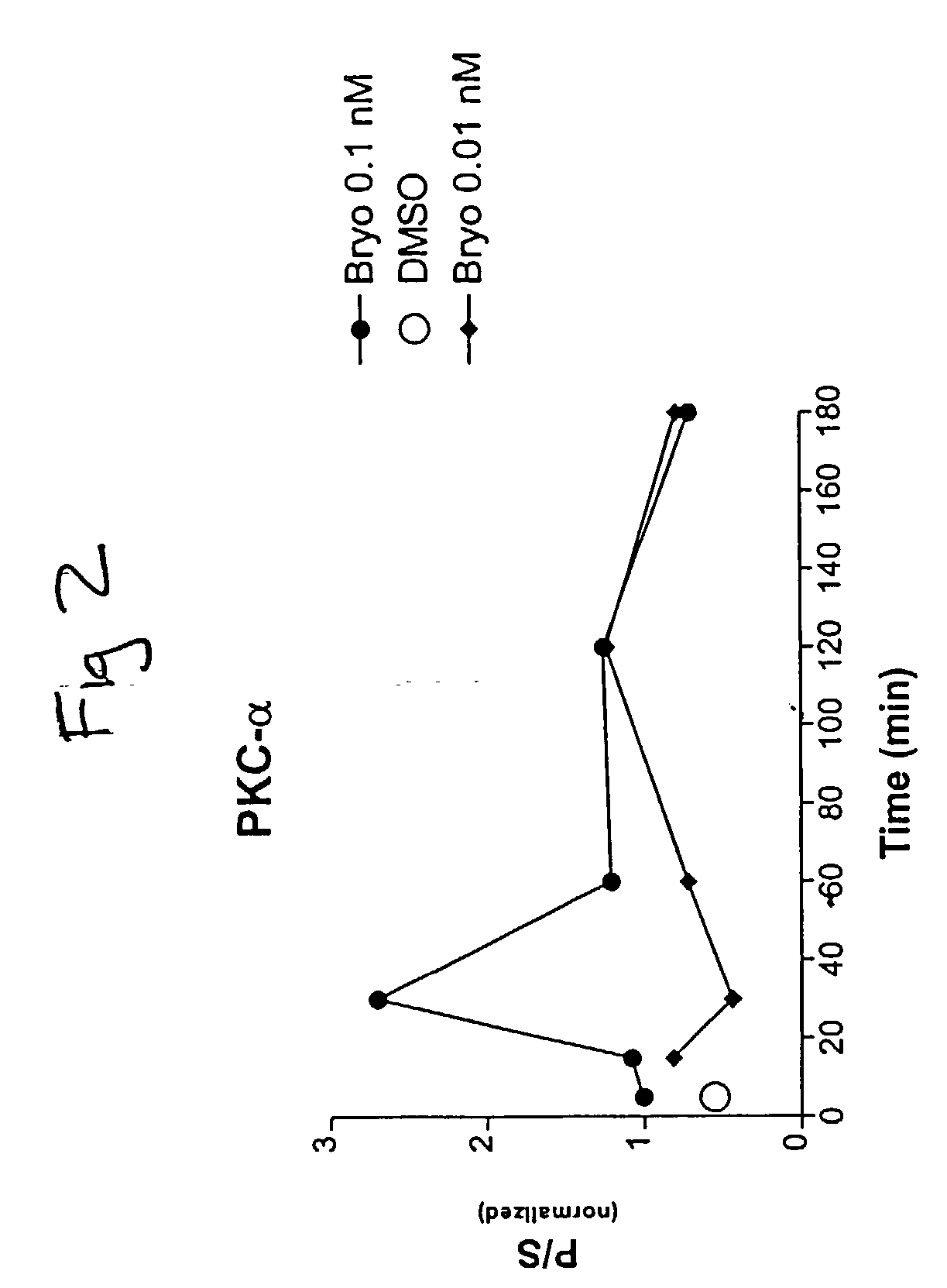
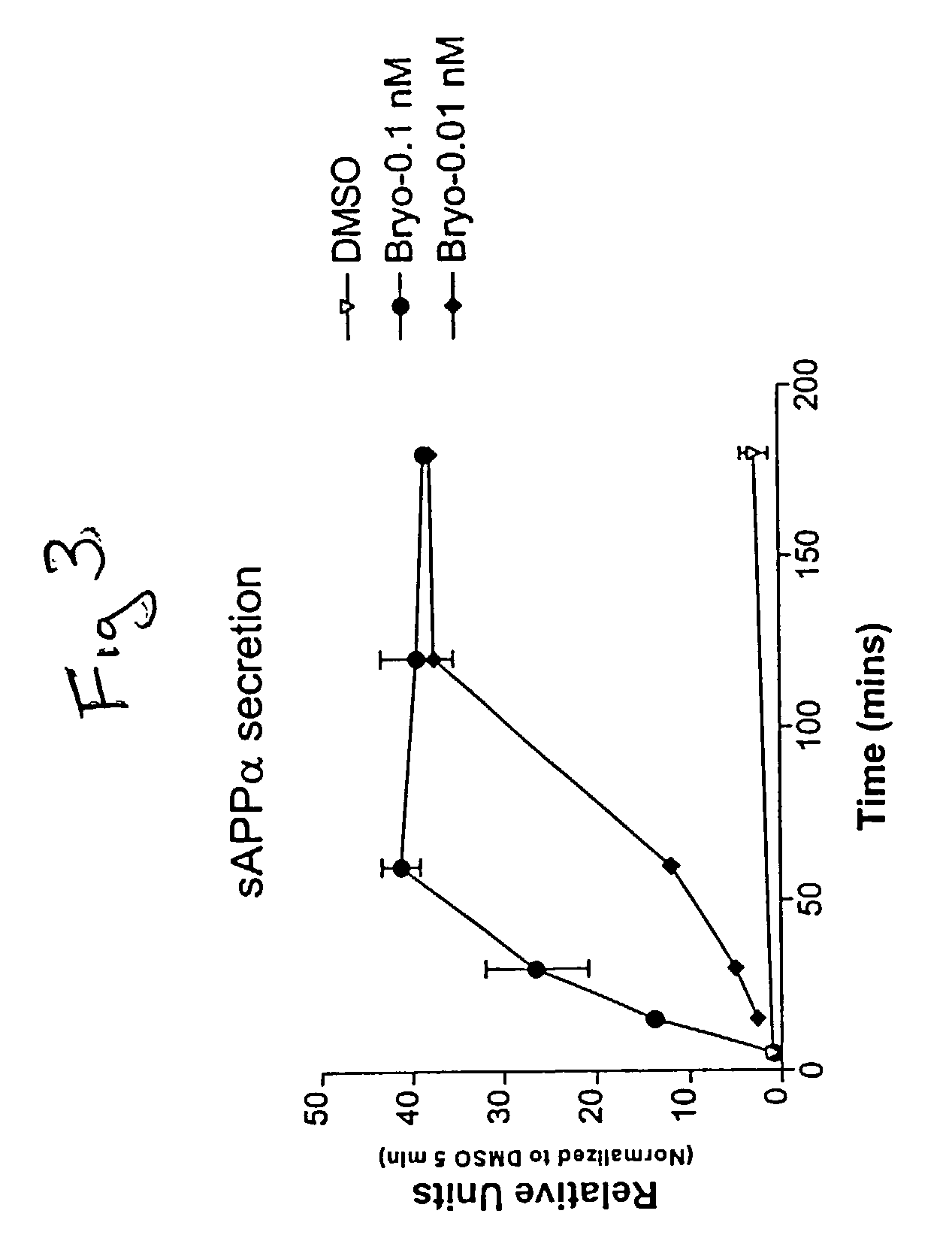
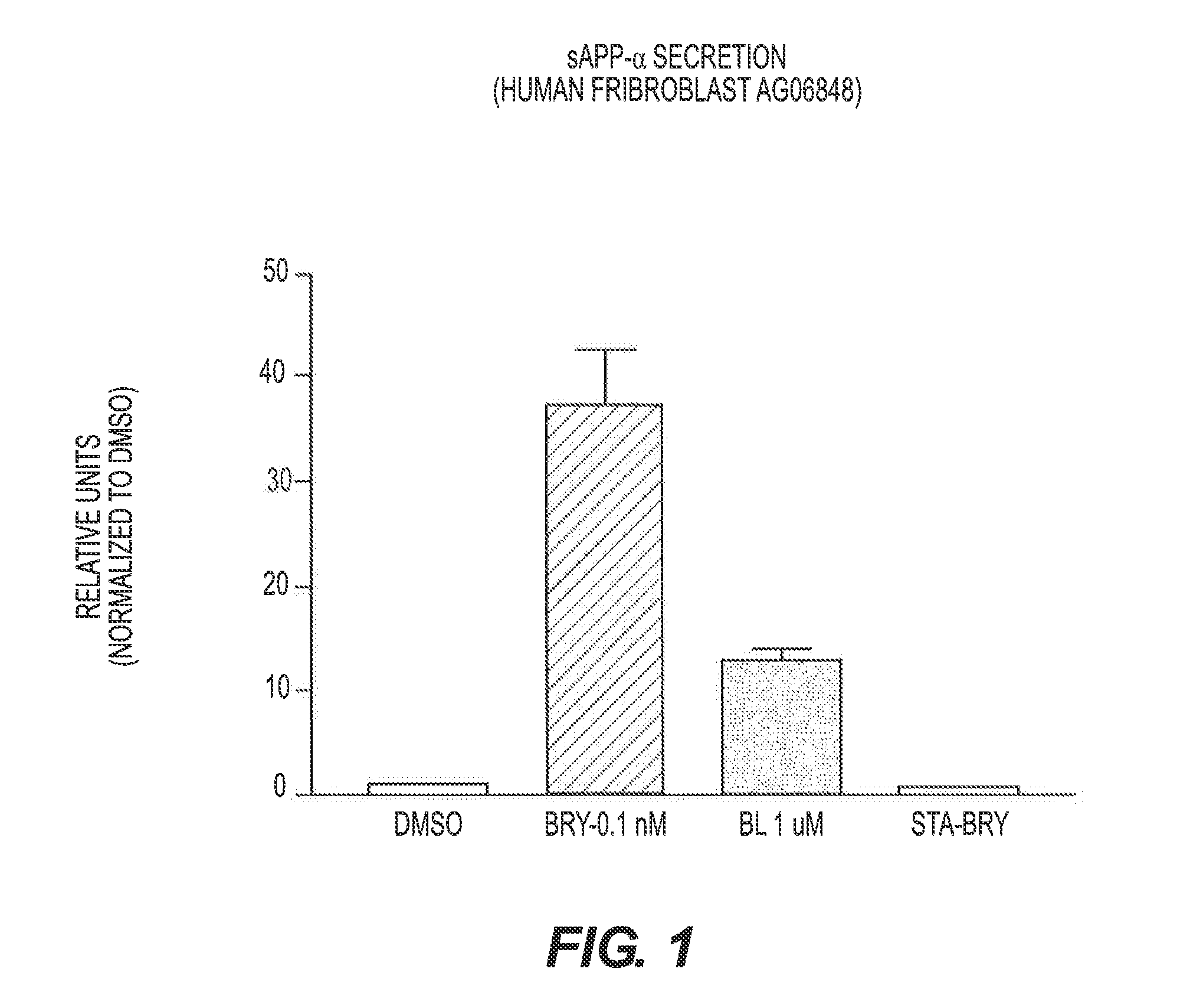
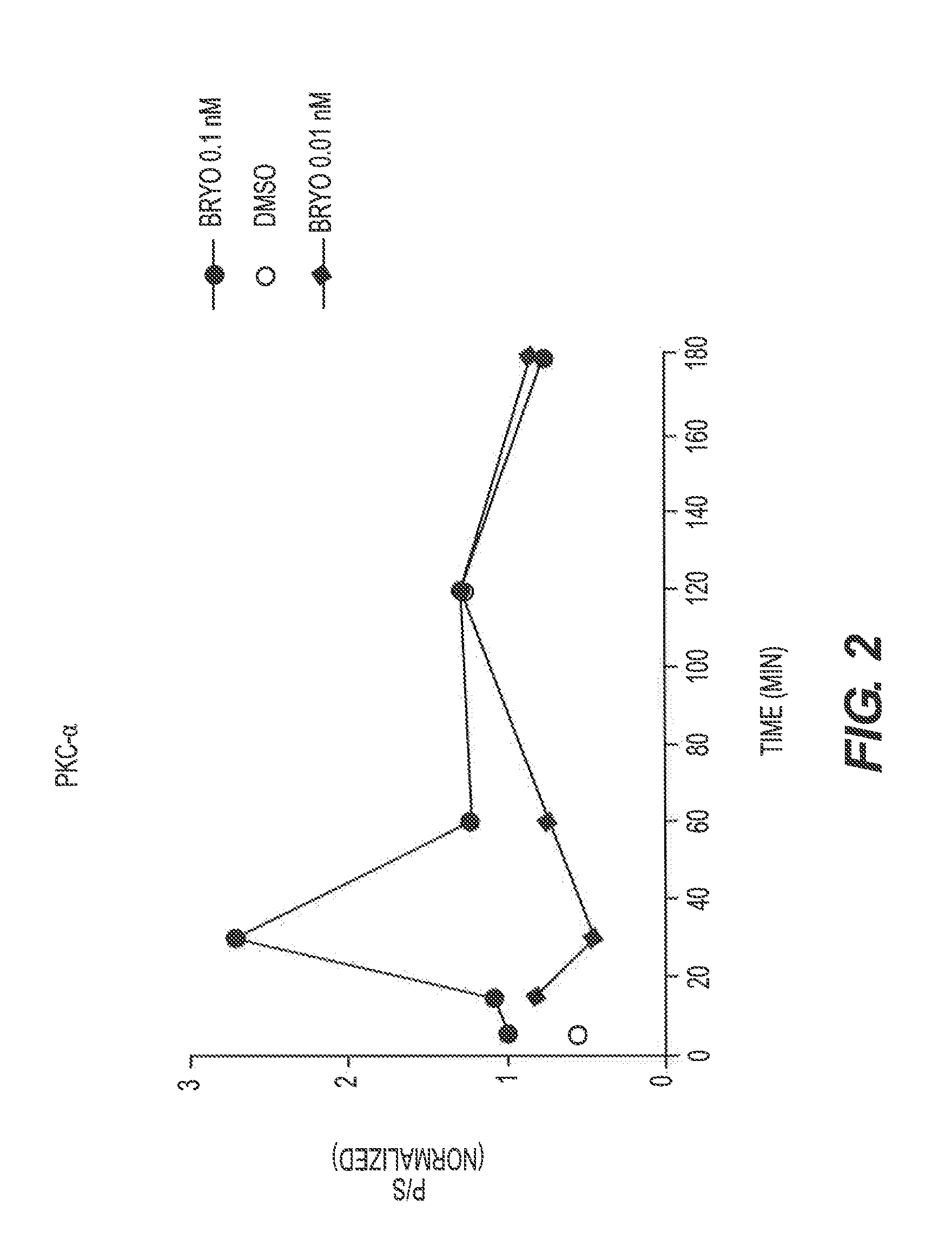
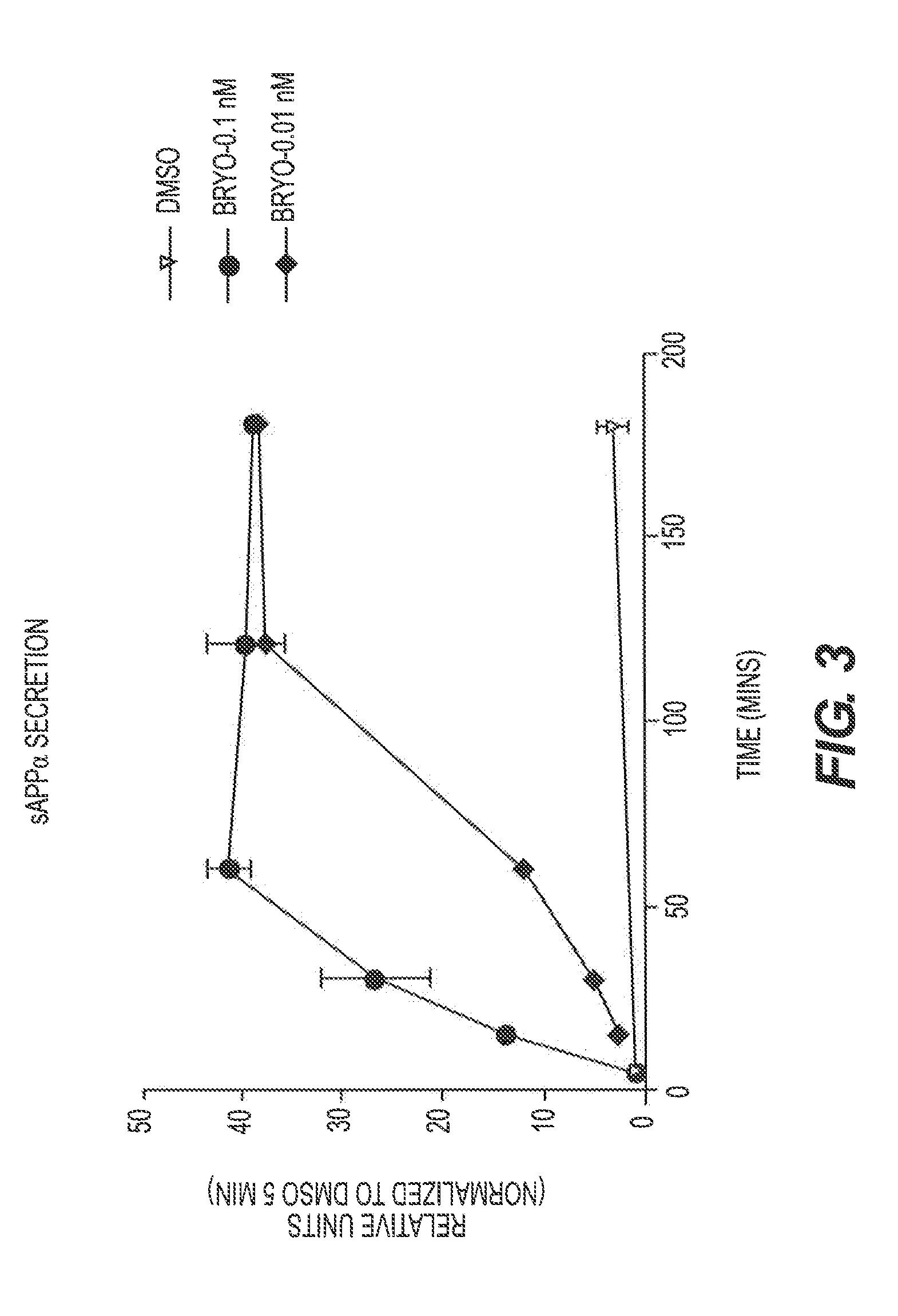
The present invention relates to compositions and methods to modulate alpha-secretase and / or to improve cognitive ability. The invention further relates the improved / enhanced cognitive ability in diseased individuals, particularly Alzheimer's Disease patients, and treatment thereof through increased sAPP production. Macrocyclic lactones (i.e. bryostatin class and neristatin class) are compounds preferred for use with the present composition. The present invention also provides methods for increasing the generation of non-amyloidogenic soluble APP comprising the activation of protein kinase C (PKC) by administering an effective amount of PKC activator(s).
Owner:COGNITIVE RES ENTERPRISES INC
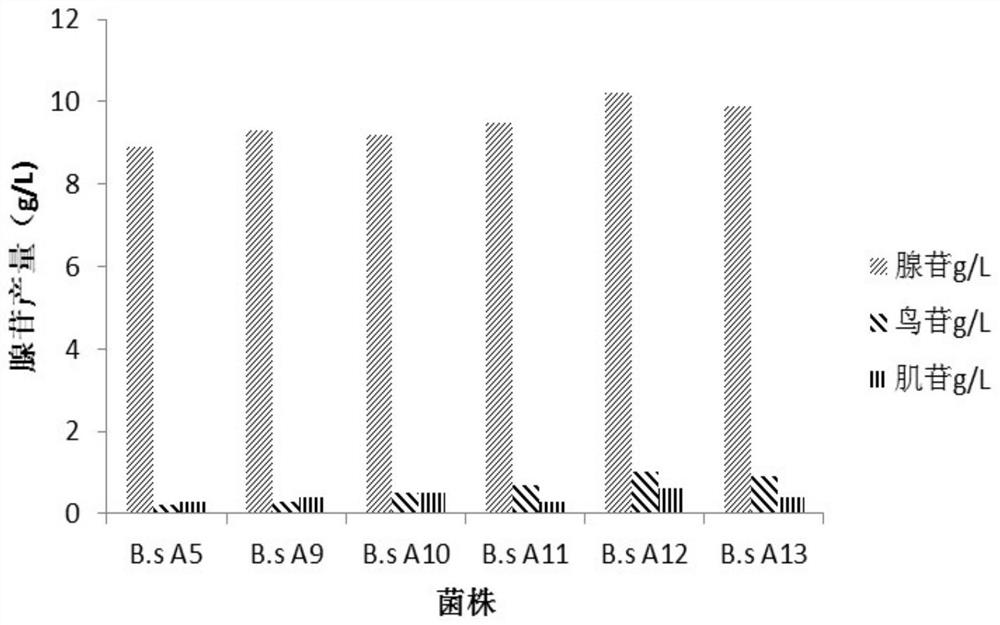
High-nucleoside-yield bacillus subtilis engineering bacterium as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN112143751AEfficient accumulationIncrease productionBacteriaStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyGenetic enhancement
The invention provides high-nucleoside-yield bacillus subtilis engineering bacterium as well as a construction method and application thereof The invention also provides a method for producing nucleoside by fermentation. The method comprises the following steps of (1) enhancing a glutamate synthase gene gltA for encoding an NCBI reference sequence WP-009967365.1 on a bacillus subtilis chromosome;and / or enhancing a glutamine synthetase gene glnA for encoding an NCBI reference sequence WP-003231737.1 on the chromosome of the bacillus subtilis; and (2) applying the gene-enhanced strain obtainedin the step (1) to fermentation production of nucleoside. The bacillus subtilis engineering bacterium provided by the invention is a high-nucleoside-yield strain, can effectively accumulate nucleoside, improves the yield of nucleoside, and lays a foundation for industrial production of nucleoside.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
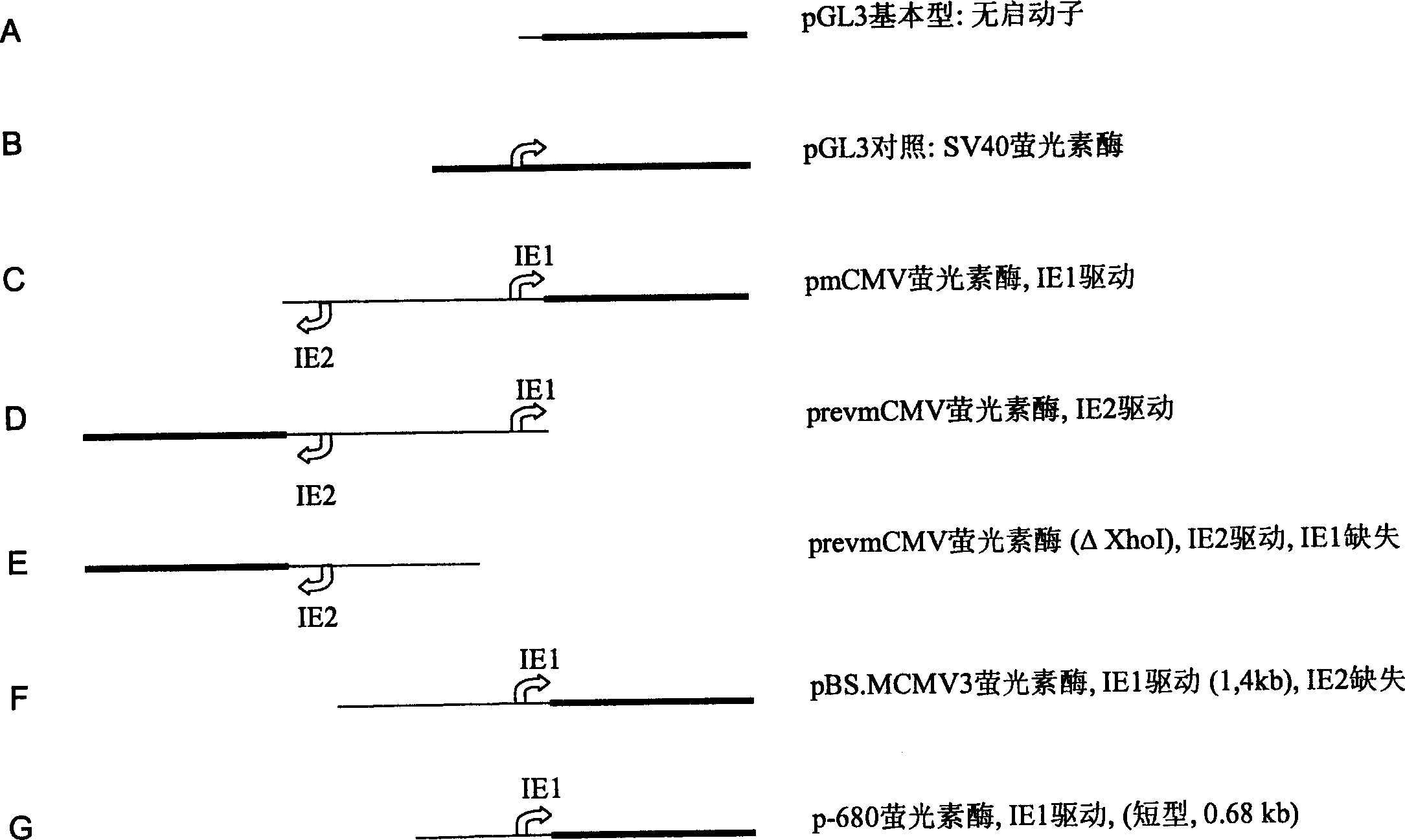
Expression vectors comprising the MCMV IE2 promoter
The invention relates to an expression vector comprising the promoter of the mCMV-IE2 gene, or a functional expression promoting fragment thereof, and / or an enhancer of the mCMV-IE2 gene, or a functional expression enhancing fragment thereof, wherein the expression vector does not contain any complete gene of the mCMV.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
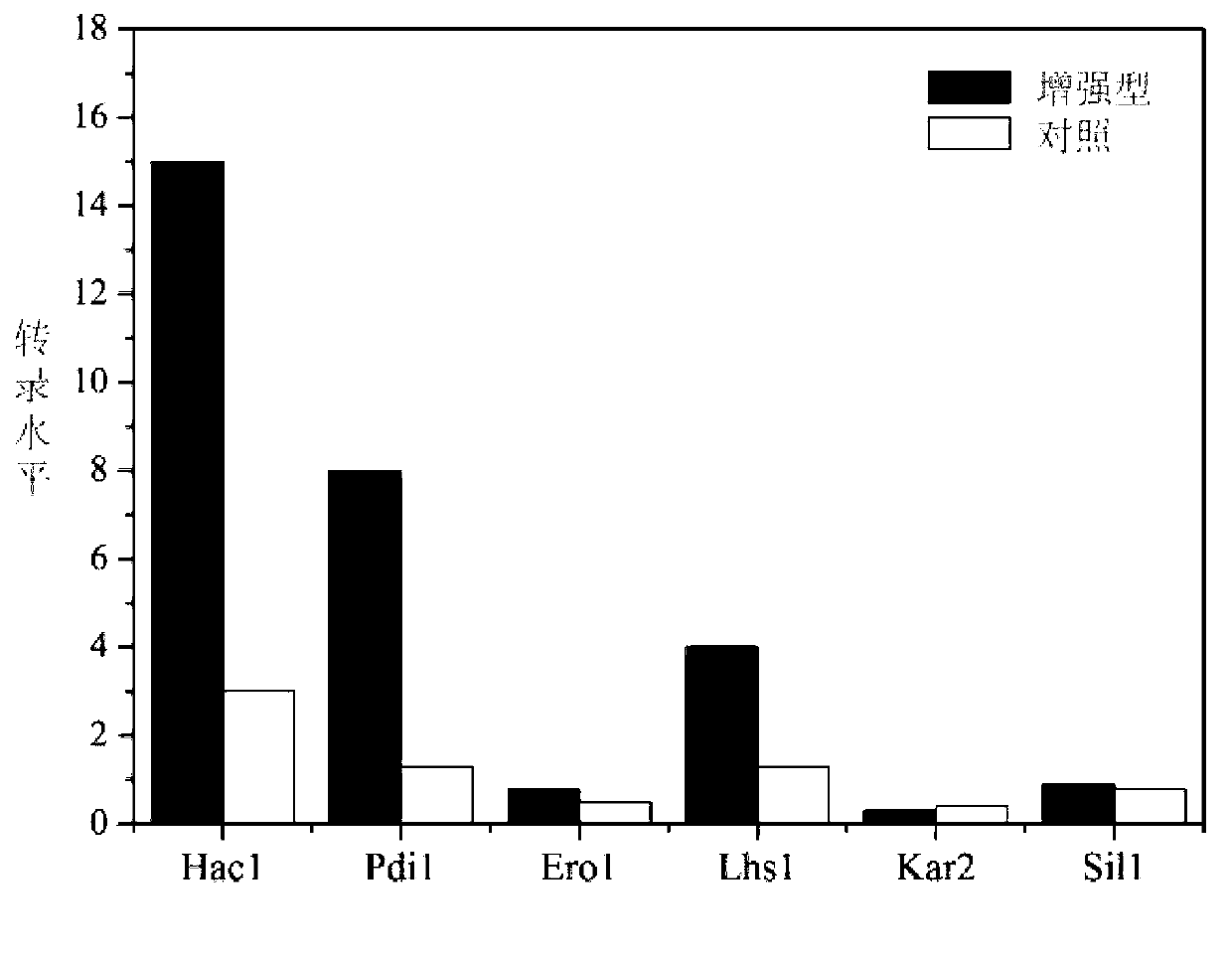
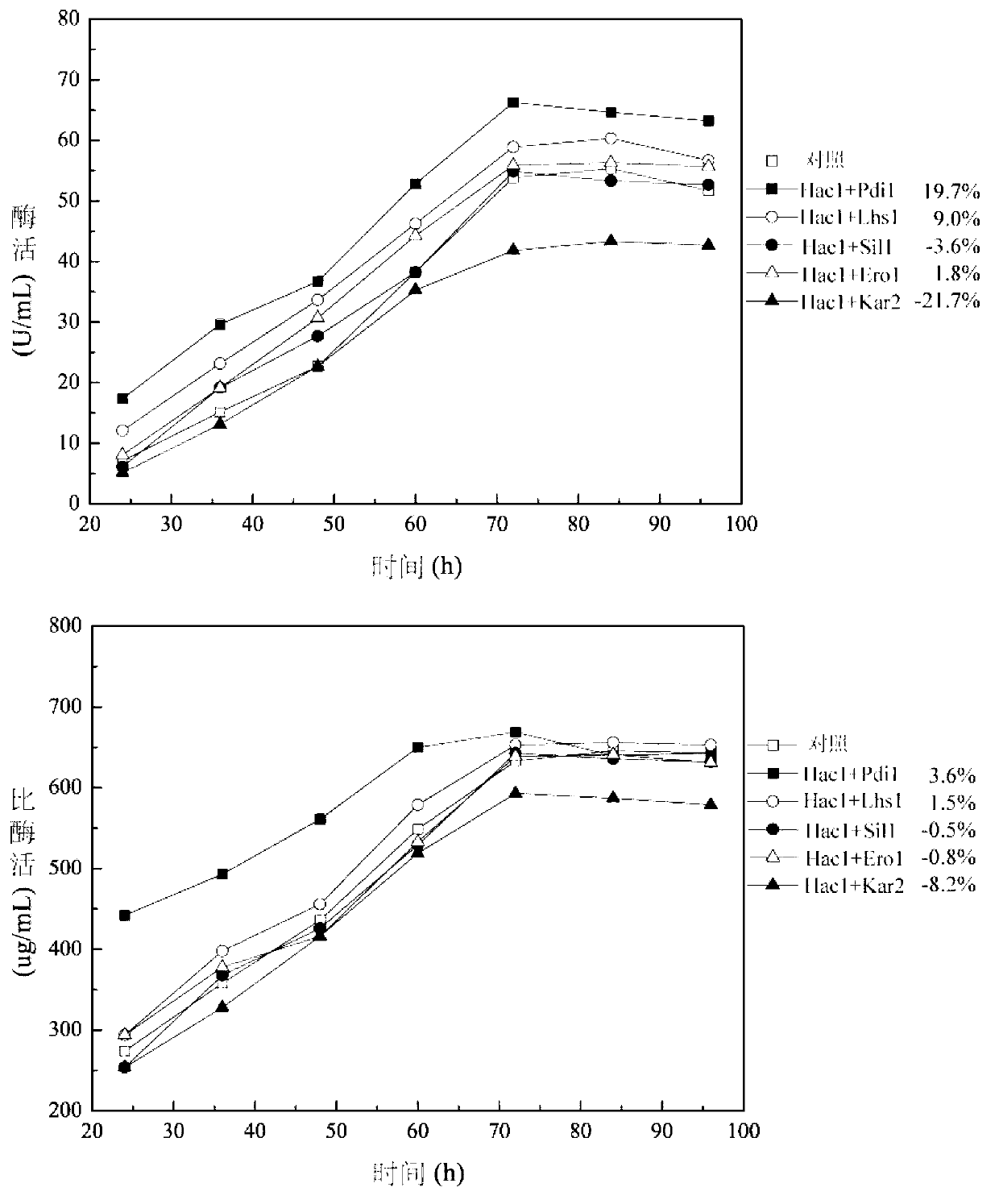
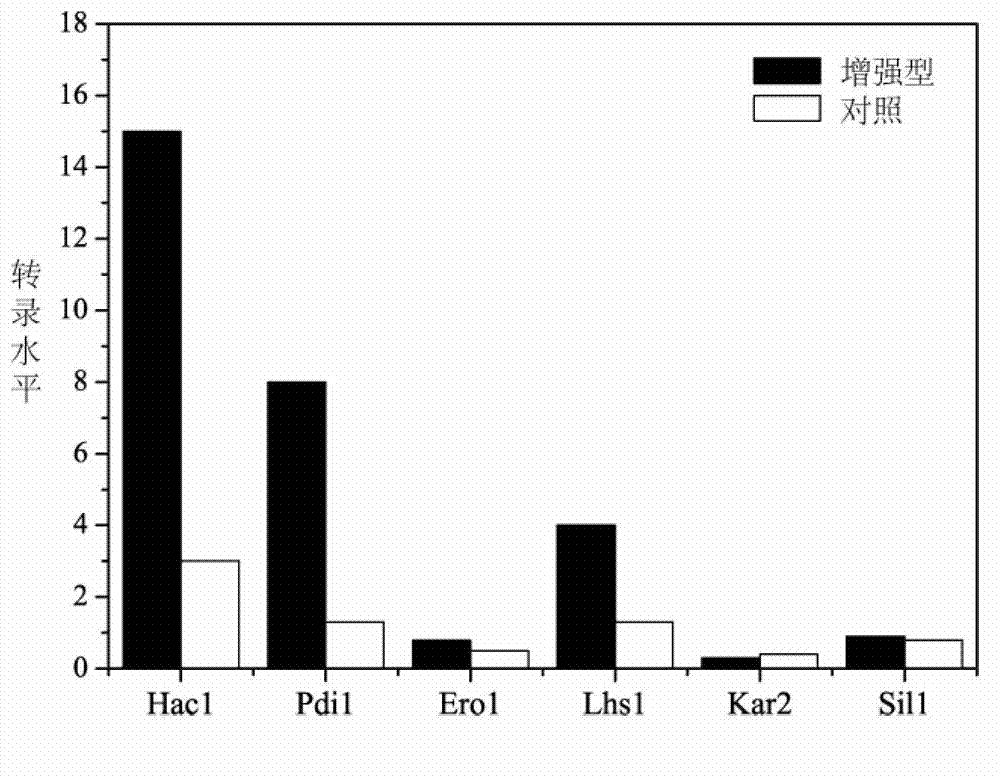
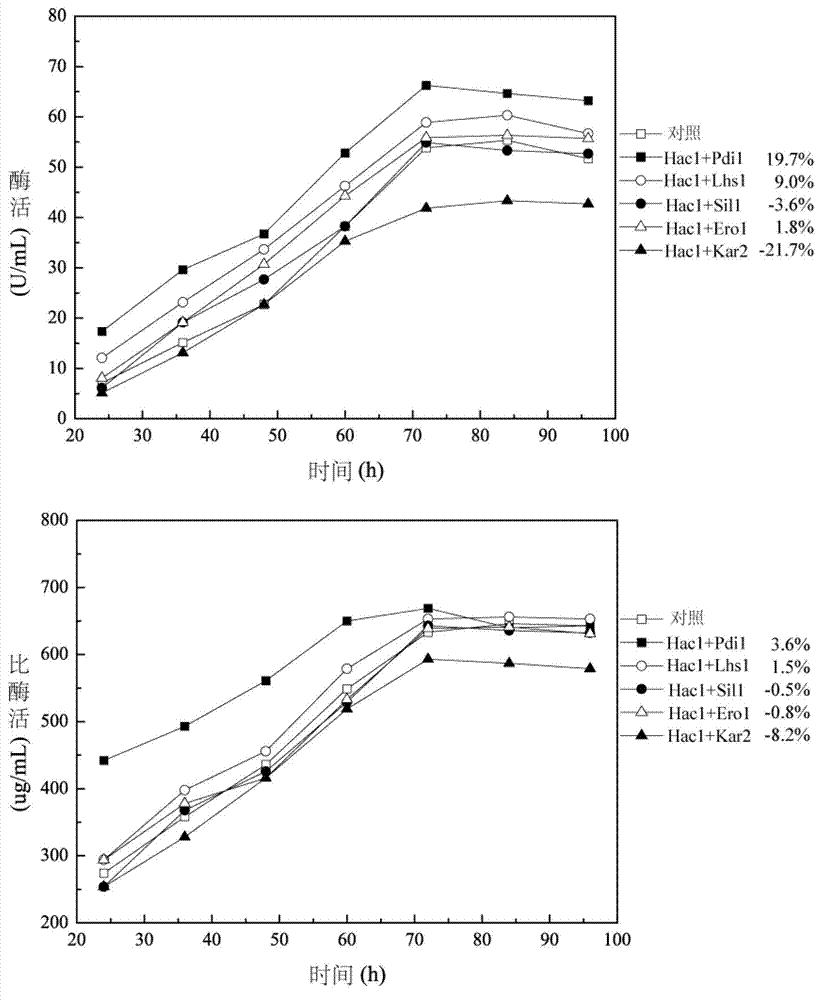
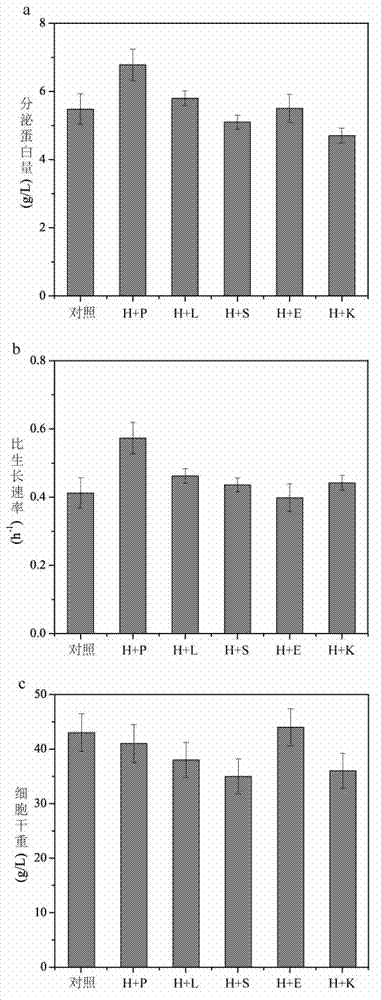
Method for enhancing secretion of glucose oxidase by coexpression of UPR (unfolded protein response) key genes and downstream target genes
ActiveCN102994541AIncrease enzyme activityFungiMicroorganism based processesGenetic enhancementBiotechnology
The invention discloses a method for enhancing secretion of glucose oxidase by coexpression of UPR (unfolded protein response) key genes and downstream target genes, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The method comprises the steps of respectively cloning and connecting pichia pastoris UPR key gene Haclp and the downstream target genes Pdi1, Erol, Lhs1, Kar2 and Sil1 to pichia pastoris expression carriers pPICZ alpha and pPIC3.5K, transforming into a Pichia pastoris GS115-pPIC9K-GOD strain of which the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2012266, and obtaining a strain with enhanced secretion expression of the glucose oxidase compared with the original strain by screening and identifying. The enzyme activity of the glucose oxidase expressed by the strain on a 3L of fermentation tank is 585U / mL. Therefore, good foundation is established for large-scale production of the glucose oxidase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Enhancement of stress tolerance in plants
Novel dehydrin promoters isolated from Eucalyptus dunnii and Eucalyptus macarthurii are cold-inducible and can be used for driving CBF genes in plants, including trees, to enhance tolerance to freezing temperatures or water stress and reduce undesirable effects associated with CBF gene expression.
Owner:ARBORGEN
gRNA for knocking out BCL11A genes or BCL11A gene enhancers, gRNA composition and electrorotation method
PendingCN109706148AImprove cutting efficiencyImprove efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsStable introduction of DNAGenetic enhancementSickle cell anemia
The invention provides gRNA for knocking out BCL11A genes or BCL11A gene enhancers, a gRNA composition, an expression vector, CRISPR-Cas9 RNP, a CRISPR-Cas9 RNP composition, a CRISPR-Cas9 system, an electrorotation method, a reagent kit and applications thereof. A CRISPR-Cas9 technique is adopted to perform targeted cutting on hemopoietic stem cells, so that the BCL11A gene expression amount is reduced, and the hemochrome expression quantity of fetuses is high. The technique is hopeful to become a new means for treating thalassaemia and sickle cell anemia. The CRISPR-Cas9 technique is adoptedto realize mutation of BCL11A genes. The design is simple, the use is convenient, the cost is low, and the efficiency is high.
Owner:广东赤萌医疗科技有限公司
Gene GmWRKY148 capable of improving resistance to phytophthora sojae and application of gene
ActiveCN110408626AIncrease productionImprove service qualityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHigh resistance
The invention discloses a gene GmWRKY148 capable of improving resistance to phytophthora sojae and application of the gene, wherein the gene can enhance resistance of soybean to the phytophthora sojae. According to the disclosed gene GmWRKY148, the nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. Phenotype and phytophthora accumulation indexes of soybeans Williams with GmWRKY148 overexpression under the phytophthora stress condition indicate that the GmWRKY148 plays an important regulatory role in improving plant resistance to phytophthora. The gene is used for genetic engineering improvement of plant resistance to phytophthora root rot, it is found that the gene has the certain effect on breeding plant varieties with high resistance to phytophthora root rot, and by improving plantresistance to the phytophthora, the plant yield and quality service are improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Genetically enhanced cyanobacteria for the production of a first chemical compound harbouring zn2+, co2+ or ni2+ -inducible promoters
InactiveUS20140370575A1Faster and thereby efficient accumulation of biomassIncreased risk of contaminationUnicellular algaeBiofuelsGenetic enhancementPhylum Cyanobacteria
One embodiment of the invention is directed to a genetically enhanced cyanobacterium for the production of a first chemical compound, comprising at least one first recombinant gene encoding a first biocatalyst for the production of the first chemical compound, wherein the gene is under the transcriptional control of a Co2+ or Zn2+-inducible promoter. Such a cyanobacterium can provide a tighter control of the production of the first chemical compound.
Owner:ALGENOL BIOTECH
Construction for tissue engineering cartilage modified by transforming growth factor beta2 gene
InactiveCN101148657APotential for differentiationConvenient sourceSkeletal/connective tissue cellsOn/in organic carrierGenetic enhancementIn vivo
The present invention discloses process of constructing transforming growth factor beta2 gene modified tissue engineering cartilage. The process includes the separation, culturing and proliferation of adult stem cell from human fat, the transfection of type 5 copying defect adenovirus to the adult stem cell from human fat, the compound of the transfected cell and the polyhydroxy acetic acid / calcium alginate composite as the carrier material, and the formation of in vivo tissue engineering cartilage. Experiment shows that it is possible to form in vivo tissue engineering cartilage through inoculating adult stem cell from human fat to the polyhydroxy acetic acid / calcium alginate composite, and this shows the application foreground of gene reinforced tissue engineering in repairing cartilage defect.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
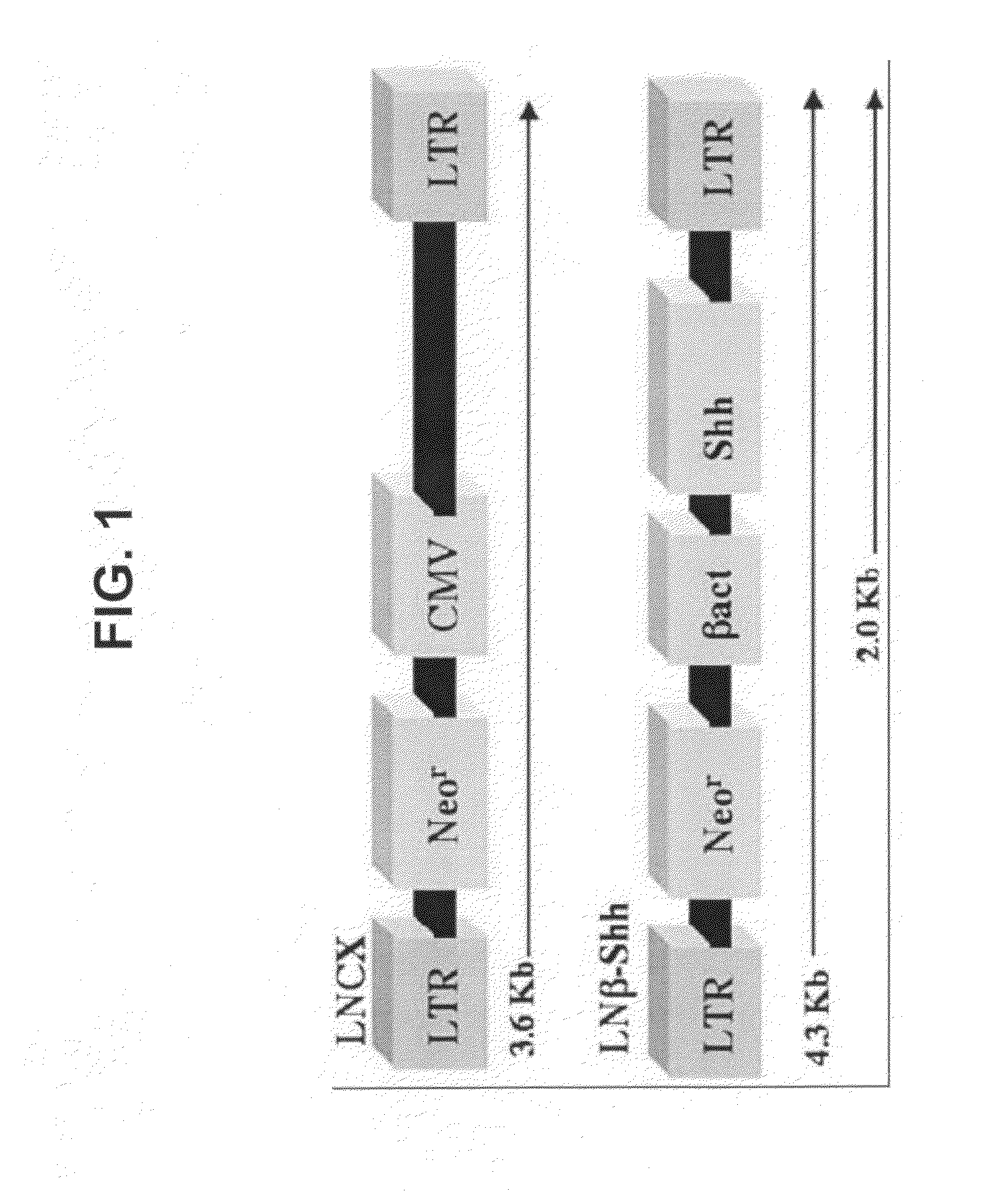
Gene-enhanced tissue engineering
Provided are mammalian cells comprising a recombinant sonic hedgehog (SHH) gene such that a recombinant SHH protein can be expressed by the cell. Also provided are matrices suitable for applying to a tissue defect. Additionally provided are tissue regeneration compositions. Methods of regenerating tissue at the site of a tissue defect in a mammal are also provided.
Owner:MASON JAMES M +2
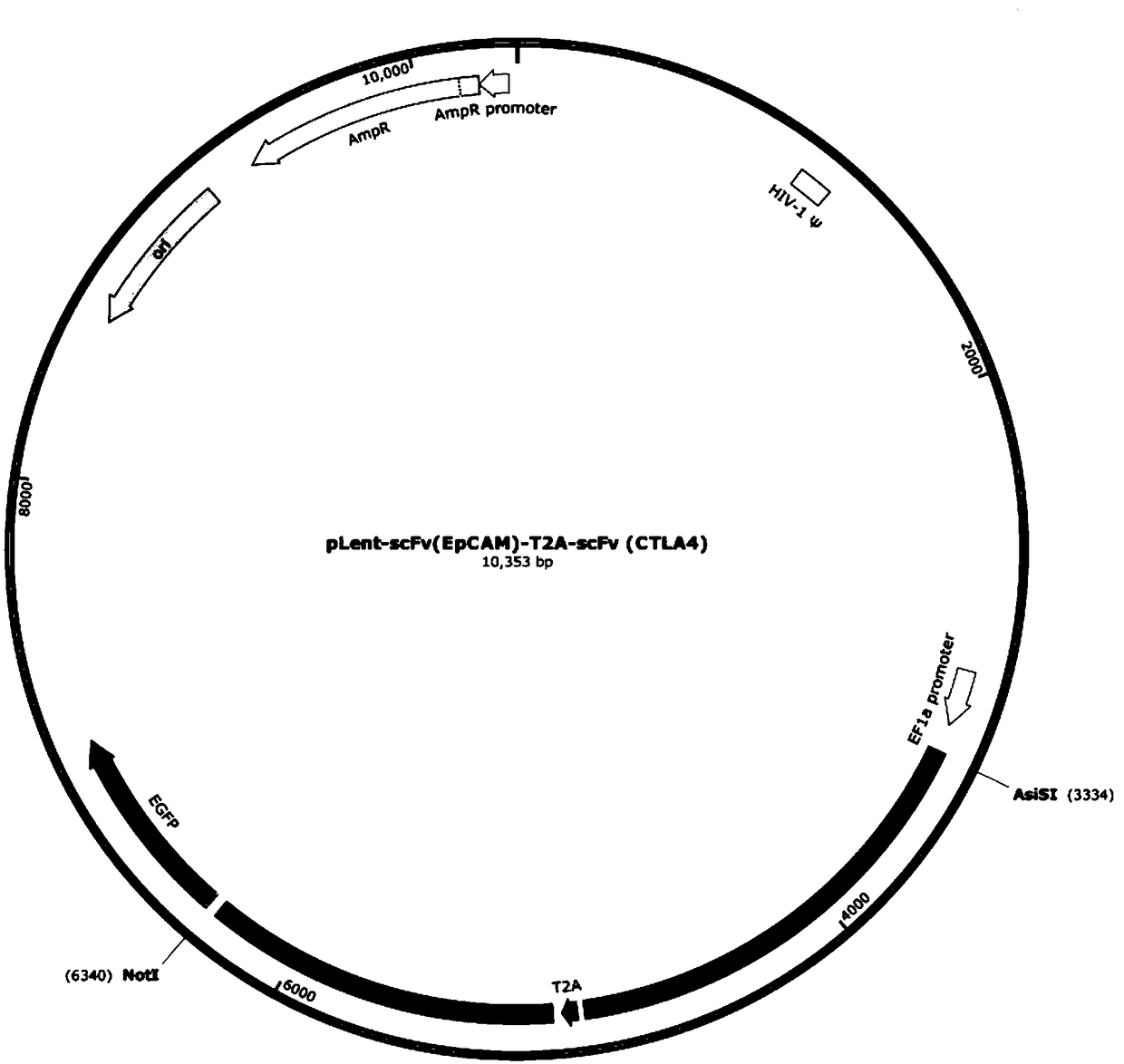
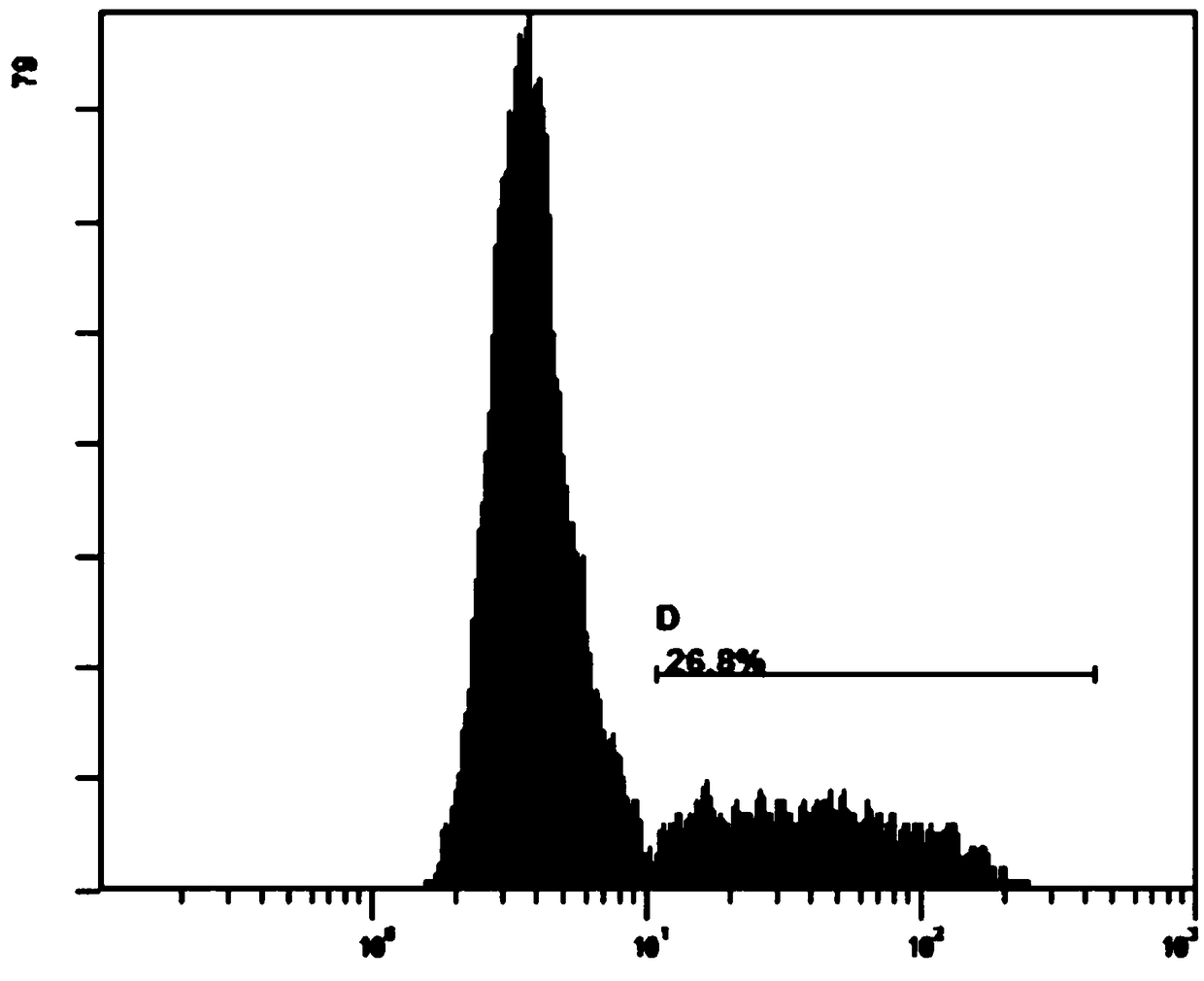
Anti-EpCAM chimeric antigen receptor encoding gene, preparation method, plasmid and immune cell with gene and application of encoding gene
InactiveCN108893484ADecreased killing activityGood treatment effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyWilms' tumorCAR - Chimeric antigen receptor
The invention discloses an anti-EpCAM chimeric antigen receptor encoding gene, a preparation method, plasmid and immune cells with the gene and application of the encoding gene. The encoding gene at least comprises an EpCAM bond zone and a CTLA4 bond zone, and comprises a T2A nucleic acid artificial sequence between the two bond zones as well; the anti-EpCAM chimeric antigen receptor encoding genealso comprises a transmembrane-stimulation structure domain; and the transmembrane-stimulation structure domain is selected from all or partial segments of CD8, CD27, CD28, CD226, 4-1BB, OX40 and ICOS molecules. By adopting the anti-EpCAM chimeric antigen receptor encoding gene disclosed by the invention, the killing effects of T cells upon tumor cells can be improved.
Owner:SHANDONG XINRUI BIOTECH CO LTD
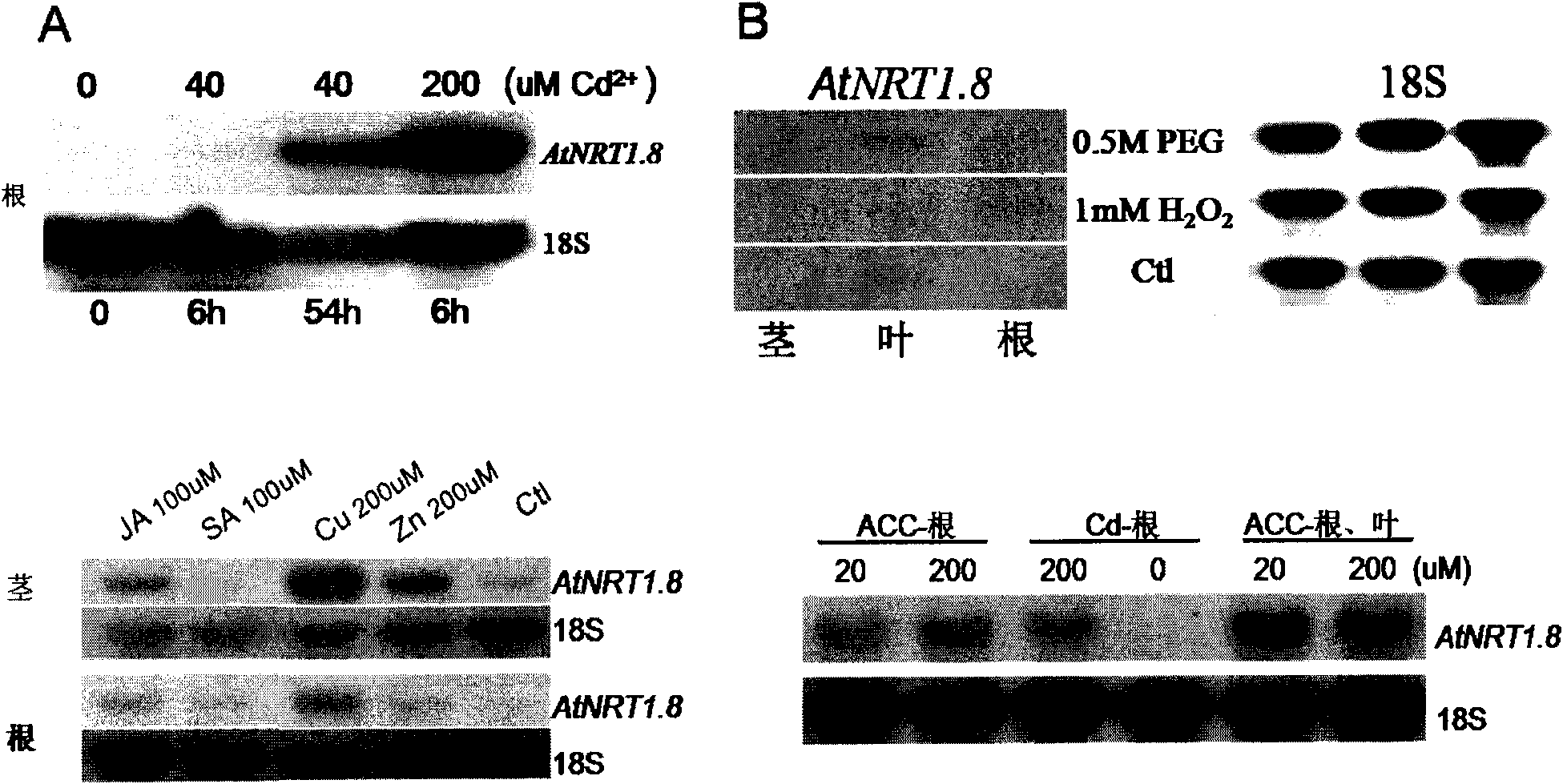
Application of AtNRT1.8 gene to strengthening resistance of crops to stress of heavy metals or salts
InactiveCN101818168AIncrease resistanceImproved resistance to salt or drought stressFungiBacteriaGenetic engineeringGMO Plants
The invention relates to application of an AtNRT1.8 gene to strengthening the resistance of crops to the stress of heavy metals or salts, in particular to application of an AtNRT1.8 gene or encoded protein or polypeptide thereof to strengthening the resistance of plants to the stress of heavy metals, salts or draught. The invention also provides a genetic engineering method for strengthening the resistance of plants to the stress of heavy metals, salts or draught by utilizing the AtNRT1.8 gene, a vector and a host cell containing the AtNRT1.8 gene, a method for preparing transgenosis plants and the transgenosis plants. The method can strength the resistance of the plants to the stress of the heavy metals, the salts and the draught and has active effects for improving the yield and properties of crops and wide application potential.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Liriodendron hybrids LhMKK2 gene and expression protein and application thereof
ActiveCN104293808AEnhanced Stress ResponseAffect growth and developmentTransferasesFermentationResponse processGenetic enhancement
The invention discloses a Liriodendron hybrids LhMKK2 gene, expression protein of the Liriodendron hybrids LhMKK2 gene and application of the liriodendron hybrids LhMKK2 gene. The nucleotide sequence is showed in SEQID NO.1 and the amino acid sequence is showed in SEQID NO.2. On the basis of the completely established somatic embryogenesis system of the Liriodendron hybrids and the fact that part of the transcriptome data is already obtained, the full length of the Liriodendron hybrids LhMKK2 gene, through the adoption of homology-based cloning, is obtained and is named as LhMKK2. Through gene expression analysis, that the Liriodendron hybrids LhMKK2 gene is widely expressed in plants and is involved in the growth and development of plants, and the adversity stress response process are proved; through functional analysis of the gene, it is discovered that the overexpression LhMKK2 gene is capable of enhancing resistance of plants to salt stress response, influencing the growth and development of plants and providing theoretical basis for stress resistance molecular breeding of Liriodendron hybrids and can be further widely used in adversity resistance stress of plants.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
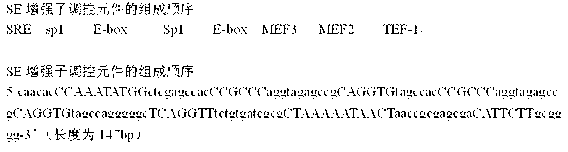
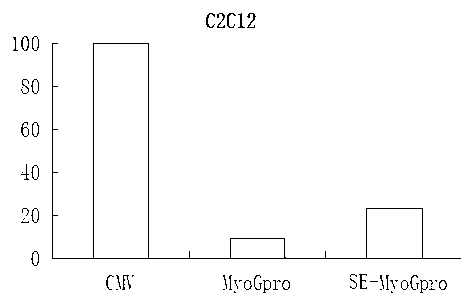
Myogenin (MyoG) gene enhancer
The invention relates to a myogenin (MyoG) gene enhancer, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. The MyoG gene enhancer consists of regulatory elements, namely E-box, SRE, KLF3, E-box, Sp1, E-box, Sp1 and TEF-1. The MyoG gene enhancer is characterized in that the sequence of the regulatory elements of the MyoG gene enhancer is E-box, SRE, KLF3, E-box, Sp1, E-box, Sp1 and TEF-1; and the SE nucleic acid sequence of the MyoG gene enhancer is shown in Seq ID No: 1 and has the length of 147 bp. Due to an artificially-synthesized enhancer sequence, the expression of a MyoG gene can be promoted at the proliferation and differentiation stages of myoblasts, and the expression activity of the MyoG gene can be remarkably improved.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Enhanced transport with a plastid membrane transport protein
InactiveUS6353153B1Improve efficiency levelsReduce the possibilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic enhancementCell membrane
A novel method to enhance translocation of molecules across or into cellular membranes using a plastid protein transport gene is described. The method can also be used to incorporate substances into membranes of organisms. Nucleic acid constructs include those which express a plastid protein transport protein or its equivalent in cells of all organisms.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
Method for enhancing environmental stress resistance of plant using environmental stress controlling gene
InactiveUS20060168681A1Improve the immunityImprove plant resistanceMirrorsOther foreign material introduction processesGenetic enhancementBiology
The present invention relates to a method for enhancing the environmental stress resistance of plants using an environmental stress resistance-controlling gene. More specifically, the invention relates to a method for enhancing the environmental stress resistance of plants and a method for producing environmental stress-resistant plants, each of the methods comprising introducing into the plants an environmental stress resistance-controlling gene derived from Arabidopsis thaliana, as well as environmental stress-resistant plants produced by the method.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
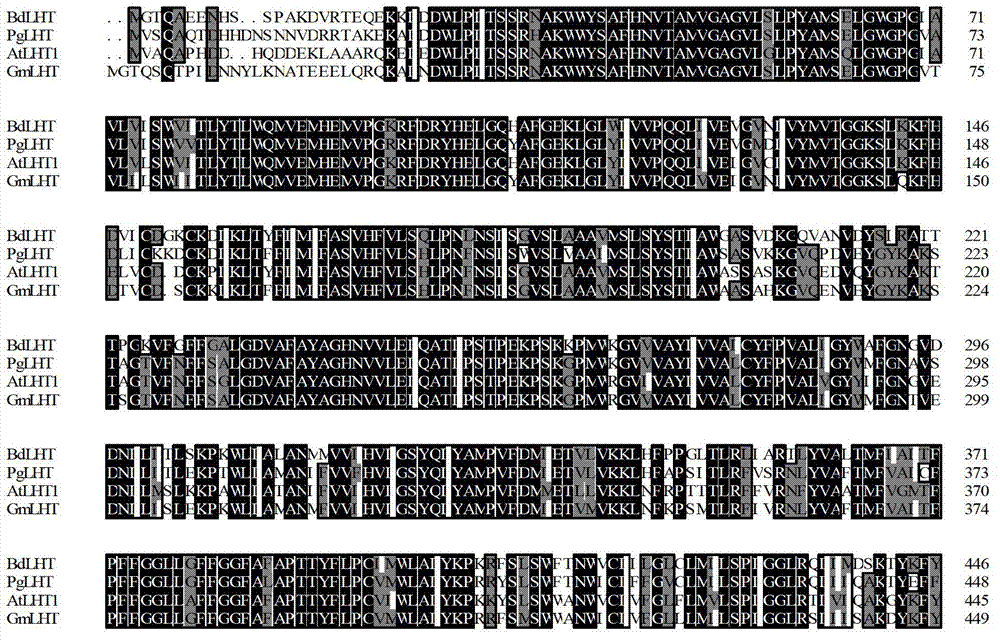
Ginseng amino acid transport protein gene PgLHT and encoding protein and application thereof
InactiveCN102952812APromote organic nutrient metabolismIncrease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationTransgeneAminoacid transport
The invention discloses a ginseng amino acid transport protein gene PgLHT and an encoding protein and an application thereof. The amino acid transport related gene PgLHT has a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the encoding protein has the sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. Researches find that PgLHT genetic expression has the tissue specificity and is closely related to ginseng stress response. The PgLHT gene has obvious effect in enhancing the ginseng plant resistance and the like. Ginseng and other plants can be screened or improved through the gene or derivatives thereof, so that excellent plant varieties with strong environment adaptivity can be obtained. The organic nutrition metabolism of plants of ginseng and the like can also be promoted through adopting a tissue culture or transgene mode.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
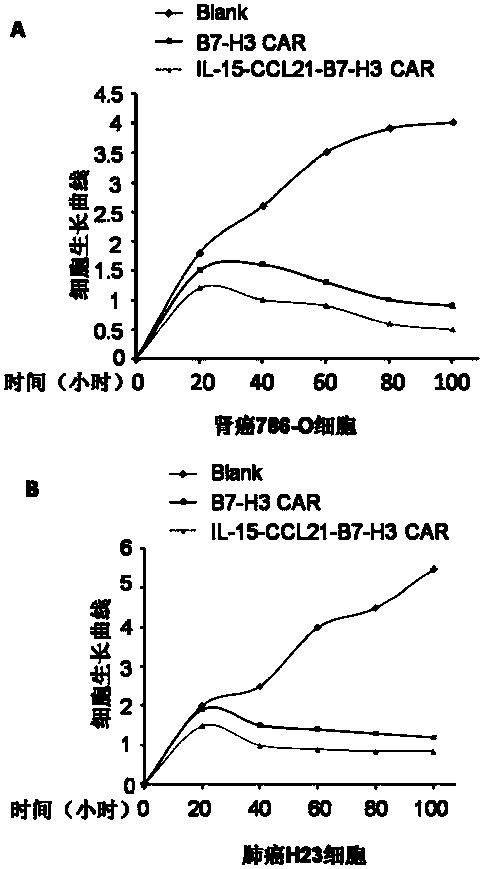
Coding gene of anti-B7-H3 chimeric antigen receptor, preparation method, plasmid with gene, immune cell and application thereof
InactiveCN110684790APromote aggressivenessEffective treatmentPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigenGenetic enhancement
The invention discloses a coding gene of an anti-B7-H3 chimeric antigen receptor, a preparation method, a plasmid with the gene, an immune cell and an application thereof, and the coding gene of the anti-B7-H3 chimeric antigen receptor is characterized by at least comprising an artificial nucleotide sequence for expressing IL15 and CCL21. The coding gene of the anti-B7-H3 chimeric antigen receptorprovided by the invention enhances the killing effect of CIK cells on solid tumor cells.
Owner:SHANDONG XINRUI BIOTECH CO LTD
Cancer classification and characteristic gene selection method
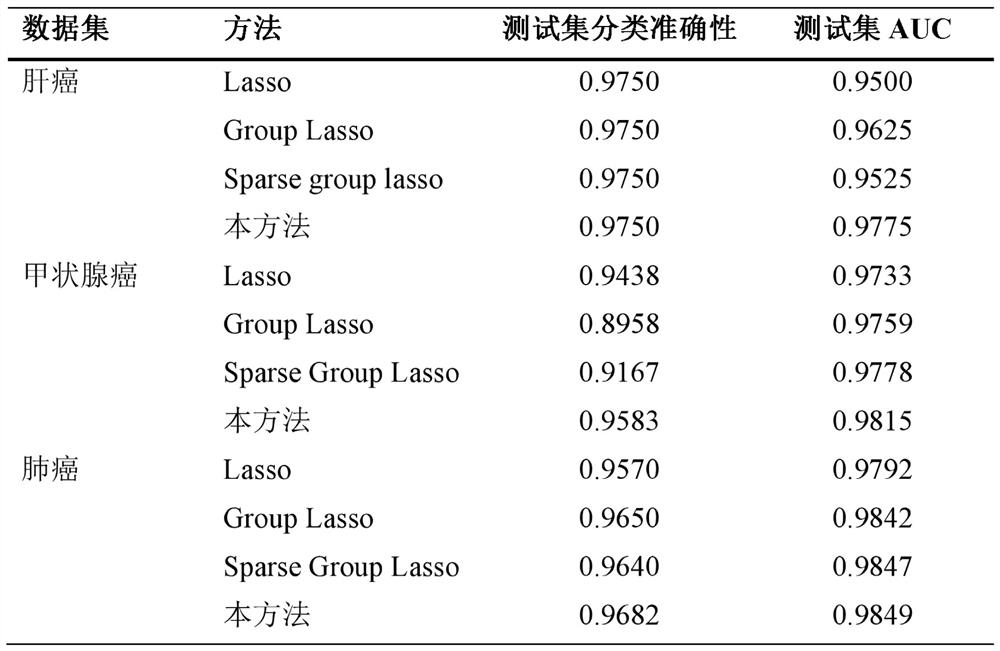
ActiveCN113436684AImprove accuracyImprove stabilityBiostatisticsSystems biologyGenetic enhancementGene selection
The invention belongs to the field of biological information, and discloses a cancer classification and characteristic gene selection method, which comprises the following steps of: establishment of a primary learner: establishing T logistic regression models and a spark group lasso regularized loss function solving model corresponding to the T logistic regression models, and outputting a secondary learner training set; establishing a secondary learner: establishing a multi-response regression model and a loss function solving model corresponding to L1 regularization, and outputting a training set prediction result; and a prognosis feature selection model: establishing a prognosis feature selection SGL model. According to the cancer classification and feature gene selection method, the three standards of prediction, stabilization and selection are met, the accuracy and stability of the model on cancer classification prediction are improved through stacking integration, oncogenes and cancer-related genes are accurately selected, and the interpretability of the model is enhanced; gene and gene pathway priori knowledge are fused, and the accuracy of cancer classification and the effectiveness of feature selection are improved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Application of antigen causing antibody-dependent enhancement of Tembusu virus
ActiveCN108676078APromote proliferationHigh virus contentSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsAntibody-dependent enhancementGenetic enhancement
The present invention discloses application of an antigen causing antibody-dependent enhancement of Tembusu virus. The antigen causing the antibody-dependent enhancement of Tembusu virus has an aminoacid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The antigen causing the antibody-dependent enhancement of the Tembusu virus is applied to preparation of a Tembusu virus vaccine. According to the invention, the epitope protein expressed by escherichia coli is used for immunizing ducklings, so that high-level specific antibodies can be induced in the ducklings, and the antibodies can promote virus proliferationand increase the titer of the virus in the ducklings. In the future research and development of the Tembusu virus vaccine, this kind of antigen can be removed through molecular design to avoid the antibody-dependent enhancement caused by the vaccine and ensure the protection effect. Therefore, identifying the antigen causing the antibody-dependent enhancement of the Tembusu virus has an importantapplication value in developing effective and safe vaccines and preventing and controlling the epidemic of the Tembusu virus.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods for alzheimer's disease treatment and cognitive enhancement
InactiveUS20130281522A1Improving/enhancing cognitive stateIncrease productionBiocideNervous disorderGenetic enhancementDisease patient
The present invention relates to compositions and methods to modulate α-secretase and / or to improve cognitive ability. The invention further relates the improved / enhanced cognitive ability in diseased individuals, particularly Alzheimer's Disease patients, and treatment thereof through increased sAPP production. Macrocyclic lactones (i.e. bryostatin class and neristatin class) are compounds preferred for use with the present composition. The present invention also provides methods for increasing the generation of non-amyloidogenic soluble APP comprising the activation of protein kinase C (PKC) by administering an effective amount of PKC activator(s).
Owner:COGNITIVE RES ENTERPRISES INC
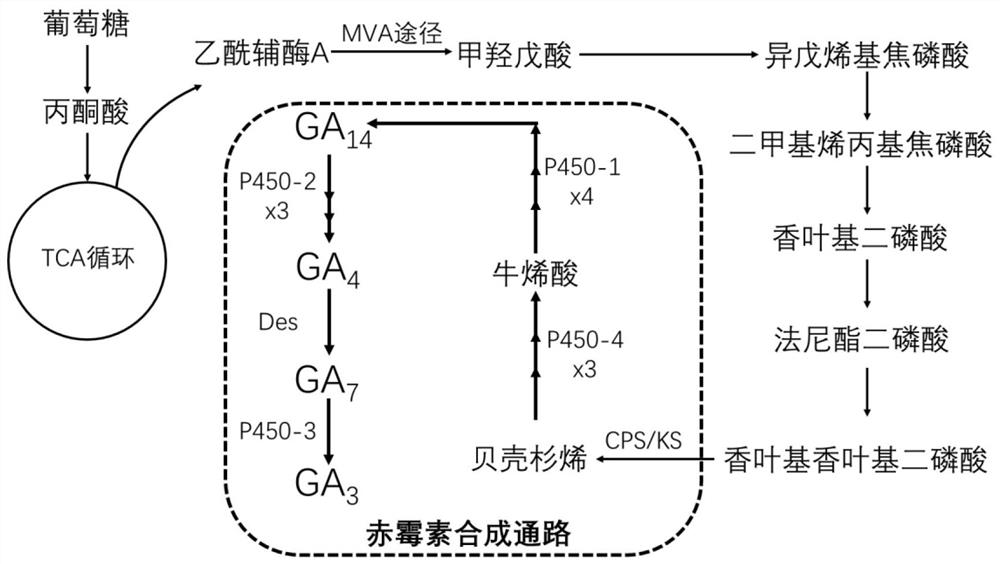
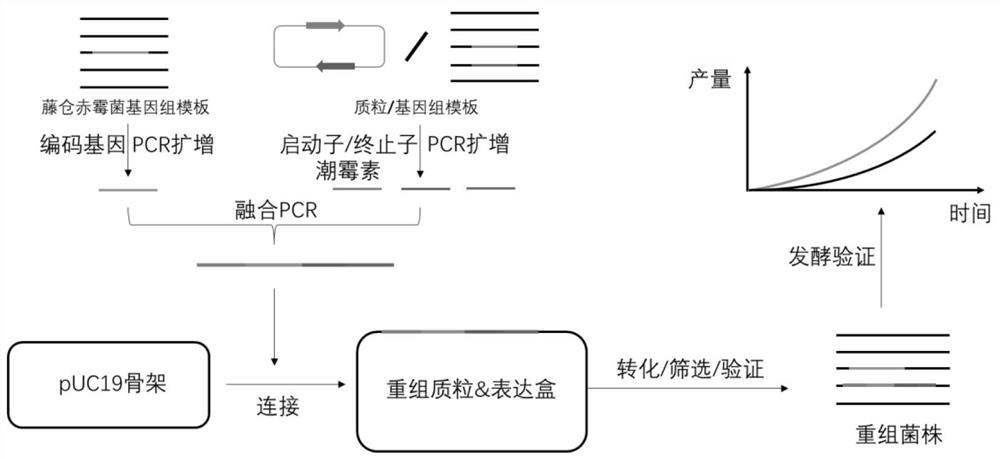
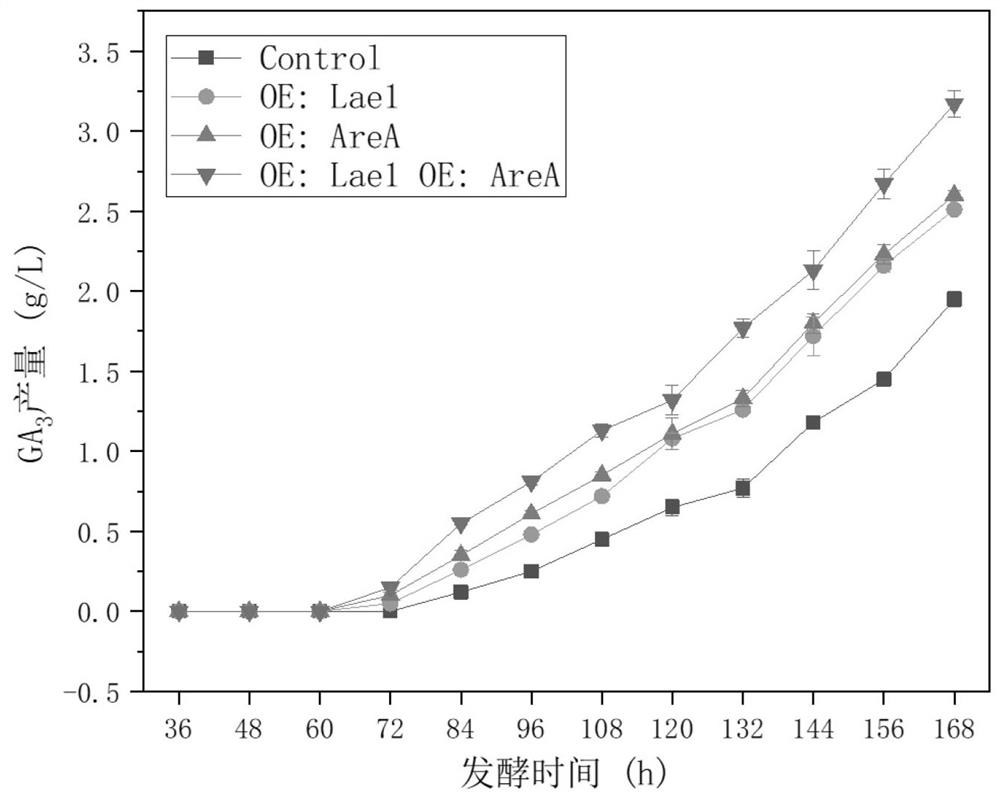
Genetically engineered bacterium of high-yield gibberellin GA3, construction method and application
PendingCN114517161AIncrease production capacityIncreased transcript levelsFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGenetic enhancement
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing gibberellin GA3 at high yield, a construction method and application. According to the present invention, by enhancing the gene expressing the nitrogen source regulatory factor AreA and the gene expressing the global regulatory factor Lae1 in the gibberella zeylanica, the positive regulation effect of the gibberella zeylanica on the related gene in the gibberellin anabolism path is enhanced, the transcriptional level of the related gene is improved, and the accumulation of gibberellin GA3 is improved. According to the recombinant gibberellin GA3 high-yield recombinant gibberellin GA3 provided by the invention, compared with wild gibberellin GA3, the transformed recombinant gibberellin GA3 has the advantages that the overall transcriptional level of a GA gene cluster is enhanced, the synthesis capability of a metabolic process is improved, the transcriptional inhibition of GA3 synthesis related genes is weakened, a carbon source substance and a nitrogen source substance can be better utilized for producing gibberellin GA3, and the yield of gibberellin GA3 is improved. The level of the transformed strain with the optimal performance for producing gibberellin GA3 through fermentation is improved from 2 g / L to 3.25 g / L compared with the original strain, the production capacity of gibberellin GA3 is remarkably improved, and the strain can be applied to large-scale production of gibberellin GA3.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
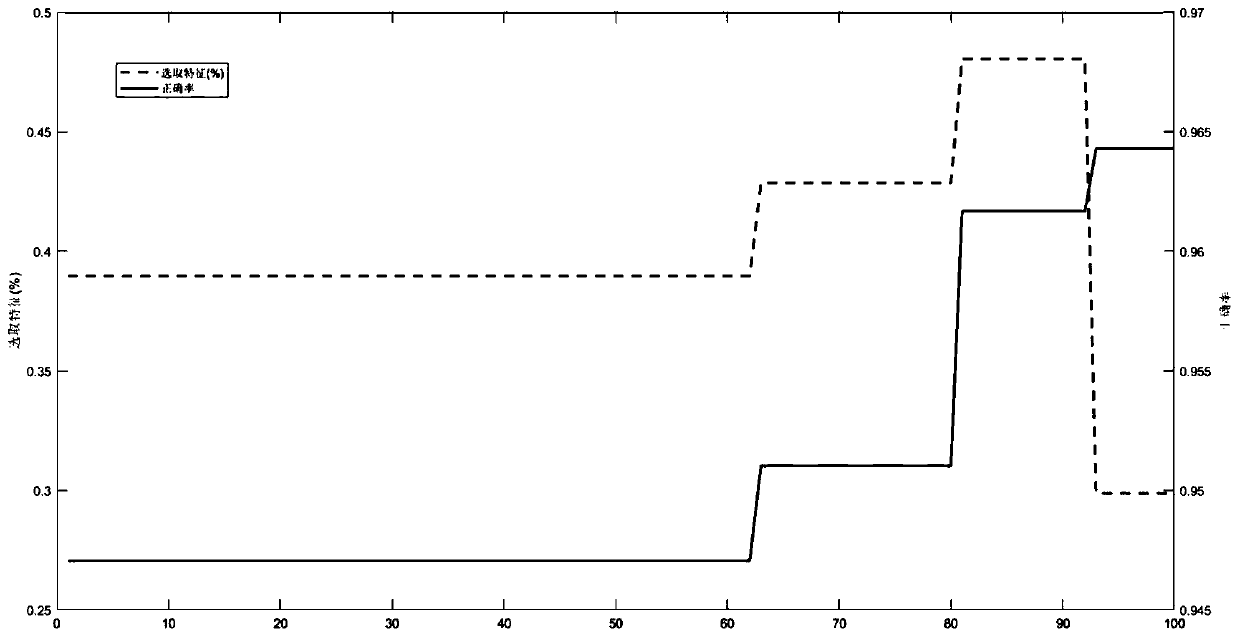
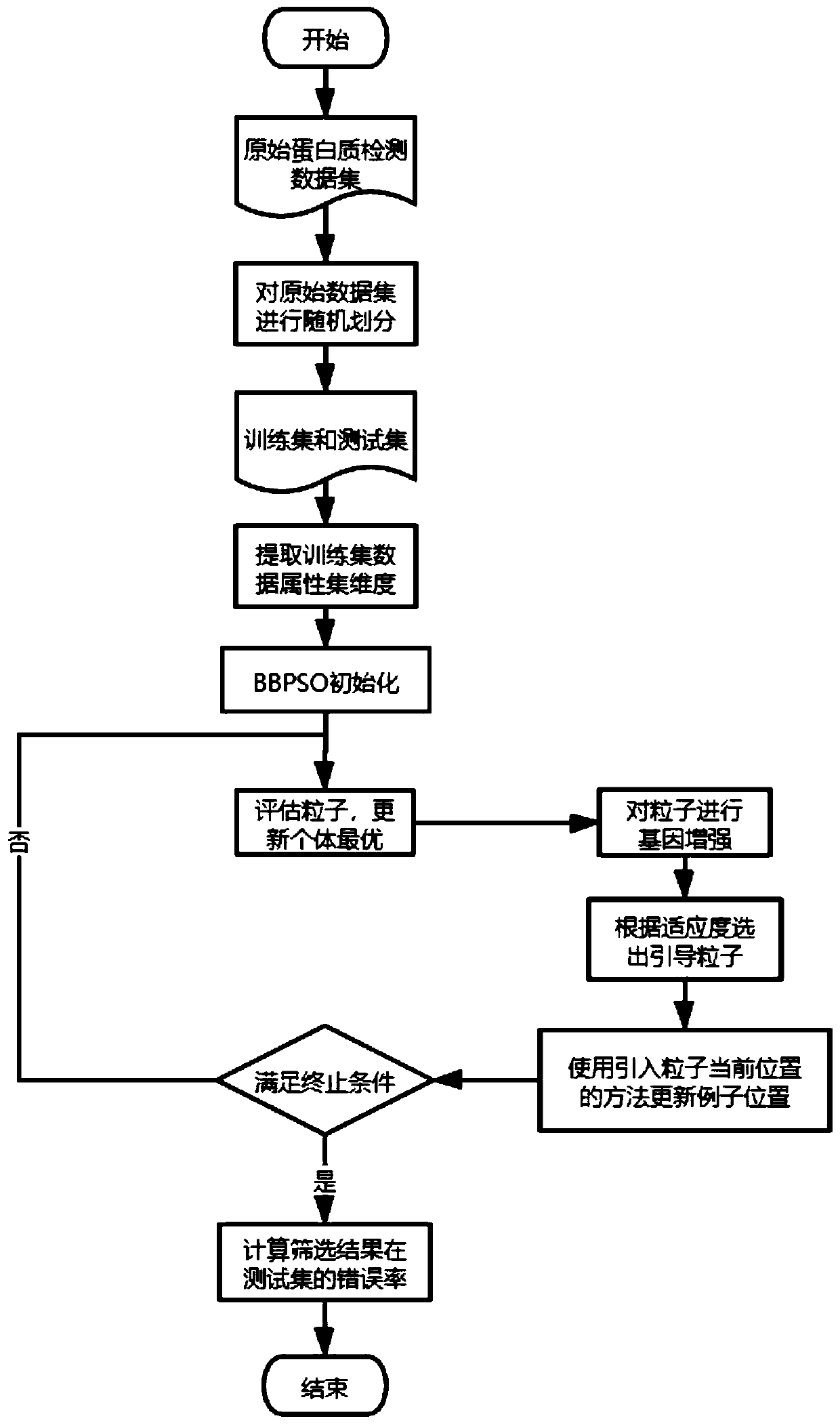
Mouse Down's syndrome key protein screening method based on gene-enhanced skeleton particle swarm optimization feature selection algorithm
ActiveCN111354415AExpand your searchGuaranteed correctnessBiostatisticsArtificial lifeGenetic enhancementProtein detection
The invention discloses a mouse Down's syndrome key protein screening method based on a gene-enhanced skeleton particle swarm optimization feature selection algorithm, which comprises the following steps: randomly dividing an original data set into two parts, namely a training set and a test set, for original mouse cerebral cortex protein detection, which are used for optimizing a particle swarm and testing a final result; carrying out dimension extraction on the data set to initialize a population to obtain an original population; calculating the fitness of each dimension of gene in the initial population, determining whether the gene of the dimension is selected or not, calculating the accuracy of particle prediction according to the selected gene, and identifying the key category protein for detecting the Down's syndrome of the mouse. In the aspect of particle swarm optimization, compared with a traditional mouse Down's syndrome key protein screening method, the method can quickly and efficiently identify a small number of key feature subsets with good classification performance in an original data set.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
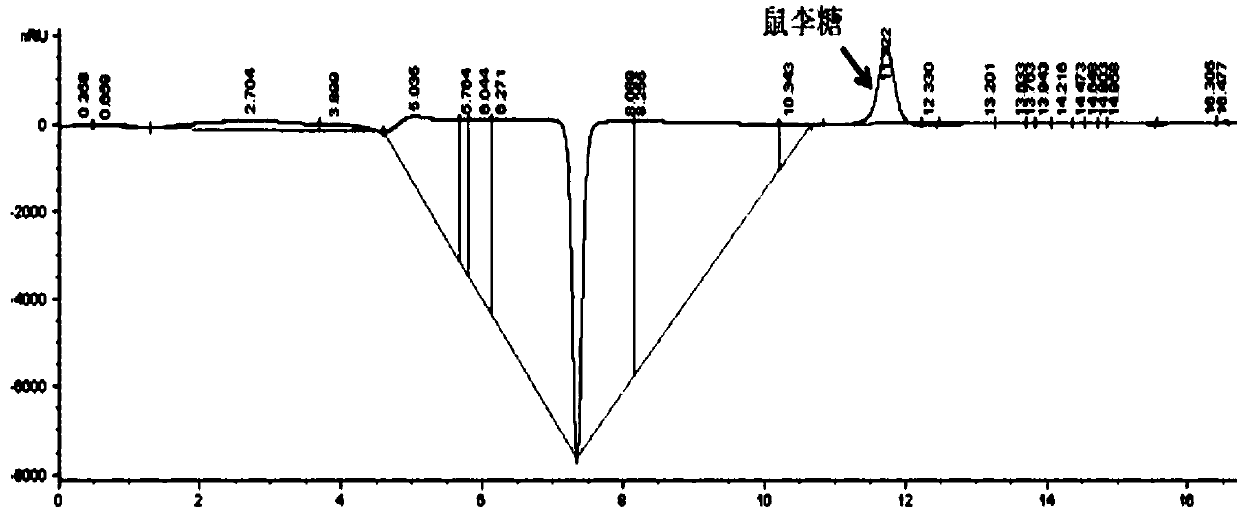
Engineering bacteria for producing L-rhamnose, and construction method and application of engineering bacteria
ActiveCN110527692AEfficient synthesisAvoid complex hydrolysis stepsBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliGenetic enhancement
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for producing L-rhamnose, and a construction method and application of the engineering bacteria. Genes associated with synthesis of the L-rhamnose are over-expressed in escherichia coli, a synthesis pathway of the L-rhamnose is enhanced, meanwhile, through blocking of a bypass path, the accumulation amount of a precursor L-lactic aldehyde is increased,a set of efficient whole-cell catalytic synthesis method of free L-rhamnose is developed, and the L-rhamnose is synthesized firstly in the escherichia coli by taking glucose as a single substrate. Inthis way, the cheap glucose can serve as raw materials, the L-rhamnose is efficiently synthesized through whole-cell catalysis of the escherichia coli, the synthesized rhamnose is in a free state, thecomplex hydrolysis step is avoided, the synthesized rhamnose can be directly used for separation purification, an obtained product does not contain other monosaccharides or proteins either, and thusthe burden of subsequent separation purification is reduced.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
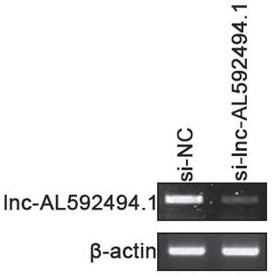
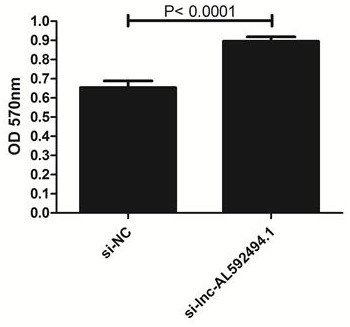
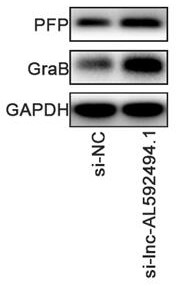
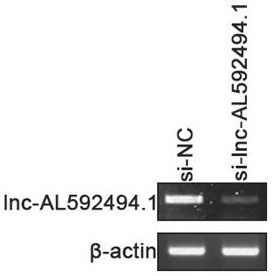
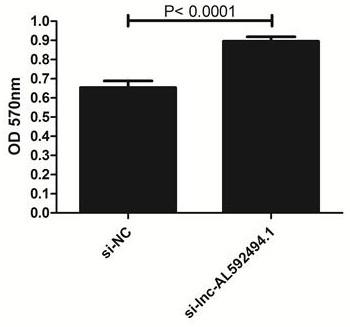
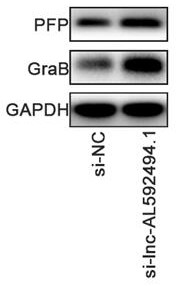
Application of gene enhanced immune cells in lung cancer
ActiveCN113925877AGood lethalityImprove proliferative abilityOrganic active ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsGenetic enhancementNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
The invention provides application of gene enhanced immune cells in lung cancer, and belongs to the technical field of immunology. The gene enhanced immune cells provided by the invention are NK (Natural Killer) cells transfected with siRNA (Small Interference Ribonucleic Acid) of lnc-AL592494.1. The NK cells provided by the invention have stronger multiplication capacity, and have stronger killing activity on lung cancer cells.
Owner:青岛西凯生物技术有限公司
Recombinant bacteria for producing 3-hydroxy propionic acid, preparation method therefor, and applications thereof
ActiveUS11155839B2High in proteinHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGenetic enhancementPropanoic acid
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of gene-enhanced immune cells in lung cancer
ActiveCN113925877BGood lethalityImprove proliferative abilityOrganic active ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsGenetic enhancementNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
The invention provides the application of gene-enhanced immune cells in lung cancer and belongs to the technical field of immunology. The gene-enhanced immune cells provided by the present invention are NK cells transfected with lnc‑AL592494.1 siRNA. The NK cells provided by the invention have stronger proliferative ability and stronger killing activity for lung cancer cells.
Owner:青岛西凯生物技术有限公司
Engineering bacteria producing l-rhamnose and its construction method and application
ActiveCN110527692BEfficient synthesisAvoid complex hydrolysis stepsBacteriaHydrolasesLactaldehydeEngineering
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium producing L-rhamnose, a construction method and application thereof. The present invention enhances the synthesis pathway of L-rhamnose by overexpressing genes related to L-rhamnose synthesis in Escherichia coli, and at the same time increases the accumulation of precursor L-lactaldehyde by blocking the bypass pathway, A set of high-efficiency whole-cell catalytic synthesis of free L-rhamnose was developed, and the synthesis of L-rhamnose with glucose as a single substrate was realized for the first time in Escherichia coli. In this way, L-rhamnose can be catalyzed and efficiently synthesized by whole cells of Escherichia coli with cheap glucose as raw material. Not only is the synthesized rhamnose in a free state, which avoids complicated hydrolysis steps, but can be directly used for separation and purification, and can be obtained The product does not contain other monosaccharides or proteins, which reduces the burden of subsequent separation and purification.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
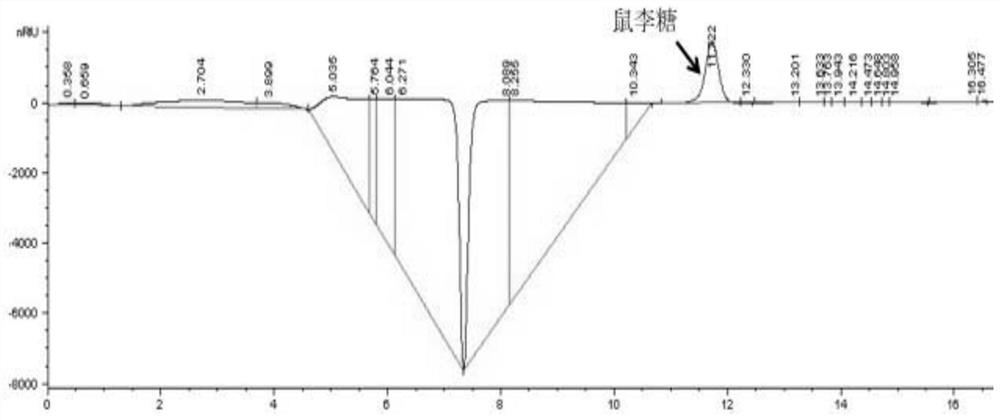
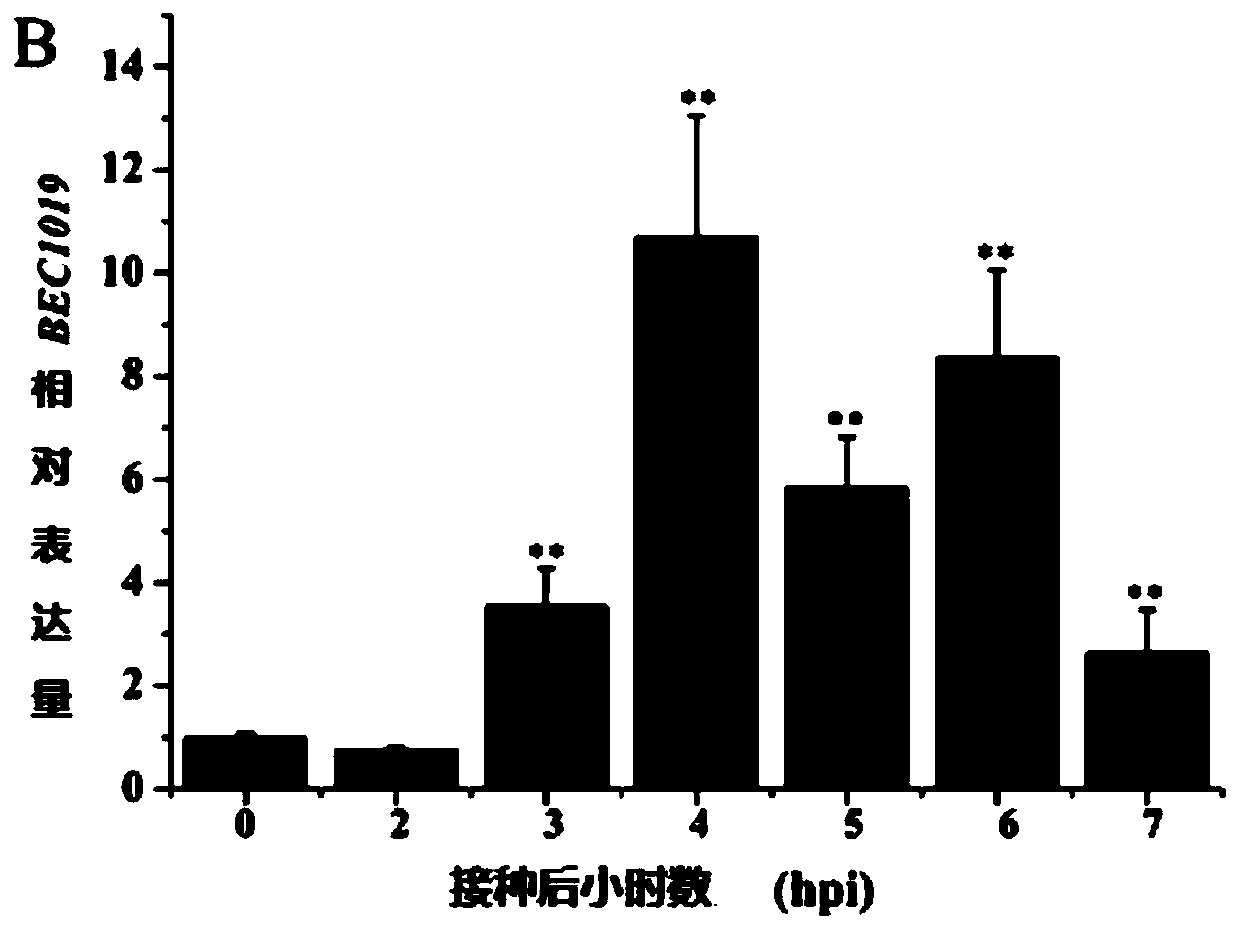
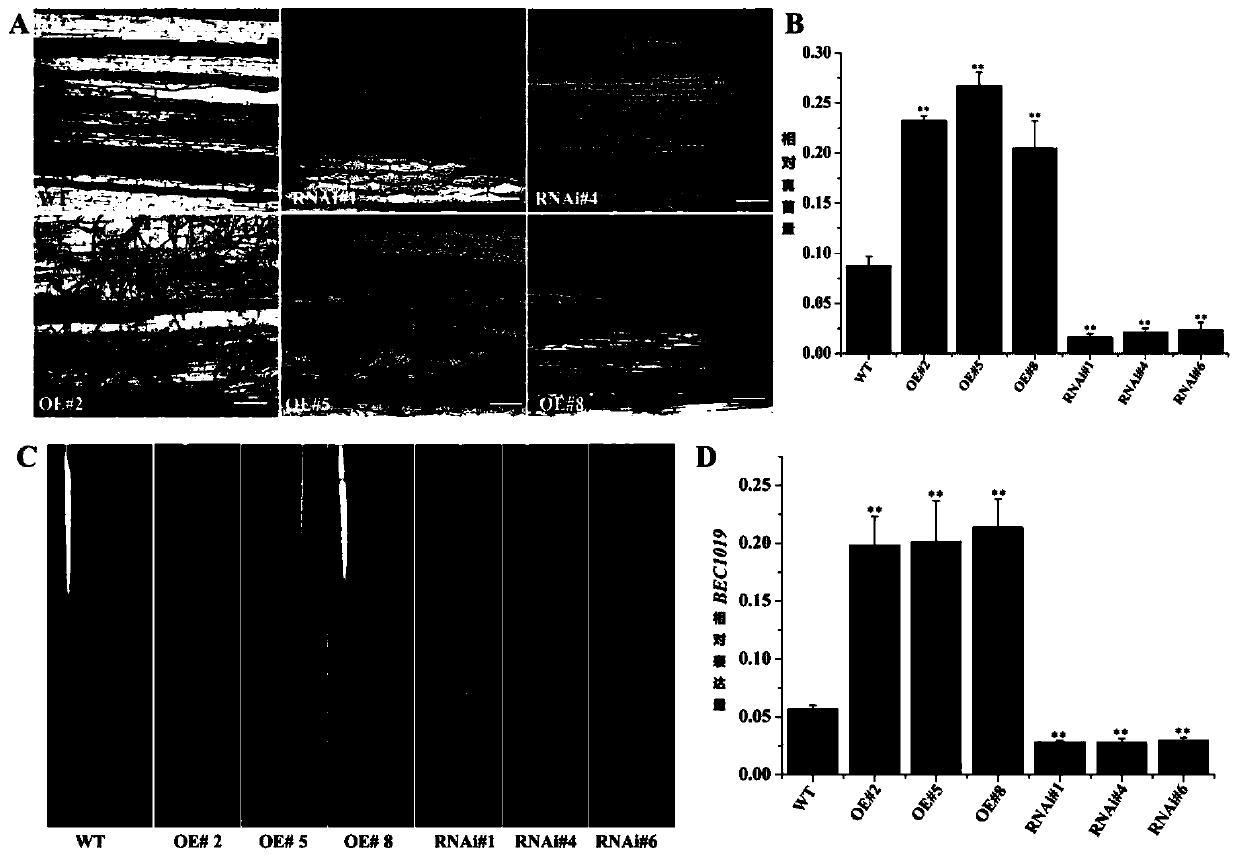
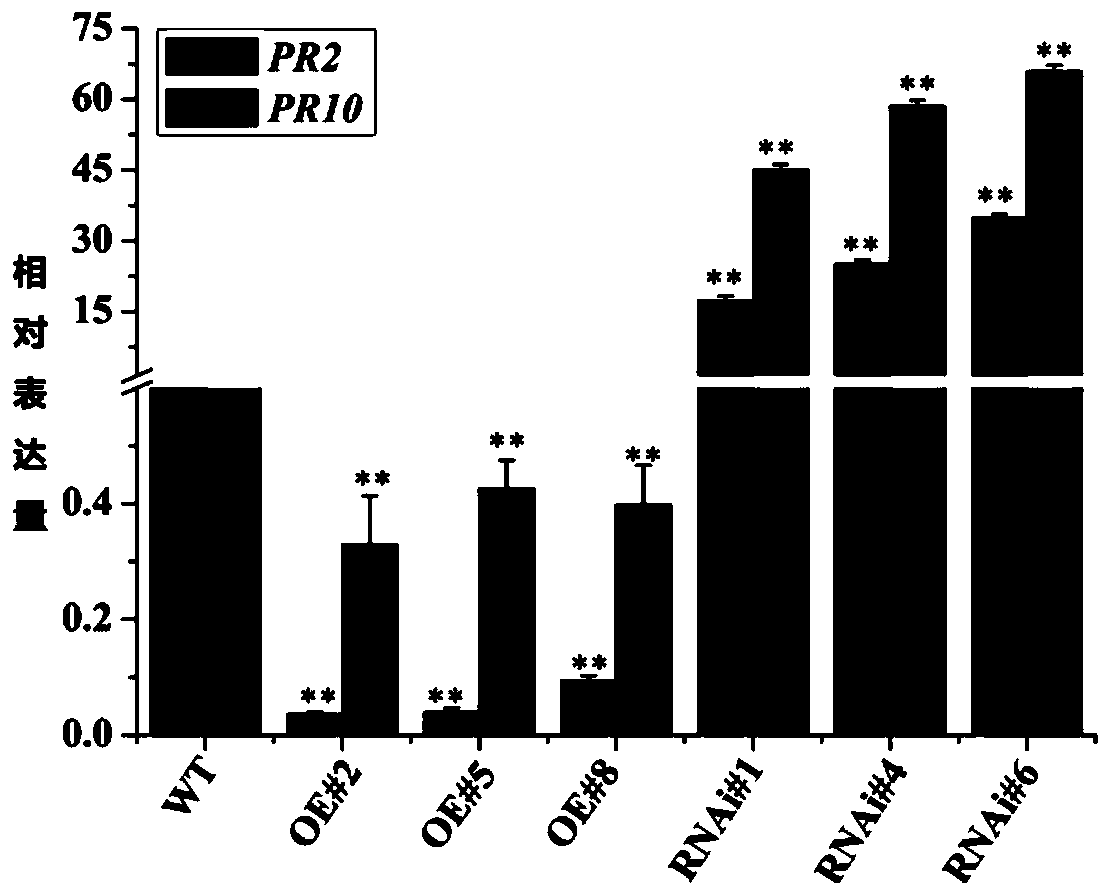
Application of gene BEC1019 in improvement of full rot resistance of wheat
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural biology and particularly relates to application of a gene BEC1019 in improvement of full rot resistance of wheat. A method for improving the full rot resistance of wheat comprises a step of silencing the gene BEC1019 in the wheat. The gene BEC1019 is an important effector gene in full rot of the wheat, the gene can be used for enhancingresistance of the wheat to multiple pathogenic bacteria, and new wheat species with durable and broad spectrum resistance can be bred.
Owner:ZHOUKOU NORMAL UNIV
Method for enhancing secretion of glucose oxidase by coexpression of UPR (unfolded protein response) key genes and downstream target genes
ActiveCN102994541BIncrease enzyme activityFungiMicroorganism based processesGenetic enhancementBiotechnology
The invention discloses a method for enhancing secretion of glucose oxidase by coexpression of UPR (unfolded protein response) key genes and downstream target genes, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The method comprises the steps of respectively cloning and connecting pichia pastoris UPR key gene Haclp and the downstream target genes Pdi1, Erol, Lhs1, Kar2 and Sil1 to pichia pastoris expression carriers pPICZ alpha and pPIC3.5K, transforming into a Pichia pastoris GS115-pPIC9K-GOD strain of which the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2012266, and obtaining a strain with enhanced secretion expression of the glucose oxidase compared with the original strain by screening and identifying. The enzyme activity of the glucose oxidase expressed by the strain on a 3L of fermentation tank is 585U / mL. Therefore, good foundation is established for large-scale production of the glucose oxidase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com