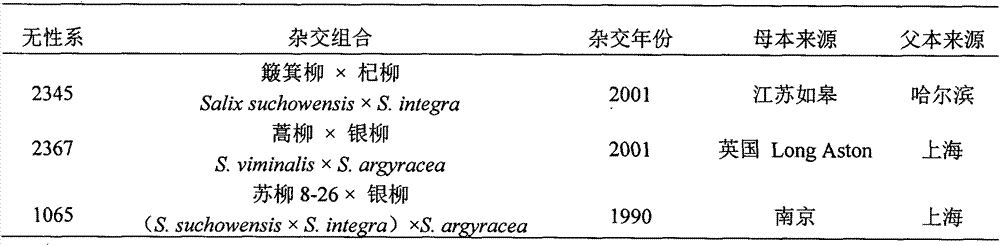
Salix saposhnikovii tissue culture method
A tissue culture and shrub willow technology, applied in the field of willow breeding, can solve the problems of not being able to maintain the excellent characteristics of fine varieties, small seeds, etc., and achieve the effects of not being limited by time and external conditions, shortening the growth time, and shorting the seedling cycle.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0030] Basic medium configuration:
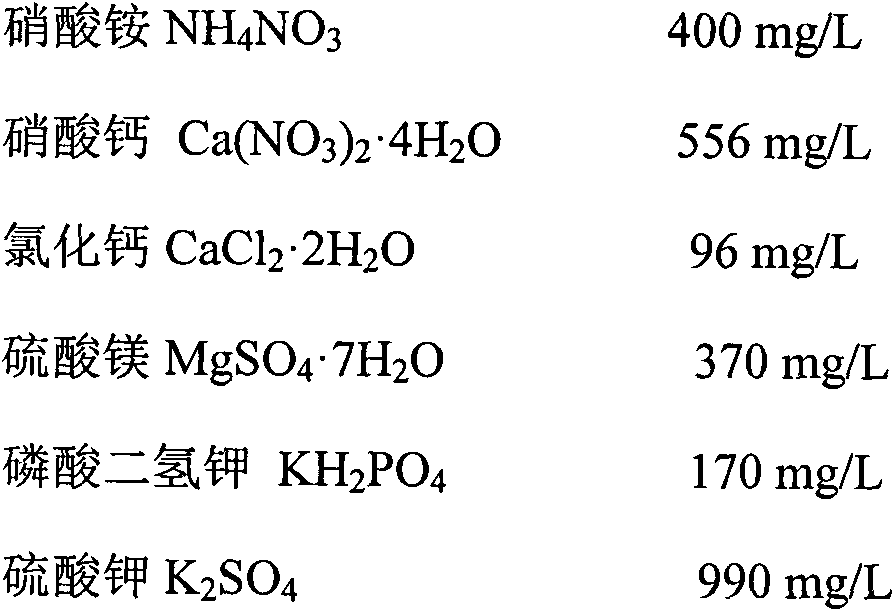
[0031] The basic medium is WPM medium, in which the components of the major elements and their corresponding use concentrations are as follows: ammonium nitrate (NH 4 NO 3 )400mg / L, calcium nitrate (Ca(NO 3 ) 2 ·4H 2 O)556mg / L, calcium chloride (CaCl 2 ·2H 2 O) 96mg / L, magnesium sulfate (MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O)370mg / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH 2 PO 4 )170mg / L, potassium sulfate (K 2 SO 4 )990mg / L;
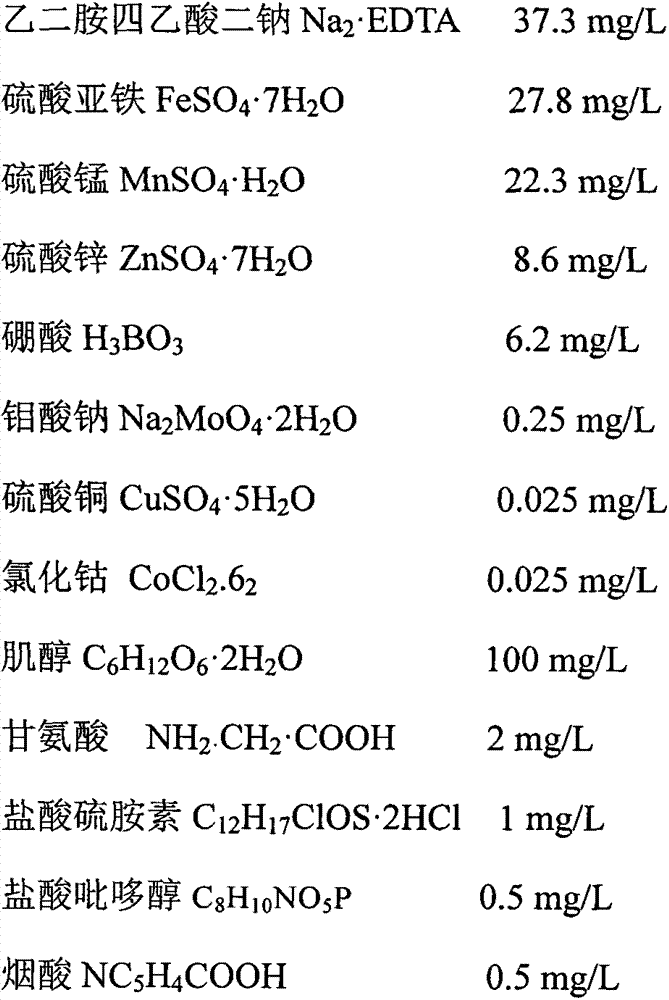
[0032] The components of trace elements and their corresponding use concentrations are as follows: Manganese sulfate (MnSO 4 .H 2 O) 22.3mg / L, zinc sulfate (ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O)8.6mg / L, boric acid (H 3 BO 3 )6.2mg / L, sodium molybdate (Na 2 MoO 4 ·2H 2 O) 0.25mg / L, copper sulfate (CuSO 4 ·5H 2 O) 0.025mg / L, copper sulfate (CuSO 4 .5H 2 O) 0.025mg / L, cobalt chloride (CoCl 2 .6 2 )0.025mg / L;
[0033] The composition of the iron salt and its corresponding concentration are as follows: Disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate (Na 2 ·EDTA) 37.3mg / L, ferrous sulfate ...
example 2
[0045] Basic medium configuration:
[0046] The basic medium is MS medium, in which the major element components and their corresponding use concentrations are as follows: ammonium nitrate (NH 4 NO 3 )1650mg / L, potassium nitrate (KNO 3 )1900mg / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH 2 PO 4 )170mg / L, magnesium sulfate (MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O)370mg / L, calcium chloride (CaCl 2 ·2H 2 O) 440mg / L;
[0047] The components of trace elements and their corresponding use concentrations are as follows: potassium iodide (KI) 0.83mg / L, manganese sulfate (MnSO 4 ·H 2 O) 22.3mg / L, zinc sulfate (ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O)8.6mg / L, boric acid (H 3 BO 3 )6.2mg / L, sodium molybdate (Na 2 MoO 4 ·2H 2 O) 0.25mg / L, copper sulfate (CuSO 4 .5H 2 O) 0.025mg / L, cobalt chloride (CoCl 2 .6 2 )0.025mg / L;
[0048] The composition of the iron salt and its corresponding concentration are as follows: Disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate (Na 2 ·EDTA) 37.3mg / L, ferrous sulfate (FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O) 27.8mg / L;
[0049] The components of the organic i...
example 3
[0060] Basic medium configuration:
[0061] The basic medium is 1 / 2MS medium, in which the major element components and their corresponding use concentrations are as follows: ammonium nitrate (NH 4 NO 3 )825mg / L, potassium nitrate (KNO 3 )950mg / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH 2 PO 4 )85mg / L, magnesium sulfate (MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O) 185mg / L, calcium chloride (CaCl 2 ·2H 2 O) 220mg / L;
[0062] The components of trace elements and their corresponding use concentrations are as follows: potassium iodide (KI) 0.83mg / L, manganese sulfate (MnSO 4 ·H 2 O) 22.3mg / L, zinc sulfate (ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O)8.6mg / L, boric acid (H 3 BO 3 )6.2mg / L, sodium molybdate (Na 2 MoO 4 ·2H 2 O) 0.25mg / L, copper sulfate (CuSO 4 .5H 2 O) 0.025mg / L, cobalt chloride (CoCl 2 .6 2 )0.025mg / L;
[0063] The composition of the iron salt and its corresponding concentration are as follows: Disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate (Na 2 ·EDTA) 37.3mg / L, ferrous sulfate (FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O) 27.8mg / L;
[0064] The components of the organic ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com