Method for separating and culturing endothelial clone formative cell
A technique of separating and culturing endothelium, applied in animal cells, vertebrate cells, artificial cell constructs, etc., can solve the problems of inconvenient bone marrow sampling, difficult cord blood sampling and operation, and low number of EPCs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0062] Example 2 Observation of the primary cell culture and passage process of umbilical cord-derived ECFCs
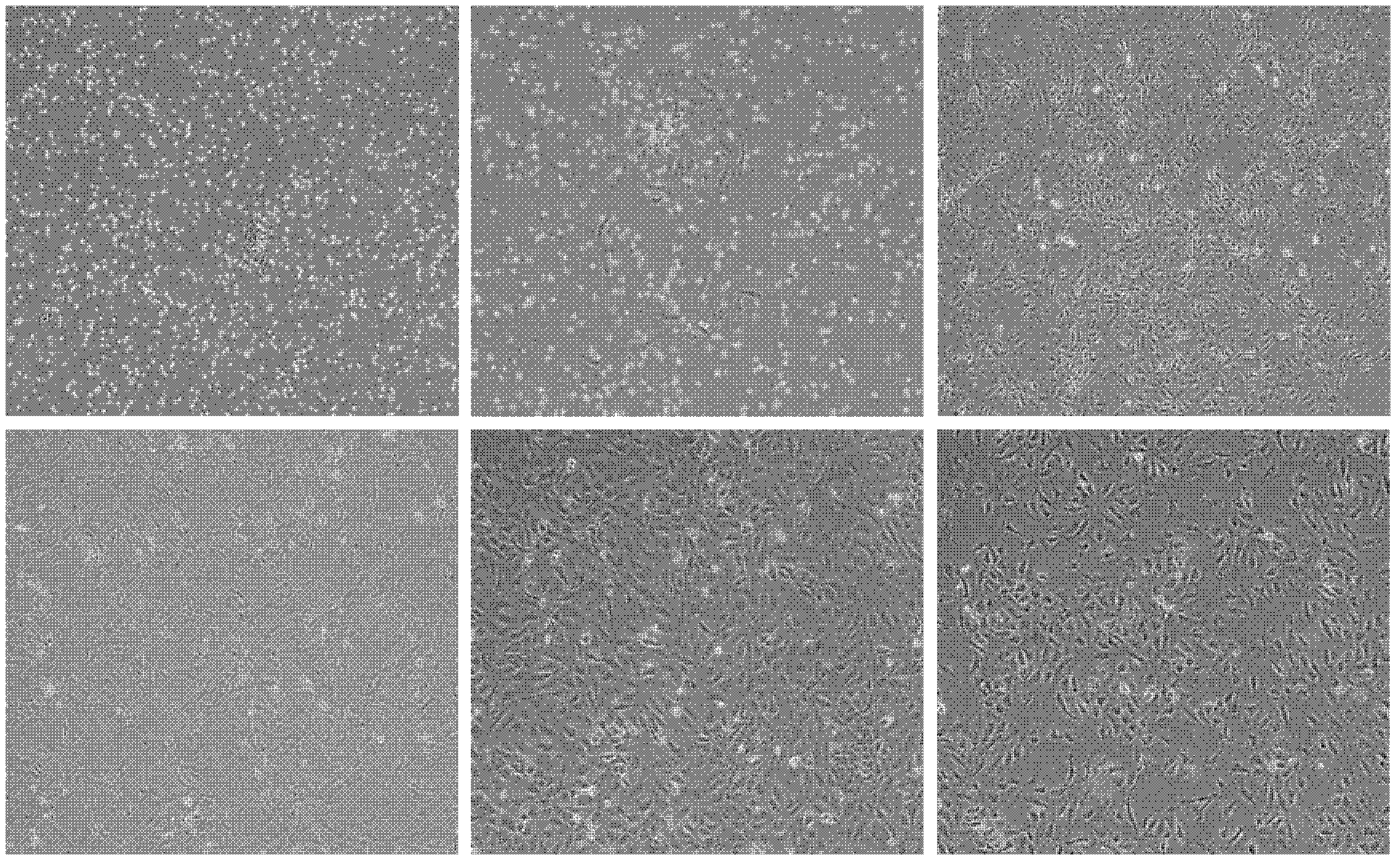
[0063] The primary cells of the umbilical cord-derived ECFCs isolated by the method in Example 1 adhered to the wall more than 24-36 hours later, and spindle-shaped and round adherent cells were seen. After being cultured for 3-7 days, scattered cell clones were observed under an inverted microscope. Fusiform, polygonal, round, with large cell bodies. After 7-10 days, the growth rate is faster, and many cell clones appear. About 10-14 days, 80% of the cells are fused, and they are arranged like paving stones. After 10 passages, the cell morphology did not change significantly. ( figure 1 )
[0064] figure 1 Cell morphology of umbilical cord-derived ECFCs. (A), primary cell culture for 36 hours; (B), primary cell culture day 5; (C), primary cell culture day 14; (D), P1 generation cells; (E), P3 generation cells; (F), P10 generation cells.
Embodiment 3
[0065] The determination of the growth curve of embodiment 3 umbilical cord source ECFCs
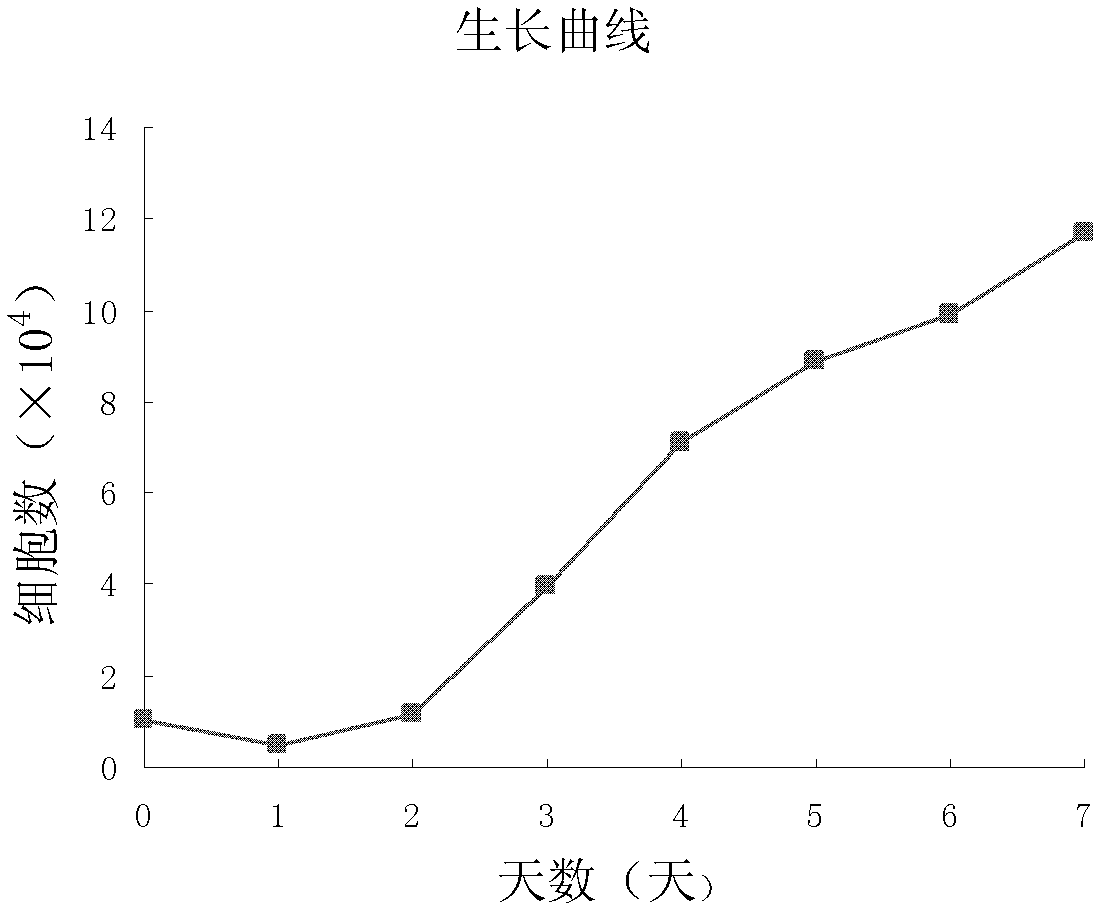
[0066] After the adherent cells obtained according to the method of Example 1 reached 80% confluence, they were digested with 0.25% trypsin, and then divided by 2×10 4 The cells / well were seeded in a 24-well plate, and 3 wells were digested every 24 hours, and the cells were collected, and the living cells were counted with 0.4% trypan blue, observed for 7 days, and the growth curve was drawn.
[0067] The growth curve of umbilical cord-derived ECFCs basically conformed to the law of cell growth curve, which was divided into incubation period, logarithmic period and plateau period, which were 1-2d, 3-7d and 7d later. It suggested that the proliferation of umbilical cord-derived ECFCs was relatively stable in vitro, and the growth status was normal. The cells proliferated rapidly, and in the logarithmic growth phase, the cell doubling time was about (43.53±5.38) h ( figure 2 ).
Embodiment 4
[0068] Example 4 Cell cycle assay of umbilical cord-derived ECFCs
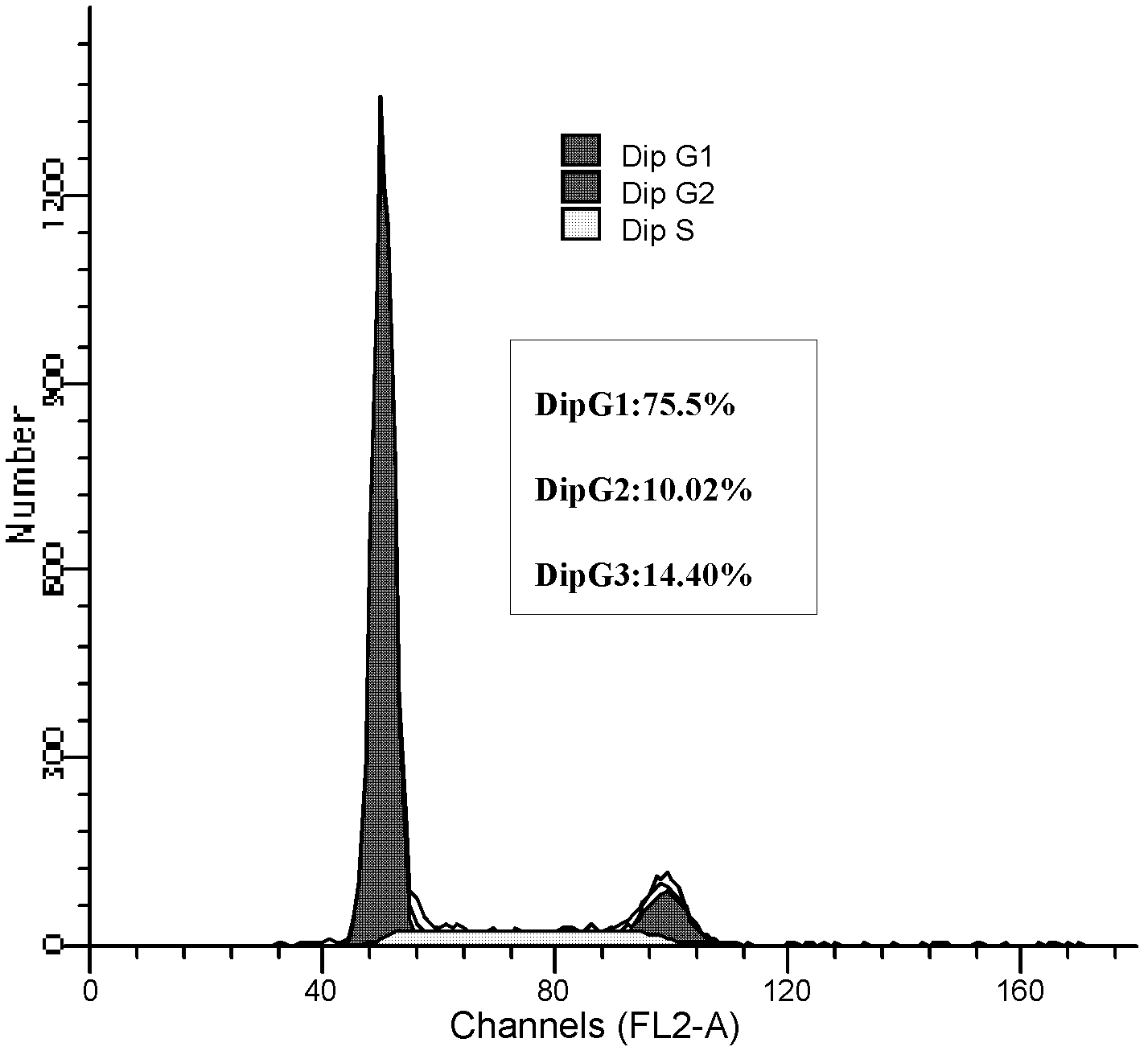
[0069] In the logarithmic phase of the growth of the umbilical cord-derived ECFCs obtained in Example 1, digest the cells, freeze 75% ethanol and fix at 4°C for 1 hour, incubate with 10 μg / mL RNase A at 37°C for 30 minutes, add 50 μg / mL propidium iodide at 4°C and protect from light Incubate for 5 min, detect with flow cytometer (FACA Calibur, USA), and analyze the results with ModiFIT software.
[0070] Flow cytometry analysis of the cell cycle showed that G 0 / G 1 Period accounted for 75.58%, S+G 2 Cells in +M phase accounted for only 24.42% ( image 3 ).
[0071] The results showed that most of the cells in umbilical cord-derived ECFCs were in G0 / G1 phase, and a few were in S phase, which had typical characteristics of stem cell proliferation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com